Part 1. DSS platform Universal algorithms
Greetings, dear community!
Looking ahead, I apologize to those who expect novelty or revolutionary ideas. They are not here. But there is a very good application system.
Decision support systems are gaining momentum. And I will not particularly dwell on the list of implementation methods. I will only mention the basic properties. I would very simply and generically call these systems probabilistic. That is, they issue recommendations with a certain degree of probability using the accumulated and analyzed statistics. I will not say that this is bad. The theme of BigData and Machine learning is now trending. Also, these systems operate on the principle of a black box. Therefore, it is not always possible to verify the reliability of the embedded model.
I’ll try to describe a decision support system based on a slightly different one, someone can say it’s archaic, we will conditionally call it evaluative. That is, the system models the principle of how a person actually acts - evaluates the situation and makes a decision based on the assessment made in this particular situation. And not on generalized data.
The simplest example: you enter a room. Evaluate lightly or not. If it’s dark, turn on the light and go into the room. If it is light, then immediately go into the room. And a new assessment ...
Simplified, approximately the same approach is used by the solution I am describing. That is, for decision-making, analysis is not carried out on the basis of BigData with the identification of certain trends and patterns. A specific situation is assessed. And based on a specific assessment, a very specific decision is made.
To avoid much criticism, I can say that BigData is very useful. And the data obtained on their basis should be used in DSS. But DSS should not rely on BigDta as a fundamental basis. This is a topic for a separate discussion.
The solution is based on the methodology of the private algorithms of the doctor’s actions. In this case, abstraction is added and the scope of application is expanded.
There are a lot of algorithmic descriptions. Not everyone is comfortable. And even more so, far from everyone can claim that they could equally well describe the expert system. Yes, and in various professional fields.
I personally liked the fairly simple description model, which uses 3 main elements: question, answer and recommendation. It is noteworthy that this technique made it possible to describe the most complex industry from the point of view of formalization - medicine. That is, this technique had a successful practical application. And it is also important that with the availability of tools, DSS logic can be created by specialists from their professional fields without the involvement of developers.
To get started, an algorithm for a specialized ambulance team, “Coma, Poisoning, Collapses,” was taken on paper. They did not give it to me. Temporary use only. In fact, it was a set of instruction cards.
Ideologically, I wanted to get solutions for various professional fields except medicine. Therefore, it was decided to develop a platform with which it will be possible to both create algorithms (create DSS logic) and use the created DSS. The way was chosen not to contrast the system with existing solutions, but rather, create as an addition that allows you to expand the functionality. That is, the system must have an API that would allow integration into existing systems.
So the concept of the DSS platform Universal Algorithms appeared. Which is based on 3 pillars:
• Methodology for creating and describing an algorithmic model
• Algorithm Designer - an application for the visual creation and editing of DSS algorithms
• Algorithm Navigator - a web application that implements the use of a logical DSS model.
Everyone understands that this is a graph model. To be honest, I did not want to reinvent the wheel, but one ill-wisher, with his caustic remark, prompted me to draw a model to be created. Therefore, there was a ready-made Graphviz solution that perfectly copes with such a task. Another plus is that this package allows you to create interactive graphs with URLs.
It makes no sense to draw a graph of the whole algorithm, otherwise it will not fit on a huge wall. Therefore, the way was chosen to create a graph for each situation. If an element leads to another situation, then this is displayed on the graph.
Algorithm-Designer allows you to create a logical model according to the methodology. The content algorithm is divided into situations. And in situations, a model of reasoning is implemented.
Algorithm Designer - Windows application. So far, the concept has not been invented how else it is possible to implement all the functionality of such an application as an alternative solution (for example, web).
