Fire, water and fine spray. How will the inhabitants and visitors of Lakhta Center be protected from fire?
In Russia, there are no buildings above 50 meters. This statement looks absurd, but from the point of view of the domestic urban and fire prevention legislation, this is exactly the case.
What about those who decided to visit the highest European and, most importantly in the context under discussion, the Russian skyscraper? It's safe?

Check under the cut!
Requirements for the organization of fire protection systems apply only to objects up to 50 m in height, and skyscrapers fall under Article 78 of the Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements, which invites designers of more impressive structures to develop and coordinate “special technical conditions”.
Each Moscow-City tower and the skyscrapers of Ekaterinburg were built and operated according to unique fire regulations.

MIBC Moscow-City
Lakhta Center fire safety system is being formed according to special specifications.

These standards are much tougher than for ordinary buildings - potentially skyscrapers are more dangerous in case of fire. According to statistics, in buildings with a height of over 100 m, half of the people are not able to leave them quickly due to physical fatigue when going down stairs.

It is the evacuation that is the main problem that confronts the designers of high-rise fire systems. The number of people who can be inside at the same time is in the thousands. Comparable to the number of visitors to a huge shopping center, only there evacuation routes sometimes lead to ten exits.
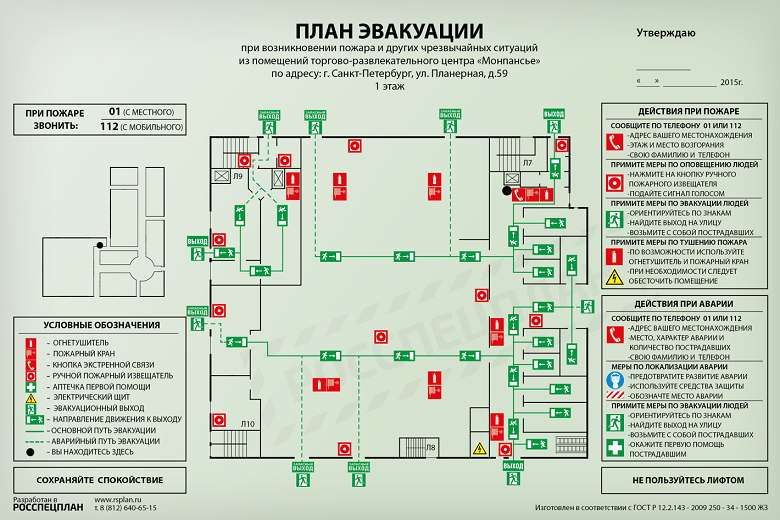
In a skyscraper dozens of exits will not work. The floor area of such buildings is limited, you cannot build many stairs, you cannot use elevators in case of fire. What to do?
When calculating take into account various factors, but the main one is the number of evacuees. Up to 8 thousand people can be located in the tower of Lakhta Center. Each of these thousands is counted - how many people can be on each floor in one moment, how many can be evacuated simultaneously. In most cases, a complete evacuation of the building is not required. But you need confidence that it is possible and an understanding of how everything will happen.
Every evacuation begins with anxiety. The warning system about the fire in Lakhta Center is fully automated, responds to smoke. When the detector worked, the person on duty at the remote control of the fire protection systems knows exactly where it happened. The evacuation alert is activated automatically after the second detector is activated in the same room. The alert can be enabled by the dispatcher in manual mode if he decides that there is a threat to people.
In the MES, the signal arrives automatically when a fire alarm is triggered. The arrival time of the first settlements from the nearest fire station is 3-5 minutes.

While the firemen are driving, the population of the tower is already going to the ground.

The staircase in a skyscraper seems to be the subject of archaic, a strange nostalgia for low-rise centuries, a refuge for elevator claustrophobes and healthy lifestyles ... Anything, but not a means of transportation. And yet in the world you will not find a single skyscraper where there are no stairs - even if it has hundreds of elevators and megawatts of reserve electricity in its rolling stock. The ultra-high flagship, the Burj Khalifa towers, has 57 elevators, but there is a staircase up to the 160th, the last inhabited level. It has 2,909 steps.
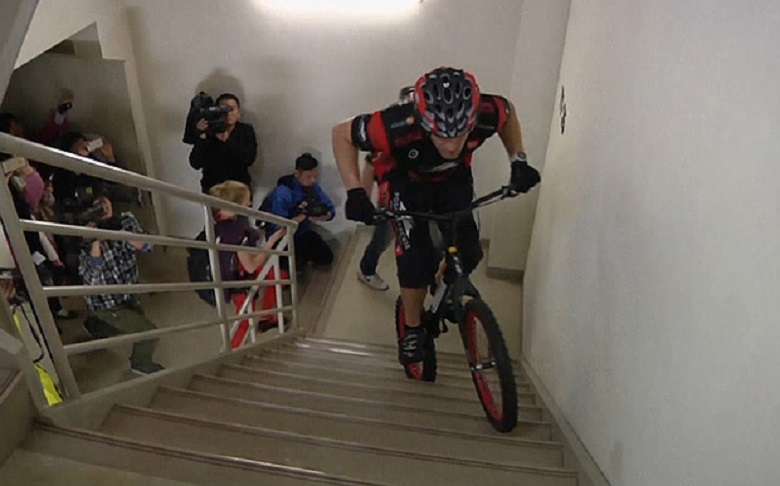

At the tower Tiapei 101 (509 m) - 3139 steps. In the photo - setting a world record: Polish cyclist Christian Herba made his way up the bike in 2 hours 13 meters.
These endless stair monsters are built for one reason - in any skyscraper and if there are any additional opportunities to leave the rear, the stairs are the main road. You can say the road to life. And since the responsibility placed on this constructive element is so great, then the requirements for it are special.
Want to find out how to find the central core in any skyscraper? There is a true sign.
In modern residential high-rise buildings, SNiP provides for “the organization of non-smokeable stairwells with an entrance through the non-smokeable air zone along open passages.” Translated from the language of rule-making - this is such an open loggia, through which people go to the stairs at the door at the opposite end.
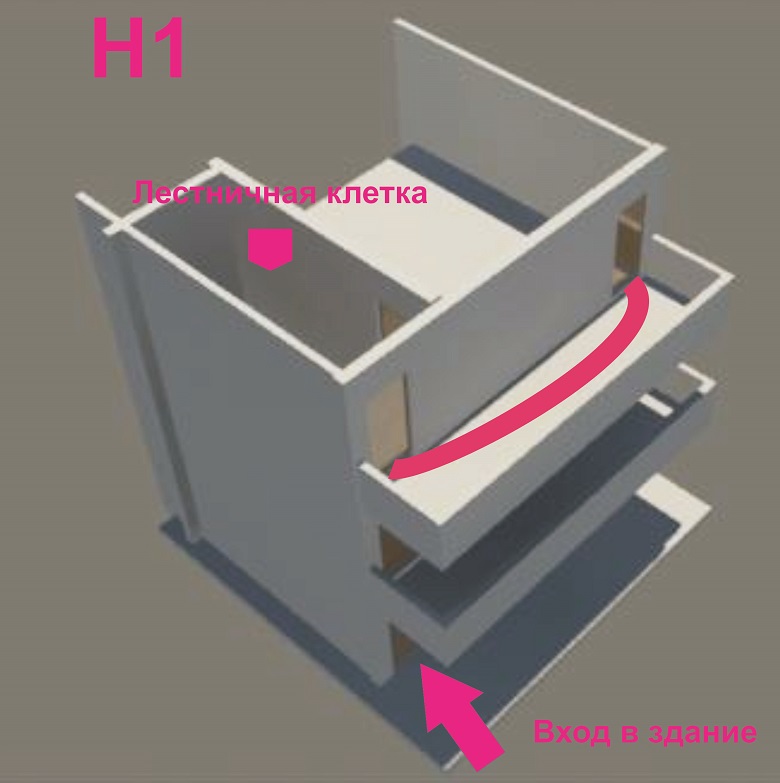
Photo from here
In the skyscraper, this option is not applicable. The creation of any unauthorized way "outboard" air into the building, will turn the high-rise into a chimney, through which fire and smoke will spread from floor to floor with space speed. Therefore, the escape route in any modern tower is always inside the central core. The staircase is a sure sign that you are in that very space - in the heart of a high-rise.
The core of Lakhta Center is the safest place in the tower in all respects. Fire resistance design - 4 hours without deformation and loss of load-bearing properties. Being inside of him means leaving the main danger behind his back.
Each floor is designed so that from anywhere to the nearest emergency exit - less than a minute to go.

