Implementation Details for RSTP and Proprietary Extended Ring Redundancy
On the network you can find a lot of materials about the RSTP protocol. In this article, I propose comparing the RSTP protocol with the proprietary protocol from Phoenix Contact - Extended Ring Redundancy.
RSTP Implementation Details
General Information
Convergence Time - 1-10 c
Possible Topologies - Any
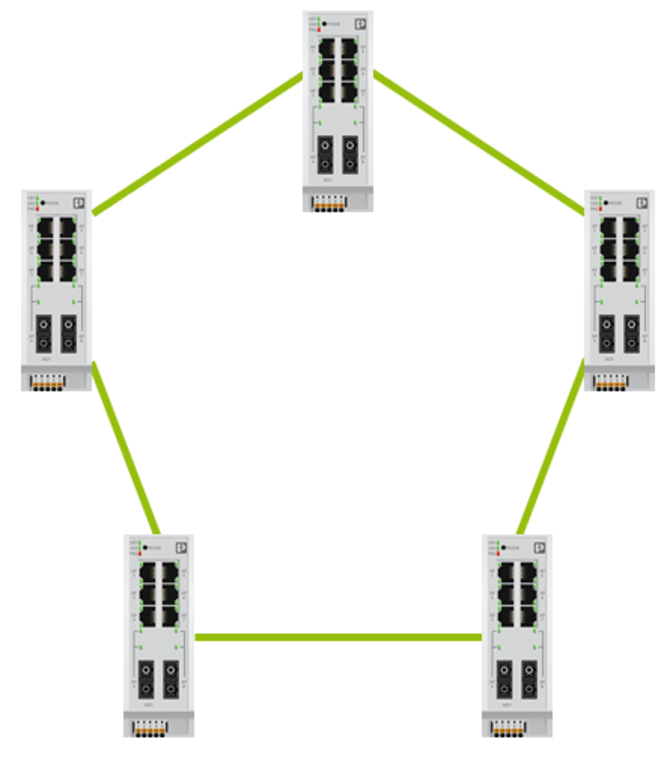
It is widely believed that RSTP allows you to combine switches only in a ring:
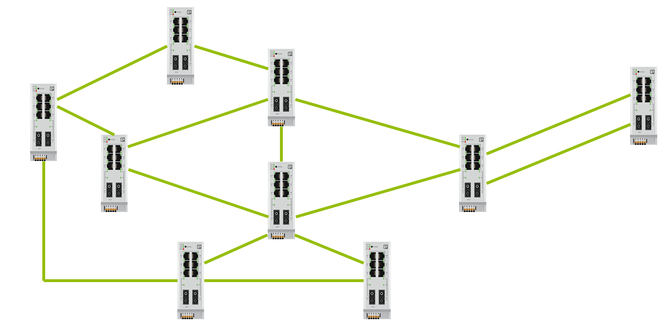
But RSTP allows you to connect switches arbitrarily. For example, RSTP can handle this topology.
The principle of operation of
RSTP reduces any topology to a tree. One of the switches becomes the center of the topology - the root switch. The root switch passes most of the data through itself.
The principle of operation of RSTP is as follows:
Choosing a Root Switch
RSTP switches exchange BPDU packets. BPDU is a service package that contains RSTP information. BPDUs come in two types:
Configuration BPDU is used to build the topology. Only the root switch sends it. Configuration BPDU contains:
Topology Change Notification can be sent by any switch. They are sent when the topology changes.
