How to simplify verification of a bank card holder for online payments?
Compare 3-D Secure and CheckCode (Payture).
Banking solutions: 3-D Secure (Verified by Visa, MasterCard SecureCode and JCB J / Secure).
The 3-D Secure technology, which is announced as an additional protection against card fraud for all participants in the transaction, ultimately transfers the responsibility to ordinary bank card holders. If the purchase was made by a fraudster using 3DS, the card holder will not be refunded. At the first stage, the card details must be entered (on the TSP or gateway side), at the second stage, a code (dynamic or static) must be entered on the website of the issuing bank to confirm authorization. The security level of payments with 3DS is high, but does not give a 100% guarantee. In addition, the payment process itself is becoming more complicated. The use of such technologies forces the buyer to switch from page to page of different sites and adversely affects the conversion of online payments.
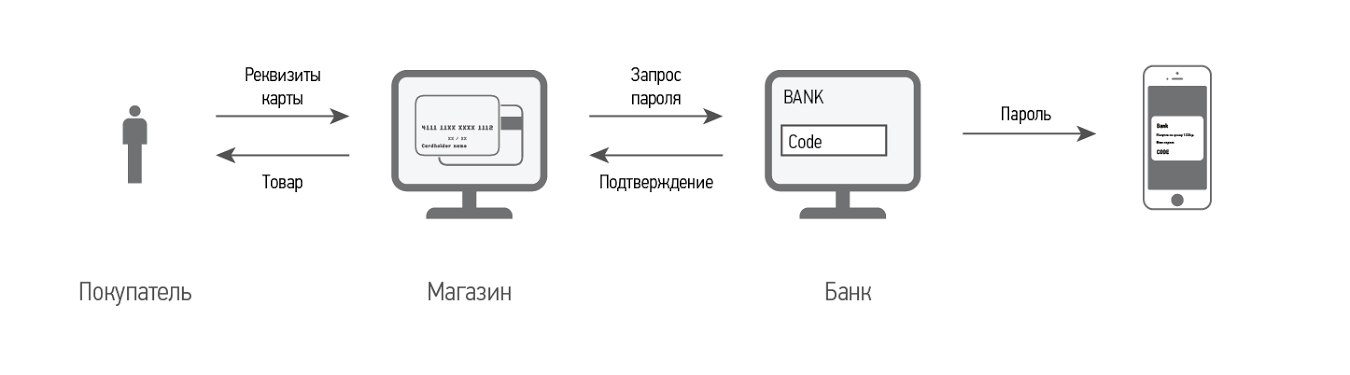
3DS is a user authentication protocol on the issuer's website, which is needed to provide additional security for online payments by credit card. The protocol was developed for the international payment system VISA, then the services based on it were implemented by MasterCard, American Express and JCB International.
Non-Banking Solutions: CheckCode.
When conducting a financial transaction in an online store, there are only two main players - the online store itself (TSP) and the buyer. The rest (MPS, bank, payment gateway) that receive a percentage of the transaction, the main thing is to relieve responsibility for fraud, since the profit from one transaction is tiny, and the consequences can be serious. Therefore, our method of verifying the authenticity of the card holder was developed in accordance with the needs of our customers (online stores) and simplifying their work with customers.
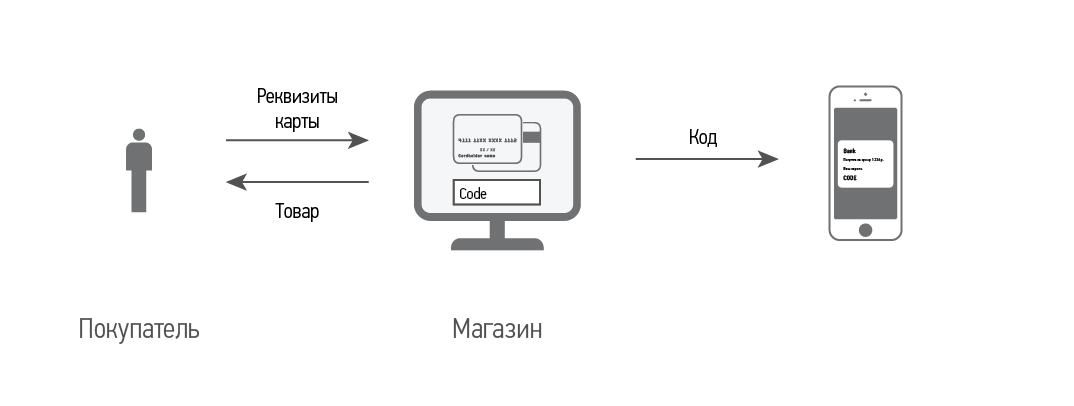
CheckCode is an authentication protocol that allows the TSP to verify the user regardless of the MPS and banks, and does not require significant effort from the buyer when making a payment in the online store. The essence of the invention lies in the difference between the sent and received signal (alphanumeric code) during the interaction of the acquirer and the issuer systems. If the signal sent and received matches, the authentication of the card holder is considered successful. Otherwise, the card holder is considered unverified.
