Why is NginX with Fast-CGI faster than Apache with mod_php?
- Transfer
I recently heard that NginX running PHP through FastCGI was faster than Apache with mod_php. I have also seen that people both deny and agree with this hypothesis. Let's do a little test and find out the performance of these systems.
For testing, I created a small Hello world script. Why didn’t I choose something more complicated? The answer is simple: there should not be much performance difference in the PHP interpreter. Why, then, did I not create a completely blank page? The fact is that I wanted to test bidirectional data transfer. The goal is to test the speed of the web server as a whole, and not just PHP.
Basic tests give us the following results :.
Apache with mod_php NginX with PHP-FPM
Apache managed to process 2400 requests per second, unlike Nginx. He handled 5200 requests. I have never seen such a large amount. I performed the same requests with -c -f for Apache to find out the reasons for this difference. -c displays the time of system requests, -f follows the branches. What is the result for the first 10 lines? getcwd? But why? After I remembered that I had AllowOverwrite (.htaccess) activated. I performed the same tests after disabling this feature. With 5352 requests processed, Apache outperformed NginX. But what happens then when the amount of data transferred increases? I created about 100k of content and tried again. Apache nginx
This time the difference was more noticeable. Some changes are being felt. PHP is built into Apache mod_php, which should speed it up. If only PHP is running on your server, then this should be the best performance solution.
If you work with different languages like CSS, JS and images, then NginX is more suitable for you. Its performance will be higher, but PHP will not become faster. It will also be more reliable in terms of protection against DDoS, but CDN is still the best solution.
Below are the graphs for comparing performance:
For testing, I created a small Hello world script. Why didn’t I choose something more complicated? The answer is simple: there should not be much performance difference in the PHP interpreter. Why, then, did I not create a completely blank page? The fact is that I wanted to test bidirectional data transfer. The goal is to test the speed of the web server as a whole, and not just PHP.
Basic tests give us the following results :.
Apache with mod_php NginX with PHP-FPM
Total transferred: 3470000 bytes
HTML transferred: 120000 bytes
Requests per second: 2395.73 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 4.174 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.417 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 811.67 [Kbytes/sec] receivedTotal transferred: 1590000 bytes
HTML transferred: 120000 bytes
Requests per second: 5166.39 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 1.936 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.194 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 801.82 [Kbytes/sec] receivedApache managed to process 2400 requests per second, unlike Nginx. He handled 5200 requests. I have never seen such a large amount. I performed the same requests with -c -f for Apache to find out the reasons for this difference. -c displays the time of system requests, -f follows the branches. What is the result for the first 10 lines? getcwd? But why? After I remembered that I had AllowOverwrite (.htaccess) activated. I performed the same tests after disabling this feature. With 5352 requests processed, Apache outperformed NginX. But what happens then when the amount of data transferred increases? I created about 100k of content and tried again. Apache nginx
% time seconds usecs/call calls errors syscall
------ ----------- ----------- --------- --------- ----------------
33.65 0.042063 4 10003 getcwd
16.10 0.020127 2 10001 writev
16.00 0.019994 2 10001 shutdown
10.54 0.013179 0 51836 40118 open
9.01 0.011263 1 20008 semop
5.22 0.006522 0 54507 10002 read
2.53 0.003158 0 10024 write
1.91 0.002386 0 88260 66483 close
1.57 0.001959 245 8 clone
1.16 0.001455 0 54832 384 stat64Total transferred: 3470000 bytes
HTML transferred: 120000 bytes
Requests per second: 5352.41 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 1.868 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.187 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 1813.40 [Kbytes/sec] receivedTotal transferred: 1051720000 bytes
HTML transferred: 1048570000 bytes
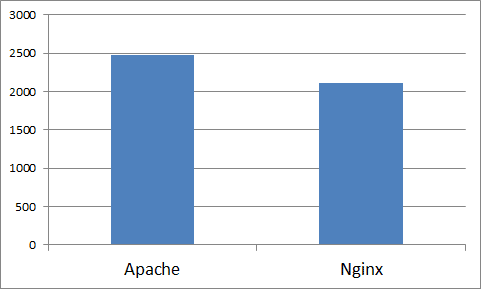
Requests per second: 2470.24 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 4.048 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.405 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 253710.79 [Kbytes/sec] receivedTotal transferred: 1050040000 bytes
HTML transferred: 1048570000 bytes
Requests per second: 2111.08 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 4.737 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.474 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 216476.53 [Kbytes/sec] receivedThis time the difference was more noticeable. Some changes are being felt. PHP is built into Apache mod_php, which should speed it up. If only PHP is running on your server, then this should be the best performance solution.
If you work with different languages like CSS, JS and images, then NginX is more suitable for you. Its performance will be higher, but PHP will not become faster. It will also be more reliable in terms of protection against DDoS, but CDN is still the best solution.
Below are the graphs for comparing performance:

