Background: Roscosmos State Corporation and its work

Roscosmos has a long history, in which there are many interesting points. Not so long ago, the organization turned 26 years old. The official date of birth is February 25, 1992. A respectable term for any organization. But what is Roskosmos? Another "Help" will tell about the history of the organization and some aspects of its work, including, for example, plans to create an orbiting lunar station.
When did Roscosmos appear?
The state corporation originates in the USSR. In fact, Roscosmos absorbed almost everything that remained of the space program of the country, which is now gone.
In 1992, all this was transformed into the Russian Space Agency under the Government of the Russian Federation. The new organization was engaged in the implementation of state policy of Russia in space.

Then this organization was transformed into the Russian Space Agency. After a while, the Russian Aerospace Agency (Rosaviakosmos) appeared, which was created in 1999. Finally, Roscosmos (at that time the Federal Space Agency) appeared in 2004. True, in 2014 the United Rocket and Space Corporation was withdrawn from Roskosmos, led by Igor Komarov, the former deputy director of Roskosmos.
Finally, in 2015, the Government of the Russian Federation decided to create a new state corporation, which would deal with the withdrawal of Russian cosmonautics from the crisis. According to officials, the main features of the newly created organization should have been transparency, including management and financing schemes. In addition, they had to expand the scope of activities of Roscosmos.