The open space of the typical floor of the tower Lakhta Center. To the right is one of the doors of the emergency exit leading to the core zone.
For the evacuation, there is no difference on which floor the fire occurred. On the first or the last - the path still lies on the stairs inside the fire-resistant core, and from there - to the exit.
Once at the emergency exit, you open the door and enter the vestibule-gateway.
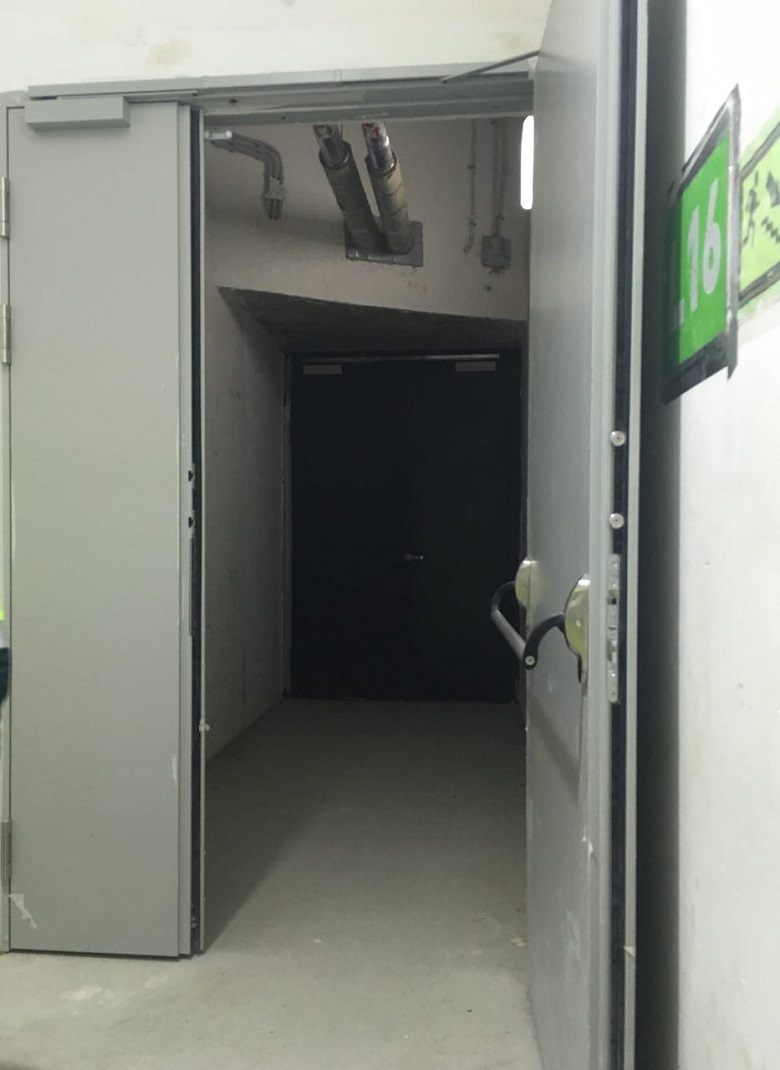

Tambour Gateway, 16th floor of the tower of Lakhta Center.
From there - to the stairs. The door to the lock space behind you will close itself and you will find yourself in the area of high pressure.
Ventilation systems located on the technical floors force air into the airlock and onto the stairs. Air support does not allow smoke and carbon monoxide to penetrate the path of salvation. Smoke-free ventilation is designed for at least three hours of work during a fire of any complexity.
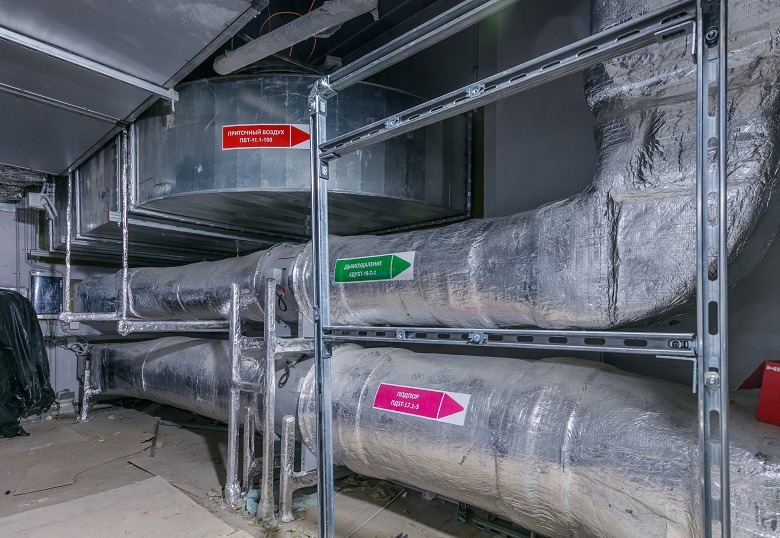

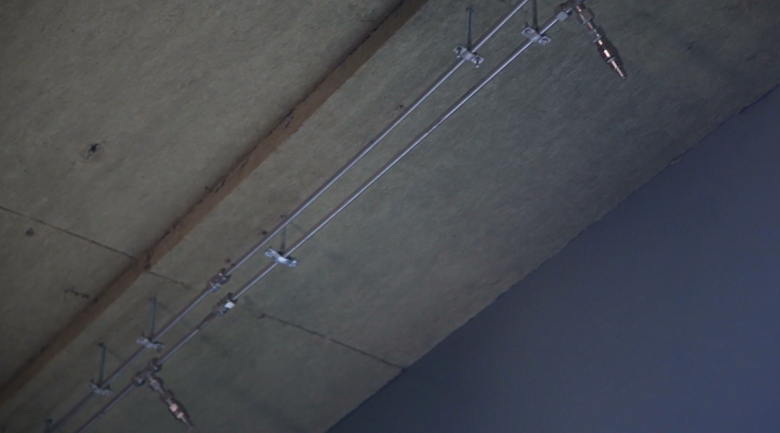
Pipes of the systems of inlet ventilation, smoke removal and air overpressure in the complex Lakhta Center
What air pressure is forced on the stairs and into the gateway? Wouldn't it be dangerous, for example, for hypertensive patients, who are already stressful and increased physical activity from hiking?
A little more than 1 mm of mercury plus a standard atmospheric plus - enough to repel smoke attacks, imperceptibly and harmlessly to humans. And even useful, considering why it is done.
Well, the staircase goes to the core, and it will hide from the fire on the floor - at least the first, even the last. But what if a fire happens inside the core itself?
The likelihood of this is as small as possible. It's safer there than in your home or in your car. First, there is nothing to burn.
All that is located inside the core, gets there, only by proving its incombustibility with certificates and markings or being treated with fire-retardant coatings. Secondly, all this non-combustible kingdom is equipped with firebreak walls, cut-offs and other special devices - traps in the path of fire.
Obviously - this question was very exciting and he was given the maximum attention, calling for help the whole experience and arsenal of means to protect the main escape route.
Escape from smoke and fire, but twist your foot in the dark narrow staircase? If there is no other alternative, then the option is normal. The rescuers will carry them down, the leg will heal ... In general, we will return to this story.
As for the alternatives, they are. Make a good ladder - according to regulations, and even better. What makes her different?
First is the width.
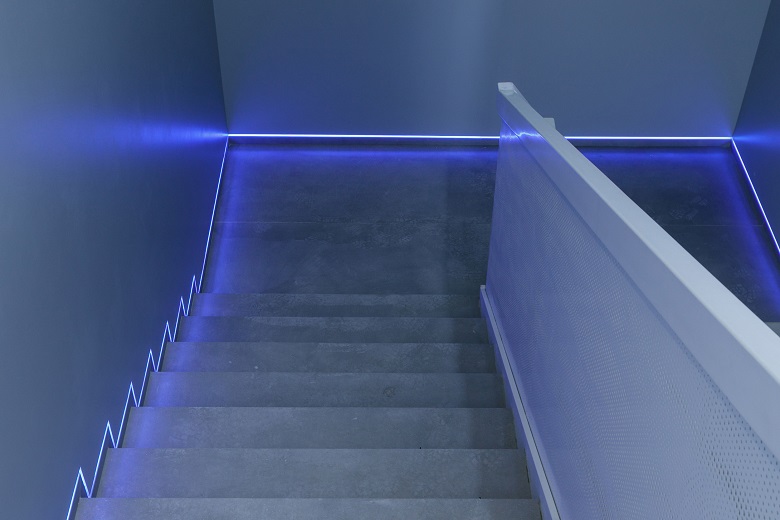

Evacuation stairs in the core of the Lakhta Center tower The
standards clearly favor slender citizens: the minimum required width is one meter. But imagine, there is a thousand down stream leaving the building, and upwards - hundreds of firefighters with their equipment ... It’s cramped. The designers took this into account and carved out an additional 35% of the standard. Total - 1, 35 m - full-fledged two-way road.
Secondly - the light.
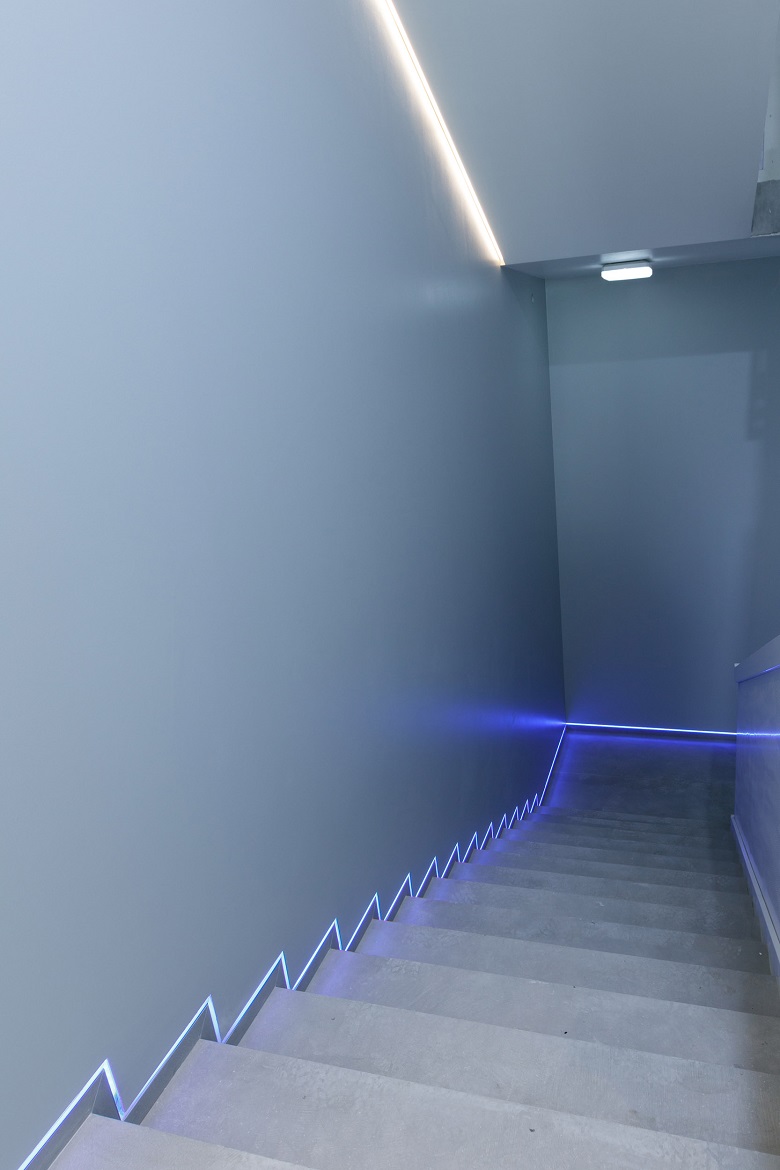

