Do not think about seconds down
Those who are interested in web hosting know that today a number of providers offer hosting with the SSD (Solid State Drive) option. How much is needed for a website? What gives the use of solid-state drives in comparison with traditional drives - HDD? Is the game worth the candle?
As you know, SSDs do not contain moving parts and can read and write data much faster than HDD. SSDs are storage devices whose speed is significantly higher than that of conventional hard drives with mechanically moving read / write heads.


Progress in surface recording density of HDD and flash memory (GB per square inch).
Although the linear read speed on the HDD has grown significantly in recent years, and the recording density on the plate continues to increase, the speed of the read / write head changes little, so often these disks are slow. The speed of solid state drives can be several times higher than the potential of hard drives.

Currently, 90% of hosting providers in the world use servers with HDDs, since this is the cheapest option, disk drives have a large capacity, are easily configured to work with servers, and do not require special hardware.
Meanwhile, according to Gartner's forecast, already in 2017, enterprise-class SSDs will be sold more than HDDs. Over the next three years, in the corporate segment, SSD sales (in monetary terms) will grow by an average of 20% per year, while HDD - by only 4%. Transparency Market Research (TMR) also believes that by 2022 the segment of enterprise-class SSD drives will develop most rapidly: the average annual sales growth rate of such products may exceed 76%.

Along with an increase in performance, the capacity of SSDs is also growing. In 2016, Seagate, Samsung, Toshiba, Western Digital, and a dozen other vendors introduced large-capacity SSDs that can be used for data archiving, which is previously unusual for flash drives. Samsung by 2020 is going to release a flash drive form factor 2.5 inches with a capacity of 100 TB. Its high-capacity SSD uses 64-layer 3D V-NAND memory. The data transfer speed of a single chip with a capacity of 64 GB reaches 800 Mbps.
Samsung also introduced the BGA (Ball-Grid Array) SSD with three bits per cell. Weighing 1 g, it holds 1 terabyte of data. The sequential read speed is 1500 MB / s, and the write speed is 900 MB / s. Among other new Samsung products is the SSD of the M.2 form factor with a capacity of 2 TB.
Many SSDs are designed specifically for data centers. For example, Intel's SSD DC P3520 Series, released in August 2016, are PCIe SSD devices that are optimized for high performance at a reasonable price. SSD DC P3520 series drives are suitable for working in cloudy environments in applications with a large number of read operations, for example, during storage virtualization or for organizing web hosting. Intel PCIe SSDs powered by 3D NAND technology are becoming an affordable alternative when deploying NVMe-enabled storage arrays where you need to process large data sets.

According to Intel, Intel SSD DC S3520 SSDs offer a good combination of low cost and high performance for data centers and provide significant performance gains and reduced latency compared to traditional HDDs used in the data center. SSD DC S3520 Series devices are aimed at those who want to replace disk drives with SATA SSDs.