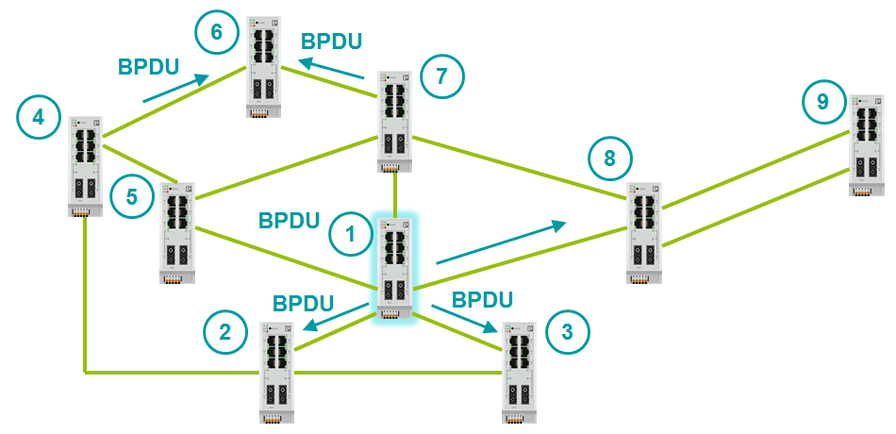
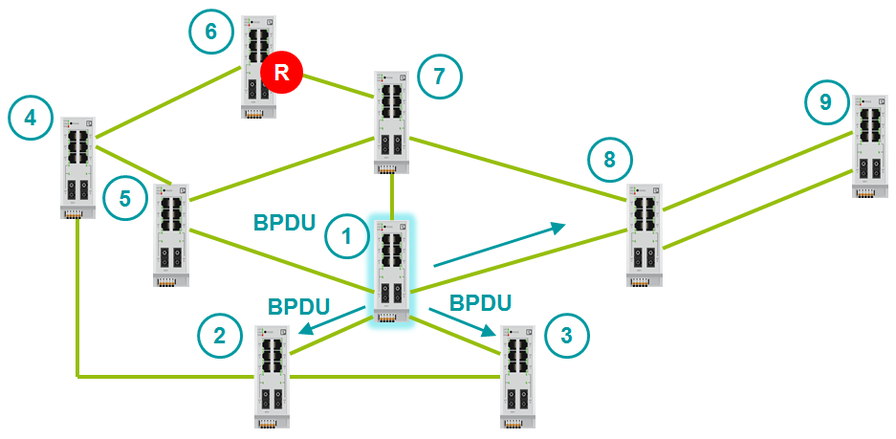
After switching on, all switches consider themselves root. They begin to transmit BPDU packets. As soon as the switch receives a BPDU with a smaller Bridge ID than its own, it ceases to consider itself root.
Bridge ID consists of two values - MAC address and Bridge Priority. We can’t change the MAC address. Bridge Priority is 32768 by default. If you do not change Bridge Priority, the switch with the lowest MAC address will become the root. The switch with the lowest MAC address is the oldest and perhaps not the most productive. It is recommended that you manually determine the topology root switch. To do this, you need to configure a small Bridge Priority on the root switch (for example, 0). You can also define a backup root switch by giving it a slightly larger Bridge Priority (for example, 4096).
Choosing a path to the root switch
The root switch sends BPDU packets to all active ports. BPDU has a Path Cost field. Path Cost means the cost of the path. The higher the cost of the path, the longer the packet is transmitted over it. When the BPDU passes through the port, the cost is added to the Path Cost field. The added number is called Port Cost.
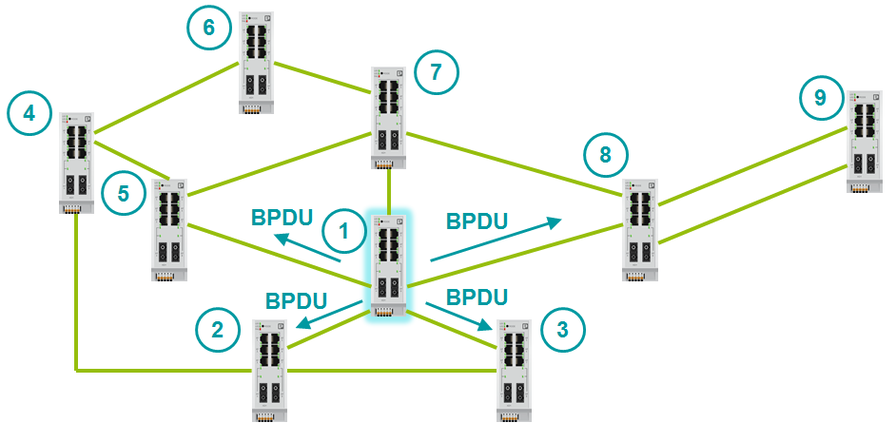
Adds a specific value to Path Cost when a BPDU passes through a port. The value that adds is called the Port Cost and can be determined either manually or automatically. Port Cost can be determined both manually and automatically.
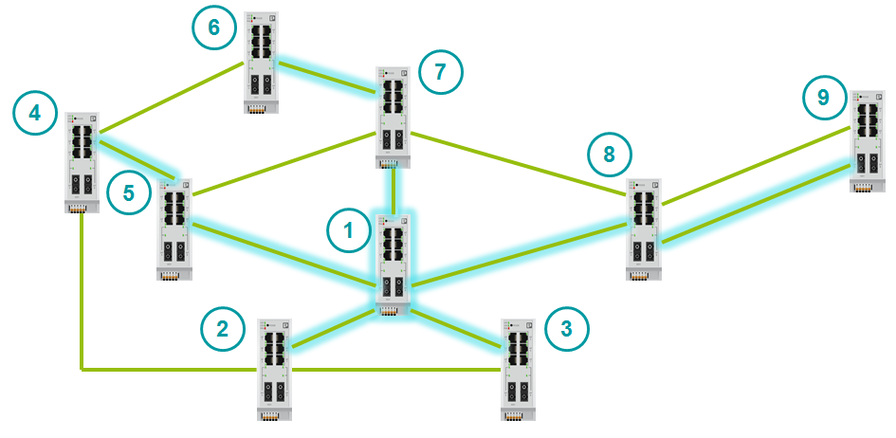
When a non-root switch has several alternative paths to the root, it chooses the fastest. He compares the path cost of these paths. The port from which the BPDU came with the lowest Path Cost becomes the root (Root Port).