Evacuation stairs in the core of the tower of Lakhta Center
There is overhead lighting, and there is also a backlight of the steps - you can clearly see where you put your foot.
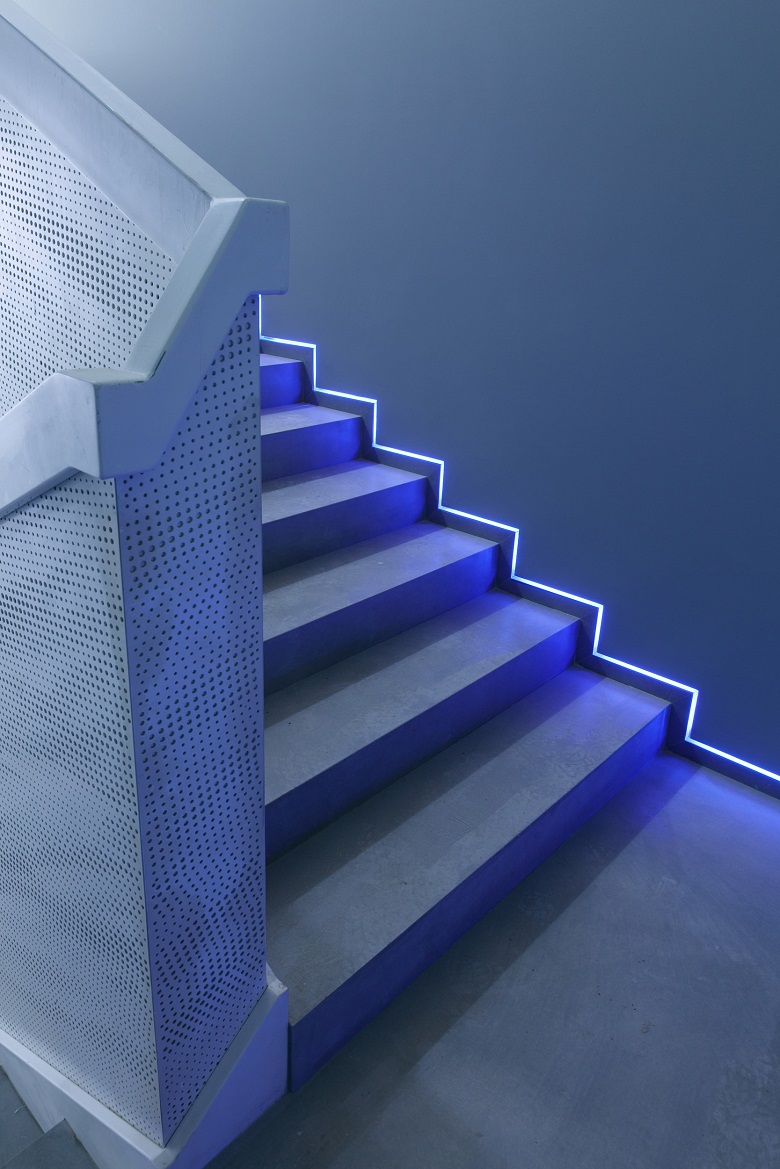

Evacuation stairs in the core of the tower of Lakhta Center
Lighting will work, even if some kind of trouble happens at the power plant, the backup power supply will last for several hours.
And most importantly - not one but two stairs in the core - evacuation is twice as fast and there is an option in case one of the paths is blocked. People will not be trapped - they will simply be redirected to another staircase.
It is difficult to imagine how the designers managed to fit on a compact area with a diameter of 26 m and a shaft of 40 elevators, and all communications of the tower, and two ladders with excess centimeters of width.
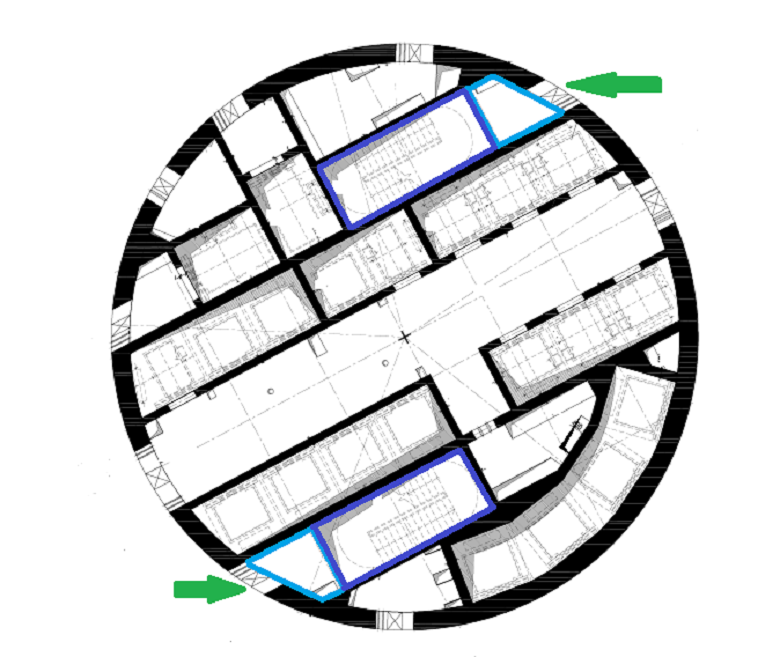
Core design: emergency exits, vestibule gateways and stairs
In the comments to the previous post, an excerpt from a book devoted to the topic of survival in disasters was cited. Among other things, the authors of the study came to the conclusion that during the events of 9/11 the victims could have been smaller, but those who were escaping let forward those who slowed down the descent — obese people, the disabled ... Please comment on the situation with these “mistakes”, angry our firefighters:
But nevertheless - what should be done by those whose possibilities for such descent are limited? Go to the "tail" of the column, so as not to interfere with the rest? How will these others feel? There is no need to make a difficult moral choice.
For those who are not able to walk on foot, security zones are created on each floor. These are the shelters where the ventilation system with a positive balance is organized: during the transition to the “Danger” mode, the inlet ventilation supplies more fresh air than the exhaust air removes. An area of high pressure is formed that prevents smoke from entering the shelter. In winter, the air is additionally heated - so as not to freeze people.
Is it possible to wait out the whole fire?
Theoretically, yes. But the idea to lay low and wait until the danger has passed is a bad one. The weakest element of the shelter - partitions and doors. They can resist fire for one hour. Why exactly so much?
Inside the shelter is equipped with a direct connection with the dispatcher. He should be contacted immediately, once in the security zone. From the dispatcher, the signal will go to the Fire Extinguishing Manager. In addition, the first and main task is evacuation, so that the unit’s forces will first of all be sent to ensure exit from the danger zone. The wounded will be carried on a stretcher, the wheelchair will be escorted to the elevator - all to the exit from the building.
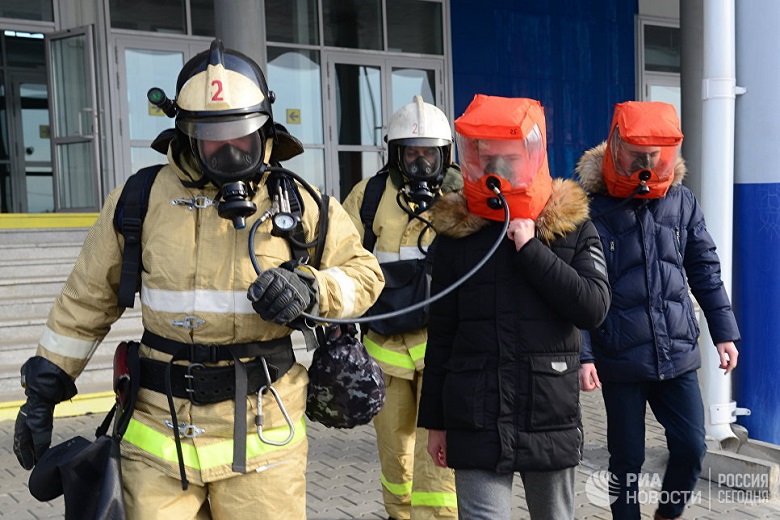