Equipped with flash drives, servers and storage systems today can solve the most demanding tasks, such as searching in large databases, online transaction processing, business analytics and large-scale virtualization in cloud computing.
The problem of SSD durability has been practically solved: modern drives are designed for five years of intensive use. SSDs have every chance in the near future to replace the HDD in the servers, and in the future - in the storage. A 16 TB SSD has already been announced, and by 2020 a 40 TB flash drive will appear. New developments can lead to significant changes in many segments of the IT industry.
But what does all this mean in terms of today's website hosting tasks?
In general, when using the SSD, the operating system and applications load faster, access to data is accelerated, while the HDD has more attractive cost indicators, it is more profitable to store large amounts of data on them. Capacity on an SSD is so far noticeably more expensive. Let's try to weigh in more detail all the pros and cons.
Hard disks, HDD
Flash Drives, SSD
And in specific numbers :
And here is another comparison, more obvious (for different models of drives and interfaces the data may differ):
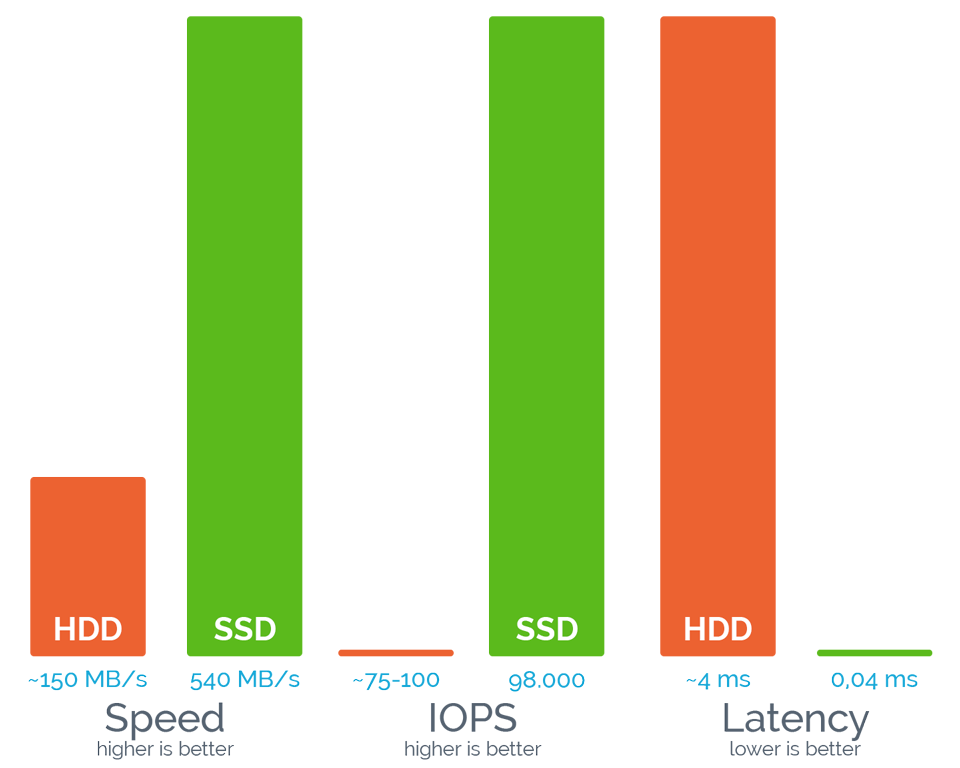
HDD vs SSD: speed, performance, delay.
It follows that the SSD is at least 15 times faster, 4-10 times more reliable than the HDD. On a large server, using them will save about 100 watts of power consumption and free up 6% of computing power. But what are the benefits of all this when hosting websites?
In fact, several factors affect the load time of a page on a site:
As you can see, the total loading time of a page on a site depends not only on the speed of reading data, but this time is a critical component. When a website is hosted on an SSD, it gets all the benefits of high speed access to this medium.

