Business processes: how not to automate the mess
The years 2006-2008 in business circles were marked by endless discussions on project and process management. Scientific organizations and institutes gathered whole conferences with the participation of prominent international experts and literally without a break for a coffee break, they discussed projects and a process approach. A little later, in 2009, at one of the international round tables, a graduate student of a large university thoroughly and very convincingly proved that the process approach and project management in Russia had a sad end, because "everything that is done in companies is a constant mess."
Fortunately, he was mistaken. Modern business proves that project and process management is at the heart of eliminating mess in the company. Business processes, in turn, have shifted from a theoretical plane to a practical one, largely thanks to corporate software. If you pay attention to the market of corporate information systems, including CRM and XRM, there is an obvious tendency to integrate a module for creating and / or managing business processes into the system. Some vendors use standard BPMN 2.0 notation, some prefer native logic circuits - this depends on the goals of the developer and the general architecture of the system. When we developed our Ruli24 XRM system

, business processes were almost the highest priority for us: we studied foreign solutions, examined available cases, tried to understand the successes and failures of business processes. In general, the accumulated expertise allowed us to formulate our approach, which we will discuss later. In the meantime, the quintessence of the experience gained by the experts of the Ruli24 team.
If we turn to the theory of organization and cybernetics, a process is a sequential change of states, stages of change and development of a system or other object. For the purposes of company management, search, design, production and information processes are distinguished.
Consider all the groups and find out what classic business processes that are paid attention to in the management belong to.
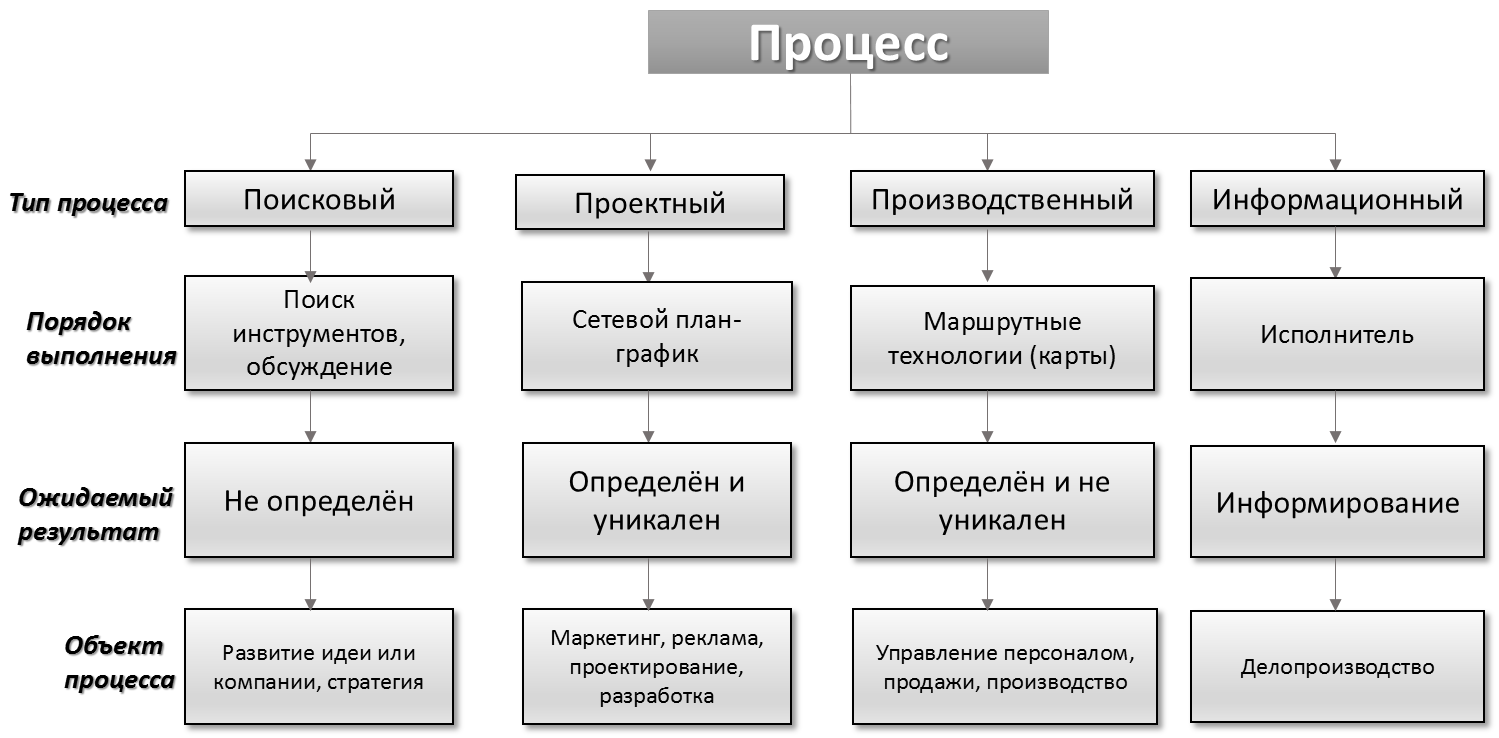
Typology of processes and their attributes
Search processes are a sequence of actions that has a research focus: the search for concepts, development strategies, generation of ideas, etc. The result of such a process cannot be determined in advance. Also, such a process is difficult to formalize, but there are forms of its organization, for example, a meeting, a forum or a brainstorming session.
