Hyper-V or KVM?
Server virtualization technology with its more than thirty-year history has become one of the key in IT today, formed the basis of next-generation cloud computing and services. Companies that choose a platform for VPS or virtualization in their IT infrastructure, along with VMware products, consider solutions based on other hypervisors, primarily Microsoft Hyper-V and developed as part of the Open Source KVM hypervisor, as an alternative.
A variety of virtualization tools makes you wonder: what exactly to choose? This can be a daunting task. For example, proponents of Xen consider it a reliable and flexible platform with a good set of management tools. Fans of Hyper-V and KVM will give weighty arguments in favor of these solutions and list their advantages.

You can proceed when choosing from such parameters as productivity, cost, openness, efficiency, manageability, platform support ... However, experts advise choosing a virtualization solution, first of all, guided by business requirements. Deployed in a corporate environment, it should be suitable for an extensive stack of certified business applications (ERP, MRP, HR, CRM, etc.), and the developer, if it is a commercial product, should have clear plans for product development in different directions (disaster recovery, backup copying, SDN, etc.). Finally, good virtualization software is scalable and flexible enough.
For example, KVM performance with increasing load decreases faster than that of Xen (according to the test results). Xen is scalable — the ability to support a large number of concurrent VMs. Xen is thought to be superior to KVM in backup and storage management capabilities.
A similar dilemma arises when analyzing rental offers for virtual servers (VDS / VPS). Hosters offer a variety of virtualization tools, including Xen, KVM, Microsoft Hyper-V, OpenVZ, Virtuozzo, VDS manager, etc. (VMware is very rare due to the high cost), while the provider is always ready to talk about the advantages of the system used, but virtualization products are rare compare and just as rarely mention their shortcomings.
Let's try to partially fill this gap. In particular, to compare two popular virtualization hypervisors - Microsoft Hyper-V for server operating systems of the Windows family and KVM for Linux. However, you should immediately make a reservation that there is no ideal virtualization system for VPS , each is suitable for its own tasks. For example, many of those who use the KVM platform also use Linux-based virtual machines (VMs).

Need VPS with Linux or FreeBSD? You can select KVM. VPS on KVM with Windows is also an option, but Microsoft Hyper-V is preferable for this OS. The latter is considered the best solution for server virtualization with Windows, and is actively used by hosting providers.
Xen and KVM are open source products that are very similar in function and performance, but if in the Citrix XenServer version the first is gradually turning into a cloud platform, the development of KVM keeps pace with the evolution of distributions such as Red Hat's RHEV. Hyper-V is commercial software from Microsoft. Not surprisingly, Hyper-V works great on the Windows infrastructure. All of them allow you to virtualize x86-64 server platforms and are hardware virtualization systems for VPS hosting and more.
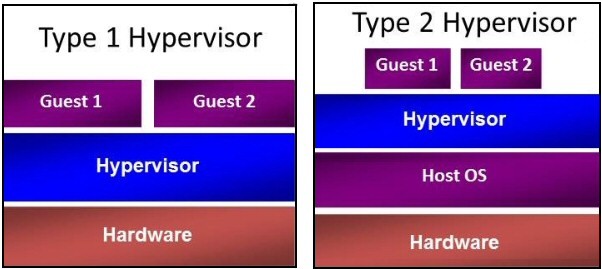
Hyper-V, KVM, ESXi - the first type of hypervisors (Type-I). They work directly on the physical hardware that the operating system accesses through the hypervisor. Hypervisors of the second type (Type-II), for example, VMware Workstation, Oracle Virtual Box, OpenVZ, operate on top of the operating system, so the VM and the hypervisor interact with the equipment through the OS. It is believed that the performance of hypervisors of the second type is lower than the first, since it also depends on the host OS.
Use of Hyper-V and KVM in different industries,% of respondents (data from IT Central Station ).
Using Hyper-V and KVM in companies with different numbers of employees,% of respondents (data from IT Central Station ).
These two hypervisors are not only comparing with each other. KVM is sometimes associated with VMware ESXi and IBM PowerVM, while Microsoft Hyper-V is often associated with Oracle VM VirtualBox, and occasionally with Proxmox VE.