Providers often use reliable and fast enterprise-class SSDs with an eMLC memory type. Disks integrated into RAID arrays achieve data transfer speeds of up to 100 thousand IOPS, and Windows VPS starts within 7 seconds.
Optimization of site performance by speeding up data reading by the server, especially and instant work with files on SSD is desirable for sites of the following categories:
What is the potential gain from hosting on an SSD? If your site is already working well and the page loading speed is quite decent, do I need to switch to solid state drives? To feel the difference, you need to experiment with the SSD. Here is some gain promised by some foreign hosting providers:
From this it can be seen that in most cases the loading time of pages on a site due to SSDs is reduced by three times. In fact, in each case, the gain may be different. The high speed of SSDs is most noticeable for sites with high dynamics of working with data or with intense traffic (like social networks). The only real way to evaluate the benefits for a particular site is to try the SSD in practice.
The price of the question
And how much is this pleasure? Prices for SSD hosting usually start at a few dollars a month. Here are examples of some offers from providers:
So hosting on an SSD is the right solution not only for serious projects. For 95 rubles a month, you can completely promote a small gigabyte website for ten on an SSD. Of course, sites that require additional capacity, dedicated computing cores, bandwidth or other services will cost more, but if large capacity is not required, then hosting on an SSD is an affordable option.
Before proceeding to the conclusion, we summarize what has been said:
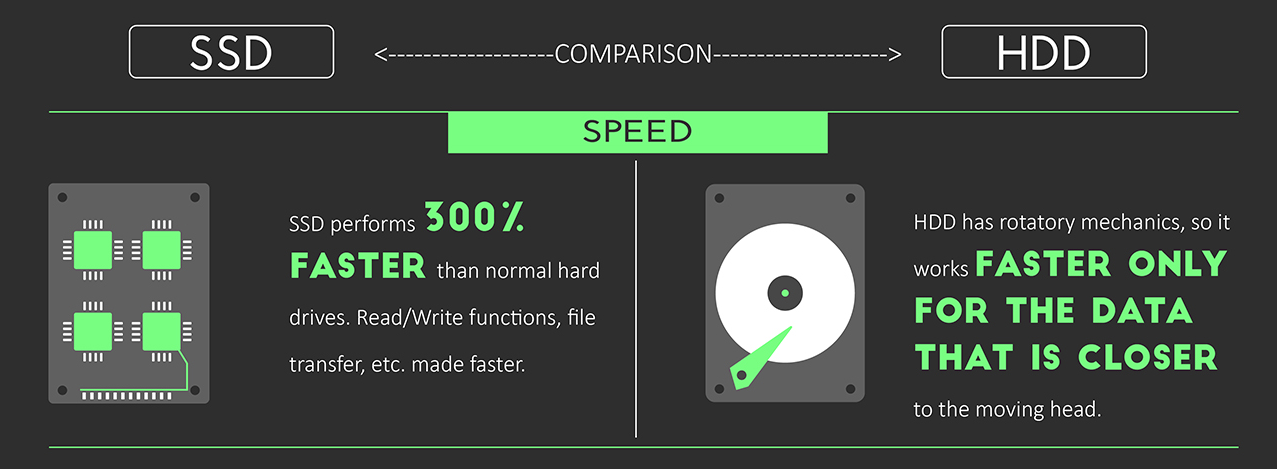
Speed. SSDs are 300% faster than HDDs, which affects the speed of read-write, file transfer, etc. The HDD quickly reads only data that is close to the read head.
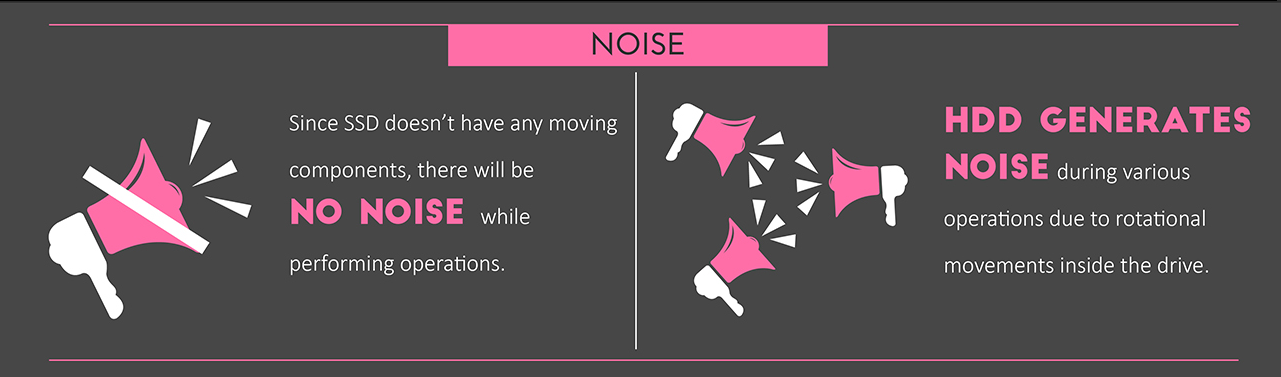
Noise. Since SSDs do not have moving parts, they work silently.
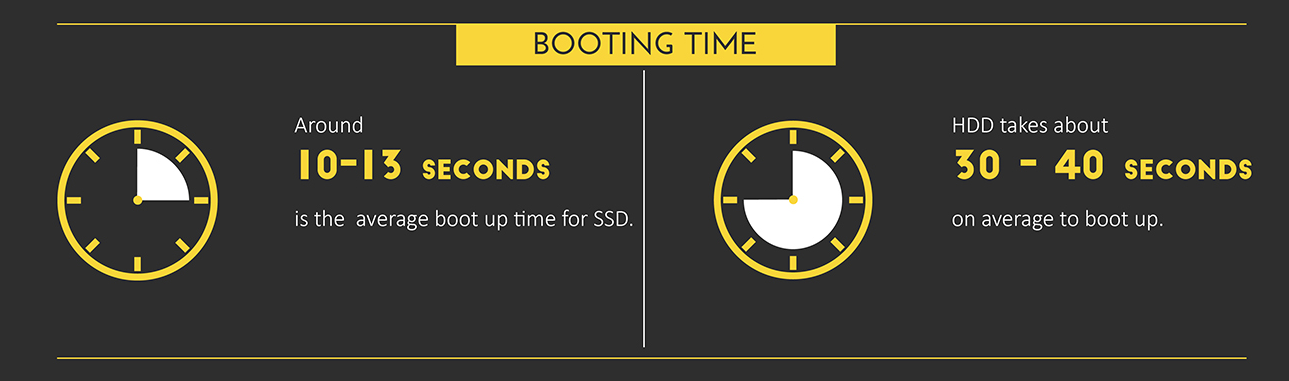
System boot time. In the case of SSD-drives, it averages 10-13 seconds, HDD - 30-40 seconds.