Design processIt occupies a significant place in each company - it is unique and, as a rule, is repeated once: a one-time advertising campaign, a software implementation project, design and development of a new product. To control such processes, there are network schedules (such as a special case, a Gantt chart) that determine the order and coherence of work, as well as the resources involved. The result of the project process is predetermined (planned) and unique. The process is controlled using the Project Management methodology, uses project management automation tools (in the case of Ruli24 it is a separate module).
Information process- a process with a single purpose - to inform participants in related processes and other interested parties. Such processes most often occur in connection with the management of notifications and document circulation, are automated using EDMS.
Production process - a periodic routine process, which is determined by the repetition of the same actions in different time periods. The result of such a process is always planned and not unique. Management of such processes is carried out using route technologies. It is in this group that the business processes that are so popular today fall - regulated and automated sequences of actions within the company aimed at achieving the planned goals.
Why all this theory? In fact, the statement that only business processes work in the company is incorrect. For example, consider the activities of a sales department. All processes can be involved here: research (search for markets) and information (email and advertising) and design (work with large customers) and production (work on the mass market, regular promotions, standard cold calling). Therefore, it is important to understand that there are various types of processes in a company, they can be combined, be embedded, but they are never just a business process.
However, business turnover currently pays great attention to repetitive, regular, production business processes, so we will focus on them later.
 Let's try to figure out what caused the interest in business processes. Many of us have heard about the classic example of an algorithm that even university professors like, heating a kettle on a gas stove. Almost every no-no yes is mistaken in describing the sequence of actions: someone forgets to light a match, someone does not mention the need to check for water in the kettle, etc. ... For all the primitiveness, this is a very revealing example, from which many properties of business process as an algorithm for performing a chain of actions leading to a result.
Let's try to figure out what caused the interest in business processes. Many of us have heard about the classic example of an algorithm that even university professors like, heating a kettle on a gas stove. Almost every no-no yes is mistaken in describing the sequence of actions: someone forgets to light a match, someone does not mention the need to check for water in the kettle, etc. ... For all the primitiveness, this is a very revealing example, from which many properties of business process as an algorithm for performing a chain of actions leading to a result.
Goals and objectives of the business process.Debugged interaction should solve some problems. It is best if they are formulated as a goal and several tasks on the way to this goal. For example, the process “New Year's sale of books”: the goal is to get the maximum income from the sale of books at a discount, the task is to establish discounts, make changes to the catalog on the site, update the design, do the newsletter. Again, if we are talking about the optimal configuration of the business process, then we need to understand that the range of tasks should be maximally fragmented and taken into account for all involved departments.
Business process time.Any business process should be limited in time. This is one of his key principles - the organization of work and interactions. Each participant in the process must be within the established time frame. By the way, the use of business process automation systems allows you to quickly find the “weak link” that drags out work on the process and minimize the human factor that is not linked to objective reasons for the delay (for example, in Ruli24 you can always see what stage the process is currently at).
Stages and key points of a business process.Accurate definition of stages and control points helps to distribute responsibility among the participants in the process and establish significant events. Back to our book sale. In the process of preparing the action, there are three key milestones: changing prices on the site, creating a mailing list, and actually the fact of sending a letter to the customer base. At the stage from point to point, the work schedule can be shifted, but these points must be completed at the appointed time - only then can the business process be considered successful.
