Parallels RAS versus alternative technologies

A few years ago, virtual workplaces were in demand only in large enterprises of the Enterprise segment with a large number of branches. This, in the first place, was due to the fact that the deployed work environment required expensive, complex software and qualified staff to properly install and configure the system. Today solutions are becoming more economical, ergonomic and easy, and successfully conquer the market of small and medium businesses. This is evidenced by the growing demand for virtualization technologies of workplaces, and many alternative solutions offered on the market. Under the cut a story about the decision of Parallels RAS and its comparison with alternative technologies.
The following features bring the popularity of remote access to desktops and applications:
- Security and reliable protection of corporate data . This is probably one of the key factors for geographically distributed companies with divisions without qualified IT staff - to prevent leakage of corporate information. All user data is securely stored not on the local computers of employees, but in a single secure data center, which avoids data leakage. When working in a virtual machine, all user actions are recorded. The administrator gives access only to authorized applications and can close the file exchange of individual employees.
- Centralized workplace management . Your tech support team can install applications, configure policies, back up and perform system software updates simultaneously on hundreds and thousands of client devices — all through a single management console. At the same time, it will take just a few minutes to deploy another virtual workplace.
- Reducing the cost of organizing physical jobs and the purchase of expensive equipment . Virtualization can be an excellent solution for small companies seeking to expand, and provide a kind of virtual transformation and expansion of the organization without large financial investments. Moreover, virtualization of workplaces allows turning old PCs into thin clients with the possibility of continuing to use them for several more years.
- The possibility of disaster recovery is another important factor. In case of any problems with the computer on the user's side (accidents, breakdowns, theft of the device), the server administrator will be able to quickly restore user settings and data access, and the user will be able to continue working from any device.
- Autonomy and mobility of specialists of the company - your employee can get access to his virtual workplace anywhere in the world and from any device based on Windows, Linux, iOS, Android, who likes what more, without being tied to a specific OS.
- Virtualization of resource-intensive applications . This particular item will be important, first of all, for professionals who work not with simple office software, but with programs that have increased requirements for the graphics system (3D applications, CAD / CAM systems, Photoshop, multimedia content transfer, etc. ). Using virtual machine resources, employees can work with heavy applications even when their local PC does not have enough power.
Today, there are two main technologies for virtualization of workplaces:
- Publication of sessions, or applications (session-based publishing) . This solution is ideal for the small and medium-sized business segment, as well as in cases when remote specialists are required to provide terminal access to only one or several specific programs without full access to the system.
- How the technology works: virtual applications run in one operating system on a remote physical server, and users work with them over the network. Server resources in this case are distributed to all applications of all users.
- Desktop Publishing (VDI deployment). This solution comes to the rescue when remote employees need full-fledged, isolated access to the desktop. In contrast to the terminal access to the application, the user receives a separate virtual machine (VM) with its own operating system and the necessary programs. At the same time, depending on the situation, both client OS (Windows 7, 8, 10) and server OS (Windows 2012, 2016) can be published. It turns out ready workplace to which you can connect from any device, as well as through any interface - a web browser, client application, thin client. What is important is that if the user is assigned local administrator rights, then even in this case he cannot do any harm to the virtual desktop. And in case of any failures, the administrator can always perform disaster recovery remotely.
How the VDI technology works: several VMs work on the same physical server, which are isolated from each other and controlled using a special software - the hypervisor. If a single virtual machine fails, it will not spread to all other VMs on the server. The most famous hypervisors today are VMware vSphere, Microsoft HyperV, KVM, Citrix XenServer.
Virtualization of workplaces is most prevalent in trade, financial institutions, industry, medical institutions, that is, where it is required to ensure the smooth operation of remote employees or small regional offices. In Telecom, Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) technology is gaining momentum. An excellent example is education or development, where it is necessary to be able to quickly deploy desktops of very different configurations from scratch.
Flour choice ...
When it comes to choosing the infrastructure for delivering applications and virtual desktops, companies have a difficult task. There are a lot of technologies, and for the final choice, many factors need to be taken into account: the complexity of the tasks and applications used, the cost of acquiring licenses, ease of installation and configuration, and administration capabilities.