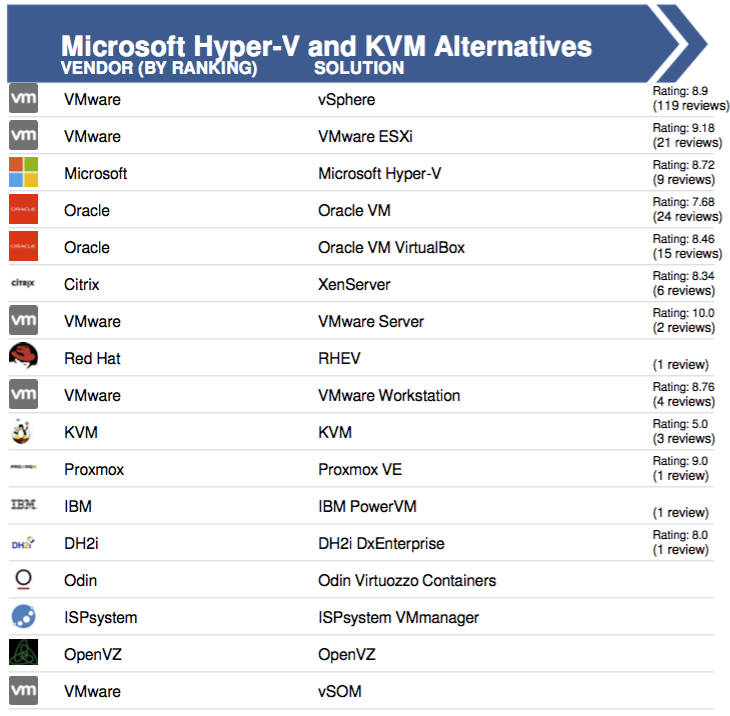
Alternatives to Hyper-V and KVM (in the Open Source version), according to the industry press (in descending order; rating compiled by IT Central Station , 2016).
Microsoft product exists in two ways: as a standalone Hyper-V Server (in the latest version - Hyper-V Server 2012 R2) or as one of the components of Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2 or 64- bit version of Window 8/10 Pro. In any case, it is used to create a virtual environment on the server, providing appropriate services and tools for this.
You can also virtualize jobs by deploying a VDI infrastructure, or create a convenient environment for developing and testing software. The cost-effective and stable Hyper-V virtualization environment allows you to simultaneously run several operating systems on the host, including Windows, Linux, and others. Currently, Hyper-V is used by companies and organizations of almost any industry, including the largest customers. What does it give? For example, Hyper-V can serve as the basis for deploying a private cloud, it can optimize the use of hardware resources, consolidate servers by running several virtual machines on the same physical system, and provide fault tolerance for the continuity of business processes. However, this is not unique to this hypervisor.
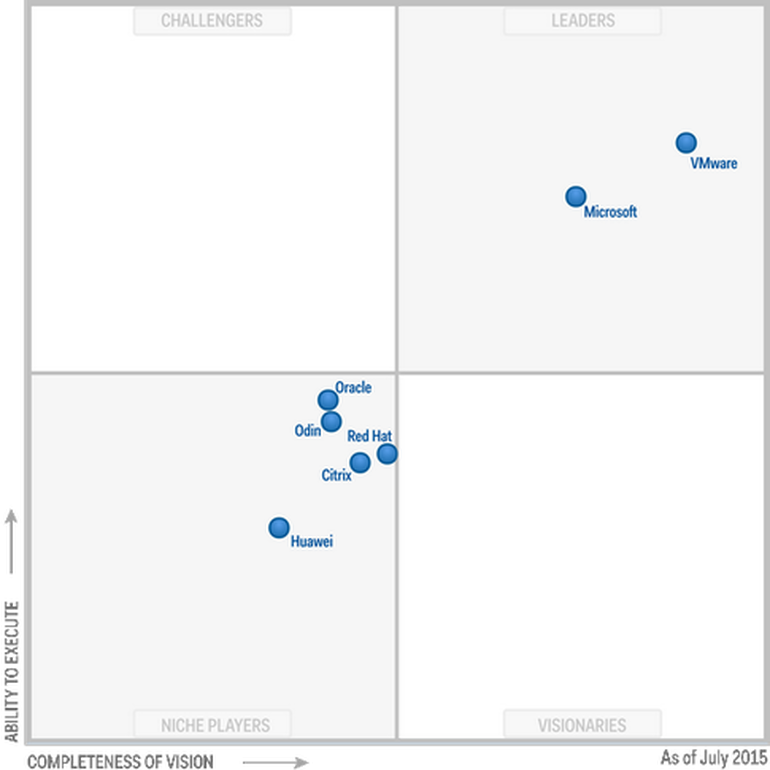
The "Magic Quadrant» Gartner for x86 server virtualization infrastructure (Magic Quadrant for x86 Server Virtualization Infrastructure ), issued in July 2015, leading Microsoft and VMware. Xen and KVM are represented by vendors of Citrix and Red Hat.