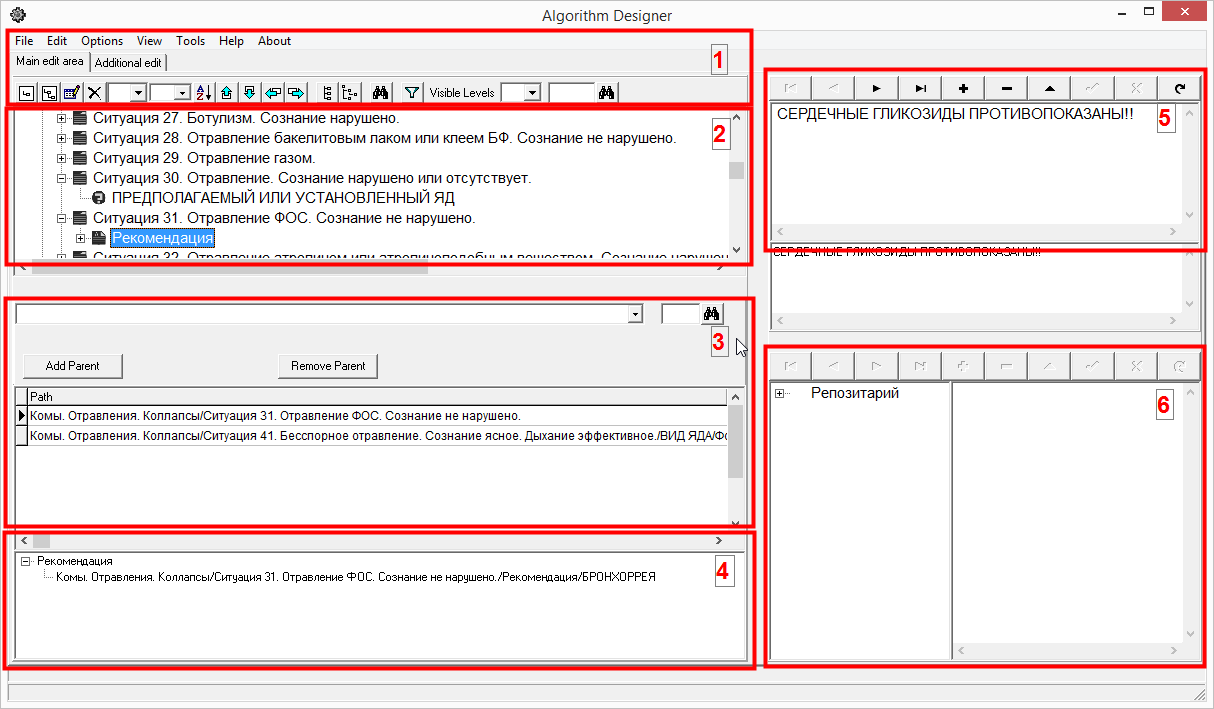
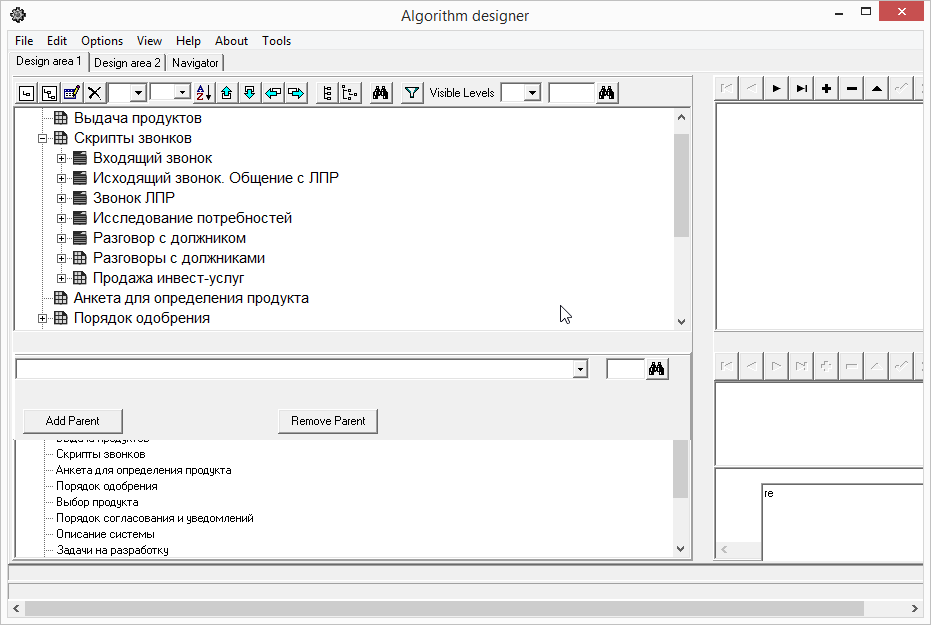
The screenshot shows the main elements in the Algorithm Designer:
As already mentioned, in fact, the structure of the algorithm is a graph model. But working at the application level is convenient with a tree structure. And it’s more convenient to logically separate a common data model in a tree view.
The main logic element is the Algorithm.

An algorithm may contain nested elements of the same type. That is, the element of the ambulance algorithm may contain algorithm elements for specialized ambulance crews.
Further, the Algorithm is divided into Situations. The situation exists in order to divide the algorithm into logical sections. This allows you to select a separate logical task from the general algorithm.
Note: In terms of programming, we can assume that the Algorithm is a program, and the Situation is a subprogram, procedure, or function.
Naturally, all the elements are interconnected. Therefore, the logical elements of the Algorithm allow you to establish connections and transitions between Situations.
Next comes the element - Question. The system works on the principle of assessing the "current situation". Therefore, it constantly works in the mode of asking a question and receiving a response from the user.
The answer is the logical element associated with the question. What the user will choose to evaluate the "current situation"
A recommendation is a logical element that, on the basis of an assessment, suggests or requires certain actions to be performed. Recommendations are divided into simple ones and those that set the time for execution. That is, for such recommendations, a time period is determined during which an action must be performed before the movement according to the algorithm continues - the minimum and maximum interval.
