Delivery: we solve the problem of optimizing the paths and open the "leftists"

An example of a map from a GIS system, on which delivery zones are indicated - for different machines its color.
A hundred couriers from the point of view of the leader is such a branch of hell with short-term planning . This wording, of course, does not convey the feeling of the Ryazan highway, a tightly embarked jumper, a jumper on the tracks on Novokuznetskaya and a girl operator who sent a car to Zelenograd instead of Moscow. Well, to the heap - an accident with a truck carrying urgent goods.
From the client’s point of view, even being 5 minutes late turns into a tragedy. And this, by the way, is correct and understandable. From a marketing perspective, every courier miss is a lost customer. But from the point of view of some drivers - automation is a clear evil. Because even gasoline does not allow to merge for pleasure. In reality, we met with real riots of drivers against the introduction of IT-systems.
So, for companies in which the bulk of the transportation is intra-city delivery, the issue of route planning is strictly enough. The key feature is taking into account the transport conditions of the city. That is, the system should be able to count traffic using all types of transport, take into account problems on the road and optimize resources at the same time.
"Leftists" and riots of drivers
Even in our practice for large retail it quickly became clear that the system reveals just a huge number of violations that were made by drivers. They’re draining gas, they’re not driving like that, there’s a lot of things. And IT tools make this entire feeder transparent. It is logical that not only the usual resistance to new processes arises, but also the desire to hide behind and return everything as it was. We stumbled upon this situation once: in fact, the traffic according to the rules took half of our earnings from drivers — its “shadow” part.
Who needs automation and when?
- To courier services - obviously.
- Online shopping - when 50 couriers appear.
- Carrier companies - also somewhere with a staff of 50 people.
- Pizzerias and other companies with delivery by call.
- Large wholesalers, for example, to distribute perishable goods or optimize the scheme of delivery of goods to points.
- Retail for the organization of additional deliveries to stores and so on.
It is clear that when a company is small, everything is usually decided through Yandex.Maps routes and a piece of paper with a pen.
What are the features?
- We need the correct construction of routes: at what time is it better to go, where is one-way traffic and so on.
- For vehicles there is a graph of restrictions: somewhere, the car will not creep in height or tonnage, or pass. For example, in Moscow, these are several zones - pass 0, pass 2, pass 3.
- Observe traffic jams. In Moscow and St. Petersburg, for example, solutions based on GIS systems are gaining more popularity and routing based on traffic statistics. At the same time, the logic of route formation is embedded in the TMS-system, and there are separate GIS systems that are used for operational edits.
- It’s good not to enter data by hand, but to automatically receive from map services. In some solutions, it is possible to calculate data by distance and by time of the route not from their tables, but from external modules. That is, if you have somewhere a source of data on repair on the road, you will not need to bring it into the system, it will be enough to update a piece of the database of the external module.
Two main systems: TMS and GIS
As you can see, for the right plan you need to have two main systems. The first is TMS , which makes graphs of the distribution of routes by points. Information is gathered here, on the basis of which this optimal graph is constructed. Usually it is taken from directories within the system: for example, the coordinates of points for detour or the presence of vehicles in the company.
At the same time, traffic jams in Russia change everything in such a way that it is already problematic to plan for more than 12 hours according to general statistics. As you probably know, delivery may be delayed even more, especially during the holidays, at the peak. That is, here we need a picture that is updated at least once an hour - and here TMS requests GIS modules. Plus, it is checked that not only the car went this way, but restrictions are added. This car so-and-so went along such-and-such road with such and such a load and with such and such a set of documents. And it is necessary, for example, to write out a power of attorney to the driver to receive the cargo, plus a pass.