Conditions within the business process.Each stage of the business process should contain important controls: notifications, reports, documents, calls. Based on the results of processing each element, the transition to the next stage will be carried out. Suppose, for one of the mailing design options, you need to buy a couple of photos in stock, paying for them with a corporate card. If the photos are bought, the letter goes to the layout, if for some reason the purchase failed, the designer remains the task and he tries to solve it in another way.
Means and resources of a business process.A business process should never be considered in isolation from the resources necessary for its implementation: time, people, equipment, software, stocks (in the case of production), transport (in the case of logistics), etc. If the employment of resources is not taken into account when developing a business process, it may remain incomplete and thereby the work efficiency will be reduced to zero.
Participants in the business process. No matter how perfect the automation system, it can never guarantee the execution of a business process. Therefore, at each stage, executors and responsible persons who will control the key points of the project should be established. Most often, the holder or initiator of the process is responsible, but in large production companies often several people are the holders.
Information inside a business process. At each stage of the business process, information should be configured: about the transfer of the stage, its acceptance into work, notification of the holder. Information can pass through e-mail, created manually by participants, or through automatic messages generated by the system in response to the occurrence of a significant event. Of course, the second option is preferable - the system does not waste time and does not forget to report.
The result of a business process. Positive or negative, the result must be: either this is the achievement of the goal, or it is a failure. If the goal is not achieved, a business process map with logging will help to figure out which omissions led to an undesirable result. Based on the results of such an analysis, an existing project can be adjusted.
The advantages and benefits of introducing automated business processes are obvious: it is accelerating market entry for new companies, increasing the speed of work, increasing the quality and speed of customer service, reducing costs due to the redistribution of labor. The combination of workflow automation tools, integration with other automation tools (for example, in the case of Ruli24 these are modules), management and monitoring can give significant advantages to the company: automation and organization of the workflow, reducing the risk of errors, meeting deadlines, reducing training costs and staff adaptation and so on. The combination of these benefits ultimately has a positive impact on the profitability of the business.
You should not limit the application of technologies for creating and managing business processes to large companies with a complex organizational structure - small and medium-sized businesses need them no less. We can say with confidence that the business process begins from the moment when more than three people appear in the company and do some kind of routine work: bookkeeping, mailing, cold calling, orders, delivery, working with suppliers, issuing media numbers and so on ... Activities can be recognized as a process if it is periodically repeated, consists of the same steps, uses the same resources. Process management affects the management of marketing, production, supply, sales, etc. ...
In general, business processes are characterized by three essential elements:
It happens that the team is not ready for automation, but even in this case, you should not go away from regulating business processes: the minimum action plan drawn up on the marker board will bring a tangible order to the work of the company. Actions to automate business processes should be carefully thought out, since there can be many hidden problems and exceptions within the process, which, of course, can lead to a restructuring of the entire implementation concept and the cost of the company's automation project.
At the beginning of the post, we said that we met with cases of the collapse of business process automation. Typically, such problems are inherited from the general difficulties associated with the implementation of CRM, BPM, XRM, but there are also reasons.
Working on a comprehensive Ruli24 system , we approached the issue of automating business processes from different perspectives and were guided by the principle “Everything is a process”. The difference is in the execution order, evaluation of the result and the object the process is aimed at. In most business publications, as well as in many CRM systems, a business process is understood as a chain of actions related to sales or approval of documents. Recently, a trend has appeared to expand understanding of the automated business process, but we at Ruli24 have long come to the need to formalize any routine: from the meeting to the development of new software versions (we ourselves use the processes when releasing new system releases, which is why all releases occur on the appointed term).
So inRuli24 specialists customize business processes individually for each business, taking into account the most delicate details. In fact, during the implementation, we create a team of a technical employee, Ruli24 business analyst and a manager who owns the process of the customer company. It turns out a typical business process that has a beginning (start condition), work, intersection events, and end (end condition). The business process is attached to the object responsible to the executor - the owner of the process. When describing the work, the performers are indicated, the complexity of the work. When describing intersection events, incoming and outgoing work and the conditions for starting outgoing work are indicated.