Weight. An SSD is much lighter, as it consists mainly of microchips.
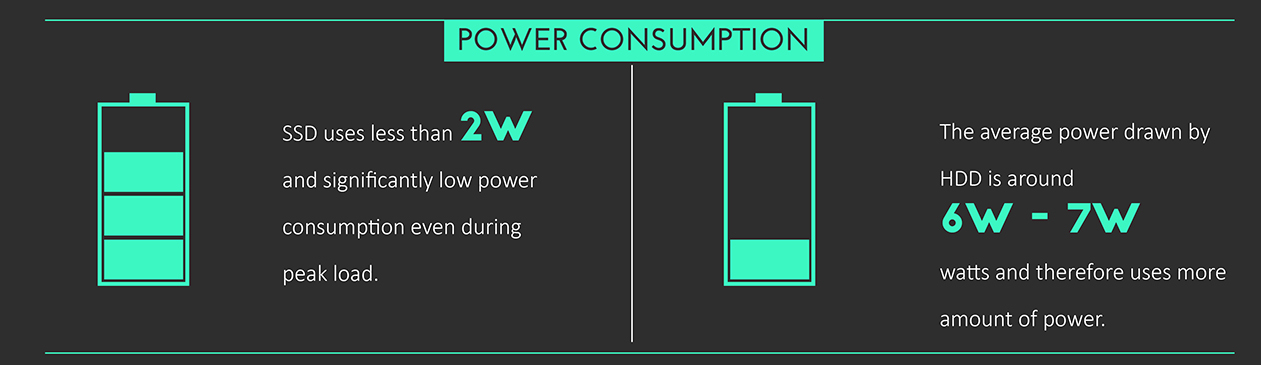
Power usage.SSD consumes less than 2 watts even at peak load, HDD - 6-7 watts. The use of SSD-drives can reduce energy consumption by 80%, they do not require significant cooling costs. If we take into account the economies of scale in the data center, then it becomes obvious the prospect of using solid-state drives to reduce operating costs.
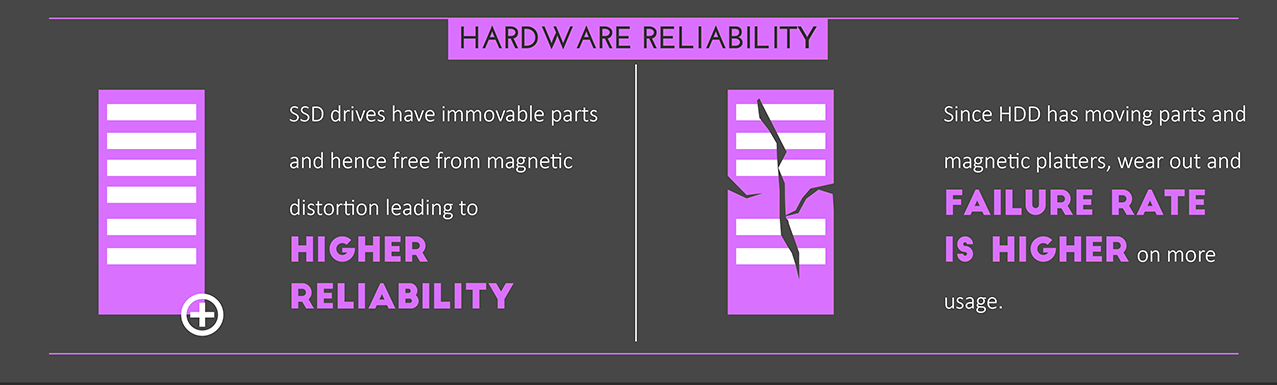
Reliability. Modern SDD drives are highly reliable, while disk failures are not uncommon.
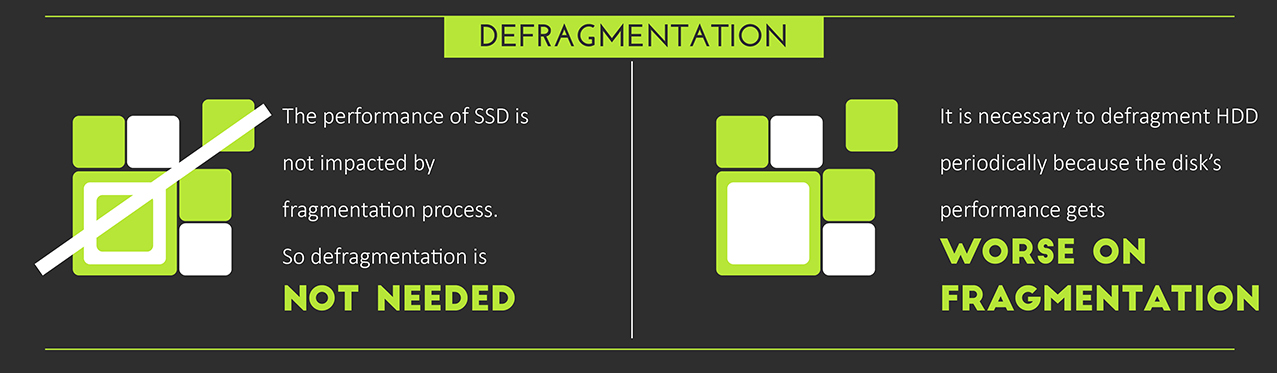
Defragmentation. SSDs do not need it. An HDD without defragmentation loses performance.
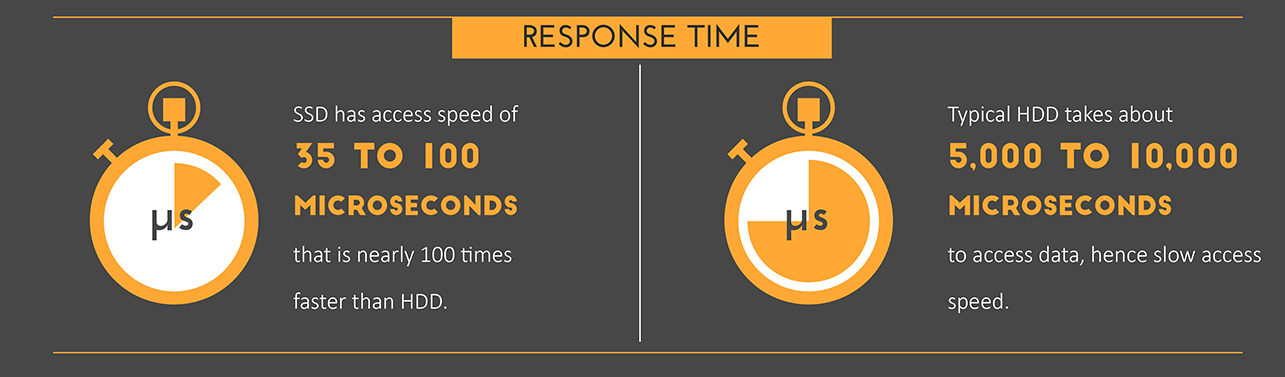
Response time. For SSD-drives it is almost a hundred times smaller than that of the HDD and is 35-100 ms compared to 5000-10000.