The Parallels Remote Application Server (or Parallels RAS) solution , which will be discussed today, was introduced in 2015, but over several years it has already managed to gain a strong position in the global market, putting simplicity, budget and availability of the product at the forefront.
In today's article, we will conduct a small analysis of the capabilities and benefits of the Parallels RAS platform compared to today's leading systems - MS RDS, Citrix XenApp & XenDesktop and VMware Horizon.
Parallels RAS Architecture
Parallels RAS is a platform for delivering virtual desktops and applications that provides access to the workplace from any device. When developing, the company focused primarily on creating Easy-to-Deploy, Easy-to-Maintain solution - a simple, reliable and inexpensive product for a wide range of consumers. But, despite the ease and simplicity of use, RAS is a serious product that is not inferior in functionality to its competitors. The program combines the capabilities of VDI and the publication of applications and is focused on the small and medium business segment. According to the G2Crowd portal, the leading platform for the selection of business software, Parallels RAS has been included in the list of leaders in spring 2018 (Leader Spring 2018).
Unlike competitive technologies, RAS does not require prior training and certification of administrators. All actions for managing servers, applications and users are performed in a few clicks by any system administrator from the state of your technical support. Product development is carried out mostly in Moscow, and technical support is also located here.
Before turning to a comparison of systems, we will briefly review the components and the installation process of a terminal farm using Parallels RAS. Why a farm? Because several servers (virtual or physical) are combined into a single system and work in parallel, which ensures load distribution between servers and the resiliency of resource delivery.
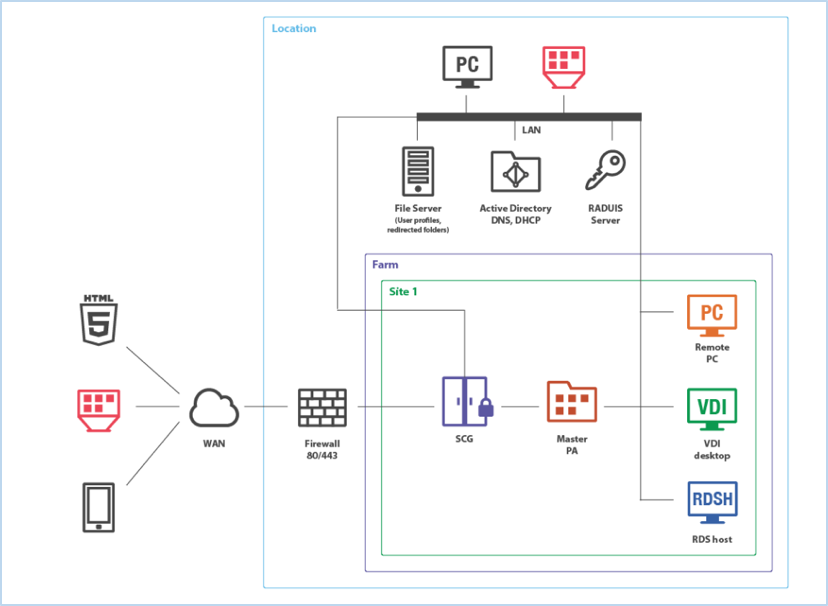
Parallels RAS Desktop and Application Virtualization System(or PRAS farm) is a structure of objects logically grouped for convenient centralized management of the entire virtual infrastructure.
Each farm ( Farm ) consists of one or more sites ( Site ). The visualization presents a farm with a single site, but there can be as many of them as you like. With the help of sites, the farm is divided into control zones. Suppose there are several offices distant from each other, and each office has its own technical department. In this case, a site is created for each office and the administrator is given the rights to manage only his site, and not the entire farm.
Each site is completely separate from the others and includes the following main components:
- RAS SCG (Secure Client Gateway) is a gateway that tunnels necessary traffic into a single port and provides secure connections using SSL encryption. Multiple gateways can be used to support more users.
- RAS Master PA (Publishing Agent) - one of the most important components - an application broker that provides access to applications and desktops and performs load balancing. To ensure uninterrupted application delivery and to protect customers from interference and downtime during the connection, the ability to add multiple active agents to the site (multiple PA), which will evenly distribute the load, is implemented.
- RAS RDSH Agent is an agent that allows Parallels RAS to publish resources on the Microsoft RDSH (Remote Desktop Session Host) servers, where all programs and desktops are actually hosted to which users will receive remote access.