The cost of the ports that are assigned automatically can be found in the table:
Port Roles and Statuses
Switch ports have several port statuses and roles.
Port Statuses (for STP):
STP convergence time is 30-50 seconds. After the switch is turned on, all ports go through all the statuses. In each status, the port is a few seconds. Because of this operating principle, STP has such a long convergence time. RSTP has fewer port statuses.
Port Statuses (for RSTP):
Port Roles:
Root Port selection is described above. How is Designated port selected?
First of all, let's define what a LAN segment is. The LAN segment is a collision domain. For a switch or router, each port forms a separate collision domain. LAN segment - a channel between switches or routers. If we talk about the hub, then the hub all the ports are in the same collision domain.
Only one Designated Port is assigned to one segment.
In the case of segments where there are already Root Ports, everything is clear. The second port of the segment becomes Designated Port.
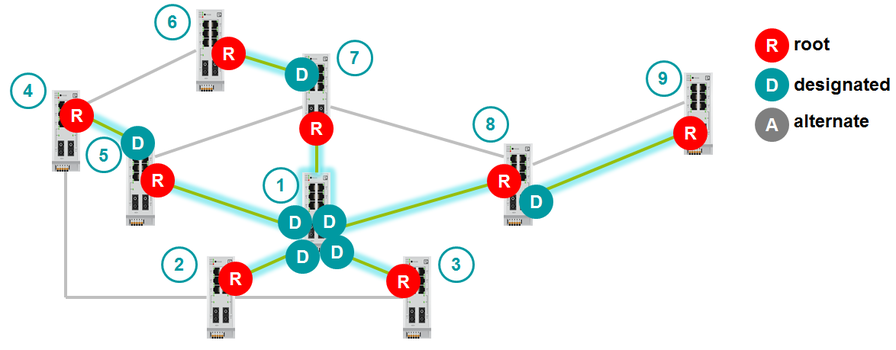
But there are backup channels where there will be one Designated Port and one Alternate Port. How will they be chosen? Designated Port will become the port with the smallest Path Cost to the root switch. If the Path Costs are equal, then the Designated Port will be the port that resides on the switch with the lowest Bridge ID. If Bridge ID are equal, then Designated Port becomes the port with the lowest number. The second port will be Alternate.
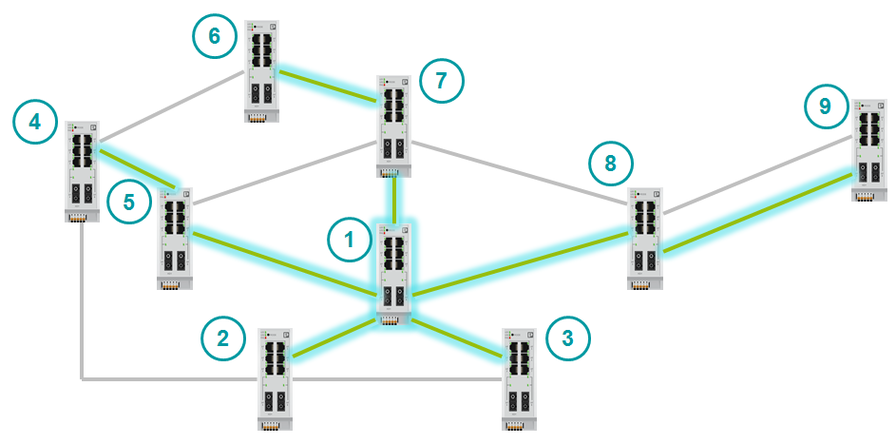
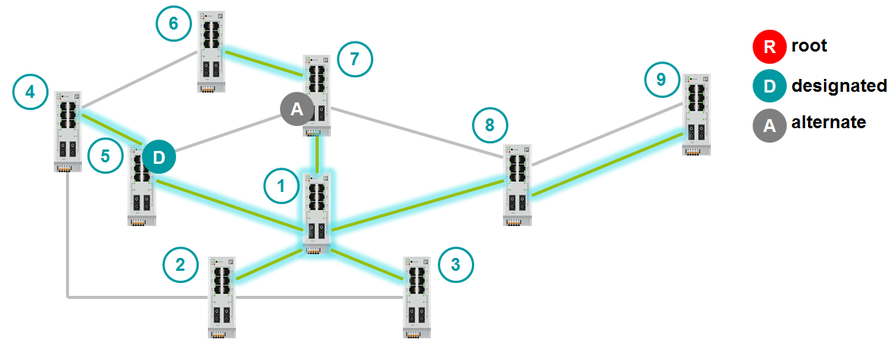
The last moment remains: when is the backup role assigned to the port? As already mentioned above, Backup port is used only when two channels of the switch are connected to one segment, that is, to the hub. In this case, the Designated Port is selected exactly according to the same criteria:
Maximum number of devices on a network
The IEEE 802.1D standard does not impose strict requirements on the number of devices on a LAN with RSTP. But the standard recommends using no more than 7 switches in one branch (no more than 7 hop), i.e. no more than 15 in the ring. If this value is exceeded, the network convergence time begins to increase.