Evacuation of people from the building. Photos from the exercise, RIA Novosti, Igor Onuchin

Evacuation from the Perseus for Children shopping center. Photo from here
Unlike the inhabitants of the high-rise, which is forbidden to move on an elevator during a fire, rescuers can use vertical transport. The elevator is in such a situation - and the lifeboat on which people are evacuated from the danger zone, and the fire engine with which they are launching the offensive. There are 5 elevators for firefighters, including a heavy truck with a lifting capacity of 5 tons, an express train, with a lifting speed of 8 m / s and a double-deck elevator, with the possibility of stopping on two floors at once. The total capacity of the fire fleet - 14, 4 tons. Features of fire elevators: individual mines, non-combustible cab design and exit gate, where the air is pumped - so the fire does not come close to them and the fire brigade at the exit does not fall into the trap.
On each floor special equipment was prepared for the fighters, because their own equipment will not be able to supply water even to the middle of the tower. By the way, this was the main problem in extinguishing the Vostok tower of the Federation complex in Moscow-City, which we described in the last article. The firefighters actually had to raise the barrels of water and the pump to a 300-meter height. In the unfinished skyscraper fire water pipe has not worked yet.

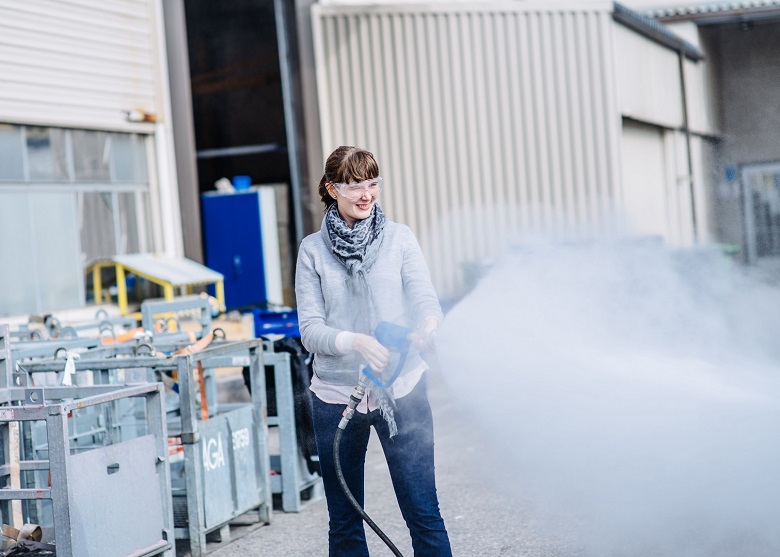
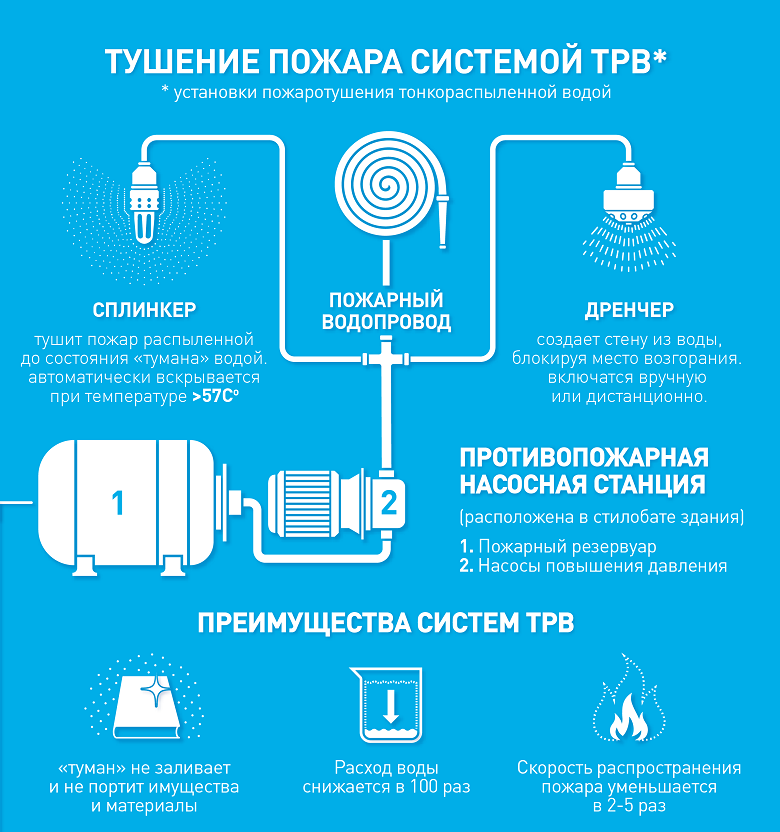
Specially designed for Lakhta Center, trunks were developed that “fired” with water spray in two modes. To reduce the temperature and protect people, water is sprayed under a pressure of about 70 atmospheres with a wide cone-cloud of 70 degrees to a distance of 10-12 meters. To extinguish a fire, the working cone narrows to 30 degrees, and the range increases to 22-27 meters. high pressure washer, only with short spray.

Water consumption of this barrel - 1.5 l / sec. For comparison - the standard fire rods consume 3.6-7.4 l / s. It is economics that made high-pressure sprayed water the basis of the Lakhta Center fire extinguishing system.
Already at the design stage of the complex, it became clear that water from the Vodokanal water supply network was not enough to effectively extinguish the fire with traditional technologies in such a large-scale structure. Creating a fire tank of sufficient volume - about 125 tons of water - is at least not efficient. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, sprayed high-pressure water to extinguish fires was first run-in on warships and oil tankers, and then on ocean cruise liners.
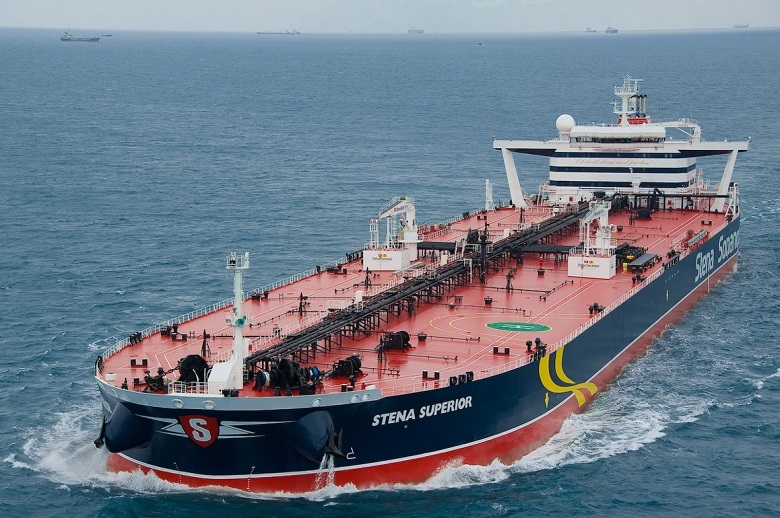

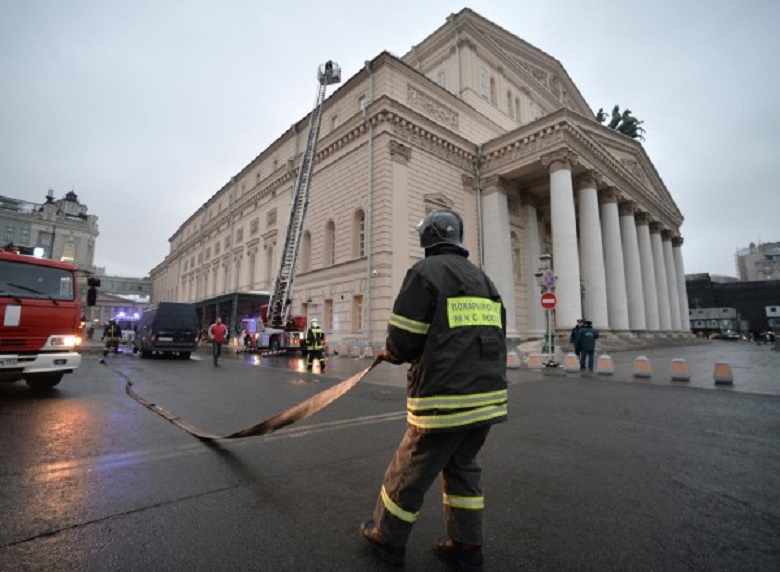
Then it quickly found application in construction, for example, such a system was installed during the reconstruction of the Bolshoi Theater in Moscow.