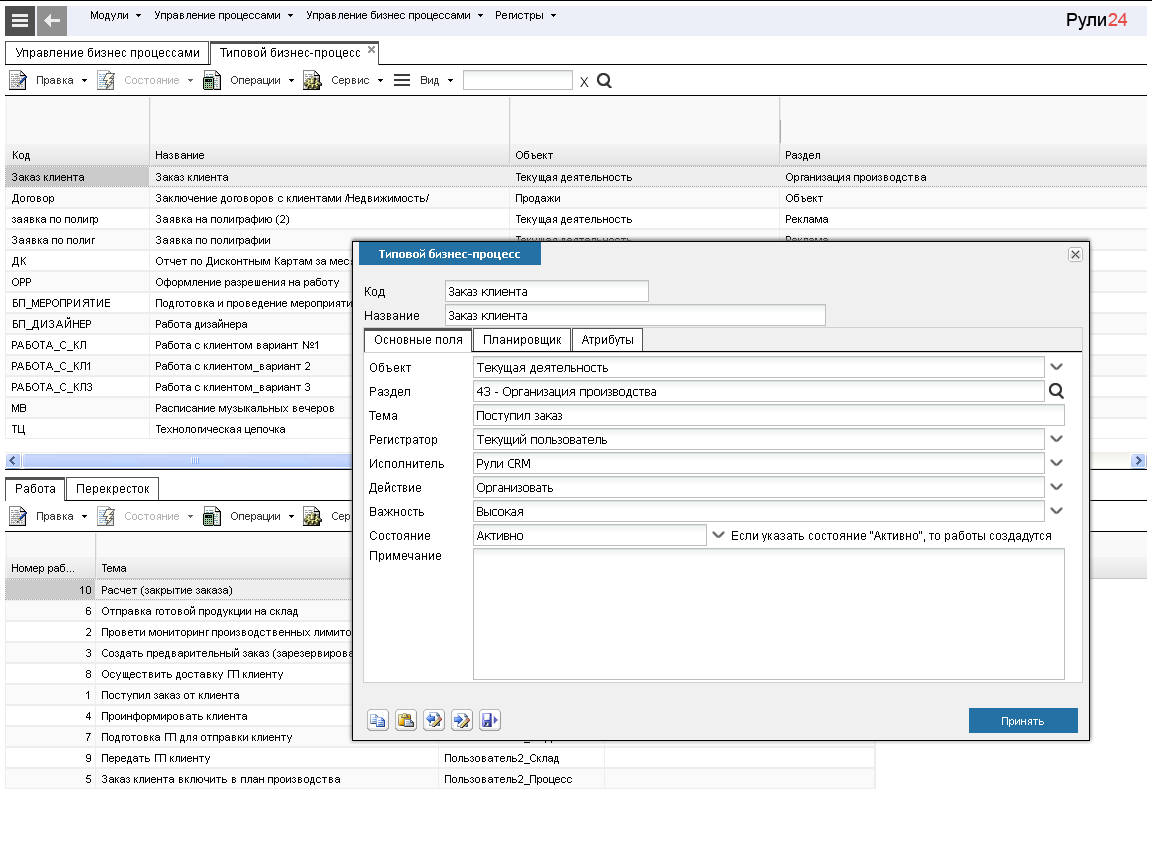
Then, based on a typical process, process instances are created with the start and end dates, as well as the basis. In this case, all parameters of the process instance are inherited from the template of the standard process and all fields are automatically filled taking into account which of the employees initiates the start of the process. Upon completion of the process, it is assigned the status of “Closed”.
Another important process management tool in the Ruli24 system is the Gantt chart, which is a dynamic process model that displays dependencies, the sequence of work performed in terms of time and resources used. The Gantt chart reflects both projects and running instances of typical business processes. Using the Gantt chart helps not only to get a complete understanding of resource utilization and the amount of work, but also to identify bottlenecks and problems with the timing of tasks.