More details. At the first stage, the TSA blocks a small amount on the holder’s card with an indication of a dynamic code in one of the fields of the authorization request. For the code, the authorization request field is used, which without fail will be included in the check and bank statement. As a result, the required verification code is known only to the TSP and the card holder. The card holder can find out the code through the Internet bank (mobile bank), via SMS notification or by calling the bank support service (in any case, the card holder must log in to the Internet bank at least once before). On the TSP page, the buyer is informed of the name of the field in which the code is located and the place where it is to be entered is indicated. To verify the authenticity of the cardholder, the TSP compares the sent and entered code.
The main working conditions of the protocol:
Banking solutions: 3-D Secure (Verified by Visa, MasterCard SecureCode and JCB J / Secure).
The 3-D Secure technology, which is announced as an additional protection against card fraud for all participants in the transaction, ultimately transfers the responsibility to ordinary bank card holders. If the purchase was made by a fraudster using 3DS, the card holder will not be refunded. At the first stage, the card details must be entered (on the TSP or gateway side), at the second stage, a code (dynamic or static) must be entered on the website of the issuing bank to confirm authorization. The security level of payments with 3DS is high, but does not give a 100% guarantee. In addition, the payment process itself is becoming more complicated. The use of such technologies forces the buyer to switch from page to page of different sites and adversely affects the conversion of online payments.

3DS is a user authentication protocol on the issuer's website, which is needed to provide additional security for online payments by credit card. The protocol was developed for the international payment system VISA, then the services based on it were implemented by MasterCard, American Express and JCB International.
Non-Banking Solutions: CheckCode.
When conducting a financial transaction in an online store, there are only two main players - the online store itself (TSP) and the buyer. The rest (MPS, bank, payment gateway) that receive a percentage of the transaction, the main thing is to relieve responsibility for fraud, since the profit from one transaction is tiny, and the consequences can be serious. Therefore, our method of verifying the authenticity of the card holder was developed in accordance with the needs of our customers (online stores) and simplifying their work with customers.

CheckCode is an authentication protocol that allows the TSP to verify the user regardless of the MPS and banks, and does not require significant effort from the buyer when making a payment in the online store. The essence of the invention lies in the difference between the sent and received signal (alphanumeric code) during the interaction of the acquirer and the issuer systems. If the signal sent and received matches, the authentication of the card holder is considered successful. Otherwise, the card holder is considered unverified.
More details. At the first stage, the TSA blocks a small amount on the holder’s card with an indication of a dynamic code in one of the fields of the authorization request. For the code, the authorization request field is used, which without fail will be included in the check and bank statement. As a result, the required verification code is known only to the TSP and the card holder. The card holder can find out the code through the Internet bank (mobile bank), via SMS notification or by calling the bank support service (in any case, the card holder must log in to the Internet bank at least once before). On the TSP page, the buyer is informed of the name of the field in which the code is located and the place where it is to be entered is indicated. To verify the authenticity of the cardholder, the TSP compares the sent and entered code.
The main working conditions of the protocol:
- verification is carried out in real time until the funds are debited
- verification is carried out using available capabilities of the Ministry of Railways and banks
- TSP can check the card holder of any bank, any country and regardless of the currency of payment (country / account)
- the functionality of automatic notification by the issuer of their cardholders is used
- verification does not require additional customer clicks between sites
- verification does not require changes in the hardware and industrial complex of banks and MPS