Calculations have shown that if high-pressure sprayed water is used in Lakhta Center, the capacity of the water supply system is more than enough. The maximum flow rate for the operation of all systems is about 60 l / s, and this is five times less than if a traditional system had to be used. Plus, the internal fire water supply, designed for eight simultaneously working trunks.
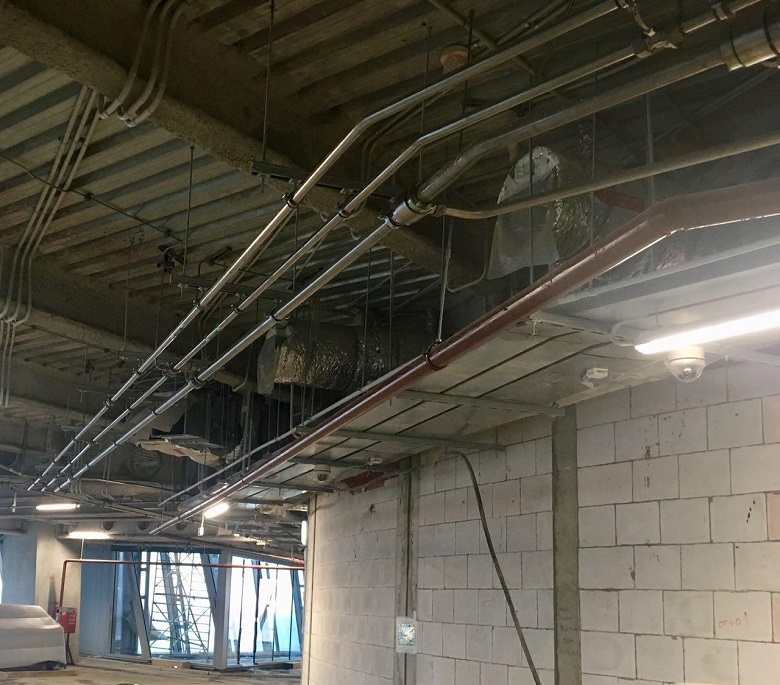

High pressure pipes of the expansion valve system.
Water extinguishing installations are serviced by two pumping stations.
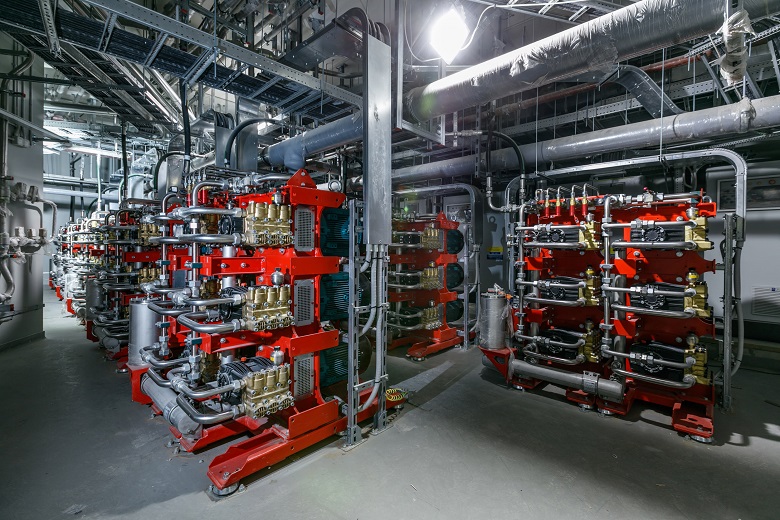
TVR system pumps. When starting up in a matter of minutes, the pressure in the fire pipe is raised by more than 80 atmospheres!
One is located on the minus 1 floor and provides fire extinguishing in the MFZ, stylobate and on the lower half of the tower’s floors. The second is installed at the height of the 50th floor and is equipped with a 12-cube tank, the water supply in which is enough to extinguish the fire for 10 minutes on the upper floors. With a decrease in the water level in this “barrel”, the lower pump is turned on and makes up for the used one. For the reliability of pumping pumps, as many as four - two main and two standby ones. They are installed in pairs and work in series.
The pumping unit provides pressure on the sprinkler at the time of operation over 80 atmospheres. At such a high pressure, water, falling into the micro-unions of the sprinkler, breaks up into small drops.
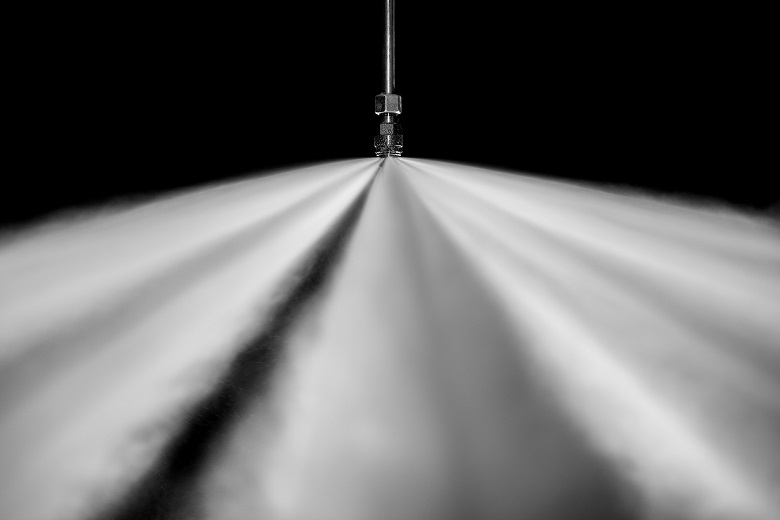

The diameter of a droplet of sprayed water is 100–200 µm. Due to this size at temperatures above 60 degrees, water evaporates quickly, reducing the temperature of the surrounding air. At the same time, fine mist is formed in the air, spreading by air currents, settling on all surfaces, and thereby preventing the spread of fire and partially binding the products of combustion - soot, gases, including poisonous.
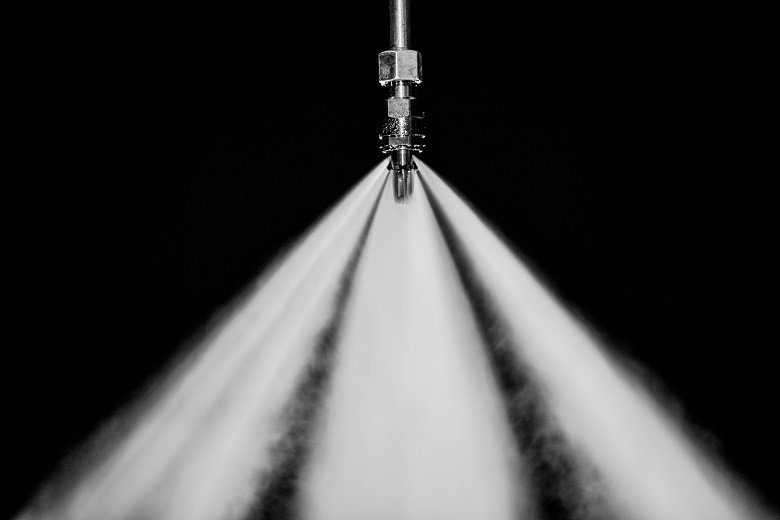
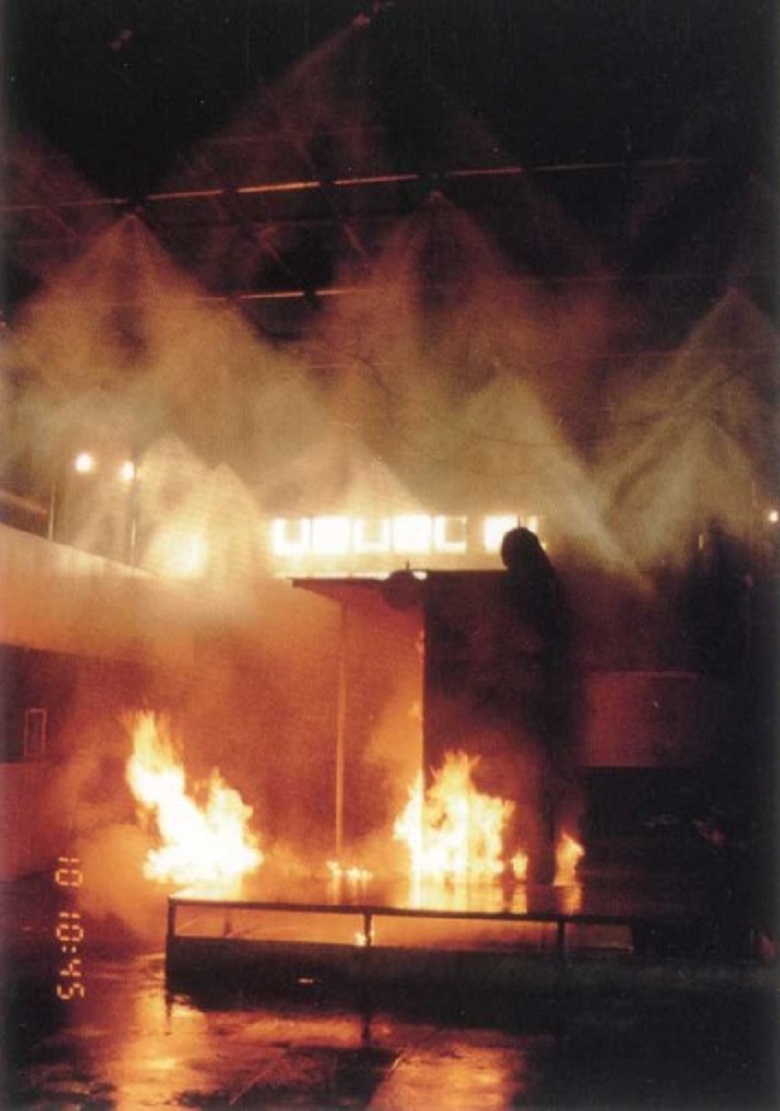