As a result, the State Space Corporation Roscosmos’s presidential bill succeeded the USSR Ministry of General Engineering, the Russian Space Agency, the Russian Aerospace Agency, and the Federal Space Agency Roscosmos. The beginning of the organization’s work can be considered the introduction of the Vostochny Cosmodrome.
What does Roskosmos do?
Functions of Roscosmos:
- Development of plans for the development of near space and the implementation of these plans;
- Fulfillment of government orders - for example, sending various kinds of cargo into space (including people, yes);
- Collaboration with international organizations is not easy, space exploration is expensive, and it is easier to do it together;
- Development and testing of various kinds of military equipment;
- Operation of the Baikonur Cosmodrome and all the work carried out here, as well as the Vostochny Cosmodrome.
Who runs Roscosmos?
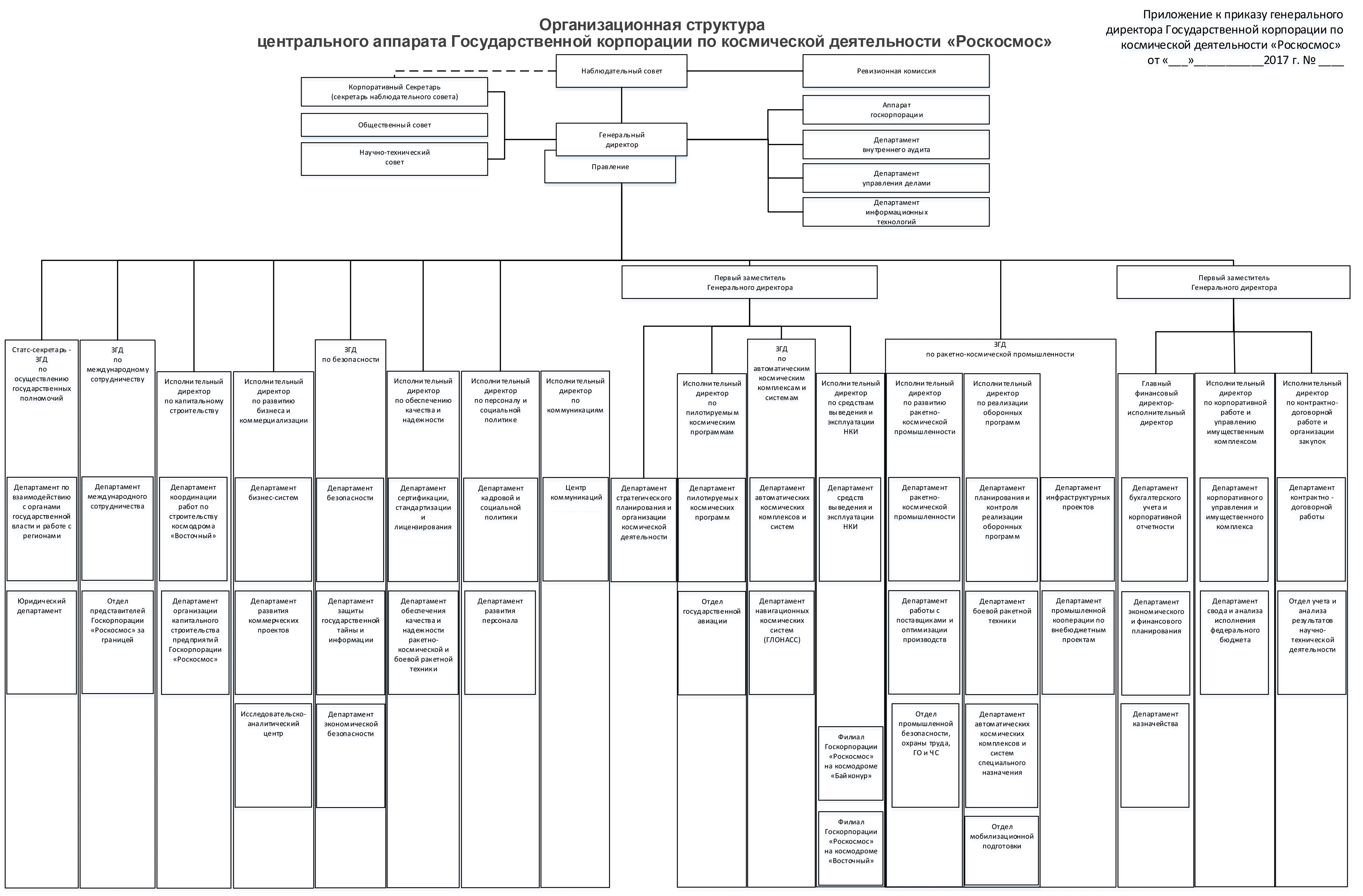
In 2015, Igor Komarov, who since March 2014 headed the ORKK, assumed the post of leader. In May this year, by decree of Vladimir Putin, Dmitry Rogozin became the general director of the State Corporation for Space Activities of Roscosmos. In addition, the governing body is the “Supervisory Board” of the corporation, in which 11 members, including Rogozin, Komarov Sergey Kiriyenko. Organizational structure of the central apparatus of the State Space Corporation Roscosmos. Source - roskosmos.ru (when you click on the image, it will open in its original size)
The attitude of the new leader to cooperation with external partners can be judged by his statement: “Firstly, we certainly won’t conduct any negotiations to impose ourselves on the Americans as partners ... Of course, the cooperation here would be good, but not at any cost, we’re definitely not let's go apprentices. "