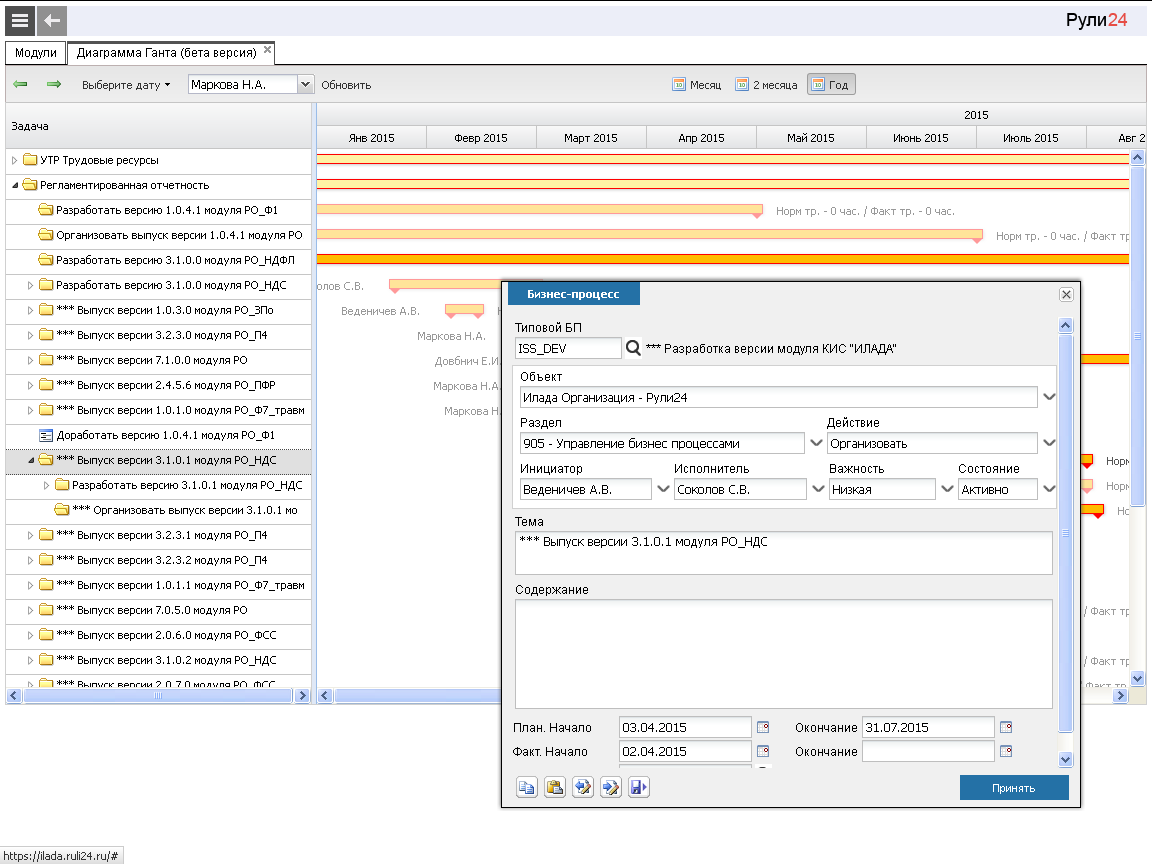
Right in the interface of the Gantt chart, you can open the project, make changes to it. Stages are visible in the right information panel and when you hover over the progress bars of tasks. By the way, in Ruli24, in addition to projects, you can also display instances of running business processes on the Gantt chart - in this case, only running work is displayed on it. If some work on the process is optional, they are not displayed on the graph.
Due to its versatility, Ruli24 meets the requirements of automation of processes of all types:
 search - automation with the help of time tracking , recording meetings and discussions;
search - automation with the help of time tracking , recording meetings and discussions;
 project - automation using the Gantt chart and project and task management module;
project - automation using the Gantt chart and project and task management module;
 production - automation through the creation of BPMN-models of business processes, the generation of typical processes and their instances;
production - automation through the creation of BPMN-models of business processes, the generation of typical processes and their instances;
 informational - electronic document management module (EDMS).
informational - electronic document management module (EDMS).
Thus, Ruli24 provides a comprehensive approach to process management in a company of any level, regardless of the assigned commercial, managerial and production tasks.
No matter how hard developers try to create systems for automating business processes, alas, the effectiveness of such programs is low if the company does not understand the process as an element of company management. Random execution of tasks, delayed deadlines, shifting responsibility - all these factors work against the company and one of the main goals of the business is to satisfy customer needs and generate income. More than once on Habré the phrase written by employees of vendors of various systems, - "the automated mess (lawlessness)" met. Therefore, we recommend that before implementing a business process management system (especially as part of XRM), conduct a comprehensive business analysis, try to describe the processes with available means, understand which points and interactions pose the most serious problems.
When an understanding of the organization of a business as an action comes, then it becomes clear that only debugged interactions, a reasonable allocation of time and resources, attention to significant actions will lead the company to an intensive development model. In such a company, automated business processes will become a reliable point of growth.