Fire extinguishing with the help of the TTR system under test:
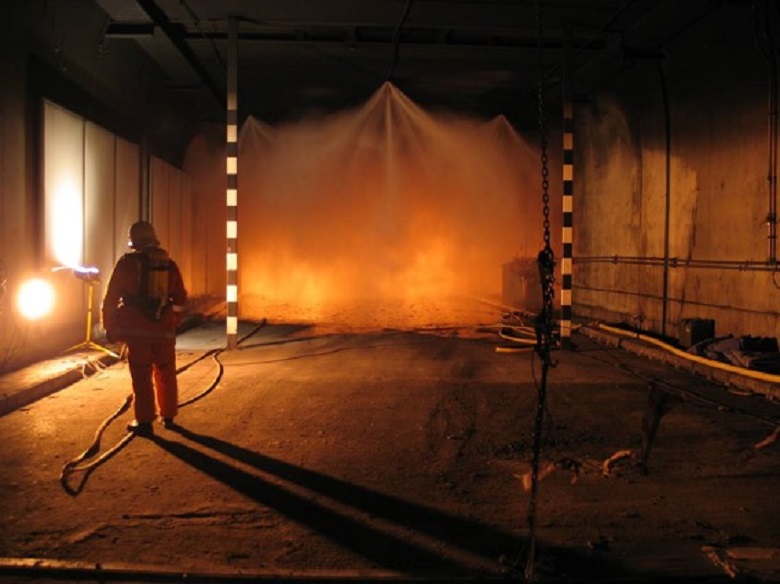

The facades have their own protection. In order for the glass not to collapse from heating - remember about the effect of the chimney during the "depressurization" of the tower? - along the facade every 1.5 m on all floors also installed high-pressure sprayers. They create a water curtain that lowers the temperature, as well as the cooling glass.

Sprinklers to create a water curtain when testing facade structures of Lakhta Center
Tests of the system showed that at an indoor temperature of 700 degrees, in 60 minutes the facade heats up only by 28-30 degrees, which is very far from critical values. Also, the use of a fire extinguishing system ensured a twofold decrease in temperature inside the test bench. Thus, if the hearth is very close to the facade, only the water curtain in front of the facades can, in principle, be used to extinguish the fire at the very beginning.
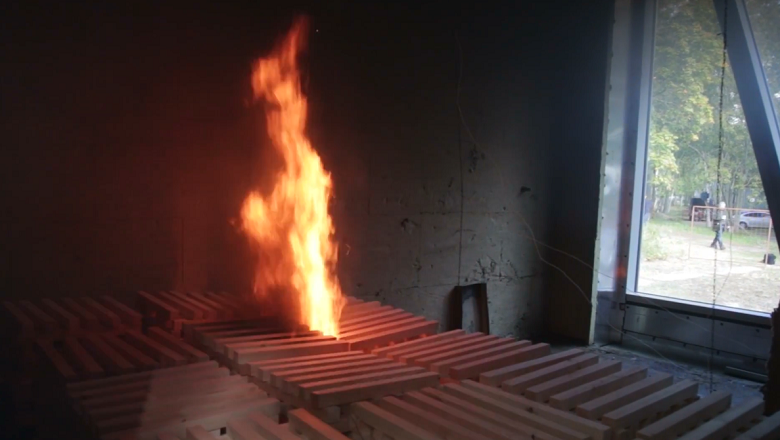

Testing of the fire extinguishing system - a water curtain for the front glass of the Lakhta Center.
Sprinklers turn on automatically after the flask installed in the instrument body bursts when the ambient air temperature exceeds 57 degrees.
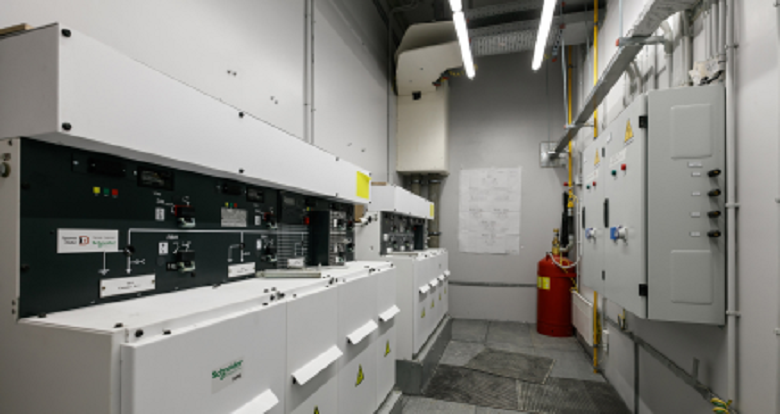

The switchboard Lakhta Center
Fire Fighting is not always about fire and water. Water is definitely not an option for rooms with electrical equipment. In the server and switchboard - only gas.
It is very effective - it fills the entire volume of the room for a maximum of half a minute, then a little more, aired - and you can continue the working day. The only problem is that freon, that carbon dioxide is dangerous for a person. Their goal is an oxygen molecule, the principle of operation is to reduce the O2 concentration in the air by a factor of two to about 12%. Carbon dioxide in fire extinguishing concentration - by itself - poison. This is problem. When you have 15 seconds left from the beginning of the alarm before the gas is started, you don’t even have time to put on the gas mask. Fortunately, the electrician does not have to wear an oxygen mask, going to the switchboard, no need to worry about the system administrator, performing his duty in the server.

In Lakhta Center, the most modern gas fire extinguishing system has been applied - with the help of fluoroketone - “dry water”. Mostly it acts by cooling. In fire extinguishing concentrations non-toxic and environmentally friendly.
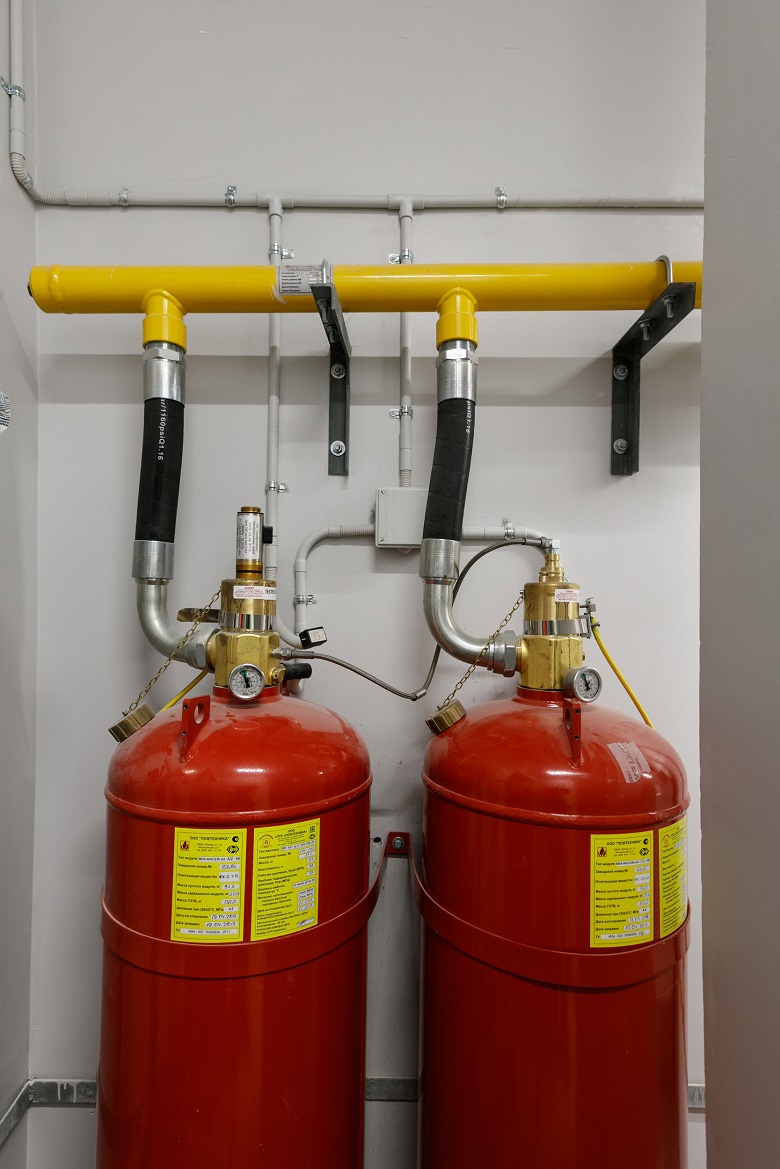

Fluorketone FK-5-1-12 fire extinguishing cylinders
***
Fire is the most obvious threat a skyscraper can face. Use of non-combustible materials in key evacuation zones and fire-resistant supporting structures, early detection and warning system, readiness for evacuation, automatic fire extinguishing system, fire ventilation and smoke removal, fast access for city fire services and its own fire group acting as coordinators for evacuation and interaction with lifeguards - perhaps this is a complete arsenal of tools from what was invented for today, in order to minimize possible damage and make your stay in the tower safe ohm It is safe to say that Lakhta Center has no chance to become a decoration for events one day, similar to those described for the film “Skyscraper”.
***
Thank you for helping to prepare the material Alexander Gladilin - the lead engineer for fire safety systems and Alexander Smirnov - fire safety engineer at the Lakhta Department of Fire and Safety
*** ***
These days, an annual forum dedicated to the unique and high-rise construction in Russia is held in Yekaterinburg - Forum 100 + Russia. This year's headliner is a thematic session dedicated to the Lakhta Center. Five top specialists, including the chief engineer of the Lakhta Center Sergey Nikiforov and the academician, one of the founders of the Ostankino television tower Vladimir Travush, will make presentations. The direct inclusion of the session from Ekaterinburg is available here . The broadcast starts today in a few minutes.
What about those who decided to visit the highest European and, most importantly in the context under discussion, the Russian skyscraper? It's safe?

