Huawei Enterprise Server
At the beginning of this summer, I returned from a trip to Huawei headquarters in Shenzhen, where the next Huawei Presales Elite Camp was held.
This time, the hospitable Chinese introduced us to their server line. With the release of new Intel Xeon V3 processors, it has undergone significant changes, which I want to tell you in this article

It's no secret that updating the server lines of most vendors is timed to coincide with the release of new generations of Intel processors. Huawei is not an exception, having released new solutions based on Intel Xeon V3. Below I propose to get acquainted with them and understand what they can offer us at the moment
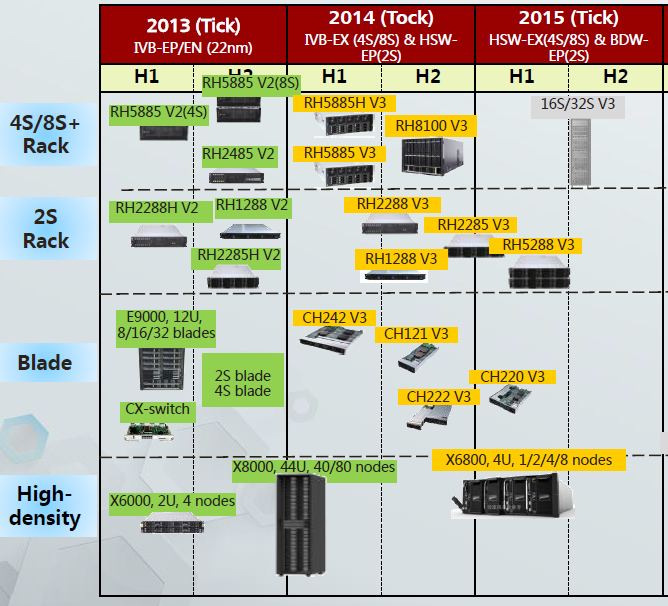
A fairly large number of reviews have appeared on Huawei rack servers, so I will not dwell on them in detail. I will mention only a few facts that may be of interest to you. You can always find more detailed specifications on all models in the official website of Huawei Enterprise .
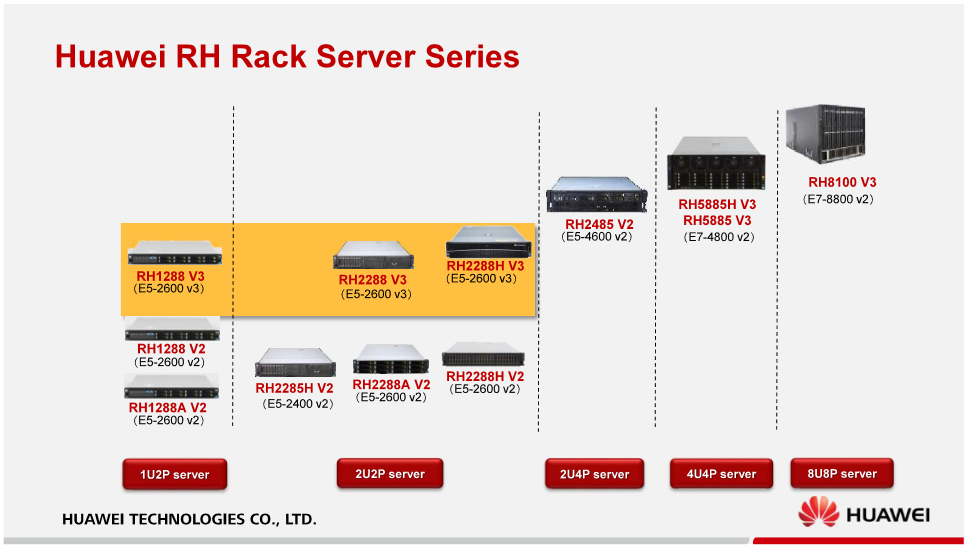
The name of all rack models is as follows: RH **** (For example: RH 1288)
• R stands for Rack-mount.
• H means that the servers are equipped with Intel processors. For if you turn the letter I on 90⁰, you will receive the letter H . Here is such a mysterious oriental logic.
• The first digit corresponds to the server height in units.
• The second digit corresponds to the number of processor sockets.
• The last two digits correspond to the “level” of the model. Releasing a new model, Huawei collects reviews from the market. And if there is a great need, they can "adjust" the parameters of their servers to a greater or lesser extent. So there are various gradations of the same model, differing in processors, number of maximum supported memory and PCIe slots:
o 85 - the first version;
o 88 - “reissued” version with older processor models;
o 85A / 88A - “weakened” budget version;
o 85H / 88H - enhanced version (high-end).
However, having carefully studied the lineup, you can notice a discrepancy: the RH5885 / RH5885H models have a height of 4U and 4 sockets. This is explained by the fact that the number 4 in Chinese culture is unfortunate, since it is pronounced similarly to the word "death." Therefore, the Chinese in every possible way avoid this number.
And this is noticeable not only in the IT sphere: the cost of apartments on the 4th floor in any house will be an order of magnitude less than any other floor.
With the advent of V3 models in Huawei RH servers, there are:
• Intel Xeon V3 processors;
• random access memory DDR4;
• I / O cards 16 Gbs FC, 56 Gbs IB, FCoE and 10 Gbs copper (RJ-45) Ethernet;
• PCIe SSD cards up to 1.6 Tb;
• what many have been waiting for for a long time - official support of SAS HBA (LSI SAS2008) for connecting DAS and hundredths through SAS back-end;
• the ability to install up to 2 SATA DOM 32Gb.
In addition, it is worth noting less significant improvements:
• An increase in the maximum temperature threshold of the processors up to 45⁰ С;
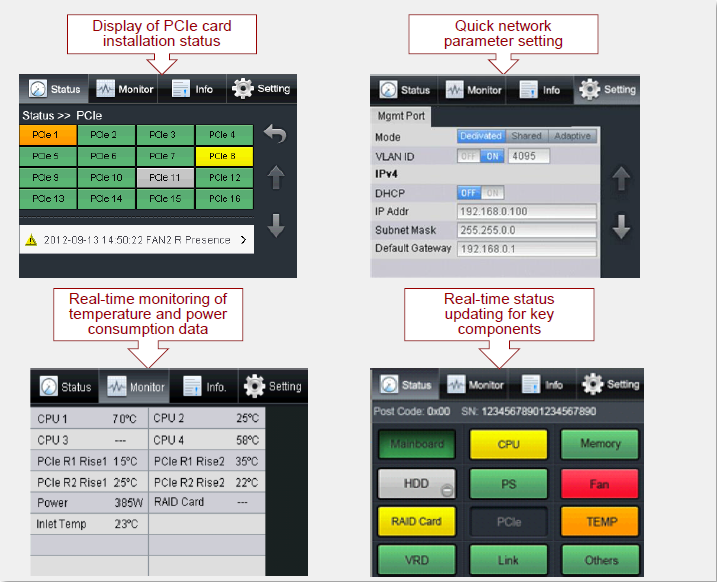
• iMana (remote management tool) was replaced by iBMC;
• The advent of LCD Touch-Screen diagnosis Panel.
Perhaps more pro rack solutions have nothing to say.
Huawei has redesigned its line of high-density servers by adding the X6800 V3 instead of the X6000. Thus, only 2 models are currently available:
1. X6800 - 4U, 8 nodes
2. X8000 - 44U, 80 nodes I will dwell
on the new X6800 solution.