What exactly is Hyper-V valued for? System administrators and IT managers call such qualities as high stability of Hyper-V and Windows, support for “live migration” of VMs (Live Migration) and clustering (for building high availability configurations), scalability, the ability to assign network cards (NICs) to virtual machines This avoids the bottlenecks that sometimes occur when a single physical network adapter is assigned to a virtual switch.
Live Migration allows you to move VMs between physical Hyper-V servers, including automatically, without user intervention.
They also mention the possibility of centralized server management - multiple Hyper-V hosts, without additional license purchase, as in the case of VMware vCenter. Relatively simple (although more complicated than in VMware), the physical server is migrated to a virtual (P2V) server. To do this, create a VHD image of the physical system and assign it to a new VM. Convenient mode Enhanced Session Mode allows you to copy / paste inside the VM.
Hyper-V is easy to use and manage - a good alternative to VMware in the SMB segment. It is included in Windows 10, and it is almost a fully functional version. The hypervisor itself does not cost anything, it can be downloaded from the Microsoft website (in the form of Hyper-V Server), it is well suited for virtualization of Microsoft OS, it is easy to install and configure, and most system administrators can work with it. Hyper-V can be installed on any server that supports Windows. Another plus: the majority of Microsoft products can work in a virtual Hyper-V environment.
Negative qualities include limited options for configuring work with storage systems (for example, the difficulty of configuring iSCSI target in Windows Server 2012 R2. Import / export, creation of templates could be more reliable and friendly.
In Hyper-V, it’s quite difficult to configure some things, for example, High Availability (HA), where Failover Clustering is required. In vSphere, for example, this is made easier and more natural. And VM migration to Hyper-V, unlike vMotion, is possible only between servers with processors of the same family. There is nothing in Hyper-V that is similar to the Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) or Storage DRS, which in the VMware virtualization environment can be used to balance the load between the resources of several hosts using vMotion and Storage vMotion.
But SCVMM (System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2012) in Hyper-V offers opportunities that go beyond the actual server virtualization. For example, you can create a private cloud with self-service features. VMware has vCloud Director, but this is a standalone solution for a fraction of the cost. Microsoft SCVMM has a free application for System Center 2012. In addition, SCVMM allows you to use hosts with Hyper-V, vSphere and the Citrix hypervisor as virtualization platforms, while vCenter only supports VMware host management.
You can also mention that Debian and the distributions based on it are able to work perfectly under Hyper-V and can be used to implement infrastructure elements that work under heavy load. Microsoft also recently released an update.Linux Integration Services 4.0 for Hyper-V , which is a package of drivers, utilities, and enhancements for Linux guest OSs running in virtual machines on the Hyper-V and Azure platforms.
Features of Microsoft Hyper-V in Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter Edition
And now a few words about KVM. Although Microsoft and VMware platforms are still the undisputed leaders in building virtualized infrastructures for large businesses, the latter have seen a growing interest in KVM.
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a complete virtualization solution for Linux / x86 platforms that supports hardware extensions (Intel VT and AMD-V). It consists of a downloadable kernel module kvm.ko, which provides the basic virtualization infrastructure, and a module for a specific processor - kvm-intel.ko or kvm-amd.ko.
Initially, KVM only supported x86 processors, but now it has been supplemented by a wide range of processors and guest operating systems, including many variations of Linux, BSD, Solaris, Windows, Haiku, ReactOS, and AROS Research Operating System.
KVM users include well-known Wiki resources: MediaWiki, Wikimedia Foundation, Wikipedia, Wikivoyage, Wikidata, Wikiversity.
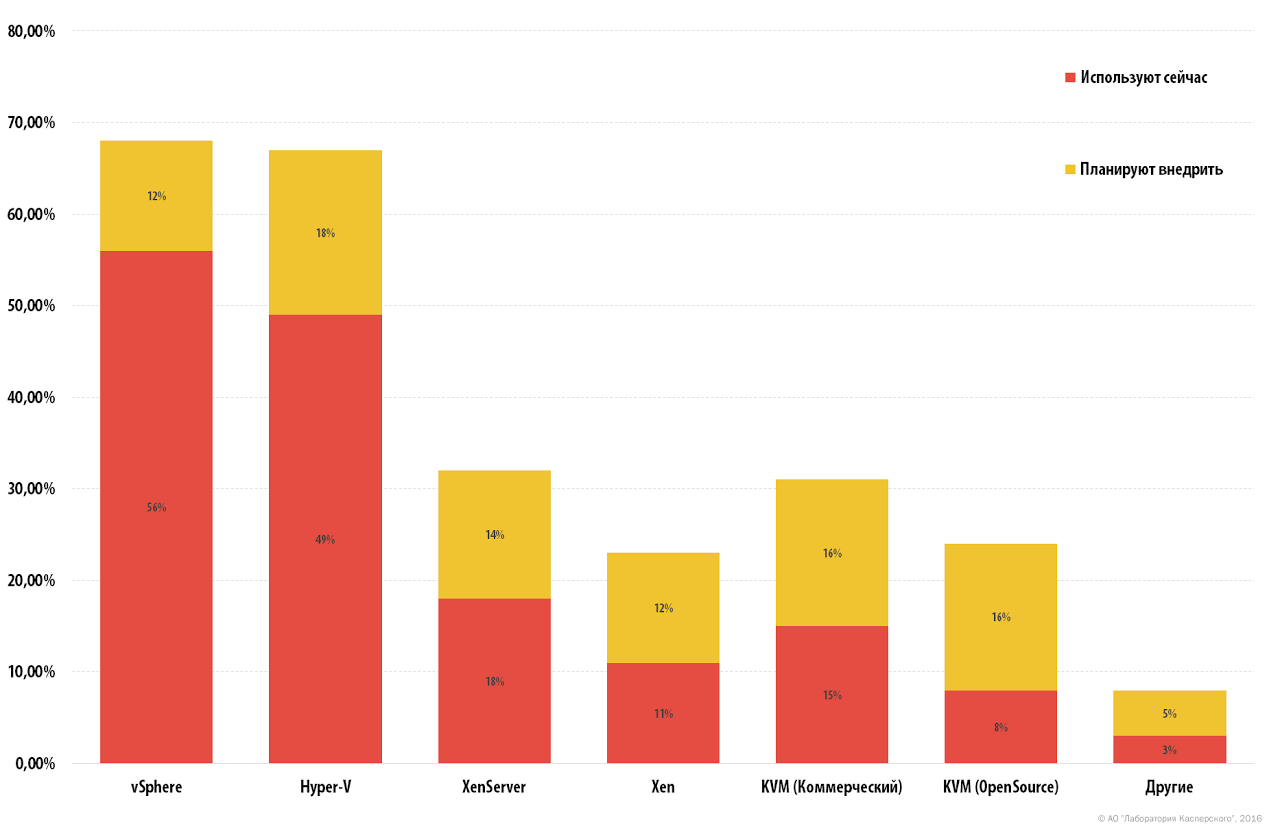
In 2015, Kaspersky Lab and B2B International conducted a study in which representatives of companies using virtualization technology were asked questions about their platforms. It turned out that 15% of companies use various options for commercial platforms based on KVM, and another 16% plan to implement them over the next couple of years. Free versions of the product are used in 8% of large organizations and another 16% of the companies surveyed will be introduced in the future.
A study by Kaspersky Lab showed that while the main hypervisors are most often VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V, they prefer to use open source solutions or commercial solutions based on Open Source as additional ones. Especially often - KVM.
Kaspersky Lab believes that there are several reasons for the popularity of KVM. Firstly, in some scenarios, the implementation of a virtualization platform based on KVM (even its commercial version) is much cheaper than using Microsoft Hyper-V and VMware vSphere. Secondly, the number of virtualized Linux servers is growing in the world. Their owners are more familiar and comfortable using the Linux-based hypervisor. In most cases, this is KVM. In addition, the Linux community contributes to the development of the platform, developing an ecosystem of solutions that support KVM.
Companies creating their own projects, integrated solutions, often choose the Open Source hypervisor, and KVM just provides ample customization options. Finally, KVM is a lightweight, easy to use, unpretentious resource and at the same time quite functional hypervisor. It allows you to deploy a virtualization platform in a short time, according to Kaspersky Lab.
Kvmin combination with the Linux kernel provides ease of implementation, flexible. Since guest operating systems interact with the hypervisor integrated into the Linux kernel, they can in all cases access the hardware directly without the need to change the virtualized operating system. This makes KVM a fast virtual machine solution. KVM is implemented in the Linux kernel itself, which facilitates the management of virtualization processes.
On the other hand, powerful tools for managing the server and KVM virtual machines do not exist. KVM needs to improve support for virtual networks and virtual storage systems, strengthen protection, improve reliability and fault tolerance, power management, support for HPC / real-time systems, scalability of virtual processors, interoperability between providers, and create an ecosystem of cloud services.
Since we are talking about management, it is worth mentioning one of the popular VPS control options in the case of KVM - SolusVM. This is a universal control panel for virtual servers Xen, KVM and OpenVZ.
Some users have noted that KVM is not stable when performing tasks with intensive I / O. There is an opinionKVM is not a very mature product for work environments and is more suitable for experiments and in cases where modification of the source code is required. Hyper-V is more stable, VM migration tools are more reliable, equipment is used more efficiently than in Linux-KVM.
Preparing KVM for work and setting up dozens of parameters is an amateur process, although there is also a Virsh management interface (and virtmanager GUI-interface) that allows running guest systems in KVM using a simple configuration file. It’s also convenient to use OpenStack tools to manage the KVM hypervisor. This helps, in particular, to implement cloud services.
There is no support service, only the community. But those who need it can choose the commercial option - RHEV (Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization).
Perhaps this information will help you make the right choice, however, as noted above, a lot depends on the problem being solved and many other conditions. And the range of such tasks today is extremely wide - from shared hosting to building software-defined data centers (SDDC) and the introduction of hybrid clouds. For example, the virtualization environment in the data center should provide a combination of several important characteristics: maturity, ease of deployment, manageability and automation, support and maintenance, performance, scalability, reliability, high availability and uptime, security.
When choosing a virtualization platform for VPS / VDS, different criteria apply. Often her wrong choice is money spent and dissatisfaction with the quality of services. Qualified consultation and selection of a server with the ability to test the selected tariff will help to avoid most problems. And you already have a background to start a dialogue with a VPS / VDS service provider.
A variety of virtualization tools makes you wonder: what exactly to choose? This can be a daunting task. For example, proponents of Xen consider it a reliable and flexible platform with a good set of management tools. Fans of Hyper-V and KVM will give weighty arguments in favor of these solutions and list their advantages.

You can proceed when choosing from such parameters as productivity, cost, openness, efficiency, manageability, platform support ... However, experts advise choosing a virtualization solution, first of all, guided by business requirements. Deployed in a corporate environment, it should be suitable for an extensive stack of certified business applications (ERP, MRP, HR, CRM, etc.), and the developer, if it is a commercial product, should have clear plans for product development in different directions (disaster recovery, backup copying, SDN, etc.). Finally, good virtualization software is scalable and flexible enough.
For example, KVM performance with increasing load decreases faster than that of Xen (according to the test results). Xen is scalable — the ability to support a large number of concurrent VMs. Xen is thought to be superior to KVM in backup and storage management capabilities.
A similar dilemma arises when analyzing rental offers for virtual servers (VDS / VPS). Hosters offer a variety of virtualization tools, including Xen, KVM, Microsoft Hyper-V, OpenVZ, Virtuozzo, VDS manager, etc. (VMware is very rare due to the high cost), while the provider is always ready to talk about the advantages of the system used, but virtualization products are rare compare and just as rarely mention their shortcomings.
Let's try to partially fill this gap. In particular, to compare two popular virtualization hypervisors - Microsoft Hyper-V for server operating systems of the Windows family and KVM for Linux. However, you should immediately make a reservation that there is no ideal virtualization system for VPS , each is suitable for its own tasks. For example, many of those who use the KVM platform also use Linux-based virtual machines (VMs).

Need VPS with Linux or FreeBSD? You can select KVM. VPS on KVM with Windows is also an option, but Microsoft Hyper-V is preferable for this OS. The latter is considered the best solution for server virtualization with Windows, and is actively used by hosting providers.
Xen and KVM are open source products that are very similar in function and performance, but if in the Citrix XenServer version the first is gradually turning into a cloud platform, the development of KVM keeps pace with the evolution of distributions such as Red Hat's RHEV. Hyper-V is commercial software from Microsoft. Not surprisingly, Hyper-V works great on the Windows infrastructure. All of them allow you to virtualize x86-64 server platforms and are hardware virtualization systems for VPS hosting and more.