How many spaceports does Roskosmos have?
Now there are four - but part of the sites is managed by other organizations, Roscosmos has access to them.
Baikonur

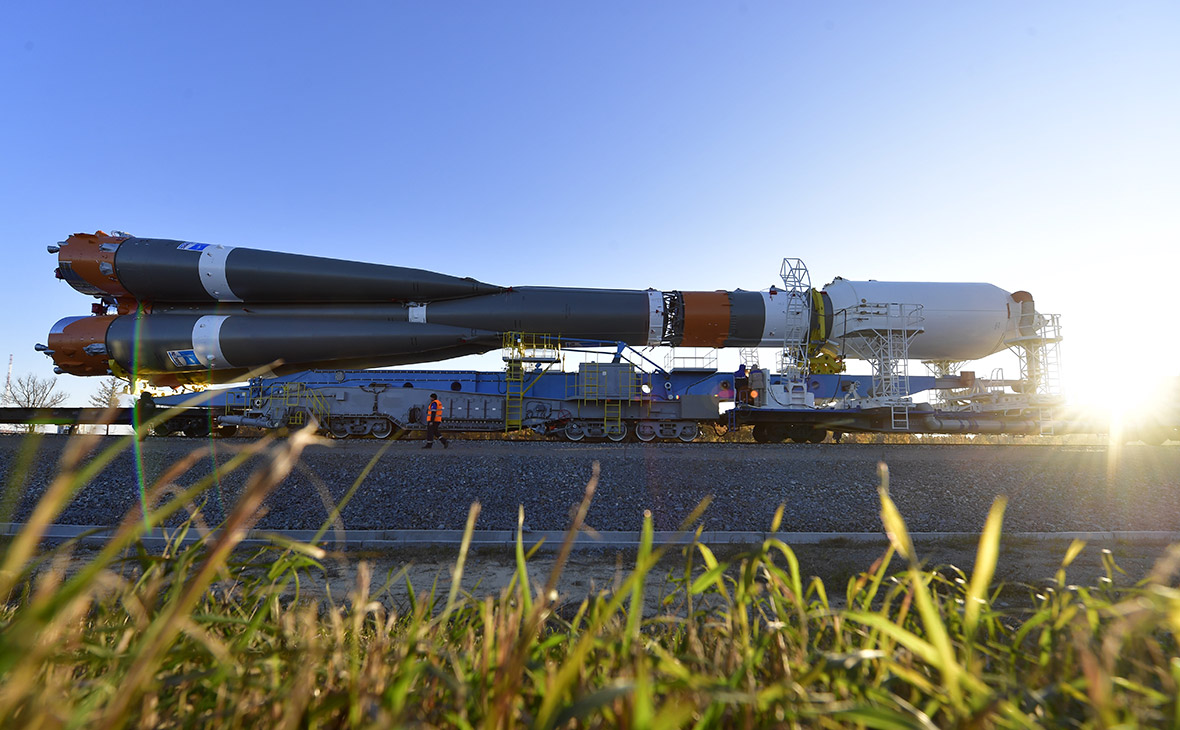
Cosmodrome Baikonur is the first and largest cosmodrome in the world. It is located in Kazakhstan. The city of Baikonur and the spaceport form the complex of the same name, which Russia rented from Kazakhstan. The lease expires in 2050. A spaceport operation costs the Russian budget 9 billion rubles a year. Of these, 7.4 billion - rent, 1.5 billion - the maintenance of spaceport facilities. In addition, Russia is investing about 1.16 billion rubles a year in the budget of the city of Baikonur (this is the figure from 2012, there are no more accurate data yet).
Oriental

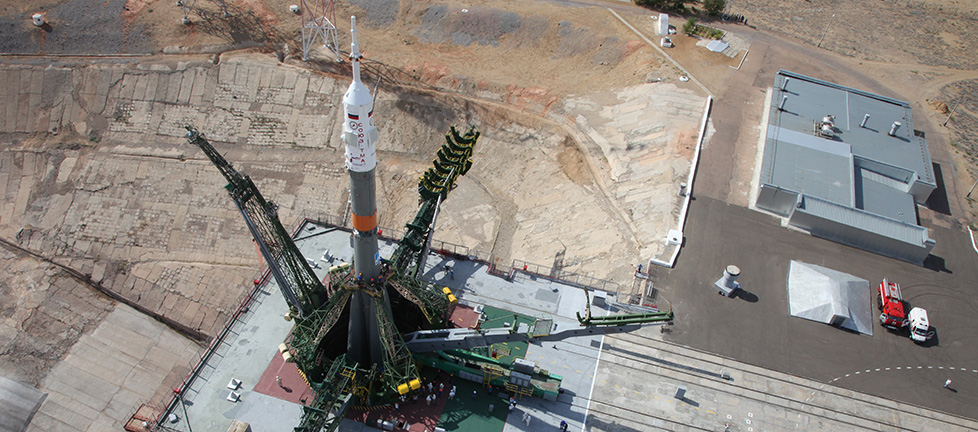
Civil spaceport, rebuilt from scratch. The order on its creation was signed in November 2007. It was created to ensure independent access of Russia to space, guaranteed implementation of space programs for various purposes, to reduce costs at the Baikonur Cosmodrome and to improve the overall socio-economic situation in the Amur Region.
In 2016, the first successful launch took place at the cosmodrome with the launch of three artificial Earth satellites into orbit. Well, by 2021, it is planned to launch the manned ship Federation. True, first in unmanned mode.
The spaceport cost the budget about 100 billion rubles. In total, it is planned to spend about 300 billion. The construction of the cosmodrome was accompanied by(and accompanied by) high-profile corruption scandals. As far as one can judge, about 8 billion rubles were stolen - but this is only the theft of which we are aware.
Plesetsk
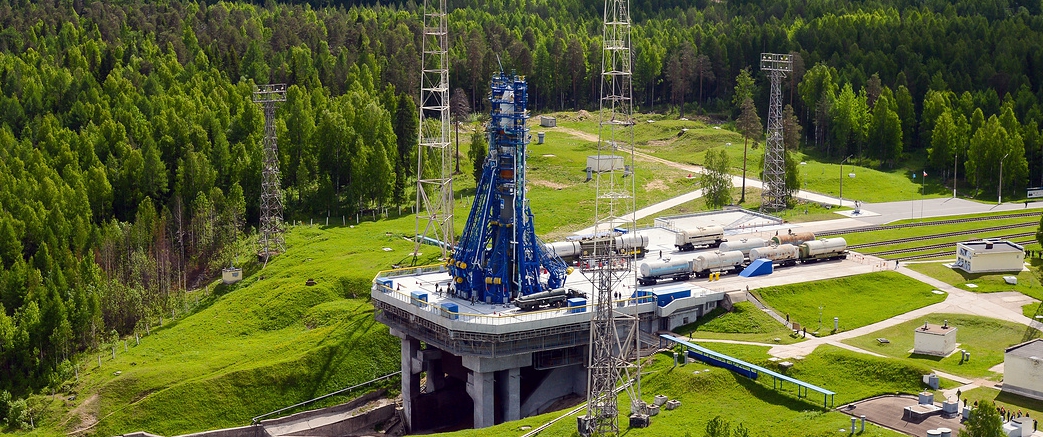

This is the northernmost spaceport, which is located in the Plesetsk district of the Arkhangelsk region of Russia. Light launch vehicles Angara-1.2, Soyuz-2.1v, Rokot, the middle class Soyuz-2.1a, Soyuz-2.1b, and the heavy class Angara-A5 are operated at the launch site. The technical facilities of the spaceport allow launching various spacecraft into all types of orbits, including geostationary.
Kuru

This is not a Russian cosmodrome; Roscosmos only leases capacities through Glavkosmos JSC. Nevertheless, the preparation of Russian rocket and space technology and the maintenance of ground processing equipment at the Guiana spaceport are carried out by Roskosmos enterprises.
Two-thirds of the spaceport's annual budget is funded by the European Space Agency. It is difficult to name the amount of expenditures from the Russian budget - there is little necessary data in the public domain.
Future plans
Roscosmos has an approved space program for 2016–2025. Within its framework it is planned to perform the following tasks:
- Development and maintenance of the orbital group;
- Ensuring flight tests of the Angara with a new generation manned transport ship;
- Ensuring launches to the ISS from Vostochny Cosmodrome in 2023;
- Methane rocket engine development;
- Creation of a superheavy rocket capable of delivering more than 100 tons of cargo into space;
- Solar research in the framework of the Resonance project;
- Basic space research, including the study of the moon (it is planned to send five spacecraft to the Earth’s satellite;
- Participation in the Exomars program;
- Support for the work of the ISS;
- Preservation of a place in the world market of space launches;
- Creating an inflatable module for the ISS.
About 1.5 trillion rubles are allocated from the budget for this program.
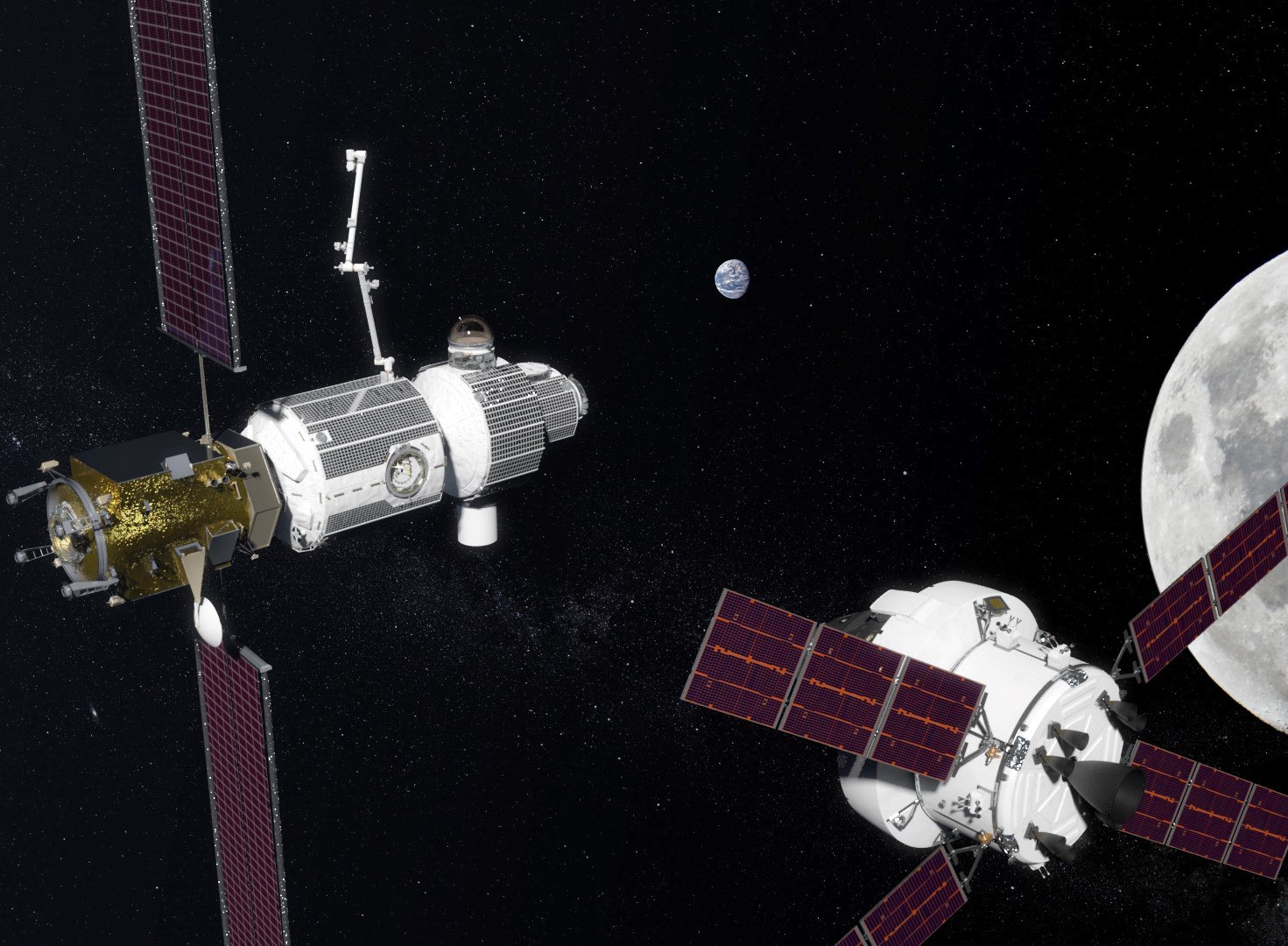
In addition, last year, NASA and Roscosmos signed a statement on exploration and exploration of deep space. Both organizations will take part in the construction of the Deep Space Gateway base in near-moon space. According to the preliminary plan, this base will become a platform for traveling to Mars and for other space missions.
Problems of Roscosmos
