I see you: machine learning and artificial neural networks in the study of the sight of fruit flies

Not all people love insects. What really hide, some of them are frankly afraid. But this does not mean that our small neighbors on the planet exist solely in order to chase people with a phobia, to entangle them with their hair, so that they shout “Remove it from me! Take off! Any living organism on the planet has its own unusual, sometimes unique skills and characteristics. If we talk about a person, then among other things it will be movement on two limbs, opposed thumb, etc. Studying such features, scientists better understand our world and the creatures inhabiting it. Also, many studies with animals or insects have pushed scientists toward discoveries in areas not related to biology. Today we talk about the study, the main character of which is a creature delivering a lot of trouble in the summer months - fruit fly Drosophila. Scientists decided to answer the question - how does the world around him see fruit flies? And it goes far not only about the visual apparatus. Machine learning, artificial neural networks - all for the sake of such a small creature. What did scientists know how their artificial fly worked and was created and what is the use of such a seemingly strange research? Let's look for the answers in the scientists report. Go. how did their “artificial fly” work and was created and what is the use of such a seemingly strange research? Let's look for the answers in the scientists report. Go. how did their “artificial fly” work and was created and what is the use of such a seemingly strange research? Let's look for the answers in the scientists report. Go.
Entomology
Before we sort through the report, let's take a closer look at the main character.

Drosophila fruit is a diptera insect, the size of which does not exceed 2.5 mm (in females, the male is smaller). Many of us are familiar with these insects firsthand. Summer comes, we buy fruits and vegetables, put them somewhere in the public domain, and after a while we notice how these little creatures have already chosen our purchases. If you do not attach any importance to this, then in a few days you will have a whole army in the kitchen, capable of capturing a small state. Ok, this is a hyperbole, but there are a lot of them (I know from my own experience). For the development of Drosophila much is not necessary: a warm enough environment and the presence of food, which often serves as a place for laying eggs. Fruit flies, as the name implies, feed on vegetables and fruits (in the wild, even the sap of trees).
The life cycle of Drosophila is quite standard: egg (24 hours) - larva (5 days) - pupa (5 days) - adult. Under the most favorable environmental conditions (temperature 25 ° C), the cycle takes about 10 days. That is, when you bring fruit from the store, and after a couple of days the flies appear, you know - their larvae (or even eggs) were already on the products. So wash the fruit before eating.
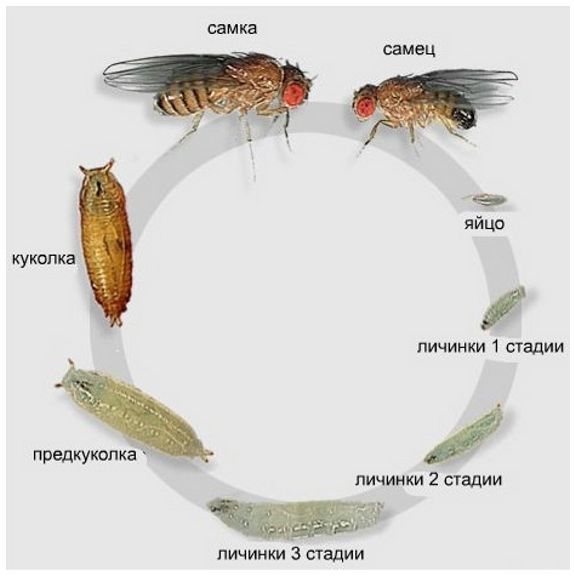
The cycle of ontogenesis of the fruit fly.
As you can see, the cycle of ontogenesis (development from egg to adult) takes not so little time, but Drosophila compensates for the probability of loss of offspring during this period by the number of eggs laid. Over the course of her entire life, the female lays about 400. At the same time, she is ready to breed only 12 hours after the completion of her ontogenesis cycle.
The study showed that the fruit flies are capable of extremely quickly adjusting their position in the air. The destabilization of the situation was carried out by the action of a magnetic field on the fly.
It will be correct to assume that Drosophila scientists are interesting not only by ontogenesis, but also, like many insects, by their method of movement and vision. The wings of the fruit flies make about 250 strokes per second. If you find it difficult to assess how much this is, just wave your hands and see how many such movements you will make. For comparison, hummingbirds (smaller species) make about 100 strokes. Also, the fruit flies have become the object of great interest of geneticists. The unique structural features of the Drosophila genome made it an ideal experimental in the study of human diseases (Parkinson's, Alzheimer's). Also Drosophila help in studies of the human immune system, cancer, diabetes and other things.
As you can see, this little annoying creature is unique in its own way and has great potential for researchers.
The basis of the study
Sometimes you ask yourself how and why scientists come to these or other questions, to which sometimes they are looking for answers. But sound curiosity and a desire to uncover some secrets, even if not the most sacred, is even good. In our case, the researchers decided to determine how the fruit fly sees the world. And we are not talking about vision, this question has already received its answer. We are talking about understanding what the fruit flies see.
It is also worth considering that the Drosophila eye is not as cool as it may seem at first glance. Yes, her eye has about 850 ommatidia *, each of which handles one point of space. This is far from perfect. For example, a praying mantis shrimp has about 10,000 ommatidia in each eye. So the phrase “I will even find a pimple on the body of an elephant” is quite applicable here.
How do the unique eyes of mantis shrimp work?
Ommatidium * is an integral part of the insect and crustacean facel eyes.Scientists note that earlier experiments have shown that Drosophila is able to see an object at 1.16˚ (the viewing angle of ommatidia). Thus, it is the number of ommatidia, and not their viewing angle, that is the main limiting factor of Drosophila vision. In this case, scientists believe that the fruit fly can fully take place along with honey bees, which can even distinguish the faces of people. It remains to find out whether the fly is capable of this trick.