Another auxiliary element is used - Close the line. This was dictated by the fact that I wanted to visually highlight the moment when the line of reasoning ends. This element can be used repeatedly in the algorithm. In this case, there is redundancy. But it is better to neglect it for the sake of clarity.
An algorithm is a graph. But the display is tree-like. Therefore, the tree displays only one parent of the node. Which does not reflect the real state of things. Also, all child nodes are not visible in the tree if they are in other branches of the tree. Also needed a mechanism to establish such connections. Therefore, the “Parent” assignment functionality for the node was implemented. Child elements are just an informative display.
To simplify viewing and testing in the tree, double-clicking on an element switches to the 1st child node. Including the one that is installed in another branch. The reverse movement on the tree to the parents is carried out by double-clicking in the display field of the child nodes.
The logical model is editable and open. But the visual presentation makes it even more visual and understandable for a wider audience without special knowledge. As a means of visualization, the Graphviz tool was chosen . Because it builds charts fast, free and cross-platform. There are a number of advantages. One of them is the ability to build interactive charts. That is, each element can contain a URL.
It was decided to display according to situations. Since the whole algorithm is a fairly large canvas, which is difficult to understand. Elements of diagrams contain a display of all texts. This applies to Recommendations and additional reference commentary explanations for the Responses. This allows you to fully reflect the logical and meaningful content of the system.
For implementation, Delphi, DBMS Firebird, Graphviz were used . The binding to the DBMS is dictated by the use of the component. For use in the Algorithm-Navigator web application, the database was converted to MySql, SQLite, etc.
Algorithm-Navigator is designed as a web-application with an adaptive design. It looks quite normal on screens with different orientations and resolutions. Also, the interface is simple enough to use so that no special user training is required.
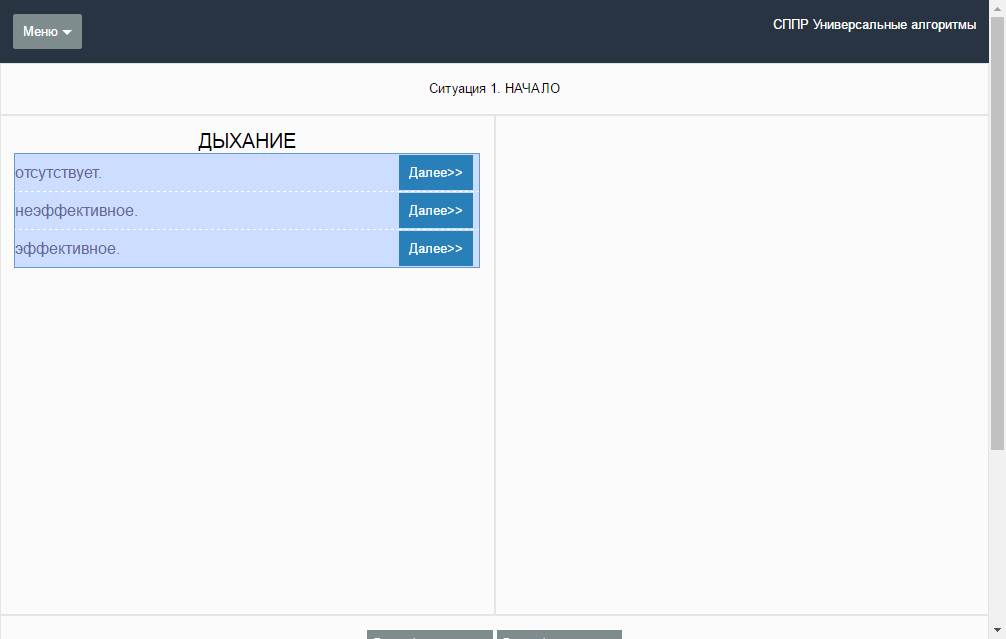
For some time I have been choosing a way to implement Algorithm-Navigator. It was known that this should be a web application, that there should be the ability to run on Linux and there should be an API for embedding into other information systems. Because initially it was planned not to contrast the system with the existing ones, but rather to supplement it.
Python was chosen for development. Bottle framework (I plan to transfer everything to django). There is no need for special explanations. I am not a specialist in design and do the project myself. Therefore, a ready-made kit for the front-end was takentiton.io , which has all the necessary functionality.
I made up the pages as they should have looked. And then based on them I made templates.
Since I wanted to have the functionality of generating diagrams in the Algorithm-Navigator, the pydot package was used .
Algorithm Designer allows you to create a logical model. In principle, you can start using it immediately after creating several steps.
As you progress through the algorithm, all user steps are fixed. According to them, the protocol is restored. This is another feature of this methodology - when passing through the algorithm, a specialist reasoning protocol is formed. Which can be used as a document. I planned to copy the text into the service desk system requests.