In fact, there are so many of them that to reveal a full-fledged picture, a full-fledged multi-page report is needed. The leadership of Roscosmos recognizes the existence of problems. Last month First Deputy General Director of the State Corporation "Roscosmos" Nikolai Sevastyanov called the following problems of the industry:
- Systematic rescheduling.
- Increasing the cost of projects.
- The lack of reliability of the equipment, which harms the image.
The causes of the problems (according to the leadership of the organization) are also three:
- Collaborative project management.
- Incorrect pricing. Prices are either too low or too high.
- Untimely quality control methodology.
In addition to the above reasons, it is possible to highlight the non-systematic work program of the organization. For example, plans to develop new launch vehicles have repeatedly changed. It is not uncommon for a situation where it is planned to develop one missile, then the program is abandoned halfway and the development of a second, different type begins. This is exactly what happened with the Rus-M project. In addition, the Roscosmos program includes Angara, Soyuz-5, Energia-5V rockets, and the Corona single-stage rocket.
In the course of their work, various departments within the framework of Roskosmos have to agree, to constantly coordinate something. All this leads to a rise in the cost of all projects, the dispersal of funds for external needs and the deterioration of the quality of project implementation. The ex-employee of "Roskosmos" tells about a number of problems in his comment on Habré.

Now Roscosmos is still holding onto a certain level in the market for launching goods and people into space. But this is largely due to the use of Soviet technology. There are innovations, but there are few of them, and their implementation, for the reasons mentioned above, is a troublesome and slow business. Now in the USA and some other countries, private space exploration is rapidly developing, which will give odds to any state space program in terms of efficiency and budget. Unfortunately, now Russia lags behind a number of countries in terms of the development of the space sector, although earlier it was ahead of almost everyone.
Perhaps it is precisely because of these problems that rumors appeared about the imminent reduction of the organization’s budget by 150 billion rubles in 2019-2021. According to experts, if this is really true, then the set goals and objectives of Roskosmos will be difficult to fulfill.