Performance.The HDD is much lower than the SSD-drives, which do not require mechanical operations.
Bounce rate. HDD mechanics fail more often. SSDs have very low failure rates.
Disk failure is a trouble for the site owner, because often all the data that is located on the hard disk is lost (if you neglect the backup). In the case of SSDs, a failure is usually not fatal: it becomes impossible for an “older” drive, but the stored information remains available. In addition, SSDs are less susceptible to mechanical damage. Testing shows that even the cheapest SSD models with daily recording can work properly for more than 10 years.
This may be an exaggeration, but for e-commerce sites, a loss of milliseconds can mean a loss of profit. And not only for them. Even a small improvement in the speed of a site’s work sometimes gives significant results: the number of visitors to the site increases, the average time the site is viewed, this affects financial performance. For example, for dynamic sites on the HDD it can be 15-20 ms, while on SSD it can be 0.2 ms.

The site may lose visitors if the pages load too long, or they will leave it faster. According to KISSmetrics statistics, if a site loads about 4 seconds, then up to a quarter of customers leave the page. So a small investment in hosting on SSDs can ultimately pay off many times. The faster the site loads, the more sales grow.
However, it is likely that SSDs will not be the best value choice for tasks such as web storage, large archives of video, photos or music, or other tasks that require storing large amounts of data. Yes, the video will start faster, but at a constant speed of data transfer, streaming, SSD practically will not give advantages.