Fortunately, he was mistaken. Modern business proves that project and process management is at the heart of eliminating mess in the company. Business processes, in turn, have shifted from a theoretical plane to a practical one, largely thanks to corporate software. If you pay attention to the market of corporate information systems, including CRM and XRM, there is an obvious tendency to integrate a module for creating and / or managing business processes into the system. Some vendors use standard BPMN 2.0 notation, some prefer native logic circuits - this depends on the goals of the developer and the general architecture of the system. When we developed our Ruli24 XRM system

, business processes were almost the highest priority for us: we studied foreign solutions, examined available cases, tried to understand the successes and failures of business processes. In general, the accumulated expertise allowed us to formulate our approach, which we will discuss later. In the meantime, the quintessence of the experience gained by the experts of the Ruli24 team.
Everything is a process: a bit of theory and cybernetics
If we turn to the theory of organization and cybernetics, a process is a sequential change of states, stages of change and development of a system or other object. For the purposes of company management, search, design, production and information processes are distinguished.
Consider all the groups and find out what classic business processes that are paid attention to in the management belong to.

Typology of processes and their attributes
Search processes are a sequence of actions that has a research focus: the search for concepts, development strategies, generation of ideas, etc. The result of such a process cannot be determined in advance. Also, such a process is difficult to formalize, but there are forms of its organization, for example, a meeting, a forum or a brainstorming session.
Design processIt occupies a significant place in each company - it is unique and, as a rule, is repeated once: a one-time advertising campaign, a software implementation project, design and development of a new product. To control such processes, there are network schedules (such as a special case, a Gantt chart) that determine the order and coherence of work, as well as the resources involved. The result of the project process is predetermined (planned) and unique. The process is controlled using the Project Management methodology, uses project management automation tools (in the case of Ruli24 it is a separate module).
Information process- a process with a single purpose - to inform participants in related processes and other interested parties. Such processes most often occur in connection with the management of notifications and document circulation, are automated using EDMS.
Production process - a periodic routine process, which is determined by the repetition of the same actions in different time periods. The result of such a process is always planned and not unique. Management of such processes is carried out using route technologies. It is in this group that the business processes that are so popular today fall - regulated and automated sequences of actions within the company aimed at achieving the planned goals.
Why all this theory? In fact, the statement that only business processes work in the company is incorrect. For example, consider the activities of a sales department. All processes can be involved here: research (search for markets) and information (email and advertising) and design (work with large customers) and production (work on the mass market, regular promotions, standard cold calling). Therefore, it is important to understand that there are various types of processes in a company, they can be combined, be embedded, but they are never just a business process.
However, business turnover currently pays great attention to repetitive, regular, production business processes, so we will focus on them later.
Everything is a process
 Let's try to figure out what caused the interest in business processes. Many of us have heard about the classic example of an algorithm that even university professors like, heating a kettle on a gas stove. Almost every no-no yes is mistaken in describing the sequence of actions: someone forgets to light a match, someone does not mention the need to check for water in the kettle, etc. ... For all the primitiveness, this is a very revealing example, from which many properties of business process as an algorithm for performing a chain of actions leading to a result.
Let's try to figure out what caused the interest in business processes. Many of us have heard about the classic example of an algorithm that even university professors like, heating a kettle on a gas stove. Almost every no-no yes is mistaken in describing the sequence of actions: someone forgets to light a match, someone does not mention the need to check for water in the kettle, etc. ... For all the primitiveness, this is a very revealing example, from which many properties of business process as an algorithm for performing a chain of actions leading to a result. Goals and objectives of the business process.Debugged interaction should solve some problems. It is best if they are formulated as a goal and several tasks on the way to this goal. For example, the process “New Year's sale of books”: the goal is to get the maximum income from the sale of books at a discount, the task is to establish discounts, make changes to the catalog on the site, update the design, do the newsletter. Again, if we are talking about the optimal configuration of the business process, then we need to understand that the range of tasks should be maximally fragmented and taken into account for all involved departments.
Business process time.Any business process should be limited in time. This is one of his key principles - the organization of work and interactions. Each participant in the process must be within the established time frame. By the way, the use of business process automation systems allows you to quickly find the “weak link” that drags out work on the process and minimize the human factor that is not linked to objective reasons for the delay (for example, in Ruli24 you can always see what stage the process is currently at).
Stages and key points of a business process.Accurate definition of stages and control points helps to distribute responsibility among the participants in the process and establish significant events. Back to our book sale. In the process of preparing the action, there are three key milestones: changing prices on the site, creating a mailing list, and actually the fact of sending a letter to the customer base. At the stage from point to point, the work schedule can be shifted, but these points must be completed at the appointed time - only then can the business process be considered successful.