An example of a simple TMS task
You have three couriers: a walking Vasya, a motorcyclist Ivan and a gazelle driver Peter. And 20 orders at the electrical goods store. TMS determines how to quickly dilute everything you need using the known parameters of couriers and points. For example, if we have two orders on the 80th and 90th kilometers of the Moscow Ring Road, and one of them is a box of perforators, and the second is a screwdriver, Peter will go there for gazelles. In this case, the “greedy” algorithm would suggest that it is not very logical to carry a screwdriver by car, but the layout of the orders helped optimization. Next, in the city you need to calculate where Vasya will go, and where Ivan will go. Two columns will be built: for the motorcycle and for the pedestrian (taking into account the carrying capacity and the movement capabilities of each). After evaluating the points, such options will be selected that fit into all the restrictions and allow you to quickly and easily withdraw orders.
Why then GIS?
Everything would be great if not for traffic jams. Our TMS-system calculates the travel time, for example, based on an average speed of 80 km / h on one of the roads. If we are talking about improving the accuracy of the planning procedure, and using data from a GIS system, then such a rule is to take information on distance and time of movement from an external system. That is, when weighing the vertices of the graph with the elements of the route, we will use the latest data.
What algorithms are used?
Habitual for solving the traveling salesman problem. As a rule, we are talking about a set of algorithms for the task: for example, on highly loaded systems with the impossibility of complete enumeration in more than 90% of cases, the solutions are deployed on fairly good hardware, therefore it is most often considered either head-on or branch-and-bound.
Monitoring module
Another important task is control. If we talk about delivery, in full view, then this is not only traffic planning, but also monitoring. When the machine is equipped with GPS equipment or the courier is holding a corporate tablet or smartphone, or a tracker. Based on GPS data, this is, firstly, it is possible to visualize the location of each vehicle on a map, and secondly, to record events that occur with this vehicle.
Events are usually divided into two types. These are force majeure events and planned events. Delay of 10 minutes for the delivery of goods to their points is an event frequent and generally uncritical and not in need of a special alert. But if the car turned off the route and went to Ryazan - this is already a reason for notification.
There are more complex options, this is when the sensor is integrated into the vehicle’s CAN bus and it is possible to register, say, the fuel level and temperature. By the way, probably the best example of temperature control is not even frozen vegetables, but laboratory tests. For example, if a blood test is frozen in the refrigerator, it can already give false negative results for a number of infections.
Return flow
For the resolution of operational situations, one of the most convenient solutions is when drivers are placed mobile terminals and, in fact, they receive tasks online. And to share part of the data for customers, for example, about where exactly their goods. Accordingly, it becomes important to make a simple web-based interface, understandable to a person "from the street." This is important because the TMS system often becomes a single source of truth for all participants in the logistics process.
If expensive or fragile cargo is busy, usually the customer himself insists on inclusion in such a system, by the way.
Analytics
3-4 years ago, everyone liked to put a big screen in the office and look at their cars and people on the map. Now this is not enough, we also need analytics. For example, a forecast on where there is a risk of being late, where it is impractical to drive vehicles instead of foot couriers and so on. When forming a deviation, the attention of the dispatcher is drawn to him.
He has recommendations - to call that, to warn. This is important for those who care about the client: for example, you can send SMS automatically 15 minutes before the courier arrives or in real time report on the delivery status.
In the TMS system, various responses to triggers can be configured. The first thing that is configured is deviations with alerts for responsible persons, and only then - different statuses for clients.
Then automatic reactions are planned. An example is re-planning a route, recalculating the time upon arrival of the car at subsequent points on the route. And the most difficult reaction is, for example, the search for a new resource, in the case of transportation - the search for a new car.
The driver is calling or an accident is visible on the monitoring. Based on GPS data, the system checks the nearest resources, checks the load and the ability to "maneuver" through TMS, and redirects it to this point. For example - there is a truck with half a body free. He goes to the point with an accident, picks up the cargo, his route is further re-planned, all participants in the chain are warned of a new timing.
What is the fight going for?
It is clear that not a single normal person wants to get involved in the introduction of yet another IT-system, which is all across the throat if there is no significant profit. So, such systems give:
- Save time That is, where 100 couriers managed before, now 75 can work just as efficiently.
