Web site prototyping. Putting it all together.
“The only possible source of economic recovery is improving the quality and, as a result, the attractiveness of a product or service. And quality improvement cannot be achieved by reducing design and programming costs. ”
Alan Cooper“ Psychiatric hospital in the hands of patients ”
Thanks to everyone who participated in the Habrahabr vote:
1. What does the prototyping process look like in your company?
2. Who is responsible for prototyping of web-projects in which you participate?
3. Does the current situation with prototyping websites in your company suit you?
It's time to discuss the results.
Survey Results “What does prototyping look like in your company?” spent on Habrahabr.
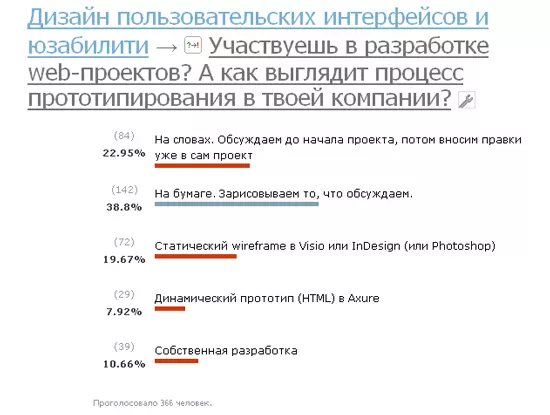
Fig. 1
I intentionally used radio buttons instead of checkboxes, forcing me to choose the only option (assuming that the person will choose the most frequent option. Thus, filtering cases when one of the options was used once, but would have the same weight as it is constantly used). Intentionally added a provocative version of "In words." How can prototyping be in words? The results of the discussions must be recorded, otherwise something will be forgotten, ignored or not verified. The effectiveness of prototyping in words tends to zero. The popularity of paper prototypes came as a surprise, as did the “Own Development” option with 39 votes. I'd love to know the details from those who voted for this option.
In order to compare the situation with prototyping in my Western colleagues, I quote the IxDA survey results. Discussion: What tools do you use for prototyping? (thanks for the link to Alexei Kopylov )
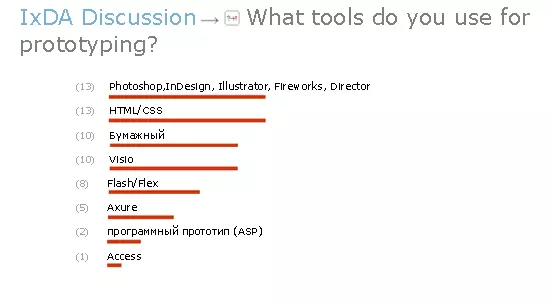
Fig. 2
Also mentioned in the IxDA discussion:
Whiteboard, Snapz Pro X, GUI Design Studio, LucidSpec, Multimedia Fusion, Intuitect and Jumpchart, SmartDraw, Microsoft Word, Inspiration, MockupScreens, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Power Point , Sketchbook Pro, Omni Graffe, ACD Canvas, Oversite, Eight Media, Magnetic Web Widgets.
I will not paint every tool and method, because using the links below it is done in more detail. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of popular tools and prototyping methods according to the following criteria:
The speed of prototyping is a very important criterion. It’s very good when the tool allows you to realize your thought “put this button here” without any difficulty, without forcing you to get bogged down in technology, settings, etc.
Interactivity - the ability of a prototype to respond to user actions and emulate real events. For details on the benefits and features of interactive prototypes, see the articles on Yuri Vetrov's blog “Interactive Prototypes”.
Detailing - the ability to reflect in the prototype everything to the smallest detail. Some of the tools listed below are only suitable for low-level prototyping at the block set level (“black boxes”).
Re-rendering required- re-drawing of the prototype takes additional time
available to all participants of the project - accessibility to all project participants, such as customer management, developers, designers - often a prerequisite for prototyping.
The possibility of making changes is also useful for prototyping in that it is possible to clarify some details of the future system, some points are discussed and clarified during the work. The prototype must be updated along with project artifacts, so the possibility of making changes is another important criterion.
(Need 2. Quickly create interactive, detailed prototypes available to all project participants, with the ability to make changes)
Prototype creation speed: high
Interactivity: none
Detailing: high
Repeated rendering is required: yes
Accessibility for all project participants: limited
Possibility to make changes: not possible

You can do it yourself! A paper with a magnetic surface is available. You can print stencils for design directly on the office printer, just be sure to check whether your printer supports printing on this type of paper.
The speed of prototyping: medium
Interactivity: no
Detail: Average
Need to re-rendering: yes
Accessibility for all project participants: limited
possibility of changes: possible with restrictions
Prototype creation speed: high
Interactivity: medium
Detailing: high
Repeated rendering is required: none
Accessibility for all project participants: full
Possibility to make changes: possible without restrictions

Prototype creation speed: medium
Interactivity: low
Detailing: high
Repeated rendering is required: none
Accessibility for all project participants: full
Possibility to make changes: possible without restrictions

Prototype creation speed: high
Interactivity: low
Detailing: high
Repeated rendering is required: none
Accessibility for all project participants: full
Possibility to make changes: possible without restrictions
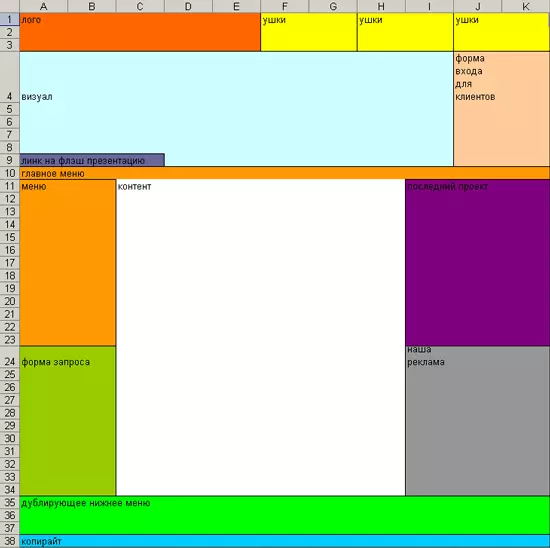
Prototype creation speed: medium
Interactivity: low
Detailing: low
Repeated rendering is required: yes
Accessibility for all project participants: full
Possibility to make changes: possible with restrictions
More information about the tools you can get from articles: gulevich Maxim Gulevich “Overview of tools for UI-designer and Information Architect ” , Alexander Sergeev ( HumanoIT ) on using Axure Pro , Vlad Golovach ( Usethics ) on prototyping interfaces in InDesign , Yuri Vetrov ( Artics) about wireframs made in Visio and even the dynamics of web 2.0 in them.
Let's move on to the results of voting on the performers.

Fig. 3
Even if we discard the last, most popular result, it turns out that the prototyping process is carried out by project participants who do not specialize in design and usability issues.
(Need 3. Consider the low level of knowledge and experience of the person performing the prototyping)
Voting results about satisfaction with the current situation.