- RAS VDI Agent is an agent that is responsible for connecting to the RAS farm of a server with a hypervisor controlling the launch of the desktops.
- RAS Guest Agent is a service that is installed on a guest OS of a virtual machine, used as a VDI template on the hypervisor, and allows you to publish resources from VDI desktops.
- RAS Remote PC Agent is a service that installs on any physical PC running Windows or on a virtual machine running Windows and allows you to publish applications and desktops from them. Even if the PC with resources is turned off, the service will be able to turn it on remotely via Wake-on-Lan
The system is installed and configured in 4 steps:
1. Install Parallels RAS on a server running Windows Server and connect to the system using Active Directory (AD) account information . The application will use ports 443 and 80, so they should be free. Next you need to enter the login / password to connect to the RAS account and activate the key. This completes the installation of the system and you can proceed to the configuration.
Configuration, as well as all subsequent actions, occurs in the Parallels RAS Console (see Figure). The console connects to the main Publishing agent or alternative agents. Starting with version 16.0, it is possible to choose PA.
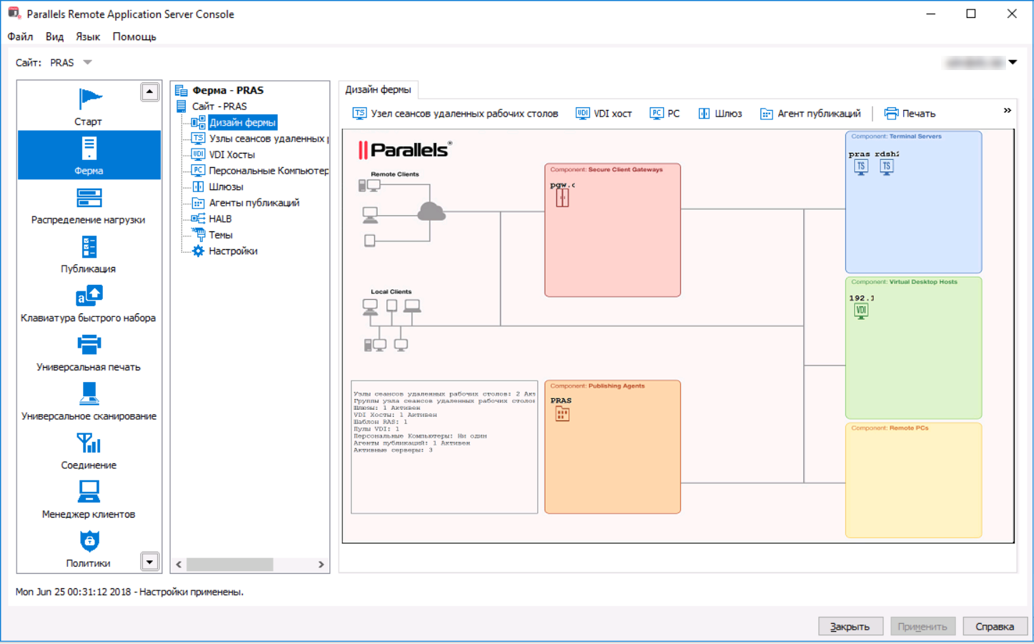
2. Add and configure RDSH servers and agents Publishing agents.Please note: when adding servers, RAS will automatically configure the following options for them: - configure the Firewall rules for the RDSH; - installs the RDSH server role on the server that you add to the farm. That is, you do not have to manually configure roles, as it happens in MS RDS; - if necessary, reboot the selected server after installation; - add the server to the server group (you just need to tick the group). That is, all the important settings have already been made to the interface, you just have to tick.
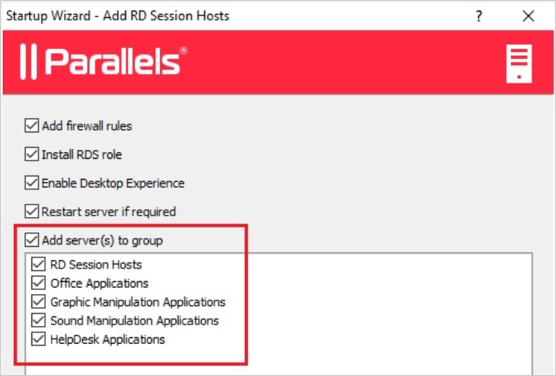
3. Add and publish applications: here, too, everything is simple, put a tick in front of the applications that will be published. After publishing for each application, you can set your own rules: for example, give access to the application to only some employees.
