Access to information by Facebook applications (in pictures)
By adding a new application to Facebook or registering with it on the site, applications get access to your information. Now developers are available about 60 different permissions (permissions), with which they can access your information, create and manage it.
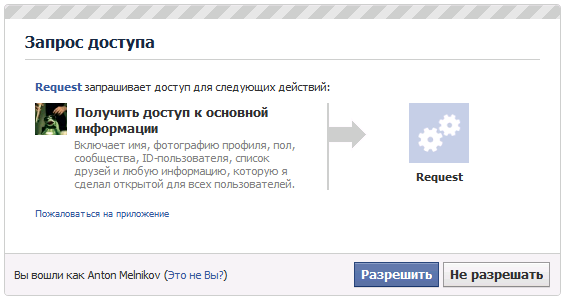
The application has access to one information (public), and the application may ask you for different permissions to the other, which is necessary for work.
How to protect yourself - read the roll.
A detailed list of permissions is available in the Facebook documentation .
Permissions can be conditionally divided into those that:
On the other hand, permissions are divided into access to user information and information of friends of the user.
You can control the level of access to your information both inside Facebook and beyond. To protect yourself, follow the recommendations described below.
Your name, profile photo, gender, community and username are open to all. You can configure access to other information in the “Privacy Settings”, through the “Account” menu in Facebook. In the “Applications and Web Sites” section, the first thing you should pay attention to is the “Information Available through Your Friends” block. Here you can set what information is available for applications and websites in case your friends use them.

From the “Privacy Settings” page, you can go to editing applications. Here you can either delete the application completely, then it can no longer work with your data until you re-enter the application and allow the necessary permissions. Remove unwanted or spamming apps. For the rest, you can go through the settings by clicking “Change Settings”.
Information is available for the selected application:
After you configure what information you leave public and what will be available to applications through your friends, and also check the settings of the added applications, look at the possible permissions that applications may request.

Individual permissions can be combined under one icon, and displayed in a list in the description. Compare the first three icons on the left.
If the application asks you for an email, then you can choose: give your proxy or email address. In the latter, an arbitrary address is assigned to you, letters from which are redirected to you. After breaking the connection, the application will not be able to send them further, since it does not know the box itself. Quite often, developers check what type of email you left, and block access until you give your real address.
There are 2 permission for event management:
The permission “Leave publications on my wall” allows you to create notes, post statuses and links, leave comments and like, upload photos. If you gave the application this permission, then it can do it at any time, regardless of your presence on the network and use of the application.
In cases where the application wants to access information at any time, it requests permission offline_access - “Get access to my data at any time”. To access information, the application uses access_token - a unique user key. But it works for about an hour and is constantly updated, so if you allow offline access, the application will receive an “eternal” access_token.
The application can manage pages in which the user is an administrator. To do this, it requests manage_pages permission - “Manage my pages”.
Finally, a few recommendations for application developers:

The application has access to one information (public), and the application may ask you for different permissions to the other, which is necessary for work.
How to protect yourself - read the roll.
A detailed list of permissions is available in the Facebook documentation .
Permissions can be conditionally divided into those that:
- They allow you to receive data (“read-only”): personal and contact information, lists of friends, groups, interests and other things.
- Manage data (create, modify, delete): publication of statuses, notes, photos, responses to event requests, messages and visits to places.
On the other hand, permissions are divided into access to user information and information of friends of the user.
You can control the level of access to your information both inside Facebook and beyond. To protect yourself, follow the recommendations described below.
Privacy management
Your name, profile photo, gender, community and username are open to all. You can configure access to other information in the “Privacy Settings”, through the “Account” menu in Facebook. In the “Applications and Web Sites” section, the first thing you should pay attention to is the “Information Available through Your Friends” block. Here you can set what information is available for applications and websites in case your friends use them.

Control applications and web sites
From the “Privacy Settings” page, you can go to editing applications. Here you can either delete the application completely, then it can no longer work with your data until you re-enter the application and allow the necessary permissions. Remove unwanted or spamming apps. For the rest, you can go through the settings by clicking “Change Settings”.
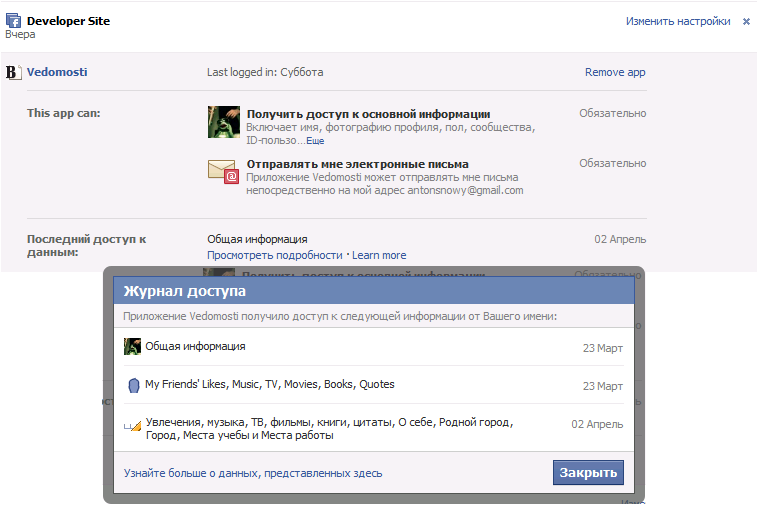
Information is available for the selected application:
- Last Login: The last time you used the application.
- Accessed information: Shows a list of access rights required for the application, as well as a list of additional access rights that you have assigned to the application. You can remove any additional access rights by clicking “Delete”.
- Last access to data: Shows when the application got access to certain information on your behalf. When you click on the "View Details" link, you will see what information the application has access to.

Permissions
After you configure what information you leave public and what will be available to applications through your friends, and also check the settings of the added applications, look at the possible permissions that applications may request.

Individual permissions can be combined under one icon, and displayed in a list in the description. Compare the first three icons on the left.
If the application asks you for an email, then you can choose: give your proxy or email address. In the latter, an arbitrary address is assigned to you, letters from which are redirected to you. After breaking the connection, the application will not be able to send them further, since it does not know the box itself. Quite often, developers check what type of email you left, and block access until you give your real address.
There are 2 permission for event management:
- create_event - allows you to create and modify events, invite friends
- rsvp_event - RSVP of an event - allows you to choose whether you will go (signature on invitation inviting the recipient to give an answer about participation in the event (Répondez s'il vous plaît - French))
The permission “Leave publications on my wall” allows you to create notes, post statuses and links, leave comments and like, upload photos. If you gave the application this permission, then it can do it at any time, regardless of your presence on the network and use of the application.
In cases where the application wants to access information at any time, it requests permission offline_access - “Get access to my data at any time”. To access information, the application uses access_token - a unique user key. But it works for about an hour and is constantly updated, so if you allow offline access, the application will receive an “eternal” access_token.
The application can manage pages in which the user is an administrator. To do this, it requests manage_pages permission - “Manage my pages”.
To developers
Finally, a few recommendations for application developers:
- Request as few permissions as possible to get started with the application. Ideally, the landing page should open regardless of whether I allowed access to the application. On this page you can tell why I should allow access and give the opportunity to do it consciously. Bounce conversion will be lower.
- If the user has allowed access, do not show the landing page. Authorize immediately on the server side, without repeated reboots of the iframe of the application, and let the user immediately get to work.
- Do not take action if you have not explicitly received their approval from the user. Spam virality reduces app loyalty. Instead of automatically posting and inviting, give similar features through Dialogs.
- Follow the terms and conditions of Facebook developers .