The general conclusion is this: it all depends on the requirements. For example, SSD hosting speeds up access to the database on the server. For many sites, this is not just a desirable indicator, but a necessary condition for their correct operation, for example, if the site is built on one of the popular CMS, then for the fast loading of pages, hosting on the SSD may be required.
Fast hosting will be useful for sites that receive advertising revenue, because the profit in this case depends on the time spent by visitors on the site, as well as on the number of page views. but there is a third option.
Despite all its advantages, SSDs are still quite expensive. Some hosting providers offer hybrid hosting - on SSD in combination with SATA drives. Space on specialized servers with SSDs is used for the most loaded site processes - for working with databases.
Combining SSDs and HDDs in one hosting plan is a rather original solution. The bulk of the data in this case can be stored on large, but relatively slow HDDs, and requests are cached on high-performance, but less capacious SSDs. The caching mechanism can work as follows: when a request arrives at the disk system, the requested data is checked first on the SSD (in the cache), and if it is not there, it is requested from the main one. disk storage, transferred to the client and cached at the same time.

This is similar to using the built-in cache, disk drive, but the capacity of the SSD cache is much larger, and it does not work more efficiently. The main advantage of this approach is the rational use of the capabilities of two technologies - high-performance SSD and high-capacity HDD (at low storage cost) without significant loss of performance. Of course, this is a compromise.
As a rule, the server will only work faster on solid-state media, although advertising offers often promise that when hosting with caching on SSDs, the speed will be as high at a lower price and with a larger capacity.
Again, it all depends on the task, on how the virtual server will be used. If this is a dynamic project with a large number of requests (visited site, 1C base, game server), then the combination of SSD-HDD will be significantly inferior to SSD in speed. If those hosted on the server are mostly not very “active” and rarely requested, then the speed for hosting with caching on SSDs can be close to “pure” SSD hosting. HDD is better to use when access speed does not play a fundamental role, for example, in small projects, with archival storage, etc.


"Game Rules" are changing

Progress in surface recording density of HDD and flash memory (GB per square inch).
Although the linear read speed on the HDD has grown significantly in recent years, and the recording density on the plate continues to increase, the speed of the read / write head changes little, so often these disks are slow. The speed of solid state drives can be several times higher than the potential of hard drives.

Currently, 90% of hosting providers in the world use servers with HDDs, since this is the cheapest option, disk drives have a large capacity, are easily configured to work with servers, and do not require special hardware.
Meanwhile, according to Gartner's forecast, already in 2017, enterprise-class SSDs will be sold more than HDDs. Over the next three years, in the corporate segment, SSD sales (in monetary terms) will grow by an average of 20% per year, while HDD - by only 4%. Transparency Market Research (TMR) also believes that by 2022 the segment of enterprise-class SSD drives will develop most rapidly: the average annual sales growth rate of such products may exceed 76%.

Along with an increase in performance, the capacity of SSDs is also growing. In 2016, Seagate, Samsung, Toshiba, Western Digital, and a dozen other vendors introduced large-capacity SSDs that can be used for data archiving, which is previously unusual for flash drives. Samsung by 2020 is going to release a flash drive form factor 2.5 inches with a capacity of 100 TB. Its high-capacity SSD uses 64-layer 3D V-NAND memory. The data transfer speed of a single chip with a capacity of 64 GB reaches 800 Mbps.
Samsung also introduced the BGA (Ball-Grid Array) SSD with three bits per cell. Weighing 1 g, it holds 1 terabyte of data. The sequential read speed is 1500 MB / s, and the write speed is 900 MB / s. Among other new Samsung products is the SSD of the M.2 form factor with a capacity of 2 TB.
Many SSDs are designed specifically for data centers. For example, Intel's SSD DC P3520 Series, released in August 2016, are PCIe SSD devices that are optimized for high performance at a reasonable price. SSD DC P3520 series drives are suitable for working in cloudy environments in applications with a large number of read operations, for example, during storage virtualization or for organizing web hosting. Intel PCIe SSDs powered by 3D NAND technology are becoming an affordable alternative when deploying NVMe-enabled storage arrays where you need to process large data sets.

According to Intel, Intel SSD DC S3520 SSDs offer a good combination of low cost and high performance for data centers and provide significant performance gains and reduced latency compared to traditional HDDs used in the data center. SSD DC S3520 Series devices are aimed at those who want to replace disk drives with SATA SSDs.

