Microsoft managed to write 200 MB of data on synthetic DNA strands
The ultimate goal of scientists - the creation of a "DNA drive" a huge capacity
Theoretically, one gram of DNA can accommodate one billion terabytes of data. Under certain conditions, the record can be stored for thousands of years. But the issue of efficiently recording and reading information from DNA has not yet been resolved. Now Microsoft and the University of Washington are working on this problem. In April of this year, the partners managed to store 150 KB of information in DNA - three pictures. Now the process has been improved, and 202 MB have already been recorded. A high-resolution OK Go music video was recorded in deoxyribonucleic acid molecules, which included the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, translated into 100 languages, the top 100 books of The Gutenberg Project, and Crop Trust’s DNA database .
The project for recording information in DNA was named Project Palix.
The work was carried out with synthetic DNA purchased from Twist Bioscience in the amount of 10 million threads. Synthetic DNA of a certain configuration is developed by request. The cost of a pair of bases of such material is 10 cents. The price is gradually falling, and the manufacturer expects to reach 2 cents for a couple of bases.
Microsoft Corporation and the University of Washington are not the first to decide to use the idea of writing data to DNA. In 2010, biologists from Hong Kong offeredmethod of introducing into the genome of the bacterium E. coli synthetic DNA. The Chinese used four-fold numbering system for coding information, according to the number of nucleotides (0 = A, 1 = T, 2 = C, 3 = G). Scientists translated the test data into figures in the ASCII table (i = 105; G = 71; E = 69; M = 77), then into the four-fold system (105 → 1221; 71 → 0113; 69 → 0111; 77 → 0131), and after that - in a chain of nucleotides.
Two years later, Harvard scientists , using another method, recorded 643 kilobytes of data in DNA. At Harvard, they decided to abandon working with living organisms. Instead, synthetic DNA was introduced into a molecule generated on a special DNA chip. The advantage of this method is the absence of danger of loss of information due to mutations of the carrier.
These scientists were able to encode the book of Church, and with preservation of formatting and illustrations.
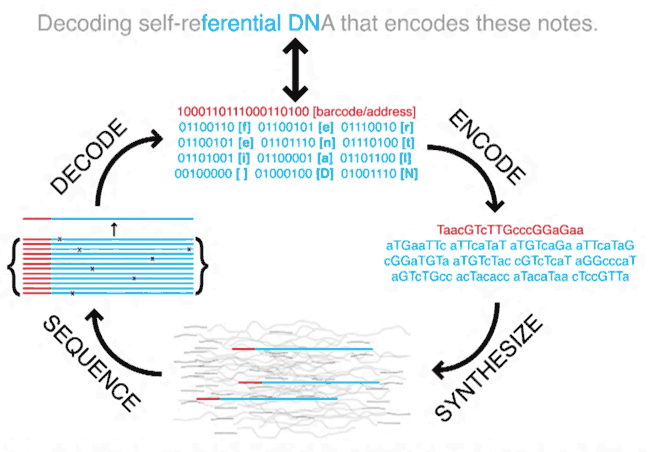
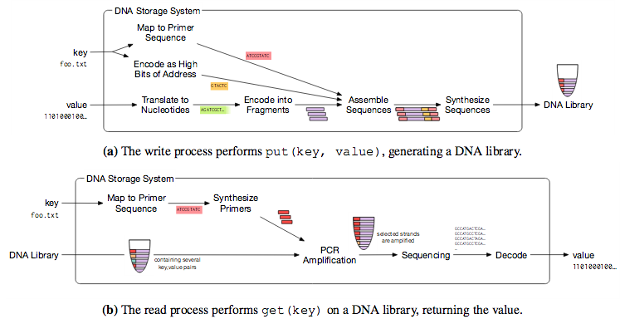
Microsoft and the University of Washington use the method proposed by experts from Harvard. First, the ones and zeros of the binary code are translated into combinations of nucleotides - adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. After that, artificial DNA is synthesized, which contains this data. The coding itself is carried out by Twist Bioscience, which provides synthetic DNA strands. Customers report the sequence, the company produces a chain from scratch. What kind of information is encoded in such molecules, Twist Bioscience does not know. To determine the end and the beginning of the recorded files, special markers are introduced into the DNA molecule.
According to Luis Henrique Ceze, one of the project participants, over the past few years, genetics have achieved great success in both coding and decoding DNA information. The accuracy of encoding information reaches 100%. Data decryption technology allows you to recover coded information without loss. But for the time being, it cannot be widely used - it can only be done under laboratory conditions. It will have to work for several years until the moment when the technology of recording data in DNA is brought to a level accessible for mass use.