There are 3 types of nodes available to the user:
1. XH628 V3 Storage Node - a double node of high disk capacity. It has a hot-swap basket containing 12 * 3.5 "disks + 2 * 2.5" disks installed separately from the basket;
2. XH622 V3 HPC (also known as Application Acceleration) Node- a double node for HPC, allowing the installation of 2 full-size dual-slot PCIe (for example, NVIDIA GPU or Xeon-Phi). Sure performance with a floating point with 4 nodes with GPGPU - 12 TFLOPS;
3. XH620 V3 Compute Node - a single node of high performance. Due to the increased density of the arrangement, the solution of 8 nodes has 16 E5-2600 V3 processors and 128 DDR4 slots in 4U.
It is worth noting that now only the same type of configuration is available. Those. mixed node type configuration is not available.
This solution will be especially interesting in projects to build an HPC cluster or public clouds.
Well, you can not help but mention the Huawei E9000 blade solution.

Appeared on the market in 2012, it still does not lose its relevance.
The chassis itself has remained unchanged. With the advent of a new generation of processors, the blades themselves have been updated, having acquired Intel Xeon V3 processors.
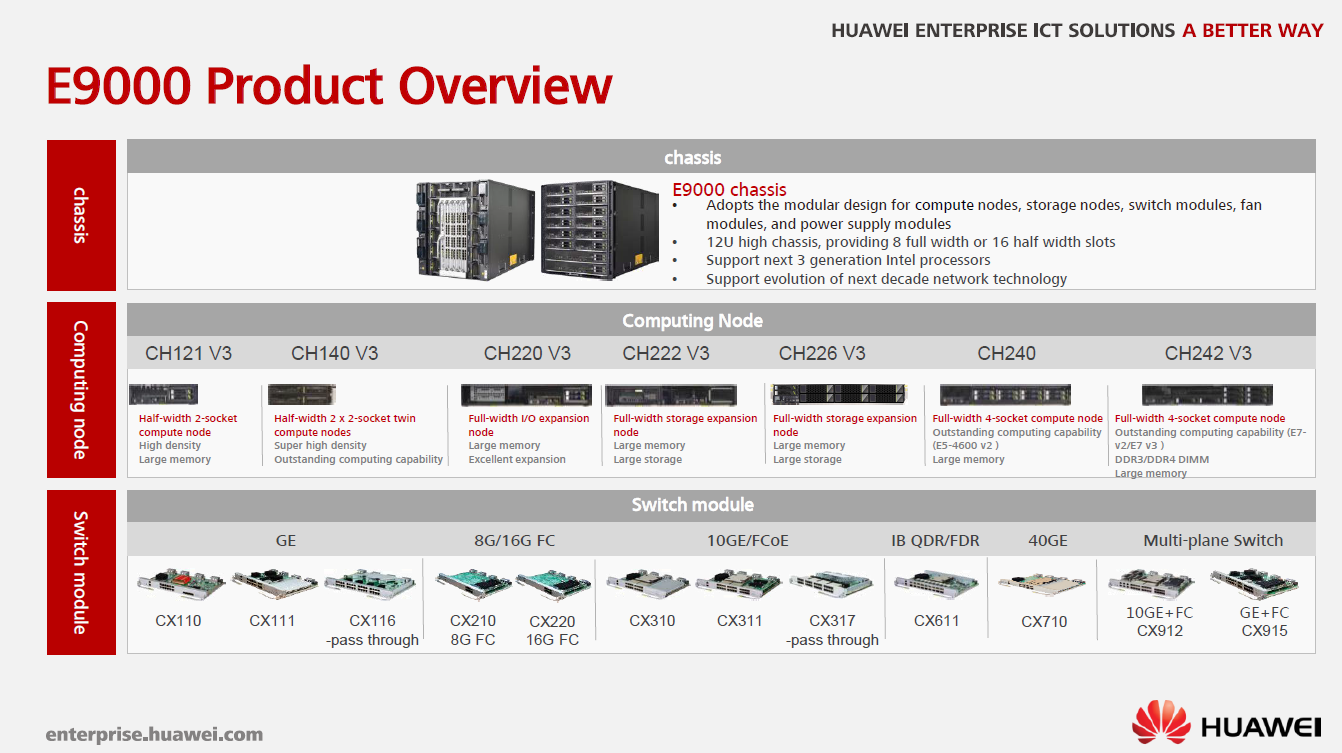
Added support for 16G FC, 10GE copper, FCoE, 56G FDR IB and 40 GE switches. But the most popular is still the converged switch 10GE + 8G FC.
In addition to current innovations, Huawei has announced support for potential technologies: IB EDR and 100 GE.
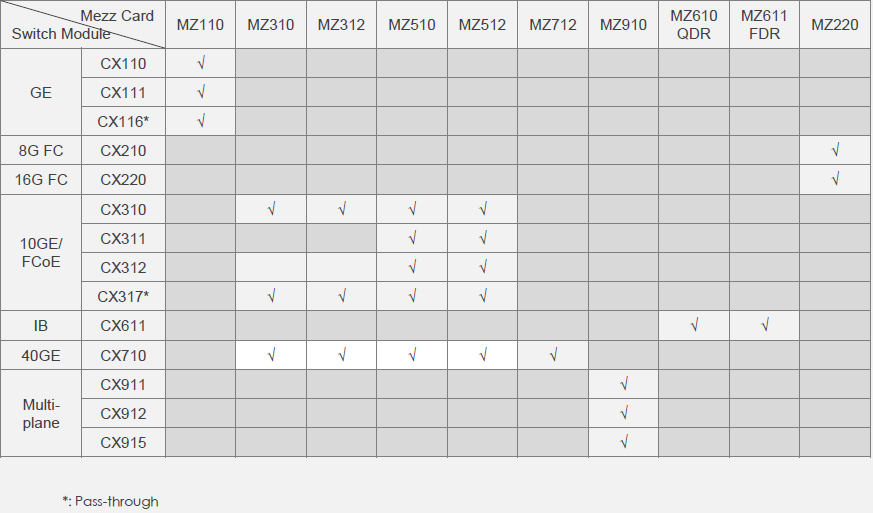