4. Inviting users . Create a list of users who will receive an invitation to email. The invitation will contain detailed instructions for accessing the server and links for downloading client applications for the types of devices from which they will log in.
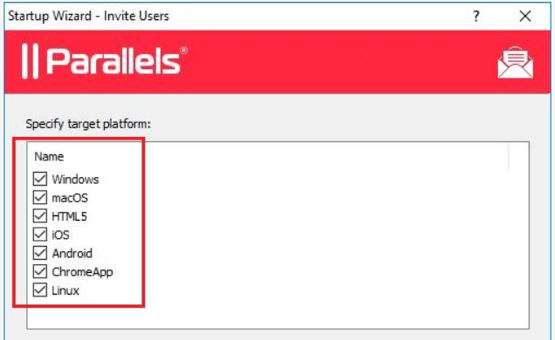
Client connection is carried out in two stages:
1. Getting a list of published resources (documents, applications, desktops). The user launches the Parallels Client application on his device. The client application connects to the SCG gateway and a secure SSL session is established between them. The gateway, in turn, builds a PA connection tunnel to trigger user authentication. If the authentication is successful, the PA agent returns a list of applications through the SSL tunnel, which is displayed in the client interface.
2. Publishing the application. The user starts the application. The gateway sends a request to all active Publishing Agents on the farm. The PAs start the load balancing check, select the least loaded server and send its IP address to the client application via the gateway. Next, the client connects to the RDSH server directly or through a gateway. The server confirms the client data and establishes an RDP session.
Parallels RAS Features for Microsoft RDS
Let's compare Parallels RAS with one of the most common technologies of remote access to applications and desktops - Remote Desktop Services (RDS) from Microsoft (formerly called Terminal Services). The undoubted advantage of MS RDS is that you do not need to purchase additional licensed software to expand the farm - terminal services are already built into the Windows Server OS. However, the solution is not the easiest to set up, and below we will tell you how Parallels RAS will allow you to optimize and simplify working with MS RDS server in many ways:
• Creating and configuring a terminal farm .
WS: in MS RDS, the process of creating a farm is quite lengthy and will require, in addition to patience, good administrator skills for working with Windows Server from the administrator. Many parameters must be configured manually: assign roles to each of the servers, add trusted certificates, create a collection of applications, go through several reboots in the process; install the necessary components - Connection Broker, Remote App for publishing applications, Microsoft NLB cluster for system scaling and load balancing.
PRAS: Using RAS, you can create a farm as quickly and easily as possible without being a virtualization expert. You will only need to run the msi installation file, and then the simple and clear installation wizard will guide you through all the configuration steps of the servers and components. Important features such as load balancing and universal printing in RAS are already pre-installed.
• Publish and deliver applications .
WS: To publish applications in Windows Server, you need to go through a lengthy procedure for installing the RemoteApp component. Moreover, in the future you will be able to publish applications only from the server on which RemoteApp is installed. MS RDS uses its own RDP protocol for publishing applications and desktops. The latest version of the protocol has the add-in RemoteFX, which provides high quality graphics and fast user experience with dynamically changing content.
For publishing VDI desktops, Windows Server only supports its Hyper-V hypervisor.
PRASalso uses RDP for publishing applications, but provides more publishing options, thanks to the RAS PA Connection Broker. RAS allows you to centrally, from a single location, publish applications from any server in the farm. You will be able to track how applications are used, limit the number of instances or the time to access applications. You can also filter access to applications based on various criteria: for example, by MAC or IP address. For VDI delivery, the RAS server is not limited to the Hyper-V hypervisor, supporting all the popular hypervisors on the market: VMware, Citrix, Nutanix, KVM.
• Balancing capabilities .
