How to organize long-term archival storage of electronic documents
Recently, in the journal " Inside " we talked about the long-term archival storage of electronic documents (ED), certified by electronic signature (ED). The article was devoted to reviewing various points of view on the organization of this process and approaches to the prolongation of the properties of the legal significance of ED. In it, we focused on the approach, which provides for the formation of receipts of the document. They are metadata containing the results of the checks performed, as well as all the necessary attributes confirming the legal significance of the document at the time of the check.
This article reveals in more detail another approach to long-term archival storage (DAH) - the formation of an improved electronic signature (CEC), namely, electronic signature in the CAdES-A and XAdES-A archive formats.

Let us try to understand in more detail how and why archival ES can extend the life cycle of electronic documents with ES. Let's start with a small theoretical educational program on the types and formats of electronic signature, and then we will consider in practice the procedure for the formation of archival electronic signature by the products developed by Gazinformservice.
Electronic Signature Type CAdES
CMS Advanced Electronic Signatures (CAdES) is an EP standard that is an enhanced version of the Cryptographic Message Syntax standard (CMS). The main document describing this standard is ETSI TS 101 733 “Electronic Signature and Infrastructure (ESI); CMS Advanced Electronic Signature (CAdES) ".
CAdES became the development of CMS, in which such major shortcomings of the predecessor were corrected, such as the lack of a stamp of the entrusted time of creating an EP, the absence of an EP content type and the absence of the possibility of long-term preservation of the properties of the legal significance of an EP.
The standard defines several CAdES formats, each of which includes the previous one (in accordance with the sequence presented below) and extends it:
The CAdES-A archive archive form consists of the following elements:
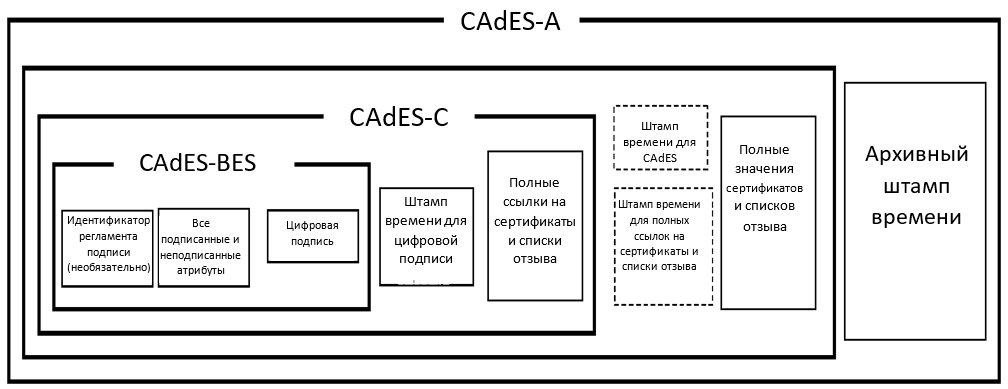
Figure 1 - The scheme of forming an electronic signature in the CAdES-A format.
Questions of the organization of DAH are associated not only with the limited period of validity of the user certificate established by Russian legislation at 1 year 3 months, but also with modifications of cryptographic algorithms, which in turn is caused by the deterioration of their robustness due to with the development of cryptanalysis methods and computing industry.
An additional time stamp may be imposed on top of the EA in the CAdES-A format, which will protect its contents when identifying vulnerabilities of the cryptographic hash functions used, when hacking the cryptographic algorithms used and when the keys are compromised. It should not be forgotten that the sequence of time stamps can provide protection against ES falsification, provided that these stamps were applied before the time stamp service key was compromised. Thus, the EA in the CAdES-A format allows to preserve its authenticity for very long periods of time, and the periodic installation of archive stamps will provide the possibility of checking the EA when updating cryptographic standards.
It is also important to note that the additional data required to create the archived ES described above are transmitted as unsigned attributes associated with a separate ES by placing the SignerInfo structure in the unsignedeAttrs field. Thus, all attributes of archived EDS are unsigned due to which its mathematical correctness is not disturbed.
Imagine everything that was described above, in a more visual tabular form:
Comparative analysis of electronic signature formats such as CAdES
XAdES
XML Signature XML Advanced Electronic Signatures (XAdES) is an EP standard that is an enhanced version of the XML Digital Signature standard (XMLDSig). The main document describing this standard is ETSI EN 319 132-1 “Electronic Signature and Infrastructure (ESI); XAdES digital signatures.
Similar to the CAdES type EP, several formats are defined for the XAdES type EP, each of which includes the previous one (according to the sequence presented below) and expands it:
We will not describe in detail the differences of each subsequent format in the list from the previous one, since it exactly repeats the description for CAdES, assuming that the signed structure is “enriched” with similar fields and attributes. The main differences are summarized directly in a tabular form:
Comparative analysis of formats of electronic signature type XAdES