- Fuel economy.
- Reduced peak loads, especially on holidays.
- Decrease in the level of non-standard goods (expired yogurts, chilled tangerines, warm meat and so on).
- Reducing incidents "HEMOEMTOVAR ?!".
- Reducing customer loss incidents.
Recently, a study was found on the American market, in which they said that leaders are ahead of outsiders in terms of the quality of their goods and delivery on time by 70%. But outsiders are not puzzled by this task, because they are outsiders.
Payback
On average from a year. But it depends, of course, on a lot. First of all, from what is most critical for the company and what the fight is for, these are all the points above. Well, of course, also on the size of the company, the number of orders per day, the complexity of the infrastructure of the city through which transportation is carried out, etc.
Screenshots
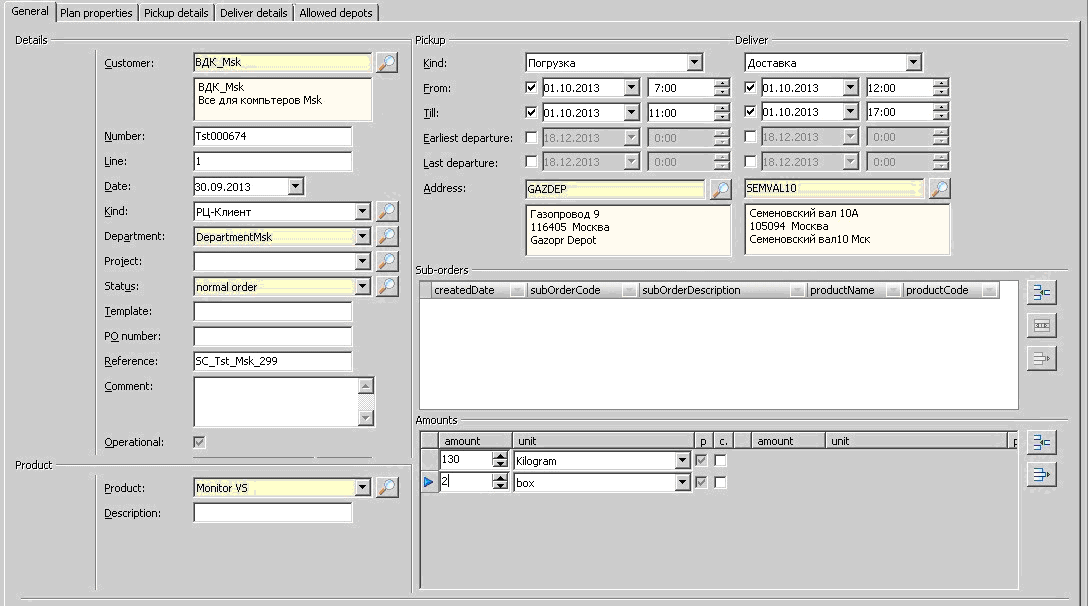
An example of an order form for delivering goods - all details are registered - the time interval for loading and delivery, all addresses, quantity and weight of goods, etc.