Equipped with flash drives, servers and storage systems today can solve the most demanding tasks, such as searching in large databases, online transaction processing, business analytics and large-scale virtualization in cloud computing.
The problem of SSD durability has been practically solved: modern drives are designed for five years of intensive use. SSDs have every chance in the near future to replace the HDD in the servers, and in the future - in the storage. A 16 TB SSD has already been announced, and by 2020 a 40 TB flash drive will appear. New developments can lead to significant changes in many segments of the IT industry.
But what does all this mean in terms of today's website hosting tasks?
SSD: Pros and Cons
In general, when using the SSD, the operating system and applications load faster, access to data is accelerated, while the HDD has more attractive cost indicators, it is more profitable to store large amounts of data on them. Capacity on an SSD is so far noticeably more expensive. Let's try to weigh in more detail all the pros and cons.
Hard disks, HDD
| Behind | Against |
| Low storage cost per gigabyte | Slow search, low read and write speeds |
| Large capacity (up to 8 TB per disk) | Drive failures are not uncommon |
| Performance can be increased with RAID | Cannot read and write at the same time |
Flash Drives, SSD
| Behind | Against |
| Fast search, high read and write speeds | Relatively high storage cost per gigabyte |
| Possible simultaneous read and write operations | Limited number of write operations (media wear) |
| Higher energy efficiency than HDD | Less available capacities |
And in specific numbers :
| Parameter | SSD | HDD (SAS, 10-15k) |
| Random Access I / O Performance (IOPS) | 6000 | 400 |
| Reliability (failure rate) | 0.5% | 2-5% |
| power usage | 2-5 watts | 6-15 watts |
| I / O timeout | 4 ms | 7 ms |
| Access time | 0.1 ms | 5.5-8 ms |
| Average backup I / O request processing time | 20 ms | 400-500 ms |
| Estimated Drive Backup Time | 6 h | 20-24 h |
And here is another comparison, more obvious (for different models of drives and interfaces the data may differ):

HDD vs SSD: speed, performance, delay.
It follows that the SSD is at least 15 times faster, 4-10 times more reliable than the HDD. On a large server, using them will save about 100 watts of power consumption and free up 6% of computing power. But what are the benefits of all this when hosting websites?
Website: load time
In fact, several factors affect the load time of a page on a site:
- The domain name server (DNS) assigns an IP address (DNS Lookup) from the text name of the site.
- When the site host server receives an HTTP GET request from the client, it needs to read the necessary data from the storage system, process it, and send information to the client.
- The client-side browser interprets and displays the received information.
As you can see, the total loading time of a page on a site depends not only on the speed of reading data, but this time is a critical component. When a website is hosted on an SSD, it gets all the benefits of high speed access to this medium.

Providers often use reliable and fast enterprise-class SSDs with an eMLC memory type. Disks integrated into RAID arrays achieve data transfer speeds of up to 100 thousand IOPS, and Windows VPS starts within 7 seconds.
Optimization of site performance by speeding up data reading by the server, especially and instant work with files on SSD is desirable for sites of the following categories:
- E-commerce site or online store.
- Web applications (work applications, games, media players).
- Popular blogs and high traffic news feeds.
- Corporate sites.
- Other valuable online resources.
What is the potential gain from hosting on an SSD? If your site is already working well and the page loading speed is quite decent, do I need to switch to solid state drives? To feel the difference, you need to experiment with the SSD. Here is some gain promised by some foreign hosting providers:
| Hosting | Claimed speed gain when using SSD |
| Monstermegs | Page load time improves to 300%. |
| Inmotion hosting | With intensive I / O requests, data access times are reduced by 20 times. |
| A2 Hosting | Pages load up to 300% faster. |
| Crocweb | Performance in IOPS is up to 100% higher. |
| Asura hosting | Speed up page loading up to 300%. |
| Wire nine | Increase productivity up to 300%. |
From this it can be seen that in most cases the loading time of pages on a site due to SSDs is reduced by three times. In fact, in each case, the gain may be different. The high speed of SSDs is most noticeable for sites with high dynamics of working with data or with intense traffic (like social networks). The only real way to evaluate the benefits for a particular site is to try the SSD in practice.
The price of the question
And how much is this pleasure? Prices for SSD hosting usually start at a few dollars a month. Here are examples of some offers from providers:
| Hosting | Starting price (dollars per month) | Capacity (GB) |
| Monstermegs | 5.95 | 10 |
| Inmotion hosting | 4.19 | Not specified |
| A2 Hosting | 3.62 | RAID-10 without limits (not the fact that everything is on SSD) |
| Crocweb | 4.95 | 10 |
| Asura hosting | 1 | 3 |
| Wire nine | 25 | fifteen |
| RUVDS (Russia) | 1,5 | 10 |
So hosting on an SSD is the right solution not only for serious projects. For 95 rubles a month, you can completely promote a small gigabyte website for ten on an SSD. Of course, sites that require additional capacity, dedicated computing cores, bandwidth or other services will cost more, but if large capacity is not required, then hosting on an SSD is an affordable option.
SSD vs HDD
Before proceeding to the conclusion, we summarize what has been said:

Speed. SSDs are 300% faster than HDDs, which affects the speed of read-write, file transfer, etc. The HDD quickly reads only data that is close to the read head.