Fig. 4 The
quite expected conclusion that the current situation with prototyping in projects is not satisfactory (there are no two in total).
(Need 4. Strong and sufficient arguments in favor of prototyping. Benefits should be expressed in numbers)
With all the variety of existing tools for prototyping, it is still not being implemented in many projects and companies (see Fig. 3). It is really difficult for a project company to answer the question: “Why do we need innovations and investments in quality (design, usability, etc.), if everything works and makes a profit?” The introduction of prototyping in such companies can only occur if management fully understands the value of quality. Qualities, as part of a corporate culture, as values for each employee (Parents instill the same feeling in young children who are capricious in the morning and do not want to wash, explaining that they wash, primarily for themselves, and not for someone). Finding an answer to the above question about the need for investment is being dealt with as Russianand foreign usabilityists.
Much more conscious about the introduction of prototyping are companies involved in the production of products. They have already felt the benefits of design and prototyping (perhaps trial and error). Unlike the first group, for them the usability of the product, user interface design and prototyping are no longer a ghostly prospect. For them, this is a real way to reduce risks, improve product quality and increase the loyalty of users (i.e. buyers) to their product. However, not all of them are ready to turn to professional companies, create a department or train (hire) a specialist, preferring to assign the design and prototyping function to the project manager, team leader, etc. (see fig. 3).
Similar to how Jacob Nielsen once created a list of levels of readiness of companies for the introduction of usability, kremien Gennady Dragun made a list of levels of this implementation:
Level 0: About usability only heard somewhere or not at all
Level 1: Use of basic usability testing methods (checklists, simple inspection, the availability check)
level 2 level 1 + introduction of interface design and graphic design
level 3: level 2 + simple "partisan" user testing, investigated ie users
Level 4: Create your own department of usability - usability lab.
Original Nielsen articles on this subject:
http://www.useit.com/alertbox/process_maturity.html
http://www.useit.com/alertbox/maturity.html
Prototyping in companies where the implementation level is rarely higher than the first usually happens as follows: The newcomer manager (team lead, etc. often not previously familiar with usability) is tasked - "create a prototype of the project." Thanks to Google, the manager finds, say, this article. He sees the described tools and methods. But they only cover the need for an instrument by answering the question: “How?”. They do not provide an answer to the question: “What?”, Already assuming that the user of the program has the appropriate knowledge. Based on the results of the voting, I’ll try to assume that the number of companies with implementation levels not exceeding level 1 is the majority.
Related Articles:
Designing an Interface as Part of TK Development
Designing user interfaces. Process Overview
Interactive Prototypes. The current model of the user interface ( Part 1 , Part 2 ,
Part 3 )
Bonus:
Stencils for Visio and similar to GUUII
Stencils for InDesign from Usethics studio
Axure Pro. The product is paid, but is it possible to hide something from the all-seeing eye of Google? Determine the moral and ethical side of using keygen for yourself. Searching results.
To obtain a positive result from the introduction of prototyping, it is necessary that it meets the following needs:
1. Automate standard solutions, giving the opportunity for creativity.
2. Allowed to create interactive, detailed prototypes available to all project participants with the ability to make changes.
3. Take into account the low level of knowledge and experience of a person performing prototyping.
4. Strong and sufficient arguments in favor of prototyping. Benefits should be expressed in numbers.
I developed a prototyping tooland some implementation techniques that meet these needs. In the near future I plan to present this project in the best possible way on the blog. You will have the opportunity to download and use this tool for free. In the meantime, I suggest you follow the news on RSS
Source: Blog about usability and project management
Alan Cooper“ Psychiatric hospital in the hands of patients ”
Thanks to everyone who participated in the Habrahabr vote:
1. What does the prototyping process look like in your company?
2. Who is responsible for prototyping of web-projects in which you participate?
3. Does the current situation with prototyping websites in your company suit you?
It's time to discuss the results.
1) For the hundredth time about the benefits of prototyping (as part of design). Problem.
The most expensive mistakes are the mistakes made at the beginning of the project, since it is at the initial stages that the most important decisions are made. As the project develops, the cost of error decreases. At the same time, the initial level of quality control is minimal and increases as the development process progresses. Full testing begins only in the later stages. The result is often the identification of the most expensive errors too late and the subsequent expensive processing of the system or its individual parts. At first glance, it might seem that some projects are the same in essence and content. Let's say a typical project for you is an online store based on your existing system. But the individuality of each project lies even in its very definition ( see the definition of “project” by PMBOK) There is an opinion that the development of similar projects can take place without a design stage. I share this opinion only in part. I would divide the design task into the creation of standard standard solutions that migrate from project to project and creative tasks that need to be addressed in each new project. (Need 1. Automate standard solutions, saving space for creativity)And no matter how you resist, claiming that the projects are of the same type, if you want to improve the quality and, as a result, achieve an economic recovery (according to Cooper), then in each new project you simply must take into account different input information. Prototyping is not a panacea, but a way to avoid some expensive mistakes and reduce risks. I think it’s obvious that users of an online store selling fertilizers and agricultural machinery will be very different from users of a store selling clothes and glamor accessories, just as their behavior on the site, objects of attention, etc. will differ. Can your standard solution accommodate user differences? The standard solution is a set of components tested and tested in various projects. Understanding the need for their adaptation (customization) often arises at the end, when full testing occurs, but there are no more free resources. This is the same error (overspending of the project time, leading to emergency, deterioration). The paradox of the new economy that Cooper wrote about is that to save, you have to pay (by investing in design).2) An overview of methods, tools and implementers. Blue or red pill?
Survey Results “What does prototyping look like in your company?” spent on Habrahabr.