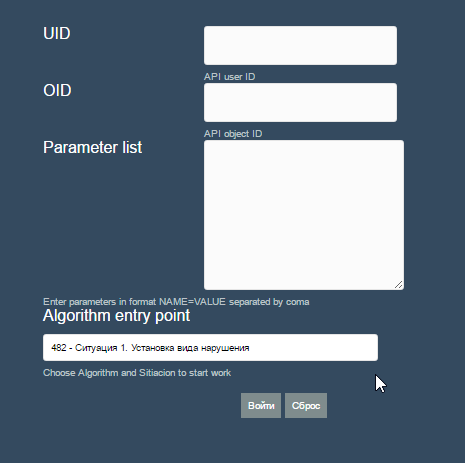
UID - user ID of the algorithm.
OID - ID of the object. In this case, there can be any object. In medicine, the patient.
Parameter list - a set of parameters of type name = value for macro substitution in the algorithm texts. As an example, name, company name, product name.
Algorithm entry point - the entry point to the algorithm. It is not always necessary to start from the very beginning. When calling an algorithm from another system, you can select a point in the algorithm (situation) with which work will begin.
First of all, the algorithms were created and used in medicine. True, this happened on the cards. It was amusing to see this method, when out of hundreds of cards with the help of a pair of knitting needles fell out the right one. Modern index searches and queries rest on the speed of providing data to the user.
Medicine: Ambulance dispatcher, Algorithms of specialized ambulance crews (I mentioned Coma, Poisoning, Collapses), Prof. examination, Pulmanology, Cardiology, Pediatrics, Obstetrics and Genicology, Recovery algorithm for medical facilities.
This is not a complete list.
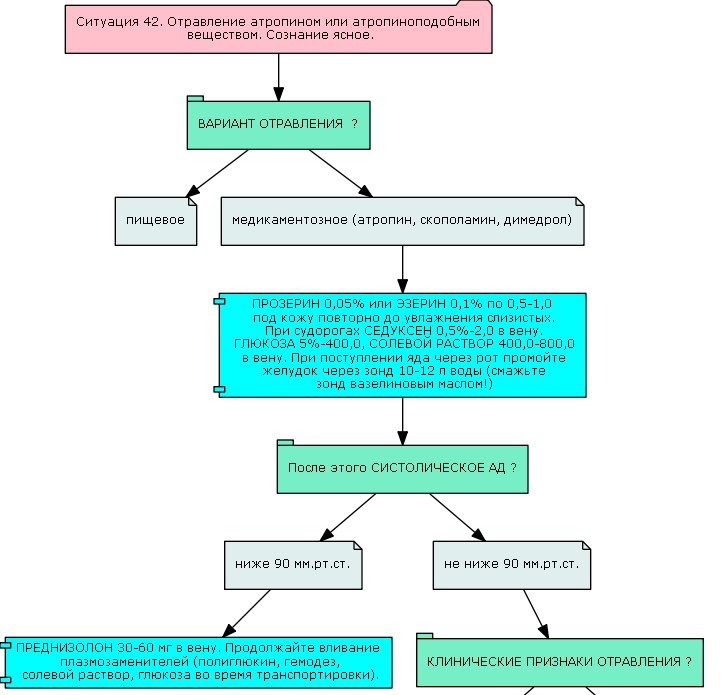
I have already described an attempt to create an expert system for a support service in a branch network of a private medical company.
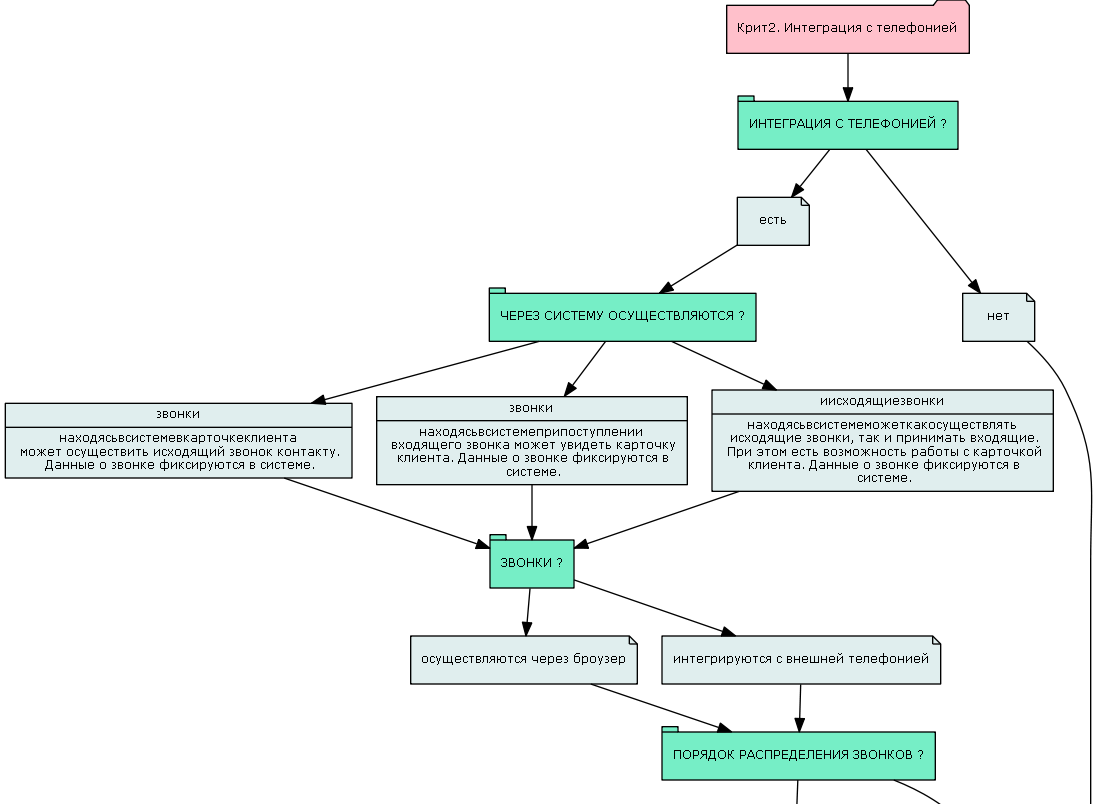
An example of a CRM criteria analysis provided that the criteria are composite.