The “Litoria Desktop 2” software package (PC) is a development by Gazinformservice, which provides the user with the ability to completely abandon paper workflow and switch to legally electronic and confidential interaction. Formation and verification of CEC in CAdES-A format are already available to users of the software package, starting with release 2.2.3. The same format ES certifies receipts, and also performs their verification of the PC of the Trusted Third Party Service "Litoria DVCS" in release 5.2.2.
Consider the process of forming archived CEC based on product data.
1. With the help of “Litoria Desktop 2” we will form the UEP on an electronic document, which we will transmit to “SDTS“ Litoria DVCS ”to generate a receipt:
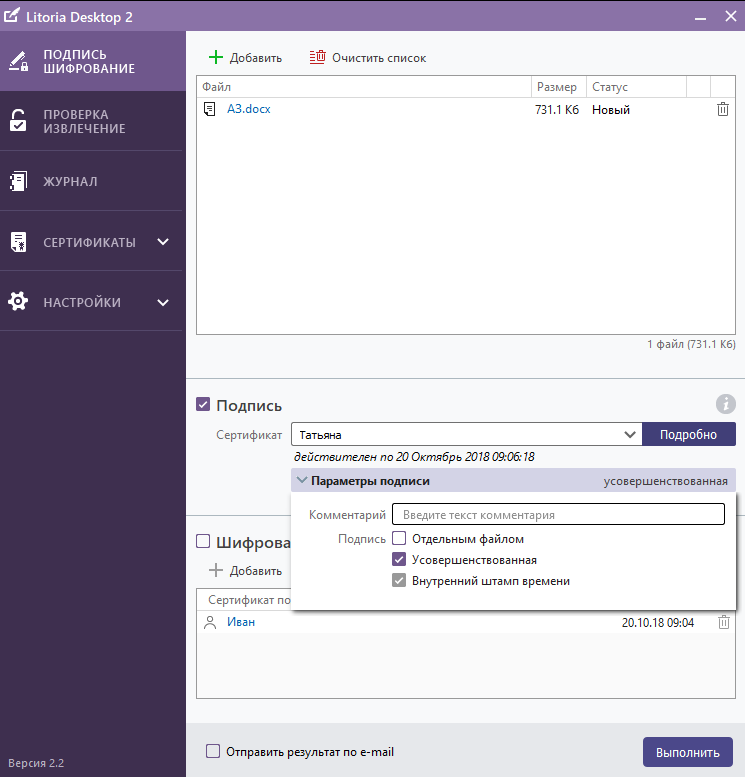
Figure 1 - Formation of the UEP using the PC "Litoria Desktop 2"
Detailed information about the generated IEP can be viewed through the tab "Check and Eject". We see that the certificate of the signatory is valid until October 20, 2018 (Figure 2), and the certificate of the TSP server, which actually added a time stamp to the signature and made it improved (Figure 3), until December 22, 2032.
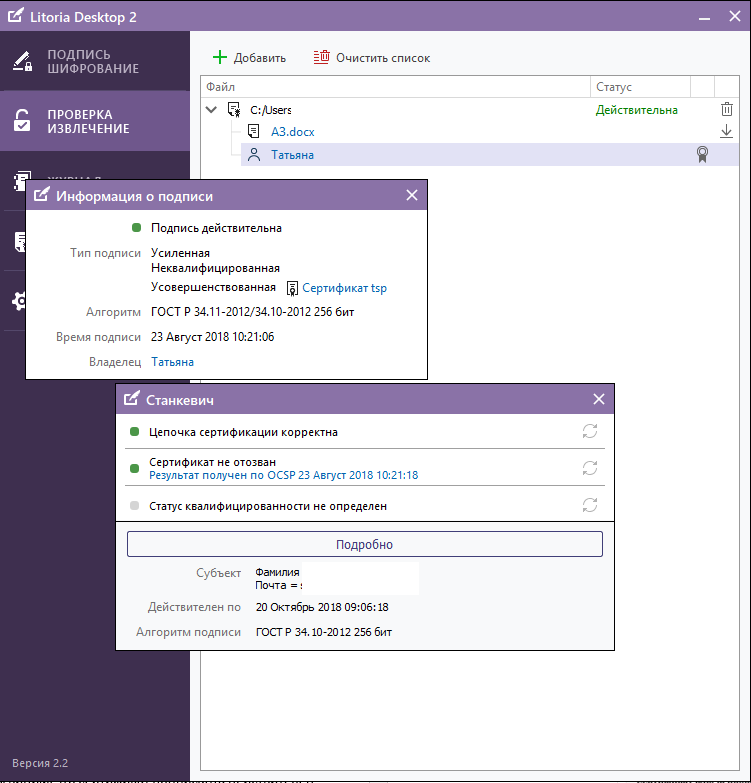