Check under the cut!
Requirements for the organization of fire protection systems apply only to objects up to 50 m in height, and skyscrapers fall under Article 78 of the Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements, which invites designers of more impressive structures to develop and coordinate “special technical conditions”.
Each Moscow-City tower and the skyscrapers of Ekaterinburg were built and operated according to unique fire regulations.

MIBC Moscow-City
Lakhta Center fire safety system is being formed according to special specifications.

These standards are much tougher than for ordinary buildings - potentially skyscrapers are more dangerous in case of fire. According to statistics, in buildings with a height of over 100 m, half of the people are not able to leave them quickly due to physical fatigue when going down stairs.

It is the evacuation that is the main problem that confronts the designers of high-rise fire systems. The number of people who can be inside at the same time is in the thousands. Comparable to the number of visitors to a huge shopping center, only there evacuation routes sometimes lead to ten exits.

In a skyscraper dozens of exits will not work. The floor area of such buildings is limited, you cannot build many stairs, you cannot use elevators in case of fire. What to do?
EVACUATION ON EARTH
When calculating take into account various factors, but the main one is the number of evacuees. Up to 8 thousand people can be located in the tower of Lakhta Center. Each of these thousands is counted - how many people can be on each floor in one moment, how many can be evacuated simultaneously. In most cases, a complete evacuation of the building is not required. But you need confidence that it is possible and an understanding of how everything will happen.
Get out! Get out! Leaving ...
Every evacuation begins with anxiety. The warning system about the fire in Lakhta Center is fully automated, responds to smoke. When the detector worked, the person on duty at the remote control of the fire protection systems knows exactly where it happened. The evacuation alert is activated automatically after the second detector is activated in the same room. The alert can be enabled by the dispatcher in manual mode if he decides that there is a threat to people.
Alexander Gladilin, Lead Engineer for Fire Systems Lakhta Center:
- Given the large number of people in the tower, it was decided that the evacuation should be done in stages. After the two detectors have triggered, the alert system turns on exactly on the floor where it happened - it is not audible on others. Then, if no fire refutation has been received within a minute, the system includes an alert on the adjacent floors - above and below. If the evacuation is not canceled and within the next minute, the alarm is announced already in the entire fire compartment between the two technical floors. Thus, we will be able to avoid the simultaneous evacuation of a large number of people with all its negative manifestations, such as crush, panic.
In the MES, the signal arrives automatically when a fire alarm is triggered. The arrival time of the first settlements from the nearest fire station is 3-5 minutes.

While the firemen are driving, the population of the tower is already going to the ground.

the main road
The staircase in a skyscraper seems to be the subject of archaic, a strange nostalgia for low-rise centuries, a refuge for elevator claustrophobes and healthy lifestyles ... Anything, but not a means of transportation. And yet in the world you will not find a single skyscraper where there are no stairs - even if it has hundreds of elevators and megawatts of reserve electricity in its rolling stock. The ultra-high flagship, the Burj Khalifa towers, has 57 elevators, but there is a staircase up to the 160th, the last inhabited level. It has 2,909 steps.

At the tower Tiapei 101 (509 m) - 3139 steps. In the photo - setting a world record: Polish cyclist Christian Herba made his way up the bike in 2 hours 13 meters.
These endless stair monsters are built for one reason - in any skyscraper and if there are any additional opportunities to leave the rear, the stairs are the main road. You can say the road to life. And since the responsibility placed on this constructive element is so great, then the requirements for it are special.
In the heart of the tower
Want to find out how to find the central core in any skyscraper? There is a true sign.
In modern residential high-rise buildings, SNiP provides for “the organization of non-smokeable stairwells with an entrance through the non-smokeable air zone along open passages.” Translated from the language of rule-making - this is such an open loggia, through which people go to the stairs at the door at the opposite end.

Photo from here
In the skyscraper, this option is not applicable. The creation of any unauthorized way "outboard" air into the building, will turn the high-rise into a chimney, through which fire and smoke will spread from floor to floor with space speed. Therefore, the escape route in any modern tower is always inside the central core. The staircase is a sure sign that you are in that very space - in the heart of a high-rise.
The core of Lakhta Center is the safest place in the tower in all respects. Fire resistance design - 4 hours without deformation and loss of load-bearing properties. Being inside of him means leaving the main danger behind his back.
Each floor is designed so that from anywhere to the nearest emergency exit - less than a minute to go.

The open space of the typical floor of the tower Lakhta Center. To the right is one of the doors of the emergency exit leading to the core zone.
For the evacuation, there is no difference on which floor the fire occurred. On the first or the last - the path still lies on the stairs inside the fire-resistant core, and from there - to the exit.
I smoke - no!
Once at the emergency exit, you open the door and enter the vestibule-gateway.

Tambour Gateway, 16th floor of the tower of Lakhta Center.
From there - to the stairs. The door to the lock space behind you will close itself and you will find yourself in the area of high pressure.

Ventilation systems located on the technical floors force air into the airlock and onto the stairs. Air support does not allow smoke and carbon monoxide to penetrate the path of salvation. Smoke-free ventilation is designed for at least three hours of work during a fire of any complexity.

Pipes of the systems of inlet ventilation, smoke removal and air overpressure in the complex Lakhta Center
What air pressure is forced on the stairs and into the gateway? Wouldn't it be dangerous, for example, for hypertensive patients, who are already stressful and increased physical activity from hiking?
Alexander Gladilin:
- The difference in pressure should be normative, as stipulated in the project: “The pressure drop on the closed doors of emergency exits should not exceed 150 Pa”
A little more than 1 mm of mercury plus a standard atmospheric plus - enough to repel smoke attacks, imperceptibly and harmlessly to humans. And even useful, considering why it is done.
Well, the staircase goes to the core, and it will hide from the fire on the floor - at least the first, even the last. But what if a fire happens inside the core itself?
Nuclear issue
The likelihood of this is as small as possible. It's safer there than in your home or in your car. First, there is nothing to burn.
All that is located inside the core, gets there, only by proving its incombustibility with certificates and markings or being treated with fire-retardant coatings. Secondly, all this non-combustible kingdom is equipped with firebreak walls, cut-offs and other special devices - traps in the path of fire.
Alexander Gladilin:
- “... All lift shafts, staircases and other rooms located in the core, have fire protection fencing structures. Elevator shafts are separated from evacuation stairs along the entire height by firebreaks. All lift doors are fireproof. Materials used for finishing stairs and elevators are certified as non-combustible. The communication shafts are separated from the premises of the building, and even more so inside the core, by fire partitions with installed fire doors and inspection doors. At each level, communication shafts are divided by ceilings with special penetrations made in them. The outputs of the engineering networks from the communication mines are sealed with special materials that provide fire resistance to penetrations in accordance with the fire resistance of the fire partition, floors, walls .... "
Obviously - this question was very exciting and he was given the maximum attention, calling for help the whole experience and arsenal of means to protect the main escape route.
Performance characteristics
Escape from smoke and fire, but twist your foot in the dark narrow staircase? If there is no other alternative, then the option is normal. The rescuers will carry them down, the leg will heal ... In general, we will return to this story.
As for the alternatives, they are. Make a good ladder - according to regulations, and even better. What makes her different?
First is the width.

Evacuation stairs in the core of the Lakhta Center tower The
standards clearly favor slender citizens: the minimum required width is one meter. But imagine, there is a thousand down stream leaving the building, and upwards - hundreds of firefighters with their equipment ... It’s cramped. The designers took this into account and carved out an additional 35% of the standard. Total - 1, 35 m - full-fledged two-way road.
Secondly - the light.

Evacuation stairs in the core of the tower of Lakhta Center
There is overhead lighting, and there is also a backlight of the steps - you can clearly see where you put your foot.

Evacuation stairs in the core of the tower of Lakhta Center
Lighting will work, even if some kind of trouble happens at the power plant, the backup power supply will last for several hours.
And most importantly - not one but two stairs in the core - evacuation is twice as fast and there is an option in case one of the paths is blocked. People will not be trapped - they will simply be redirected to another staircase.
It is difficult to imagine how the designers managed to fit on a compact area with a diameter of 26 m and a shaft of 40 elevators, and all communications of the tower, and two ladders with excess centimeters of width.