Noise. Since SSDs do not have moving parts, they work silently.

System boot time. In the case of SSD-drives, it averages 10-13 seconds, HDD - 30-40 seconds.

Weight. An SSD is much lighter, as it consists mainly of microchips.

Power usage.SSD consumes less than 2 watts even at peak load, HDD - 6-7 watts. The use of SSD-drives can reduce energy consumption by 80%, they do not require significant cooling costs. If we take into account the economies of scale in the data center, then it becomes obvious the prospect of using solid-state drives to reduce operating costs.

Reliability. Modern SDD drives are highly reliable, while disk failures are not uncommon.

Defragmentation. SSDs do not need it. An HDD without defragmentation loses performance.

Response time. For SSD-drives it is almost a hundred times smaller than that of the HDD and is 35-100 ms compared to 5000-10000.

Performance.The HDD is much lower than the SSD-drives, which do not require mechanical operations.

Bounce rate. HDD mechanics fail more often. SSDs have very low failure rates.
Disk failure is a trouble for the site owner, because often all the data that is located on the hard disk is lost (if you neglect the backup). In the case of SSDs, a failure is usually not fatal: it becomes impossible for an “older” drive, but the stored information remains available. In addition, SSDs are less susceptible to mechanical damage. Testing shows that even the cheapest SSD models with daily recording can work properly for more than 10 years.
Time is money
This may be an exaggeration, but for e-commerce sites, a loss of milliseconds can mean a loss of profit. And not only for them. Even a small improvement in the speed of a site’s work sometimes gives significant results: the number of visitors to the site increases, the average time the site is viewed, this affects financial performance. For example, for dynamic sites on the HDD it can be 15-20 ms, while on SSD it can be 0.2 ms.

The site may lose visitors if the pages load too long, or they will leave it faster. According to KISSmetrics statistics, if a site loads about 4 seconds, then up to a quarter of customers leave the page. So a small investment in hosting on SSDs can ultimately pay off many times. The faster the site loads, the more sales grow.
However, it is likely that SSDs will not be the best value choice for tasks such as web storage, large archives of video, photos or music, or other tasks that require storing large amounts of data. Yes, the video will start faster, but at a constant speed of data transfer, streaming, SSD practically will not give advantages.

The general conclusion is this: it all depends on the requirements. For example, SSD hosting speeds up access to the database on the server. For many sites, this is not just a desirable indicator, but a necessary condition for their correct operation, for example, if the site is built on one of the popular CMS, then for the fast loading of pages, hosting on the SSD may be required.
Fast hosting will be useful for sites that receive advertising revenue, because the profit in this case depends on the time spent by visitors on the site, as well as on the number of page views. but there is a third option.
SSD + HDD
Despite all its advantages, SSDs are still quite expensive. Some hosting providers offer hybrid hosting - on SSD in combination with SATA drives. Space on specialized servers with SSDs is used for the most loaded site processes - for working with databases.
Combining SSDs and HDDs in one hosting plan is a rather original solution. The bulk of the data in this case can be stored on large, but relatively slow HDDs, and requests are cached on high-performance, but less capacious SSDs. The caching mechanism can work as follows: when a request arrives at the disk system, the requested data is checked first on the SSD (in the cache), and if it is not there, it is requested from the main one. disk storage, transferred to the client and cached at the same time.

This is similar to using the built-in cache, disk drive, but the capacity of the SSD cache is much larger, and it does not work more efficiently. The main advantage of this approach is the rational use of the capabilities of two technologies - high-performance SSD and high-capacity HDD (at low storage cost) without significant loss of performance. Of course, this is a compromise.
As a rule, the server will only work faster on solid-state media, although advertising offers often promise that when hosting with caching on SSDs, the speed will be as high at a lower price and with a larger capacity.
Again, it all depends on the task, on how the virtual server will be used. If this is a dynamic project with a large number of requests (visited site, 1C base, game server), then the combination of SSD-HDD will be significantly inferior to SSD in speed. If those hosted on the server are mostly not very “active” and rarely requested, then the speed for hosting with caching on SSDs can be close to “pure” SSD hosting. HDD is better to use when access speed does not play a fundamental role, for example, in small projects, with archival storage, etc.