Figure 2 - Display of information about ES in the interface of the PC "Litoria Desktop 2" (user certificate)
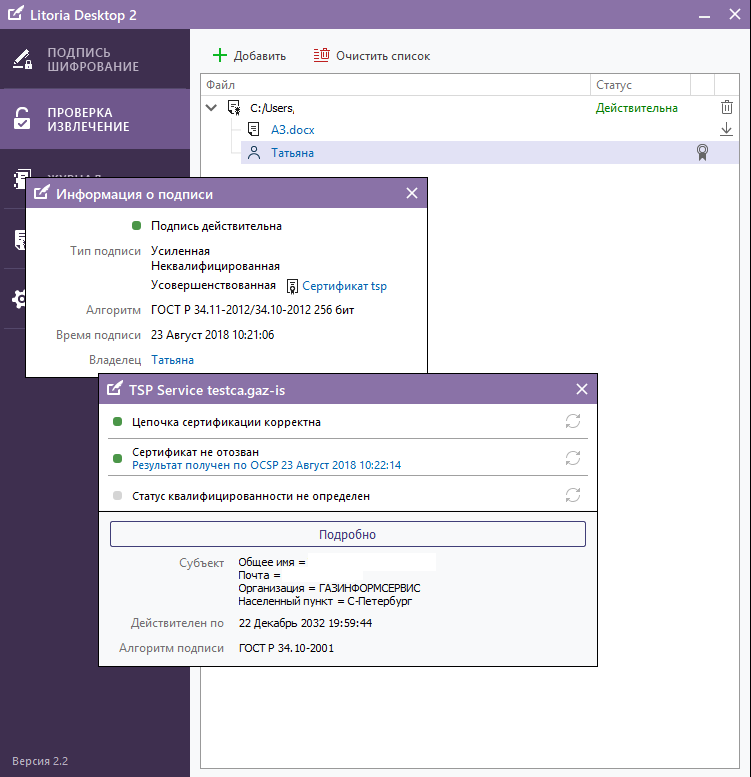
Figure 3 - Display of information about the ES in the interface of the PC "Litoria Desktop 2" (TSP server certificate)
In turn, the validity of the CEE, which is certified by the ED, is determined by the validity period of the time stamp server certificate. But here you should pay your attention that for the article we used test non-accredited CA and test TSP, for which unqualified certificates were issued. In the Russian reality, the validity of a qualified time stamp server certificate shall not exceed 15 years.
And what should we do when the document should be stored for more than 15 years? Just here the archive format of the electronic signature entered on the receipt comes into play (using the SDTS Litoria DVCS software).
2. Go to the personal account of the user of the PC “SDTS“ Litoria DVCS ”and send the signed ED to form a receipt for the check (Figures 4, 5).
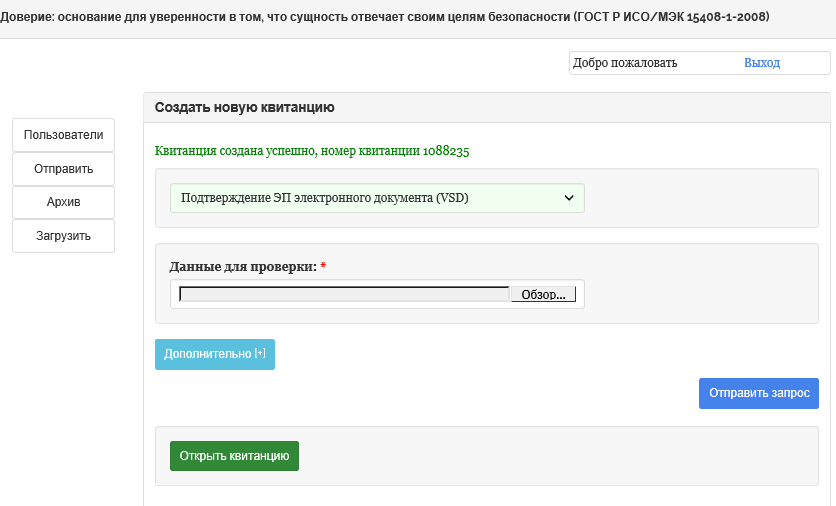
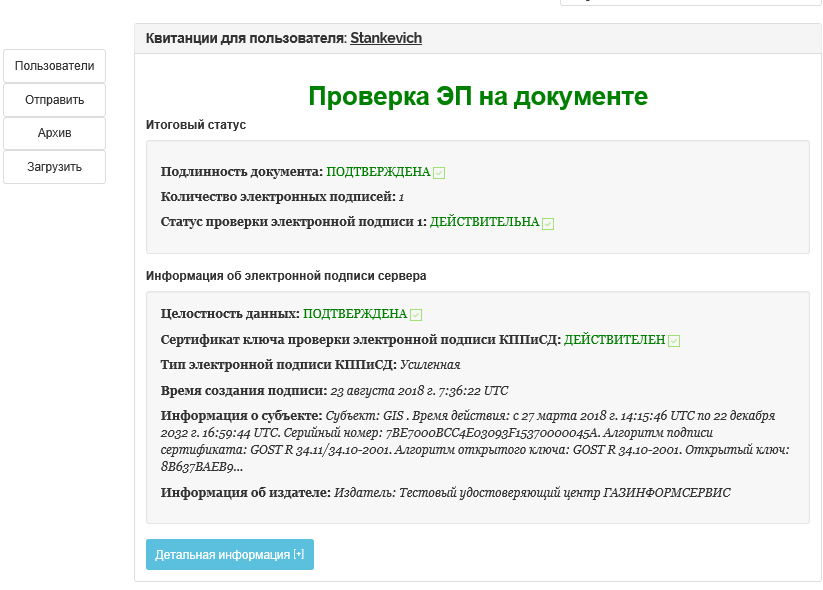
Figure 4 - Formation of a receipt for ED in PC "SDTS" Litoria DVCS "