Core design: emergency exits, vestibule gateways and stairs
Shelter
In the comments to the previous post, an excerpt from a book devoted to the topic of survival in disasters was cited. Among other things, the authors of the study came to the conclusion that during the events of 9/11 the victims could have been smaller, but those who were escaping let forward those who slowed down the descent — obese people, the disabled ... Please comment on the situation with these “mistakes”, angry our firefighters:
“There has never been, and never will be, help to anybody!” This is the human factor and the education of the individual! All instructions and in all safety regulations state that in case of emergency it is necessary to notify others, to help evacuate the wounded and infirm ... ".
But nevertheless - what should be done by those whose possibilities for such descent are limited? Go to the "tail" of the column, so as not to interfere with the rest? How will these others feel? There is no need to make a difficult moral choice.
For those who are not able to walk on foot, security zones are created on each floor. These are the shelters where the ventilation system with a positive balance is organized: during the transition to the “Danger” mode, the inlet ventilation supplies more fresh air than the exhaust air removes. An area of high pressure is formed that prevents smoke from entering the shelter. In winter, the air is additionally heated - so as not to freeze people.
Is it possible to wait out the whole fire?
Theoretically, yes. But the idea to lay low and wait until the danger has passed is a bad one. The weakest element of the shelter - partitions and doors. They can resist fire for one hour. Why exactly so much?
"The estimated time of extinguishing the floor in our case is not more than an hour",- explains Alexander Gladilin. However, no one will wait until the partitions fire limit is exhausted.
Inside the shelter is equipped with a direct connection with the dispatcher. He should be contacted immediately, once in the security zone. From the dispatcher, the signal will go to the Fire Extinguishing Manager. In addition, the first and main task is evacuation, so that the unit’s forces will first of all be sent to ensure exit from the danger zone. The wounded will be carried on a stretcher, the wheelchair will be escorted to the elevator - all to the exit from the building.

Evacuation of people from the building. Photos from the exercise, RIA Novosti, Igor Onuchin

Evacuation from the Perseus for Children shopping center. Photo from here
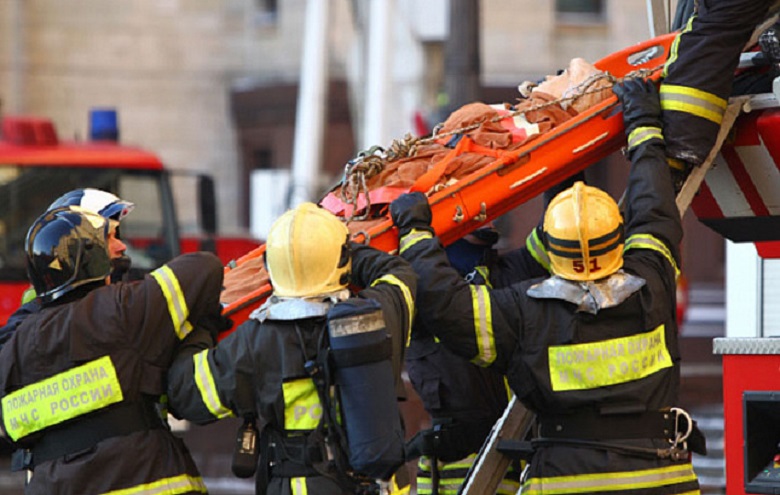
Rescue boat and fire truck
Unlike the inhabitants of the high-rise, which is forbidden to move on an elevator during a fire, rescuers can use vertical transport. The elevator is in such a situation - and the lifeboat on which people are evacuated from the danger zone, and the fire engine with which they are launching the offensive. There are 5 elevators for firefighters, including a heavy truck with a lifting capacity of 5 tons, an express train, with a lifting speed of 8 m / s and a double-deck elevator, with the possibility of stopping on two floors at once. The total capacity of the fire fleet - 14, 4 tons. Features of fire elevators: individual mines, non-combustible cab design and exit gate, where the air is pumped - so the fire does not come close to them and the fire brigade at the exit does not fall into the trap.
Long-range guns and other arsenal
On each floor special equipment was prepared for the fighters, because their own equipment will not be able to supply water even to the middle of the tower. By the way, this was the main problem in extinguishing the Vostok tower of the Federation complex in Moscow-City, which we described in the last article. The firefighters actually had to raise the barrels of water and the pump to a 300-meter height. In the unfinished skyscraper fire water pipe has not worked yet.

Specially designed for Lakhta Center, trunks were developed that “fired” with water spray in two modes. To reduce the temperature and protect people, water is sprayed under a pressure of about 70 atmospheres with a wide cone-cloud of 70 degrees to a distance of 10-12 meters. To extinguish a fire, the working cone narrows to 30 degrees, and the range increases to 22-27 meters. high pressure washer, only with short spray.

Water consumption of this barrel - 1.5 l / sec. For comparison - the standard fire rods consume 3.6-7.4 l / s. It is economics that made high-pressure sprayed water the basis of the Lakhta Center fire extinguishing system.
Already at the design stage of the complex, it became clear that water from the Vodokanal water supply network was not enough to effectively extinguish the fire with traditional technologies in such a large-scale structure. Creating a fire tank of sufficient volume - about 125 tons of water - is at least not efficient. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, sprayed high-pressure water to extinguish fires was first run-in on warships and oil tankers, and then on ocean cruise liners.

Then it quickly found application in construction, for example, such a system was installed during the reconstruction of the Bolshoi Theater in Moscow.

Calculations have shown that if high-pressure sprayed water is used in Lakhta Center, the capacity of the water supply system is more than enough. The maximum flow rate for the operation of all systems is about 60 l / s, and this is five times less than if a traditional system had to be used. Plus, the internal fire water supply, designed for eight simultaneously working trunks.

High pressure pipes of the expansion valve system.
Water extinguishing installations are serviced by two pumping stations.

TVR system pumps. When starting up in a matter of minutes, the pressure in the fire pipe is raised by more than 80 atmospheres!
One is located on the minus 1 floor and provides fire extinguishing in the MFZ, stylobate and on the lower half of the tower’s floors. The second is installed at the height of the 50th floor and is equipped with a 12-cube tank, the water supply in which is enough to extinguish the fire for 10 minutes on the upper floors. With a decrease in the water level in this “barrel”, the lower pump is turned on and makes up for the used one. For the reliability of pumping pumps, as many as four - two main and two standby ones. They are installed in pairs and work in series.
Fine spray

The pumping unit provides pressure on the sprinkler at the time of operation over 80 atmospheres. At such a high pressure, water, falling into the micro-unions of the sprinkler, breaks up into small drops.

The diameter of a droplet of sprayed water is 100–200 µm. Due to this size at temperatures above 60 degrees, water evaporates quickly, reducing the temperature of the surrounding air. At the same time, fine mist is formed in the air, spreading by air currents, settling on all surfaces, and thereby preventing the spread of fire and partially binding the products of combustion - soot, gases, including poisonous.


Fire extinguishing with the help of the TTR system under test:

Preservation of tightness
The facades have their own protection. In order for the glass not to collapse from heating - remember about the effect of the chimney during the "depressurization" of the tower? - along the facade every 1.5 m on all floors also installed high-pressure sprayers. They create a water curtain that lowers the temperature, as well as the cooling glass.

Sprinklers to create a water curtain when testing facade structures of Lakhta Center
Tests of the system showed that at an indoor temperature of 700 degrees, in 60 minutes the facade heats up only by 28-30 degrees, which is very far from critical values. Also, the use of a fire extinguishing system ensured a twofold decrease in temperature inside the test bench. Thus, if the hearth is very close to the facade, only the water curtain in front of the facades can, in principle, be used to extinguish the fire at the very beginning.

Testing of the fire extinguishing system - a water curtain for the front glass of the Lakhta Center.
Sprinklers turn on automatically after the flask installed in the instrument body bursts when the ambient air temperature exceeds 57 degrees.
Do not be afraid, gas!

The switchboard Lakhta Center
Fire Fighting is not always about fire and water. Water is definitely not an option for rooms with electrical equipment. In the server and switchboard - only gas.
It is very effective - it fills the entire volume of the room for a maximum of half a minute, then a little more, aired - and you can continue the working day. The only problem is that freon, that carbon dioxide is dangerous for a person. Their goal is an oxygen molecule, the principle of operation is to reduce the O2 concentration in the air by a factor of two to about 12%. Carbon dioxide in fire extinguishing concentration - by itself - poison. This is problem. When you have 15 seconds left from the beginning of the alarm before the gas is started, you don’t even have time to put on the gas mask. Fortunately, the electrician does not have to wear an oxygen mask, going to the switchboard, no need to worry about the system administrator, performing his duty in the server.

In Lakhta Center, the most modern gas fire extinguishing system has been applied - with the help of fluoroketone - “dry water”. Mostly it acts by cooling. In fire extinguishing concentrations non-toxic and environmentally friendly.

Fluorketone FK-5-1-12 fire extinguishing cylinders
***
Fire is the most obvious threat a skyscraper can face. Use of non-combustible materials in key evacuation zones and fire-resistant supporting structures, early detection and warning system, readiness for evacuation, automatic fire extinguishing system, fire ventilation and smoke removal, fast access for city fire services and its own fire group acting as coordinators for evacuation and interaction with lifeguards - perhaps this is a complete arsenal of tools from what was invented for today, in order to minimize possible damage and make your stay in the tower safe ohm It is safe to say that Lakhta Center has no chance to become a decoration for events one day, similar to those described for the film “Skyscraper”.
***
Thank you for helping to prepare the material Alexander Gladilin - the lead engineer for fire safety systems and Alexander Smirnov - fire safety engineer at the Lakhta Department of Fire and Safety
*** ***
These days, an annual forum dedicated to the unique and high-rise construction in Russia is held in Yekaterinburg - Forum 100 + Russia. This year's headliner is a thematic session dedicated to the Lakhta Center. Five top specialists, including the chief engineer of the Lakhta Center Sergey Nikiforov and the academician, one of the founders of the Ostankino television tower Vladimir Travush, will make presentations. The direct inclusion of the session from Ekaterinburg is available here . The broadcast starts today in a few minutes.