Scripts of conversations and sales of services.
The ability to create a questionnaire for a mystery shopper.
A side effect is the ability to describe regulations using diagrams.
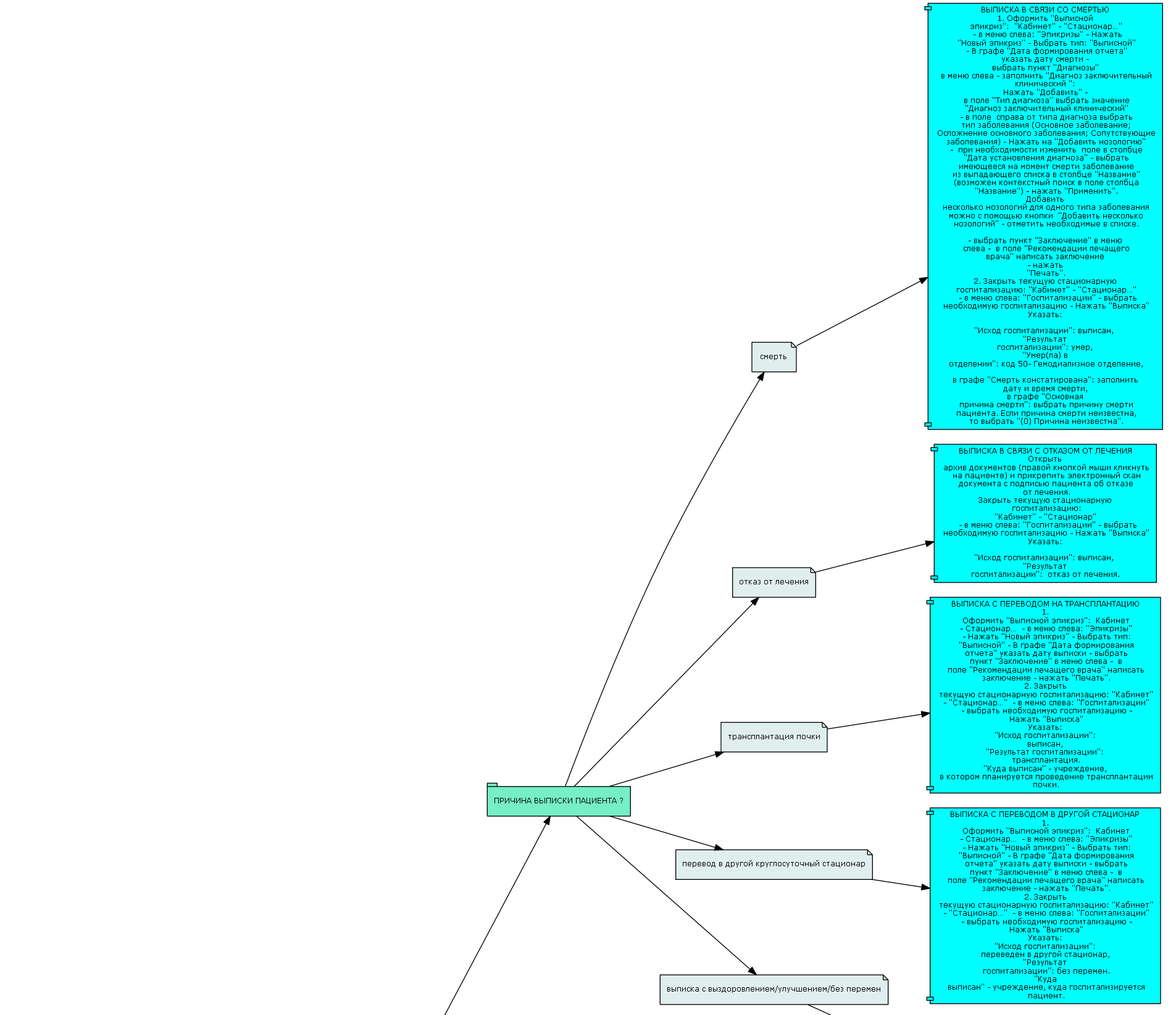
Used to describe the rules for patient discharge:
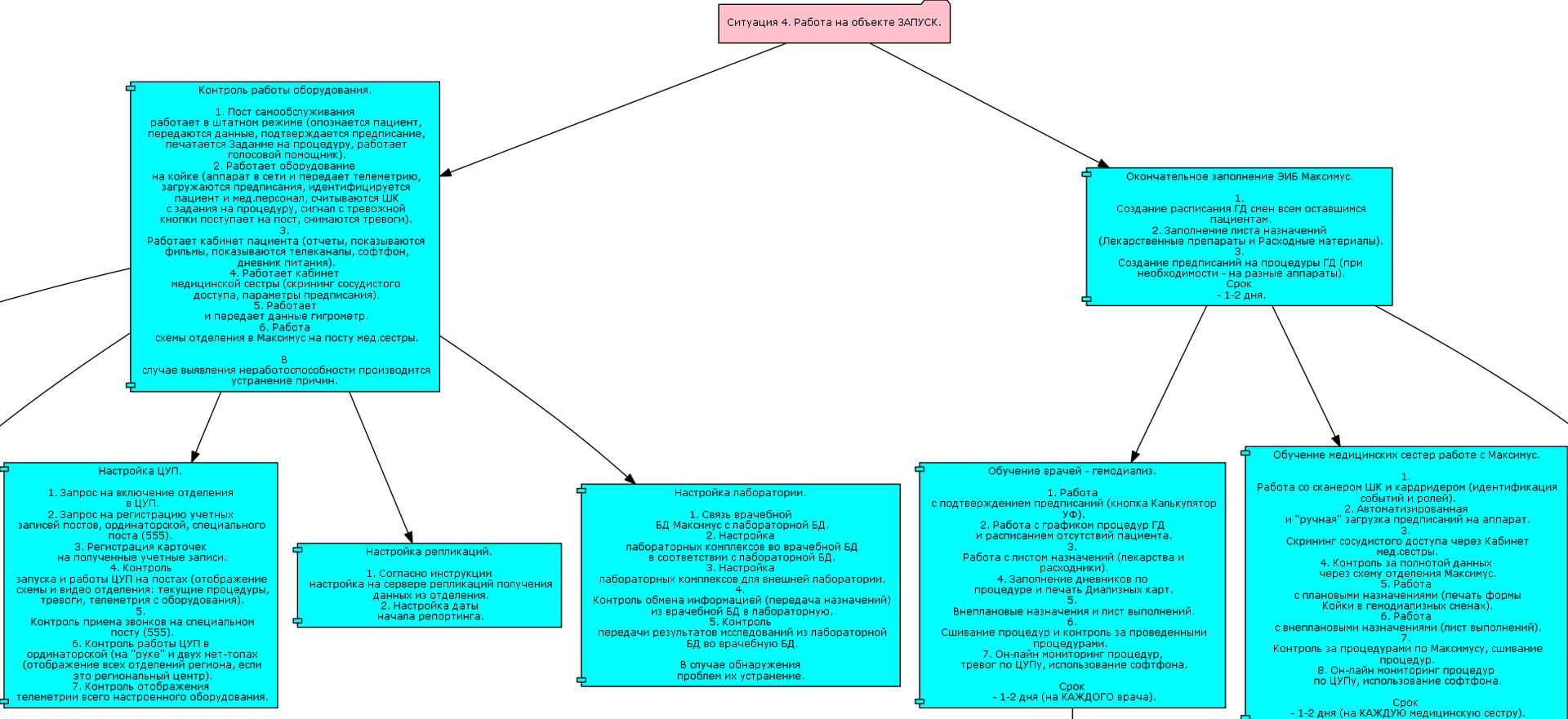
In his work, he also described the implementation process:
Previous related publications:
Part 2. DSSD Universal Algorithms - Algorithm for a support service
Part 3. Telegram chat bot on the DSS logic core (in the sandbox)
Looking ahead, I apologize to those who expect novelty or revolutionary ideas. They are not here. But there is a very good application system.