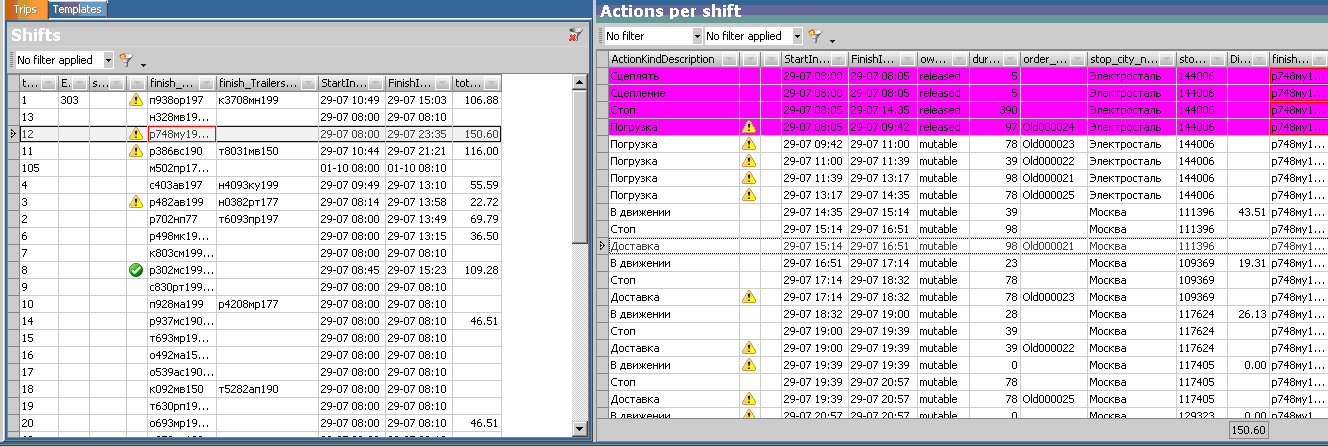
An example of a form for viewing routes with details. The details of the route highlighted in the row on the left are shown on the right. Lilac indicates what has already been completed. Exclamation marks - alerts. A green check mark is a fully developed route.
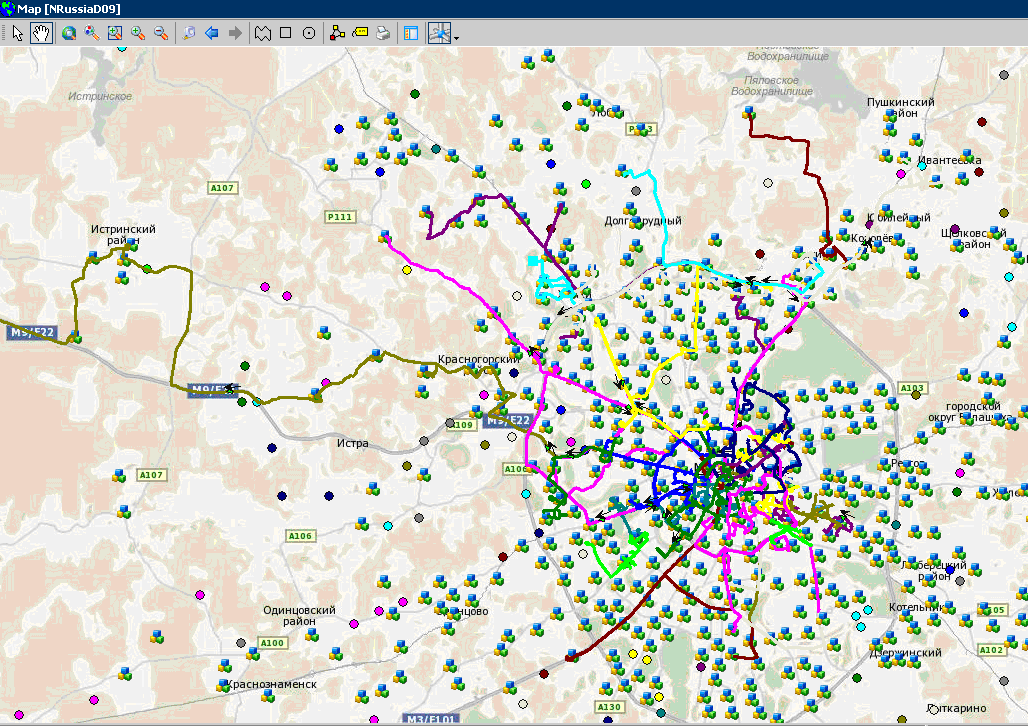
And one more screenshot from GIS. This is a map at the stage of constructing routes, so we can control so that one car does not cut circles, but moves sequentially. Icons with three cubes are points that have not yet been reached, to which goods must also be delivered.
Ready to answer your questions in the comments or by mail AlIsaev@croc.ru.