WS: RDS servers do not have a built-in load balancer. The inter-server balancing is the responsibility of the Connection Broker, which ensures that users get access to their sessions if the connection has been interrupted, and distributes the load between the servers based on their capacity and workload. However, the broker does not regulate the balancing of the gateways, and in case of failure of any of the gateways, it will continue to send requests to it. For a more reliable load distribution, you will have to install the component for clustering the Microsoft Network Load Balancing (NLB) servers, which requires fairly deep expertise.
PRAS: To prevent congestion in multi-gate environments and provide fast, guaranteed availability of applications, RAS has implemented the gateway balancing option (HA-LB). This is a secure virtual application for Hyper-V, VMware and Xen hypervisors that will not only check the availability of servers, but also intelligently distribute incoming connections between healthy gateways. Multiple HA-LB can be run simultaneously.
• Reporting Services .
WS : There is no reporting service in Windows Server.
PRAS : Reporting service in Parallels RAS is not just there, but it can generate 14 types of reports: user, group, reports on the operation of devices, servers and applications.
• Cross-platform .
WSA: Windows Server provides a client application for Windows, iOS and Android. To access from other platforms, you will need to install third-party applications.
PRAS : provides client applications for almost all devices: access is possible through Mac and Linux, through all types of mobile devices - Android, iOS, Raspberry, and also without client installation - through any HTML5 browser.
• Support and administration .
WS : in Windows Server, the administrator has the ability to connect remotely (Remote Desktop Shadowing) to any RDS user session. The remaining technical problems not related to RDS sessions cannot be resolved.
PRAS: RAS administration capabilities allow you to control not only the session, but the entire workstation through the configuration console.
• Security and authorization .
In WS, users can authenticate through Active Directory, via smart cards integrated with AD, and also through the Kerberos protocol. The remaining authorization types are only possible through the RD Gateway connections gateway. PRAS
users can also be authenticated through AD and smart cards. In addition, RAS allows two-factor authentication with one-time passwords via RADIUS, DeepNet, and SafeNet services.
CITRIX and VMware
The leaders of the virtualization market, Citrix and VMware, are known, first of all, for their complex multi-component and expensive platforms. They use the best technologies for transmitting 3D graphics, have the most advanced hypervisors and many other services for building virtual infrastructure.
All the imperfections of Citrix and VMware can be described in two words - complexity and high cost. The difficulty begins with choosing from a variety of licensing versions and continues through the process of installing, configuring, and updating the product. In most cases, it does not make sense to go through all these stages and is not economically feasible, especially if the company works in the SME segment (small and medium-sized enterprises) and has a small staff of remote employees.
We list some of the difficulties that will be faced in the process of implementing solutions.
Training costs
Citrix and VMware products can be implemented only by certified professionals. For example, a Citrix administrator must complete training, pass an exam at a test center, and receive a CCA-V (Citrix Certified Administrator - Virtualization) certificate. The cost of a five-day course in English XenApp and XenDesktop 7.1x Administration to prepare for the CCA exam will be $ 3,735 and higher. The exam itself is also held in English, in the form of testing. After receiving the certificate will be valid for three years, and then the exam will need to be retaken to confirm the qualification. Alternatively, to install the system, you can contact the integrators, but in any case, without the help of experienced specialists, you cannot deploy a farm, and their services will be quite expensive.
Cost and licensing
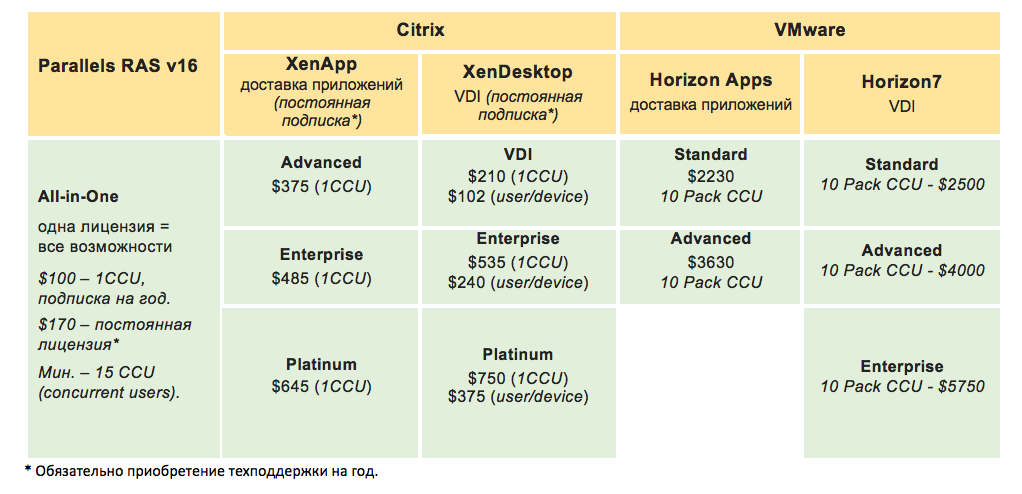
Both companies offer a large selection of virtualization tools. Both Citrix and VMware produce separate products for publishing applications and delivering VDI. That is, they are built on a single platform and are controlled from a single console, but differ in agents that are placed on the client and server OS. In the case when employees do not require high performance and personalization to work with applications, it is more convenient to use utilities for session-based publishing (XenApp, Horizon Apps, see table). If you need to work with heavy software or graphics, as well as personalized access to the desktop - you need to purchase VMware Horizon 7 or Citrix XenDesktop. They also allow you to publish applications, but additionally provide VDI delivery.