Decision support systems are gaining momentum. And I will not particularly dwell on the list of implementation methods. I will only mention the basic properties. I would very simply and generically call these systems probabilistic. That is, they issue recommendations with a certain degree of probability using the accumulated and analyzed statistics. I will not say that this is bad. The theme of BigData and Machine learning is now trending. Also, these systems operate on the principle of a black box. Therefore, it is not always possible to verify the reliability of the embedded model.
I’ll try to describe a decision support system based on a slightly different one, someone can say it’s archaic, we will conditionally call it evaluative. That is, the system models the principle of how a person actually acts - evaluates the situation and makes a decision based on the assessment made in this particular situation. And not on generalized data.
The simplest example: you enter a room. Evaluate lightly or not. If it’s dark, turn on the light and go into the room. If it is light, then immediately go into the room. And a new assessment ...
Simplified, approximately the same approach is used by the solution I am describing. That is, for decision-making, analysis is not carried out on the basis of BigData with the identification of certain trends and patterns. A specific situation is assessed. And based on a specific assessment, a very specific decision is made.
To avoid much criticism, I can say that BigData is very useful. And the data obtained on their basis should be used in DSS. But DSS should not rely on BigDta as a fundamental basis. This is a topic for a separate discussion.
Background
The solution is based on the methodology of the private algorithms of the doctor’s actions. In this case, abstraction is added and the scope of application is expanded.
There are a lot of algorithmic descriptions. Not everyone is comfortable. And even more so, far from everyone can claim that they could equally well describe the expert system. Yes, and in various professional fields.
I personally liked the fairly simple description model, which uses 3 main elements: question, answer and recommendation. It is noteworthy that this technique made it possible to describe the most complex industry from the point of view of formalization - medicine. That is, this technique had a successful practical application. And it is also important that with the availability of tools, DSS logic can be created by specialists from their professional fields without the involvement of developers.
To get started, an algorithm for a specialized ambulance team, “Coma, Poisoning, Collapses,” was taken on paper. They did not give it to me. Temporary use only. In fact, it was a set of instruction cards.
Ideologically, I wanted to get solutions for various professional fields except medicine. Therefore, it was decided to develop a platform with which it will be possible to both create algorithms (create DSS logic) and use the created DSS. The way was chosen not to contrast the system with existing solutions, but rather, create as an addition that allows you to expand the functionality. That is, the system must have an API that would allow integration into existing systems.
Implementation
So the concept of the DSS platform Universal Algorithms appeared. Which is based on 3 pillars:
• Methodology for creating and describing an algorithmic model
• Algorithm Designer - an application for the visual creation and editing of DSS algorithms
• Algorithm Navigator - a web application that implements the use of a logical DSS model.
Everyone understands that this is a graph model. To be honest, I did not want to reinvent the wheel, but one ill-wisher, with his caustic remark, prompted me to draw a model to be created. Therefore, there was a ready-made Graphviz solution that perfectly copes with such a task. Another plus is that this package allows you to create interactive graphs with URLs.
It makes no sense to draw a graph of the whole algorithm, otherwise it will not fit on a huge wall. Therefore, the way was chosen to create a graph for each situation. If an element leads to another situation, then this is displayed on the graph.
Algorithm Designer
Algorithm-Designer allows you to create a logical model according to the methodology. The content algorithm is divided into situations. And in situations, a model of reasoning is implemented.
Algorithm Designer - Windows application. So far, the concept has not been invented how else it is possible to implement all the functionality of such an application as an alternative solution (for example, web).

The screenshot shows the main elements in the Algorithm Designer:
- • Menu and toolbar - no explanation required here
- • Algorithm tree (decision tree) - the most convenient display of the algorithm structure
- • Area for working with the "parent" elements of the node.
- • Area to display the children of the node.
- • Area for filling in the “Recommendations” and “explanatory comments” - the text of the recommendation is introduced in this area. Also, for other elements, explanatory or reference information is allowed. This information turns the algorithm into a reference guide for the user, when he may not understand the meaning of the proposed element. Using the Algorithm-Navigator as an example, a way to display such comments will be shown.
- • The “Repository” area is an auxiliary tool for storing the most common logical structures. In order not to re-enter, you can simply copy from the repository. And when data changes in the repository, they are automatically replicated to all related elements in the algorithm tree.
As already mentioned, in fact, the structure of the algorithm is a graph model. But working at the application level is convenient with a tree structure. And it’s more convenient to logically separate a common data model in a tree view.
The main logic element is the Algorithm.

An algorithm may contain nested elements of the same type. That is, the element of the ambulance algorithm may contain algorithm elements for specialized ambulance crews.
Further, the Algorithm is divided into Situations. The situation exists in order to divide the algorithm into logical sections. This allows you to select a separate logical task from the general algorithm.
Note: In terms of programming, we can assume that the Algorithm is a program, and the Situation is a subprogram, procedure, or function.