Hyper-V, KVM, ESXi - the first type of hypervisors (Type-I). They work directly on the physical hardware that the operating system accesses through the hypervisor. Hypervisors of the second type (Type-II), for example, VMware Workstation, Oracle Virtual Box, OpenVZ, operate on top of the operating system, so the VM and the hypervisor interact with the equipment through the OS. It is believed that the performance of hypervisors of the second type is lower than the first, since it also depends on the host OS.
Use of Hyper-V and KVM in different industries,% of respondents (data from IT Central Station ).
| Hypervisor | Hyper v | Kvm |
| Finance | thirteen% | 21% |
| Transport | 9% | eleven% |
| Production | 7% | 7% |
| Public sector | 7% | 7% |
Using Hyper-V and KVM in companies with different numbers of employees,% of respondents (data from IT Central Station ).
| Hypervisor | Hyper v | Kvm |
| 1-100 | 17% | 25% |
| 100-1000 | 34% | thirty% |
| > 1000 | 49% | 45% |
These two hypervisors are not only comparing with each other. KVM is sometimes associated with VMware ESXi and IBM PowerVM, while Microsoft Hyper-V is often associated with Oracle VM VirtualBox, and occasionally with Proxmox VE.

Alternatives to Hyper-V and KVM (in the Open Source version), according to the industry press (in descending order; rating compiled by IT Central Station , 2016).
Microsoft Hyper-V
Microsoft product exists in two ways: as a standalone Hyper-V Server (in the latest version - Hyper-V Server 2012 R2) or as one of the components of Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2 or 64- bit version of Window 8/10 Pro. In any case, it is used to create a virtual environment on the server, providing appropriate services and tools for this.
You can also virtualize jobs by deploying a VDI infrastructure, or create a convenient environment for developing and testing software. The cost-effective and stable Hyper-V virtualization environment allows you to simultaneously run several operating systems on the host, including Windows, Linux, and others. Currently, Hyper-V is used by companies and organizations of almost any industry, including the largest customers. What does it give? For example, Hyper-V can serve as the basis for deploying a private cloud, it can optimize the use of hardware resources, consolidate servers by running several virtual machines on the same physical system, and provide fault tolerance for the continuity of business processes. However, this is not unique to this hypervisor.

The "Magic Quadrant» Gartner for x86 server virtualization infrastructure (Magic Quadrant for x86 Server Virtualization Infrastructure ), issued in July 2015, leading Microsoft and VMware. Xen and KVM are represented by vendors of Citrix and Red Hat.
What exactly is Hyper-V valued for? System administrators and IT managers call such qualities as high stability of Hyper-V and Windows, support for “live migration” of VMs (Live Migration) and clustering (for building high availability configurations), scalability, the ability to assign network cards (NICs) to virtual machines This avoids the bottlenecks that sometimes occur when a single physical network adapter is assigned to a virtual switch.
Live Migration allows you to move VMs between physical Hyper-V servers, including automatically, without user intervention.
They also mention the possibility of centralized server management - multiple Hyper-V hosts, without additional license purchase, as in the case of VMware vCenter. Relatively simple (although more complicated than in VMware), the physical server is migrated to a virtual (P2V) server. To do this, create a VHD image of the physical system and assign it to a new VM. Convenient mode Enhanced Session Mode allows you to copy / paste inside the VM.
Hyper-V is easy to use and manage - a good alternative to VMware in the SMB segment. It is included in Windows 10, and it is almost a fully functional version. The hypervisor itself does not cost anything, it can be downloaded from the Microsoft website (in the form of Hyper-V Server), it is well suited for virtualization of Microsoft OS, it is easy to install and configure, and most system administrators can work with it. Hyper-V can be installed on any server that supports Windows. Another plus: the majority of Microsoft products can work in a virtual Hyper-V environment.
Negative qualities include limited options for configuring work with storage systems (for example, the difficulty of configuring iSCSI target in Windows Server 2012 R2. Import / export, creation of templates could be more reliable and friendly.
In Hyper-V, it’s quite difficult to configure some things, for example, High Availability (HA), where Failover Clustering is required. In vSphere, for example, this is made easier and more natural. And VM migration to Hyper-V, unlike vMotion, is possible only between servers with processors of the same family. There is nothing in Hyper-V that is similar to the Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) or Storage DRS, which in the VMware virtualization environment can be used to balance the load between the resources of several hosts using vMotion and Storage vMotion.