Figure 5 - Detailed information on the receipt in the PC "SDTS" Litoria DVCS "
Check the ED is completed, the receipt is generated. Now the complex in an automated mode will perform an analysis of the validity of each of the stored receipts, which is determined by the validity of the time stamp service certificate, and upon the occurrence of the event of its expiration, the receipts will be reissued, i.e. a chain of legally significant documents is formed “source ED - receipt 1 - receipt 2 -…. - n receipt
Let us consider the second, so far mechanized, method of forming an electronic signature in the CAdES-A format using the Litoria Desktop 2 software package.
1. Start the Litoria Desktop 2 PC, create the UEP using a well-known method
2. Go to the Archive storage directory, copy the signed ED to the edsArch folder and run the Gis.ArchUpgrade utility (the installation takes place during installation of the complex in the appropriate directory specified by the user, Figure 6)
Figure 6 - Preparing the ED to the formation of EP in CAdES format
3. Upon completion of the procedure on the screen the user a notification will be displayed in the console (see Figure 7).

Figure 7 - Successful formation of CEC in the CAdES-A format
We emphasize once again that the CAdES-A signature format implies the addition of unsigned attributes to the original electronic signature, which does not violate the mathematical correctness of the original electronic signature.
4. Now go to the “edsArch” folder and the file generated by the result of the utility is checked in the Litoria Desktop 2 PC (Figures 8, 9, 10).
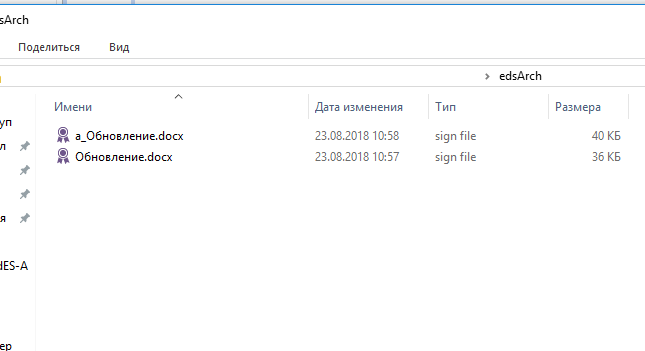
Figure 8 - Archive-signed file generated by the Gis.ArchUpgrade utility
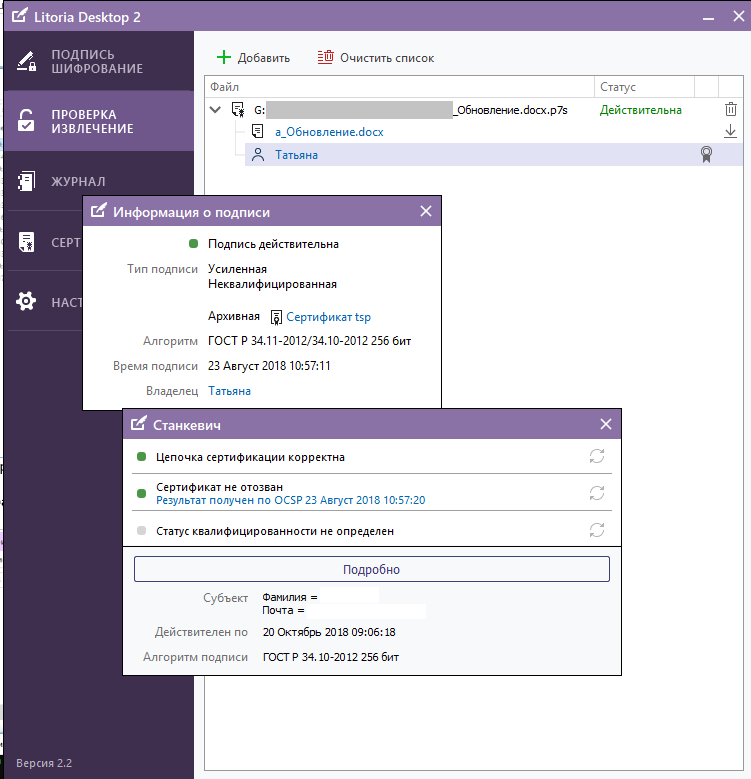
Figure 9 - Results of checking the archived electronic signature in the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (user certificate)
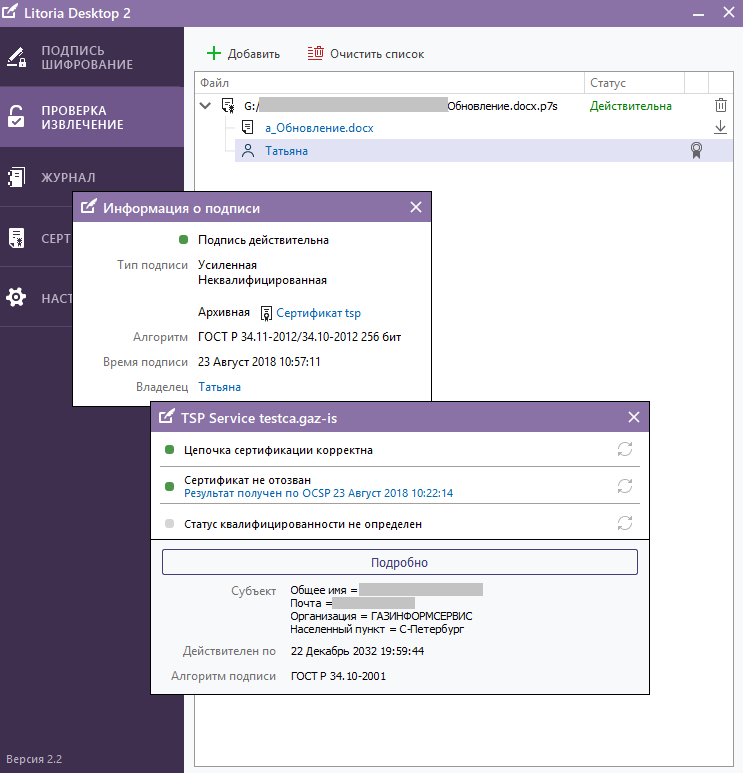
Figure 10 - The results of checking the archived electronic signature in the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (TSP service certificate)
And finally - a fragment of the ASN.1 code of the archived time stamp:
Thus, today there are already viable options for ensuring the full life cycle of electronic legally significant documents requiring long-term storage. For more information about the products designed to solve the designated task, you can find out on the website of the developer or by contacting the sales department by phone 8 (812) 677-20-53, email: salespo@gaz-is.ru.
This article reveals in more detail another approach to long-term archival storage (DAH) - the formation of an improved electronic signature (CEC), namely, electronic signature in the CAdES-A and XAdES-A archive formats.