In addition, each product from Citrix and VMware has several types of licenses (see table), differing in basic or advanced functionality. A closer look reveals that many options are available only in the most expensive edition of the product. For example, VMware has fast publishing of applications using instant cloning technology only in the edition of Horizon Apps Enterprise. In Citrix, the ability to put XenApp on Unix also appears only in the Enterprise edition, and the option to process 3D content using the HDX 3D protocol is possible only in the Citrix XenDesktop Platinum edition. For load balancing in Citrix and VMware solutions, you will have to install additional components at an additional cost.
For licensing client connections, all manufacturers offer the following options:
- User / device (by the number of named users / authorized devices) - suitable for companies with a small number of remote employees who need access to the virtual machine throughout the day.
- Concurrent user (by the number of parallel connections) is a good choice for use in companies with a large number of users, for example, when employees work in shifts.
Parallels did not tinker with licenses and many individual products and launched the All-in-One product, which combines all the components and features in one package. There is only one licensing model - according to the number of simultaneous connections. The RAS functionality is slightly inferior to competing technologies, but let's not forget that Citrix and VMware products are mainly focused on working with large companies in the Enterprise segment. The capabilities of the RAS platform will fully cover all the needs of small and medium-sized businesses.
You will not need to pay for the services of a certified specialist to install and configure the technology: RAS can easily be configured by any administrator of your technical support.
Note that the RAS, Citrix and VMware platforms are only technologies for building and managing a server farm. In order to deploy a farm, in addition to purchasing a physical server, you will also need to pay the following licenses:
- Windows Server Licensing : at least two processors of eight cores (see table);
- VDI licensing (Microsoft VDA subscription) - if you will use VDI. A subscription is purchased for each VM on the server and includes a year of access to Windows virtual desktops. Cost - $ 100 per VM;
- RDS licensing - for connecting each client device to the MS RDS server - Windows RDS CAL ($ 169 per device, $ 199 per user).
Separately, I must say about the cloud environment, because now many companies are beginning to actively use the clouds. Using a cloud environment for virtualization has many advantages. You can scale the infrastructure indefinitely, that is, continuously increase the amount of cloud resources as needed. A high level of data security is maintained, which reduces the risk of leakage. Data is not stored locally, and clients receive access through a secure connection and not to the data itself, but to the deployed images. Parallels RAS can be deployed in any private, hybrid or public cloud (for example, Microsoft Azure or Amazon). If you want to get acquainted with the capabilities of Parallels RAS, you can absolutely free to test a farm in the MS Azure cloud for 30 days.
For the SME market, Parallels RAS platform deserves more than a close look.
Technologies are designed to make our lives easier, not more difficult, and Citrix and VMware products turn out to be too complex and costly solution for companies with remote workers from 100 to 5000 people. RAS greatly simplifies the process of deploying a farm, provides serious data security protection, combines everything in a single console for comprehensive farm management, has built-in load balancing and supports excessive farm scalability. In terms of the proposed features, Parallels RAS does not lag far behind Citrix and VMware, consistently occupying top positions in the ranking of virtualization products, but at the same time it has low licensing costs and low server resource requirements.