“Using new technologies of affordable DNA sequencing and synthesis, Twist Bioscience and Microsoft can now put into practice the theory of storing information in DNA. The main goal is to develop methods that are practical. and scalable. The ability to encode digital information in DNA strands is a breakthrough in the field of data storage, since DNA molecules lack the drawbacks of most modern data storage ... Since practically all life on Earth exists due to DNA, there will always be technologies for reading DNA, so you can be sure about availability saved data. Moreover, with the increasing relevance of DNA technologies in scientific and medical research, methods for reading / writing information in DNA strands will be constantly improved. These technologies are in demand in many areas of human activity ",
Methods of working with genetic information are improving, and the cost of reading DNA is reduced. The human genome decoding project in 2003 cost $ 1 billion. Now the cost of decoding the genome of the same complexity is only $ 1000.

Theoretically, one gram of DNA can accommodate one billion terabytes of data. Under certain conditions, the record can be stored for thousands of years. But the issue of efficiently recording and reading information from DNA has not yet been resolved. Now Microsoft and the University of Washington are working on this problem. In April of this year, the partners managed to store 150 KB of information in DNA - three pictures. Now the process has been improved, and 202 MB have already been recorded. A high-resolution OK Go music video was recorded in deoxyribonucleic acid molecules, which included the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, translated into 100 languages, the top 100 books of The Gutenberg Project, and Crop Trust’s DNA database .
The project for recording information in DNA was named Project Palix.
The work was carried out with synthetic DNA purchased from Twist Bioscience in the amount of 10 million threads. Synthetic DNA of a certain configuration is developed by request. The cost of a pair of bases of such material is 10 cents. The price is gradually falling, and the manufacturer expects to reach 2 cents for a couple of bases.
Microsoft Corporation and the University of Washington are not the first to decide to use the idea of writing data to DNA. In 2010, biologists from Hong Kong offeredmethod of introducing into the genome of the bacterium E. coli synthetic DNA. The Chinese used four-fold numbering system for coding information, according to the number of nucleotides (0 = A, 1 = T, 2 = C, 3 = G). Scientists translated the test data into figures in the ASCII table (i = 105; G = 71; E = 69; M = 77), then into the four-fold system (105 → 1221; 71 → 0113; 69 → 0111; 77 → 0131), and after that - in a chain of nucleotides.
Two years later, Harvard scientists , using another method, recorded 643 kilobytes of data in DNA. At Harvard, they decided to abandon working with living organisms. Instead, synthetic DNA was introduced into a molecule generated on a special DNA chip. The advantage of this method is the absence of danger of loss of information due to mutations of the carrier.
These scientists were able to encode the book of Church, and with preservation of formatting and illustrations.


Microsoft and the University of Washington use the method proposed by experts from Harvard. First, the ones and zeros of the binary code are translated into combinations of nucleotides - adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. After that, artificial DNA is synthesized, which contains this data. The coding itself is carried out by Twist Bioscience, which provides synthetic DNA strands. Customers report the sequence, the company produces a chain from scratch. What kind of information is encoded in such molecules, Twist Bioscience does not know. To determine the end and the beginning of the recorded files, special markers are introduced into the DNA molecule.
According to Luis Henrique Ceze, one of the project participants, over the past few years, genetics have achieved great success in both coding and decoding DNA information. The accuracy of encoding information reaches 100%. Data decryption technology allows you to recover coded information without loss. But for the time being, it cannot be widely used - it can only be done under laboratory conditions. It will have to work for several years until the moment when the technology of recording data in DNA is brought to a level accessible for mass use.
“Using new technologies of affordable DNA sequencing and synthesis, Twist Bioscience and Microsoft can now put into practice the theory of storing information in DNA. The main goal is to develop methods that are practical. and scalable. The ability to encode digital information in DNA strands is a breakthrough in the field of data storage, since DNA molecules lack the drawbacks of most modern data storage ... Since practically all life on Earth exists due to DNA, there will always be technologies for reading DNA, so you can be sure about availability saved data. Moreover, with the increasing relevance of DNA technologies in scientific and medical research, methods for reading / writing information in DNA strands will be constantly improved. These technologies are in demand in many areas of human activity ",
Methods of working with genetic information are improving, and the cost of reading DNA is reduced. The human genome decoding project in 2003 cost $ 1 billion. Now the cost of decoding the genome of the same complexity is only $ 1000.