Let us try to understand in more detail how and why archival ES can extend the life cycle of electronic documents with ES. Let's start with a small theoretical educational program on the types and formats of electronic signature, and then we will consider in practice the procedure for the formation of archival electronic signature by the products developed by Gazinformservice.
A bit of theory
Electronic Signature Type CAdES
CMS Advanced Electronic Signatures (CAdES) is an EP standard that is an enhanced version of the Cryptographic Message Syntax standard (CMS). The main document describing this standard is ETSI TS 101 733 “Electronic Signature and Infrastructure (ESI); CMS Advanced Electronic Signature (CAdES) ".
CAdES became the development of CMS, in which such major shortcomings of the predecessor were corrected, such as the lack of a stamp of the entrusted time of creating an EP, the absence of an EP content type and the absence of the possibility of long-term preservation of the properties of the legal significance of an EP.
The standard defines several CAdES formats, each of which includes the previous one (in accordance with the sequence presented below) and extends it:
Formats of the CAdES standard
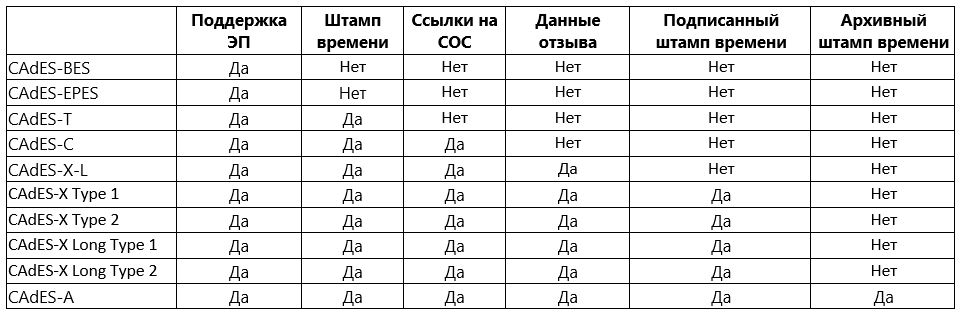
1. CAdES-BES (Basic Electronic Signature) — основной и простейший формат стандарта, обеспечивает базовую проверку подлинности данных и защиту их целостности. Он содержит следующие атрибуты:
2. CAdES-EPES (Explicit Policy-based Electronic Signature) — это формат, содержащий в себе явное указание на выбранный регламент ЭП. В CAdES-EPES добавляется подписываемый атрибут signature-policy-identifier, который определяет идентификатор выбранного регламента ЭП. Подписывая этот идентификатор, отправитель явно указывает, что он применил определенный регламент при её создании. Соответственно, получатель должен осуществить проверку ЭП по тому же регламенту.
3. CAdES-T (Timestamp) — это формат ЭП типа CAdES, в который добавлено поле для фиксации доверенного времени.
4. В CAdES-C (Complete) содержится полный наборо проверочных данных. Она отличается от CAdES-T добавлением неподписываемых атрибутов complete-certificate-references и complete-revocation-references.
Первый атрибут содержит идентификаторы всех сертификатов, используемых при проверке ЭП. Второй атрибут содержит идентификаторы сертификатов из списка отозванных сертификатов (Certificate Revocation Lists, CRL, СОС) и/или ответы, полученные по протоколу проверки актуального статуса сертификатов (Online Certificate Status Protocol, OCSP).
Включение этих атрибутов облегчает получение сведений о сертификатах ключей проверки ЭП, которые необходимы получателю для проверки ЭП, так как при этом данные о действительных и недействительных сертификатах уже будут содержаться в самой ЭП.
5. CAdES-X (Extended) — это формат ЭП типа CAdES, включающий в себя следующие подформаты, включаемые в тип CadES-C:
6. CAdES-X Long Type 1 — этот формат ЭП представляет собой объединение формата CAdES-X Long и CAdES-X Type 1
7. CAdES-X Long Type 2 — этот формат ЭП представляет собой объединение формата CAdES-X Long и CAdES-X Type 2.
8. CAdES-A (Archival) — это формат ЭП типа CAdES, сформированный на основе CAdES-X Long Type 1 или Type 2 путём добавления одного или нескольких атрибутов archive-time-stamp, представляющих собой архивные штампы времени (Рисунок 1). Именно этот формат ЭП используется для архивации долгосрочных ЭП и обеспечения ДАХ при условии возможной проверки юридической значимости хранимого ЭД на длительном временном промежутке (так называемая «интероперабельность во времени»).