The results of DCN operation under various constraints: a - 32x32 pixels, b - at a distance of 3 body lengths of Drosophila + angle 4.8, c - at the same distance, but angle 1.5.
Given the structure of the eyes of Drosophila, scientists have determined that the image they receive will be approximately 29 × 29 pixels. And this is not ultra-HD 4K and all that. Therefore, the question arises - is it enough that Drosophila could determine what or whom she sees in front of her.
For this, scientists used DCN * , where each artificial system such as a separate fruit fly should collect all the necessary information to identify what is presented in front of it.
DCN * - a convolutional neural network based on deep learning.Preparation for experiments The
artificial eye (virtual, of course) was created on the basis of Keras open neural network library and consisted of 25,000 artificial neurons. The real eye of this Drosophila has about 60,000.

Drosophila neural networks (artificial and real).
Image B shows the DCN model that was implemented during the experiments. For comparison, a model of a real Drosophila network ( C ) is also shown .
To prepare the model, a database was needed that would serve as the basis for training the neural network. The source of this knowledge was, of course, the Drosophila themselves, placed in a container with a temperature of 25˚C and 12-12 day and night cycle (that is, for 12 hours they were in darkness and under illumination). Then, after 1-4 hours, 10 females and 10 males were selected, which were divided. After three days, each individual was placed in individual containers (acrylic round arenas 60 mm in diameter and 2 mm in height). Above these "arenas" was placed an ordinary LED lamp. For 15 minutes, a survey was made using the GRAS-20S4M camera with a frequency of 16 frames / second.

Camera GRAS-20S4M-С.
The shooting was carried out three times (1 shooting per day), thus 14400 × 3 images were obtained per 1 front sight.
All data for the future of machine learning, as usual, is divided into three categories: training (training), verification and test. Training counted 12,240 frames, that is, the initial 75% of the data for the first 2 days of shooting. 2160 frames, the last 15%, have become verifiable. Test data were the third day of shooting. The original 181 × 181 frames were also processed by two methods: the first - reduction to 33 × 33, centered cropping to 29 × 29 and an increase in the result to 224 × 224, the second - increase in size to 256 × 256, centered cropping to 224 × 224.
The GUI program was written in MATLAB, which represents an observer with three points of view of the test fly: dorsal, ventral, and lateral. The observer is given the task to choose among the images of the blackflies that which suits this particular individual.
Research

results Table of the results of the experiment.
Different types of architecture were used in the experiment, but ResNet18 turned out to be the most effective with an accuracy of 0.94, but the creation of the research group - an artificial eye - also showed very impressive results - 0.75. Scientists note another important nuance: on the third day of the experiments among the fruit flies, a decrease in their determination accuracy to 37% was observed.
The researchers also decided to exclude the size of the image as a possible parameter that simplifies the definition of the object. That is, the model of an artificial eye should determine the object by its features, and not by the size of the image itself. Therefore, all the pictures, both training and test, were changed in size by 25% in random order without preserving the proportions.
In this version of the test, the artificial eye still showed a good result (approximately 0.55), which still exceeds the human performance. Even more surprising is the fact that the simulated system almost correctly distinguished females from males with an accuracy of 0.99.
Scientists knew that such a test would be extremely difficult for humans, so they did not expect high results, although they invited people involved in the study of insects as participants, which increases their chances of identifying individuals due to experience. The results, as already mentioned, were weak, but had some differences. So, with images at 29 × 29 pixels, the accuracy was 0.11, and at 181 × 181 - 0.13. The difference is not huge, but significant.
For a detailed introduction to the study I recommend to refer to the report of the research group .
Epilogue
Researchers note that hitherto the mechanism of perception of the environment by drosophila has not been fully studied, but we can already say with confidence that visual data are actively involved in this. The artificial eye model showed that flies determine other individuals not only in size, movement, distance from each other, but also in individual small details.
Any machine learning model is capable of distinguishing fruit flies with some accuracy. All of them are exactly the same in one - they are many times better than man. While scientists are not ready to answer the question why a person cannot distinguish one fly from another? The question is strange at first glance, but not without research potential. The individual definition of small dynamic objects, which at first glance seem to be completely identical, is an interesting ability. However, at the moment the person's skill in this area varies within the margin of error.
In any case, the use of modern computer technologies (artificial neural networks and machine learning) allowed us to put an end to the debate between scientists regarding the skills of Drosophila to determine objects (including their relatives) by means of certain details.
We humans are like representatives of the same species, but very different in appearance. These differences are quite noticeable to us, and help to distinguish one person from another. In the case of insects, everything is much more complicated. Drosophila does not have super-vision, one can even say that it would be one of the first insects in the queue for an optometrist, but this does not prevent her from seeing what even a person does not see.
And according to the recently established Friday tradition, there is a bit of a funny, humorous offtopic. Have a great weekend, friends.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr's users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps until December for free if you pay for a period of six months, you can order here .
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?