But SCVMM (System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2012) in Hyper-V offers opportunities that go beyond the actual server virtualization. For example, you can create a private cloud with self-service features. VMware has vCloud Director, but this is a standalone solution for a fraction of the cost. Microsoft SCVMM has a free application for System Center 2012. In addition, SCVMM allows you to use hosts with Hyper-V, vSphere and the Citrix hypervisor as virtualization platforms, while vCenter only supports VMware host management.
You can also mention that Debian and the distributions based on it are able to work perfectly under Hyper-V and can be used to implement infrastructure elements that work under heavy load. Microsoft also recently released an update.Linux Integration Services 4.0 for Hyper-V , which is a package of drivers, utilities, and enhancements for Linux guest OSs running in virtual machines on the Hyper-V and Azure platforms.
Features of Microsoft Hyper-V in Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter Edition
| Maximum number of concurrent VMs | 1024 |
| Maximum number of processors per host server | 320 |
| The number of cores per host processor | Not limited |
| Maximum number of virtual processors (vCPUs) per host server | 2048 |
| Maximum RAM capacity per host server | 4 TB |
| Memory per VM | 1 TB |
| Virtual processors on VM | 64 vCPU |
| Dynamic memory allocation | Dynamic memory |
| Deduplication of memory pages | Not |
| Support for large memory pages (Large Memory Pages) | Yes |
| Centralized management | Yes, System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) |
| Active Directory Integration | Yes (via SCVMM) |
| VM snapshots | Yes |
| Browser management | Through the self-service portal |
| Host Server / Hypervisor Updates | Yes |
| Managing Third-Party Hypervisors | Yes, VMware vCenter and Citrix XenCenter Management |
| VM update | Yes (WSUS, SCCM, VMST) |
| Maintenance Mode | Yes |
| Dynamic power management | Yes, Power Optimization |
| Backup API | Yes, VSS API |
| Virtual Machine Templates (VM Templates) | Yes |
| Host Profiles | Yes |
| Migrating physical servers to virtual machines (P2V) | Not |
| Hot Migration of Virtual Machines | Yes, without shared storage (Shared Nothing), support for compression and SMB3, unlimited number of simultaneous migrations |
| Hot VM storage migration | Yes |
| Storage Profiles | Yes |
| USB support | No (except Enhanced Session Mode) |
| Hot Add Devices | Only storage devices and / or memory |
| Floppy devices in VM | 1 |
| Network Adapters / Interfaces | 8 NIC |
| IDE Virtual Disks | 4 |
| Virtual disk capacity | 64 TB for VHDX |
| The maximum number of nodes in the cluster | 64 |
| Virtual machines in a cluster | 8000 |
| High Availability Features in Host Server Failures | Failover clustering |
| Restarting virtual machines in the event of a failure at the guest OS level | Yes |
| Application Accessibility | Yes (Failover Clustering) |
| Continuous VM Availability | Not |
| Virtual machine replication | Yes, Hyper-V Replica |
| Automatic Cluster Resource Management | Yes, Dynamic Optimization |
| Resource pools | Yes (Host Groups) |
| Checking processor compatibility during machine migrations | Yes, Processor Compatibility |
| Supported Vaults | SMB3, FC, Virtual FC, SAS, SATA, iSCSI, FCoE, Shared VHDX |
| Cluster File System | CSV (Cluster Shared Volumes) |
| Boot from SAN Support | Yes (iSCSI, FC) |
| Dynamic Storage Allocation (Thin Provisioning) | Yes, Dynamic Disks |
| USB boot | Not |
| Storage based on local server drives | Storage Spaces, Tiered Storage |
| Service Levels for the I / O Subsystem | Yes Storage QoS |
| NPIV Support | Yes (Virtual Fiber Channel) |
| Multipath Path Access Support | Yes (DSM and SMB Multichannel) |
| Caching | Yes CSV Cache |
| Storage Integration API | Yes, SMI-S / SMP, ODX, Trim |
| NIC Teaming Support | Yes |
| Private VLAN Support | Yes |
| Jumbo Frames Support | Yes |
| Network QoS Support | Yes |
| IPv6 Support | Yes |
| Traffic monitoring | Yes |
Kvm
And now a few words about KVM. Although Microsoft and VMware platforms are still the undisputed leaders in building virtualized infrastructures for large businesses, the latter have seen a growing interest in KVM.