Conditions within the business process.Each stage of the business process should contain important controls: notifications, reports, documents, calls. Based on the results of processing each element, the transition to the next stage will be carried out. Suppose, for one of the mailing design options, you need to buy a couple of photos in stock, paying for them with a corporate card. If the photos are bought, the letter goes to the layout, if for some reason the purchase failed, the designer remains the task and he tries to solve it in another way.
Means and resources of a business process.A business process should never be considered in isolation from the resources necessary for its implementation: time, people, equipment, software, stocks (in the case of production), transport (in the case of logistics), etc. If the employment of resources is not taken into account when developing a business process, it may remain incomplete and thereby the work efficiency will be reduced to zero.
Participants in the business process. No matter how perfect the automation system, it can never guarantee the execution of a business process. Therefore, at each stage, executors and responsible persons who will control the key points of the project should be established. Most often, the holder or initiator of the process is responsible, but in large production companies often several people are the holders.
Information inside a business process. At each stage of the business process, information should be configured: about the transfer of the stage, its acceptance into work, notification of the holder. Information can pass through e-mail, created manually by participants, or through automatic messages generated by the system in response to the occurrence of a significant event. Of course, the second option is preferable - the system does not waste time and does not forget to report.
The result of a business process. Positive or negative, the result must be: either this is the achievement of the goal, or it is a failure. If the goal is not achieved, a business process map with logging will help to figure out which omissions led to an undesirable result. Based on the results of such an analysis, an existing project can be adjusted.
The advantages and benefits of introducing automated business processes are obvious: it is accelerating market entry for new companies, increasing the speed of work, increasing the quality and speed of customer service, reducing costs due to the redistribution of labor. The combination of workflow automation tools, integration with other automation tools (for example, in the case of Ruli24 these are modules), management and monitoring can give significant advantages to the company: automation and organization of the workflow, reducing the risk of errors, meeting deadlines, reducing training costs and staff adaptation and so on. The combination of these benefits ultimately has a positive impact on the profitability of the business.
Business Processes: Transition Challenges
You should not limit the application of technologies for creating and managing business processes to large companies with a complex organizational structure - small and medium-sized businesses need them no less. We can say with confidence that the business process begins from the moment when more than three people appear in the company and do some kind of routine work: bookkeeping, mailing, cold calling, orders, delivery, working with suppliers, issuing media numbers and so on ... Activities can be recognized as a process if it is periodically repeated, consists of the same steps, uses the same resources. Process management affects the management of marketing, production, supply, sales, etc. ...
In general, business processes are characterized by three essential elements:
- stable connections (transitions, conditions, multiple choice, etc.)
- actions during the process (including notifications, calls, attached documents)
- result (goal achieved).
It happens that the team is not ready for automation, but even in this case, you should not go away from regulating business processes: the minimum action plan drawn up on the marker board will bring a tangible order to the work of the company. Actions to automate business processes should be carefully thought out, since there can be many hidden problems and exceptions within the process, which, of course, can lead to a restructuring of the entire implementation concept and the cost of the company's automation project.
At the beginning of the post, we said that we met with cases of the collapse of business process automation. Typically, such problems are inherited from the general difficulties associated with the implementation of CRM, BPM, XRM, but there are also reasons.
- Refusal of employees to automate or organize the process - many team members are afraid to fall under staff reductions caused by the automation of some tasks. However, an experienced and competent manager always knows that an employee trained by a company can always be moved within the company with maximum efficiency and satisfaction from all parties. In the event that the refusal to use business processes is associated with technical difficulties, it is worth spending time on the training of employees and the formation of internal expertise in the company.
- Illiterate process. This is perhaps the most common source of dissatisfaction with automation tools. Employees of the company miss important details when compiling the process - this is most often due to the lack of joint preparation for the creation of a typical business process and its instances. But the most dangerous thing that vendors are faced with is the free interpretation of BPMN notation, with which business processes are modeled. The notation itself is aimed at a wide range of users: managers, technicians, managers, etc. It does not require in-depth knowledge of programming or design; its semantic constructions are created from elements with intuitive notations. Such its apparent simplicity and similarity with the designer make a joke with users.