Fig. 1
I intentionally used radio buttons instead of checkboxes, forcing me to choose the only option (assuming that the person will choose the most frequent option. Thus, filtering cases when one of the options was used once, but would have the same weight as it is constantly used). Intentionally added a provocative version of "In words." How can prototyping be in words? The results of the discussions must be recorded, otherwise something will be forgotten, ignored or not verified. The effectiveness of prototyping in words tends to zero. The popularity of paper prototypes came as a surprise, as did the “Own Development” option with 39 votes. I'd love to know the details from those who voted for this option.
In order to compare the situation with prototyping in my Western colleagues, I quote the IxDA survey results. Discussion: What tools do you use for prototyping? (thanks for the link to Alexei Kopylov )

Fig. 2
Also mentioned in the IxDA discussion:
Whiteboard, Snapz Pro X, GUI Design Studio, LucidSpec, Multimedia Fusion, Intuitect and Jumpchart, SmartDraw, Microsoft Word, Inspiration, MockupScreens, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Power Point , Sketchbook Pro, Omni Graffe, ACD Canvas, Oversite, Eight Media, Magnetic Web Widgets.
I will not paint every tool and method, because using the links below it is done in more detail. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of popular tools and prototyping methods according to the following criteria:
The speed of prototyping is a very important criterion. It’s very good when the tool allows you to realize your thought “put this button here” without any difficulty, without forcing you to get bogged down in technology, settings, etc.
Interactivity - the ability of a prototype to respond to user actions and emulate real events. For details on the benefits and features of interactive prototypes, see the articles on Yuri Vetrov's blog “Interactive Prototypes”.
Detailing - the ability to reflect in the prototype everything to the smallest detail. Some of the tools listed below are only suitable for low-level prototyping at the block set level (“black boxes”).
Re-rendering required- re-drawing of the prototype takes additional time
available to all participants of the project - accessibility to all project participants, such as customer management, developers, designers - often a prerequisite for prototyping.
The possibility of making changes is also useful for prototyping in that it is possible to clarify some details of the future system, some points are discussed and clarified during the work. The prototype must be updated along with project artifacts, so the possibility of making changes is another important criterion.
(Need 2. Quickly create interactive, detailed prototypes available to all project participants, with the ability to make changes)
Paper prototyping

Prototype creation speed: high
Interactivity: none
Detailing: high
Repeated rendering is required: yes
Accessibility for all project participants: limited
Possibility to make changes: not possible
Whiteboard prototyping

You can do it yourself! A paper with a magnetic surface is available. You can print stencils for design directly on the office printer, just be sure to check whether your printer supports printing on this type of paper.
The speed of prototyping: medium
Interactivity: no
Detail: Average
Need to re-rendering: yes
Accessibility for all project participants: limited
possibility of changes: possible with restrictions
Axure pro

Prototype creation speed: high
Interactivity: medium
Detailing: high
Repeated rendering is required: none
Accessibility for all project participants: full
Possibility to make changes: possible without restrictions
Indesign

Prototype creation speed: medium
Interactivity: low
Detailing: high
Repeated rendering is required: none
Accessibility for all project participants: full
Possibility to make changes: possible without restrictions
Visio

Prototype creation speed: high
Interactivity: low
Detailing: high
Repeated rendering is required: none
Accessibility for all project participants: full
Possibility to make changes: possible without restrictions
Office software

Prototype creation speed: medium
Interactivity: low
Detailing: low
Repeated rendering is required: yes
Accessibility for all project participants: full
Possibility to make changes: possible with restrictions
More information about the tools you can get from articles: gulevich Maxim Gulevich “Overview of tools for UI-designer and Information Architect ” , Alexander Sergeev ( HumanoIT ) on using Axure Pro , Vlad Golovach ( Usethics ) on prototyping interfaces in InDesign , Yuri Vetrov ( Artics) about wireframs made in Visio and even the dynamics of web 2.0 in them.
Let's move on to the results of voting on the performers.