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a complete virtualization solution for Linux / x86 platforms that supports hardware extensions (Intel VT and AMD-V). It consists of a downloadable kernel module kvm.ko, which provides the basic virtualization infrastructure, and a module for a specific processor - kvm-intel.ko or kvm-amd.ko.
Initially, KVM only supported x86 processors, but now it has been supplemented by a wide range of processors and guest operating systems, including many variations of Linux, BSD, Solaris, Windows, Haiku, ReactOS, and AROS Research Operating System.
KVM users include well-known Wiki resources: MediaWiki, Wikimedia Foundation, Wikipedia, Wikivoyage, Wikidata, Wikiversity.

In 2015, Kaspersky Lab and B2B International conducted a study in which representatives of companies using virtualization technology were asked questions about their platforms. It turned out that 15% of companies use various options for commercial platforms based on KVM, and another 16% plan to implement them over the next couple of years. Free versions of the product are used in 8% of large organizations and another 16% of the companies surveyed will be introduced in the future.
A study by Kaspersky Lab showed that while the main hypervisors are most often VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V, they prefer to use open source solutions or commercial solutions based on Open Source as additional ones. Especially often - KVM.
Kaspersky Lab believes that there are several reasons for the popularity of KVM. Firstly, in some scenarios, the implementation of a virtualization platform based on KVM (even its commercial version) is much cheaper than using Microsoft Hyper-V and VMware vSphere. Secondly, the number of virtualized Linux servers is growing in the world. Their owners are more familiar and comfortable using the Linux-based hypervisor. In most cases, this is KVM. In addition, the Linux community contributes to the development of the platform, developing an ecosystem of solutions that support KVM.
Companies creating their own projects, integrated solutions, often choose the Open Source hypervisor, and KVM just provides ample customization options. Finally, KVM is a lightweight, easy to use, unpretentious resource and at the same time quite functional hypervisor. It allows you to deploy a virtualization platform in a short time, according to Kaspersky Lab.
Kvmin combination with the Linux kernel provides ease of implementation, flexible. Since guest operating systems interact with the hypervisor integrated into the Linux kernel, they can in all cases access the hardware directly without the need to change the virtualized operating system. This makes KVM a fast virtual machine solution. KVM is implemented in the Linux kernel itself, which facilitates the management of virtualization processes.
On the other hand, powerful tools for managing the server and KVM virtual machines do not exist. KVM needs to improve support for virtual networks and virtual storage systems, strengthen protection, improve reliability and fault tolerance, power management, support for HPC / real-time systems, scalability of virtual processors, interoperability between providers, and create an ecosystem of cloud services.
Since we are talking about management, it is worth mentioning one of the popular VPS control options in the case of KVM - SolusVM. This is a universal control panel for virtual servers Xen, KVM and OpenVZ.
Some users have noted that KVM is not stable when performing tasks with intensive I / O. There is an opinionKVM is not a very mature product for work environments and is more suitable for experiments and in cases where modification of the source code is required. Hyper-V is more stable, VM migration tools are more reliable, equipment is used more efficiently than in Linux-KVM.
Preparing KVM for work and setting up dozens of parameters is an amateur process, although there is also a Virsh management interface (and virtmanager GUI-interface) that allows running guest systems in KVM using a simple configuration file. It’s also convenient to use OpenStack tools to manage the KVM hypervisor. This helps, in particular, to implement cloud services.
There is no support service, only the community. But those who need it can choose the commercial option - RHEV (Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization).
Conclusion
Perhaps this information will help you make the right choice, however, as noted above, a lot depends on the problem being solved and many other conditions. And the range of such tasks today is extremely wide - from shared hosting to building software-defined data centers (SDDC) and the introduction of hybrid clouds. For example, the virtualization environment in the data center should provide a combination of several important characteristics: maturity, ease of deployment, manageability and automation, support and maintenance, performance, scalability, reliability, high availability and uptime, security.
When choosing a virtualization platform for VPS / VDS, different criteria apply. Often her wrong choice is money spent and dissatisfaction with the quality of services. Qualified consultation and selection of a server with the ability to test the selected tariff will help to avoid most problems. And you already have a background to start a dialogue with a VPS / VDS service provider.