- подписываемые данные пользователя (ЭД отправителя);
- набор обязательных подписываемых атрибутов (атрибуты называются подписанными, если генерация ЭП происходит от совокупности этих атрибутов и данных пользователя);
- значение ЭП, вычисленное для данных пользователя и подписываемых атрибутов;
- набор дополнительных атрибутов;
- набор необязательных подписываемых атрибутов.
2. CAdES-EPES (Explicit Policy-based Electronic Signature) — это формат, содержащий в себе явное указание на выбранный регламент ЭП. В CAdES-EPES добавляется подписываемый атрибут signature-policy-identifier, который определяет идентификатор выбранного регламента ЭП. Подписывая этот идентификатор, отправитель явно указывает, что он применил определенный регламент при её создании. Соответственно, получатель должен осуществить проверку ЭП по тому же регламенту.
3. CAdES-T (Timestamp) — это формат ЭП типа CAdES, в который добавлено поле для фиксации доверенного времени.
4. В CAdES-C (Complete) содержится полный наборо проверочных данных. Она отличается от CAdES-T добавлением неподписываемых атрибутов complete-certificate-references и complete-revocation-references.
Первый атрибут содержит идентификаторы всех сертификатов, используемых при проверке ЭП. Второй атрибут содержит идентификаторы сертификатов из списка отозванных сертификатов (Certificate Revocation Lists, CRL, СОС) и/или ответы, полученные по протоколу проверки актуального статуса сертификатов (Online Certificate Status Protocol, OCSP).
Включение этих атрибутов облегчает получение сведений о сертификатах ключей проверки ЭП, которые необходимы получателю для проверки ЭП, так как при этом данные о действительных и недействительных сертификатах уже будут содержаться в самой ЭП.
5. CAdES-X (Extended) — это формат ЭП типа CAdES, включающий в себя следующие подформаты, включаемые в тип CadES-C:
- CAdES-X Long — формат долгосрочной расширенной ЭП, который добавляет атрибуты certificate-values и revocation-values. Они представляют собой полные данные сертификатов и СОС, необходимых для проверки подписи CAdES-C даже если их исходный источник недоступен и исключает возможность утери этой информации.
- CAdES-X Type 1 — добавляет атрибут time-stamp, который содержит штамп времени на всей подписи CAdES-C. Это обеспечивает целостность и наличие доверенного времени во всех элементах ЭП. Тем самым, этот атрибут позволяет защитить сертификаты, СОС и ответы, полученные по протоколу OCSP, информация о которых записана в ЭП (актуален при компрометации ключа центра сертификации, ключа издателя СОС или ключа сервиса OCSP).
- CAdES-X Type 2 — добавляет в CAdES-C штамп времени, но не на всю ЭП, а только на полные ссылки на сертификаты и СОС.
6. CAdES-X Long Type 1 — этот формат ЭП представляет собой объединение формата CAdES-X Long и CAdES-X Type 1
7. CAdES-X Long Type 2 — этот формат ЭП представляет собой объединение формата CAdES-X Long и CAdES-X Type 2.
8. CAdES-A (Archival) — это формат ЭП типа CAdES, сформированный на основе CAdES-X Long Type 1 или Type 2 путём добавления одного или нескольких атрибутов archive-time-stamp, представляющих собой архивные штампы времени (Рисунок 1). Именно этот формат ЭП используется для архивации долгосрочных ЭП и обеспечения ДАХ при условии возможной проверки юридической значимости хранимого ЭД на длительном временном промежутке (так называемая «интероперабельность во времени»).
The CAdES-A archive archive form consists of the following elements:
- full set of verification data (CAdES-С);
- certificate and COC values (CAdES-X Type 1 or CAdES-X Type 2), if used;
- signed user data and an additional archived time stamp applied to all data.