For ease of configuration, I will provide here the correspondence matrix of switches and mezzanines.
In terms of the variety of blades used, this solution can close all potential cases:
1. CH121 V3 - a half 2-processor high-density blade;
2. CH140 V3 - a half double dual-processor blade of super-high density;
3. CH220 V3 - full-sized I / O blade;
4. CH222 / CH226 V3 - a full-sized blade with increased storage capacity;
5. CH240 V2 / CH242 V3 is a full-sized computing 4-processor blade.
In the end, it is worth noting that, despite such a “venerable” age, this solution still remains competitive with other technical vendors in terms of its technical characteristics.
And finally, I left a completely exotic and unknown solution.
Keeping up with the times, Huawei decided to keep up with its competitors and released their own hyper-converged FusionCube solution.
As a hardware basis, X6800 or E9000 servers can be used. The virtualization environment is the Huawei FusionCompute hypervisor (based on Xen). FusionStorage is used to virtualize disk capacities, and FusionManager is used as a management tool.
In the FusionCube X6800 configuration, scaling will occur at the chassis level, and in the FusionCube E9000 at the blade level.
The success and relevance of this solution in our market is very mixed.
This time, the hospitable Chinese introduced us to their server line. With the release of new Intel Xeon V3 processors, it has undergone significant changes, which I want to tell you in this article