 In fact, the successful creation of a business process using notation is possible only in a team consisting of a business analyst, technical specialist and an interested process manager-holder. If it is necessary to implement a complex process inside the company (production, procurement, advertising, publishing, etc.), it is better to turn to third-party specialists who will conduct a comprehensive examination of the process and create the perfect automated scheme. The participation of professionals is especially justified if it is necessary to link tasks from business processes with formalized documents in the system, for example, contracts, invoices, invoices, work orders, etc.
In fact, the successful creation of a business process using notation is possible only in a team consisting of a business analyst, technical specialist and an interested process manager-holder. If it is necessary to implement a complex process inside the company (production, procurement, advertising, publishing, etc.), it is better to turn to third-party specialists who will conduct a comprehensive examination of the process and create the perfect automated scheme. The participation of professionals is especially justified if it is necessary to link tasks from business processes with formalized documents in the system, for example, contracts, invoices, invoices, work orders, etc. - Refusal of the process. The company may abandon the existing automated business process if the activity has changed, but in the system it has remained the same. In this case, you need to make changes to the process yourself or with the help of the vendor, and not to avoid it.
How we did business processes
Working on a comprehensive Ruli24 system , we approached the issue of automating business processes from different perspectives and were guided by the principle “Everything is a process”. The difference is in the execution order, evaluation of the result and the object the process is aimed at. In most business publications, as well as in many CRM systems, a business process is understood as a chain of actions related to sales or approval of documents. Recently, a trend has appeared to expand understanding of the automated business process, but we at Ruli24 have long come to the need to formalize any routine: from the meeting to the development of new software versions (we ourselves use the processes when releasing new system releases, which is why all releases occur on the appointed term).
So inRuli24 specialists customize business processes individually for each business, taking into account the most delicate details. In fact, during the implementation, we create a team of a technical employee, Ruli24 business analyst and a manager who owns the process of the customer company. It turns out a typical business process that has a beginning (start condition), work, intersection events, and end (end condition). The business process is attached to the object responsible to the executor - the owner of the process. When describing the work, the performers are indicated, the complexity of the work. When describing intersection events, incoming and outgoing work and the conditions for starting outgoing work are indicated.

Then, based on a typical process, process instances are created with the start and end dates, as well as the basis. In this case, all parameters of the process instance are inherited from the template of the standard process and all fields are automatically filled taking into account which of the employees initiates the start of the process. Upon completion of the process, it is assigned the status of “Closed”.
Another important process management tool in the Ruli24 system is the Gantt chart, which is a dynamic process model that displays dependencies, the sequence of work performed in terms of time and resources used. The Gantt chart reflects both projects and running instances of typical business processes. Using the Gantt chart helps not only to get a complete understanding of resource utilization and the amount of work, but also to identify bottlenecks and problems with the timing of tasks.

Right in the interface of the Gantt chart, you can open the project, make changes to it. Stages are visible in the right information panel and when you hover over the progress bars of tasks. By the way, in Ruli24, in addition to projects, you can also display instances of running business processes on the Gantt chart - in this case, only running work is displayed on it. If some work on the process is optional, they are not displayed on the graph.
Due to its versatility, Ruli24 meets the requirements of automation of processes of all types:
 search - automation with the help of time tracking , recording meetings and discussions;
search - automation with the help of time tracking , recording meetings and discussions;  project - automation using the Gantt chart and project and task management module;
project - automation using the Gantt chart and project and task management module; production - automation through the creation of BPMN-models of business processes, the generation of typical processes and their instances;
production - automation through the creation of BPMN-models of business processes, the generation of typical processes and their instances;  informational - electronic document management module (EDMS).
informational - electronic document management module (EDMS). Thus, Ruli24 provides a comprehensive approach to process management in a company of any level, regardless of the assigned commercial, managerial and production tasks.
No matter how hard developers try to create systems for automating business processes, alas, the effectiveness of such programs is low if the company does not understand the process as an element of company management. Random execution of tasks, delayed deadlines, shifting responsibility - all these factors work against the company and one of the main goals of the business is to satisfy customer needs and generate income. More than once on Habré the phrase written by employees of vendors of various systems, - "the automated mess (lawlessness)" met. Therefore, we recommend that before implementing a business process management system (especially as part of XRM), conduct a comprehensive business analysis, try to describe the processes with available means, understand which points and interactions pose the most serious problems.
When an understanding of the organization of a business as an action comes, then it becomes clear that only debugged interactions, a reasonable allocation of time and resources, attention to significant actions will lead the company to an intensive development model. In such a company, automated business processes will become a reliable point of growth.