Figure 1 - The scheme of forming an electronic signature in the CAdES-A format.
Questions of the organization of DAH are associated not only with the limited period of validity of the user certificate established by Russian legislation at 1 year 3 months, but also with modifications of cryptographic algorithms, which in turn is caused by the deterioration of their robustness due to with the development of cryptanalysis methods and computing industry.
An additional time stamp may be imposed on top of the EA in the CAdES-A format, which will protect its contents when identifying vulnerabilities of the cryptographic hash functions used, when hacking the cryptographic algorithms used and when the keys are compromised. It should not be forgotten that the sequence of time stamps can provide protection against ES falsification, provided that these stamps were applied before the time stamp service key was compromised. Thus, the EA in the CAdES-A format allows to preserve its authenticity for very long periods of time, and the periodic installation of archive stamps will provide the possibility of checking the EA when updating cryptographic standards.
It is also important to note that the additional data required to create the archived ES described above are transmitted as unsigned attributes associated with a separate ES by placing the SignerInfo structure in the unsignedeAttrs field. Thus, all attributes of archived EDS are unsigned due to which its mathematical correctness is not disturbed.
Imagine everything that was described above, in a more visual tabular form:
Comparative analysis of electronic signature formats such as CAdES

XAdES
XML Signature XML Advanced Electronic Signatures (XAdES) is an EP standard that is an enhanced version of the XML Digital Signature standard (XMLDSig). The main document describing this standard is ETSI EN 319 132-1 “Electronic Signature and Infrastructure (ESI); XAdES digital signatures.
Similar to the CAdES type EP, several formats are defined for the XAdES type EP, each of which includes the previous one (according to the sequence presented below) and expands it:
XAdES Formats
- XAdES-BES (Basic Electronic Signature)
- XAdES-EPES (Explicit policy electronic signatures)
- XAdES-T (Timestamp)
- XAdES-C (Complete)
- XAdES-X (Extended Validation Data)
- XAdES-X-L (Extended Long Term)
- XAdES-A (Archival)
We will not describe in detail the differences of each subsequent format in the list from the previous one, since it exactly repeats the description for CAdES, assuming that the signed structure is “enriched” with similar fields and attributes. The main differences are summarized directly in a tabular form:
Comparative analysis of formats of electronic signature type XAdES