It's no secret that updating the server lines of most vendors is timed to coincide with the release of new generations of Intel processors. Huawei is not an exception, having released new solutions based on Intel Xeon V3. Below I propose to get acquainted with them and understand what they can offer us at the moment

RH Series Rack Servers
A fairly large number of reviews have appeared on Huawei rack servers, so I will not dwell on them in detail. I will mention only a few facts that may be of interest to you. You can always find more detailed specifications on all models in the official website of Huawei Enterprise .

The name of all rack models is as follows: RH **** (For example: RH 1288)
• R stands for Rack-mount.
• H means that the servers are equipped with Intel processors. For if you turn the letter I on 90⁰, you will receive the letter H . Here is such a mysterious oriental logic.
• The first digit corresponds to the server height in units.
• The second digit corresponds to the number of processor sockets.
• The last two digits correspond to the “level” of the model. Releasing a new model, Huawei collects reviews from the market. And if there is a great need, they can "adjust" the parameters of their servers to a greater or lesser extent. So there are various gradations of the same model, differing in processors, number of maximum supported memory and PCIe slots:
o 85 - the first version;
o 88 - “reissued” version with older processor models;
o 85A / 88A - “weakened” budget version;
o 85H / 88H - enhanced version (high-end).
However, having carefully studied the lineup, you can notice a discrepancy: the RH5885 / RH5885H models have a height of 4U and 4 sockets. This is explained by the fact that the number 4 in Chinese culture is unfortunate, since it is pronounced similarly to the word "death." Therefore, the Chinese in every possible way avoid this number.
And this is noticeable not only in the IT sphere: the cost of apartments on the 4th floor in any house will be an order of magnitude less than any other floor.
With the advent of V3 models in Huawei RH servers, there are:
• Intel Xeon V3 processors;
• random access memory DDR4;
• I / O cards 16 Gbs FC, 56 Gbs IB, FCoE and 10 Gbs copper (RJ-45) Ethernet;
• PCIe SSD cards up to 1.6 Tb;
• what many have been waiting for for a long time - official support of SAS HBA (LSI SAS2008) for connecting DAS and hundredths through SAS back-end;
• the ability to install up to 2 SATA DOM 32Gb.
In addition, it is worth noting less significant improvements:
• An increase in the maximum temperature threshold of the processors up to 45⁰ С;
• iMana (remote management tool) was replaced by iBMC;
• The advent of LCD Touch-Screen diagnosis Panel.

Perhaps more pro rack solutions have nothing to say.
X-Series High Density Solution
Huawei has redesigned its line of high-density servers by adding the X6800 V3 instead of the X6000. Thus, only 2 models are currently available:
1. X6800 - 4U, 8 nodes
2. X8000 - 44U, 80 nodes I will dwell
on the new X6800 solution.

There are 3 types of nodes available to the user:
1. XH628 V3 Storage Node - a double node of high disk capacity. It has a hot-swap basket containing 12 * 3.5 "disks + 2 * 2.5" disks installed separately from the basket;
2. XH622 V3 HPC (also known as Application Acceleration) Node- a double node for HPC, allowing the installation of 2 full-size dual-slot PCIe (for example, NVIDIA GPU or Xeon-Phi). Sure performance with a floating point with 4 nodes with GPGPU - 12 TFLOPS;
3. XH620 V3 Compute Node - a single node of high performance. Due to the increased density of the arrangement, the solution of 8 nodes has 16 E5-2600 V3 processors and 128 DDR4 slots in 4U.
It is worth noting that now only the same type of configuration is available. Those. mixed node type configuration is not available.
This solution will be especially interesting in projects to build an HPC cluster or public clouds.
E-Series Blade Solution
Well, you can not help but mention the Huawei E9000 blade solution.

Appeared on the market in 2012, it still does not lose its relevance.
The chassis itself has remained unchanged. With the advent of a new generation of processors, the blades themselves have been updated, having acquired Intel Xeon V3 processors.

Added support for 16G FC, 10GE copper, FCoE, 56G FDR IB and 40 GE switches. But the most popular is still the converged switch 10GE + 8G FC.
In addition to current innovations, Huawei has announced support for potential technologies: IB EDR and 100 GE.
For ease of configuration, I will provide here the correspondence matrix of switches and mezzanines.

In terms of the variety of blades used, this solution can close all potential cases:
1. CH121 V3 - a half 2-processor high-density blade;
2. CH140 V3 - a half double dual-processor blade of super-high density;
3. CH220 V3 - full-sized I / O blade;
4. CH222 / CH226 V3 - a full-sized blade with increased storage capacity;
5. CH240 V2 / CH242 V3 is a full-sized computing 4-processor blade.
In the end, it is worth noting that, despite such a “venerable” age, this solution still remains competitive with other technical vendors in terms of its technical characteristics.
Fusioncube
And finally, I left a completely exotic and unknown solution.
Keeping up with the times, Huawei decided to keep up with its competitors and released their own hyper-converged FusionCube solution.
As a hardware basis, X6800 or E9000 servers can be used. The virtualization environment is the Huawei FusionCompute hypervisor (based on Xen). FusionStorage is used to virtualize disk capacities, and FusionManager is used as a management tool.
In the FusionCube X6800 configuration, scaling will occur at the chassis level, and in the FusionCube E9000 at the blade level.
The success and relevance of this solution in our market is very mixed.