Fig. 3
Even if we discard the last, most popular result, it turns out that the prototyping process is carried out by project participants who do not specialize in design and usability issues.
(Need 3. Consider the low level of knowledge and experience of the person performing the prototyping)
Voting results about satisfaction with the current situation.

Fig. 4 The
quite expected conclusion that the current situation with prototyping in projects is not satisfactory (there are no two in total).
(Need 4. Strong and sufficient arguments in favor of prototyping. Benefits should be expressed in numbers)
With all the variety of existing tools for prototyping, it is still not being implemented in many projects and companies (see Fig. 3). It is really difficult for a project company to answer the question: “Why do we need innovations and investments in quality (design, usability, etc.), if everything works and makes a profit?” The introduction of prototyping in such companies can only occur if management fully understands the value of quality. Qualities, as part of a corporate culture, as values for each employee (Parents instill the same feeling in young children who are capricious in the morning and do not want to wash, explaining that they wash, primarily for themselves, and not for someone). Finding an answer to the above question about the need for investment is being dealt with as Russianand foreign usabilityists.
Much more conscious about the introduction of prototyping are companies involved in the production of products. They have already felt the benefits of design and prototyping (perhaps trial and error). Unlike the first group, for them the usability of the product, user interface design and prototyping are no longer a ghostly prospect. For them, this is a real way to reduce risks, improve product quality and increase the loyalty of users (i.e. buyers) to their product. However, not all of them are ready to turn to professional companies, create a department or train (hire) a specialist, preferring to assign the design and prototyping function to the project manager, team leader, etc. (see fig. 3).
Similar to how Jacob Nielsen once created a list of levels of readiness of companies for the introduction of usability, kremien Gennady Dragun made a list of levels of this implementation:
Level 0: About usability only heard somewhere or not at all
Level 1: Use of basic usability testing methods (checklists, simple inspection, the availability check)
level 2 level 1 + introduction of interface design and graphic design
level 3: level 2 + simple "partisan" user testing, investigated ie users
Level 4: Create your own department of usability - usability lab.
Original Nielsen articles on this subject:
http://www.useit.com/alertbox/process_maturity.html
http://www.useit.com/alertbox/maturity.html
Prototyping in companies where the implementation level is rarely higher than the first usually happens as follows: The newcomer manager (team lead, etc. often not previously familiar with usability) is tasked - "create a prototype of the project." Thanks to Google, the manager finds, say, this article. He sees the described tools and methods. But they only cover the need for an instrument by answering the question: “How?”. They do not provide an answer to the question: “What?”, Already assuming that the user of the program has the appropriate knowledge. Based on the results of the voting, I’ll try to assume that the number of companies with implementation levels not exceeding level 1 is the majority.
Related Articles:
Designing an Interface as Part of TK Development
Designing user interfaces. Process Overview
Interactive Prototypes. The current model of the user interface ( Part 1 , Part 2 ,
Part 3 )
Bonus:
Stencils for Visio and similar to GUUII
Stencils for InDesign from Usethics studio
Axure Pro. The product is paid, but is it possible to hide something from the all-seeing eye of Google? Determine the moral and ethical side of using keygen for yourself. Searching results.
3) Choose a red pill. Real needs or welcome to the real world.
To obtain a positive result from the introduction of prototyping, it is necessary that it meets the following needs:
1. Automate standard solutions, giving the opportunity for creativity.
2. Allowed to create interactive, detailed prototypes available to all project participants with the ability to make changes.
3. Take into account the low level of knowledge and experience of a person performing prototyping.
4. Strong and sufficient arguments in favor of prototyping. Benefits should be expressed in numbers.
I developed a prototyping tooland some implementation techniques that meet these needs. In the near future I plan to present this project in the best possible way on the blog. You will have the opportunity to download and use this tool for free. In the meantime, I suggest you follow the news on RSS
Source: Blog about usability and project management