New features of Litoria products to ensure DAH
The “Litoria Desktop 2” software package (PC) is a development by Gazinformservice, which provides the user with the ability to completely abandon paper workflow and switch to legally electronic and confidential interaction. Formation and verification of CEC in CAdES-A format are already available to users of the software package, starting with release 2.2.3. The same format ES certifies receipts, and also performs their verification of the PC of the Trusted Third Party Service "Litoria DVCS" in release 5.2.2.
Consider the process of forming archived CEC based on product data.
1. With the help of “Litoria Desktop 2” we will form the UEP on an electronic document, which we will transmit to “SDTS“ Litoria DVCS ”to generate a receipt:

Figure 1 - Formation of the UEP using the PC "Litoria Desktop 2"
Detailed information about the generated IEP can be viewed through the tab "Check and Eject". We see that the certificate of the signatory is valid until October 20, 2018 (Figure 2), and the certificate of the TSP server, which actually added a time stamp to the signature and made it improved (Figure 3), until December 22, 2032.

Figure 2 - Display of information about ES in the interface of the PC "Litoria Desktop 2" (user certificate)

Figure 3 - Display of information about the ES in the interface of the PC "Litoria Desktop 2" (TSP server certificate)
In turn, the validity of the CEE, which is certified by the ED, is determined by the validity period of the time stamp server certificate. But here you should pay your attention that for the article we used test non-accredited CA and test TSP, for which unqualified certificates were issued. In the Russian reality, the validity of a qualified time stamp server certificate shall not exceed 15 years.
And what should we do when the document should be stored for more than 15 years? Just here the archive format of the electronic signature entered on the receipt comes into play (using the SDTS Litoria DVCS software).
2. Go to the personal account of the user of the PC “SDTS“ Litoria DVCS ”and send the signed ED to form a receipt for the check (Figures 4, 5).


Figure 4 - Formation of a receipt for ED in PC "SDTS" Litoria DVCS "

Figure 5 - Detailed information on the receipt in the PC "SDTS" Litoria DVCS "
Check the ED is completed, the receipt is generated. Now the complex in an automated mode will perform an analysis of the validity of each of the stored receipts, which is determined by the validity of the time stamp service certificate, and upon the occurrence of the event of its expiration, the receipts will be reissued, i.e. a chain of legally significant documents is formed “source ED - receipt 1 - receipt 2 -…. - n receipt
Signed in CAdES-A format using the Litoria Desktop 2 PC
Let us consider the second, so far mechanized, method of forming an electronic signature in the CAdES-A format using the Litoria Desktop 2 software package.
1. Start the Litoria Desktop 2 PC, create the UEP using a well-known method
2. Go to the Archive storage directory, copy the signed ED to the edsArch folder and run the Gis.ArchUpgrade utility (the installation takes place during installation of the complex in the appropriate directory specified by the user, Figure 6)

Figure 6 - Preparing the ED to the formation of EP in CAdES format
3. Upon completion of the procedure on the screen the user a notification will be displayed in the console (see Figure 7).

Figure 7 - Successful formation of CEC in the CAdES-A format
We emphasize once again that the CAdES-A signature format implies the addition of unsigned attributes to the original electronic signature, which does not violate the mathematical correctness of the original electronic signature.
4. Now go to the “edsArch” folder and the file generated by the result of the utility is checked in the Litoria Desktop 2 PC (Figures 8, 9, 10).

Figure 8 - Archive-signed file generated by the Gis.ArchUpgrade utility

Figure 9 - Results of checking the archived electronic signature in the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (user certificate)

Figure 10 - The results of checking the archived electronic signature in the PC “Litoria Desktop 2” (TSP service certificate)
And finally - a fragment of the ASN.1 code of the archived time stamp:

Thus, today there are already viable options for ensuring the full life cycle of electronic legally significant documents requiring long-term storage. For more information about the products designed to solve the designated task, you can find out on the website of the developer or by contacting the sales department by phone 8 (812) 677-20-53, email: salespo@gaz-is.ru.