Naturally, all the elements are interconnected. Therefore, the logical elements of the Algorithm allow you to establish connections and transitions between Situations.
Next comes the element - Question. The system works on the principle of assessing the "current situation". Therefore, it constantly works in the mode of asking a question and receiving a response from the user.
The answer is the logical element associated with the question. What the user will choose to evaluate the "current situation"
A recommendation is a logical element that, on the basis of an assessment, suggests or requires certain actions to be performed. Recommendations are divided into simple ones and those that set the time for execution. That is, for such recommendations, a time period is determined during which an action must be performed before the movement according to the algorithm continues - the minimum and maximum interval.
Another auxiliary element is used - Close the line. This was dictated by the fact that I wanted to visually highlight the moment when the line of reasoning ends. This element can be used repeatedly in the algorithm. In this case, there is redundancy. But it is better to neglect it for the sake of clarity.
Why did you need to work with parent and child elements?
An algorithm is a graph. But the display is tree-like. Therefore, the tree displays only one parent of the node. Which does not reflect the real state of things. Also, all child nodes are not visible in the tree if they are in other branches of the tree. Also needed a mechanism to establish such connections. Therefore, the “Parent” assignment functionality for the node was implemented. Child elements are just an informative display.
To simplify viewing and testing in the tree, double-clicking on an element switches to the 1st child node. Including the one that is installed in another branch. The reverse movement on the tree to the parents is carried out by double-clicking in the display field of the child nodes.
The logical model is editable and open. But the visual presentation makes it even more visual and understandable for a wider audience without special knowledge. As a means of visualization, the Graphviz tool was chosen . Because it builds charts fast, free and cross-platform. There are a number of advantages. One of them is the ability to build interactive charts. That is, each element can contain a URL.
It was decided to display according to situations. Since the whole algorithm is a fairly large canvas, which is difficult to understand. Elements of diagrams contain a display of all texts. This applies to Recommendations and additional reference commentary explanations for the Responses. This allows you to fully reflect the logical and meaningful content of the system.
For implementation, Delphi, DBMS Firebird, Graphviz were used . The binding to the DBMS is dictated by the use of the component. For use in the Algorithm-Navigator web application, the database was converted to MySql, SQLite, etc.
Algorithm-Navigator
Algorithm-Navigator is designed as a web-application with an adaptive design. It looks quite normal on screens with different orientations and resolutions. Also, the interface is simple enough to use so that no special user training is required.

For some time I have been choosing a way to implement Algorithm-Navigator. It was known that this should be a web application, that there should be the ability to run on Linux and there should be an API for embedding into other information systems. Because initially it was planned not to contrast the system with the existing ones, but rather to supplement it.
Python was chosen for development. Bottle framework (I plan to transfer everything to django). There is no need for special explanations. I am not a specialist in design and do the project myself. Therefore, a ready-made kit for the front-end was takentiton.io , which has all the necessary functionality.
I made up the pages as they should have looked. And then based on them I made templates.
Since I wanted to have the functionality of generating diagrams in the Algorithm-Navigator, the pydot package was used .
The order and principle of work
Algorithm Designer allows you to create a logical model. In principle, you can start using it immediately after creating several steps.
As you progress through the algorithm, all user steps are fixed. According to them, the protocol is restored. This is another feature of this methodology - when passing through the algorithm, a specialist reasoning protocol is formed. Which can be used as a document. I planned to copy the text into the service desk system requests.
API Example

UID - user ID of the algorithm.
OID - ID of the object. In this case, there can be any object. In medicine, the patient.
Parameter list - a set of parameters of type name = value for macro substitution in the algorithm texts. As an example, name, company name, product name.
Algorithm entry point - the entry point to the algorithm. It is not always necessary to start from the very beginning. When calling an algorithm from another system, you can select a point in the algorithm (situation) with which work will begin.
Application examples
First of all, the algorithms were created and used in medicine. True, this happened on the cards. It was amusing to see this method, when out of hundreds of cards with the help of a pair of knitting needles fell out the right one. Modern index searches and queries rest on the speed of providing data to the user.
Medicine: Ambulance dispatcher, Algorithms of specialized ambulance crews (I mentioned Coma, Poisoning, Collapses), Prof. examination, Pulmanology, Cardiology, Pediatrics, Obstetrics and Genicology, Recovery algorithm for medical facilities.
This is not a complete list.

I have already described an attempt to create an expert system for a support service in a branch network of a private medical company.
An example of a CRM criteria analysis provided that the criteria are composite.

Scripts of conversations and sales of services.

The ability to create a questionnaire for a mystery shopper.
A side effect is the ability to describe regulations using diagrams.
Used to describe the rules for patient discharge:

In his work, he also described the implementation process:

Previous related publications:
Part 2. DSSD Universal Algorithms - Algorithm for a support service
Part 3. Telegram chat bot on the DSS logic core (in the sandbox)