Details of the implementation of ERR.
General information
Convergence
time ERR convergence time - 15 ms. With the maximum number of switches in the ring and the presence of pairing rings - 18 ms.
Possible topologies
ERR does not allow devices to be freely combined as RSTP. ERR has clear topologies that you can use:
Ring
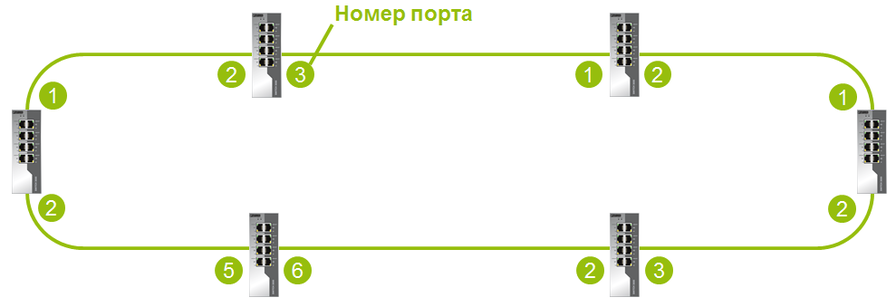
When ERR combines all the switches in one ring, then on each switch it is necessary to configure the ports that will participate in the construction of the ring.
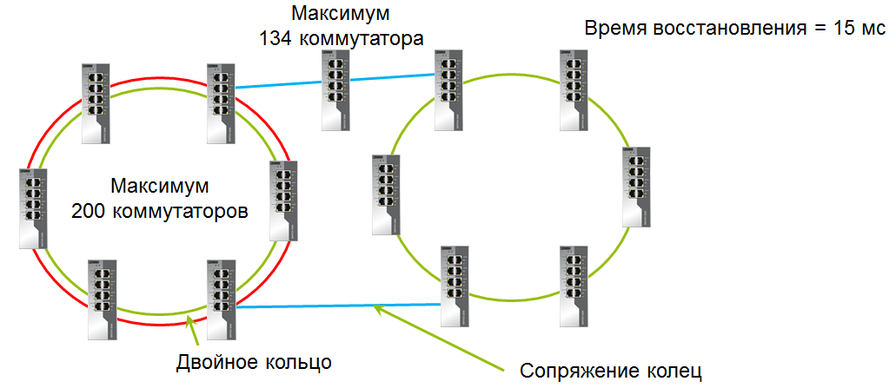
Double ring
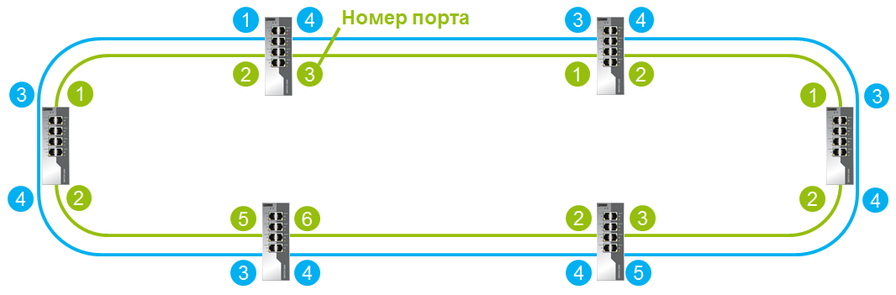
Switches can be combined into a double ring, which greatly increases the reliability of the ring.
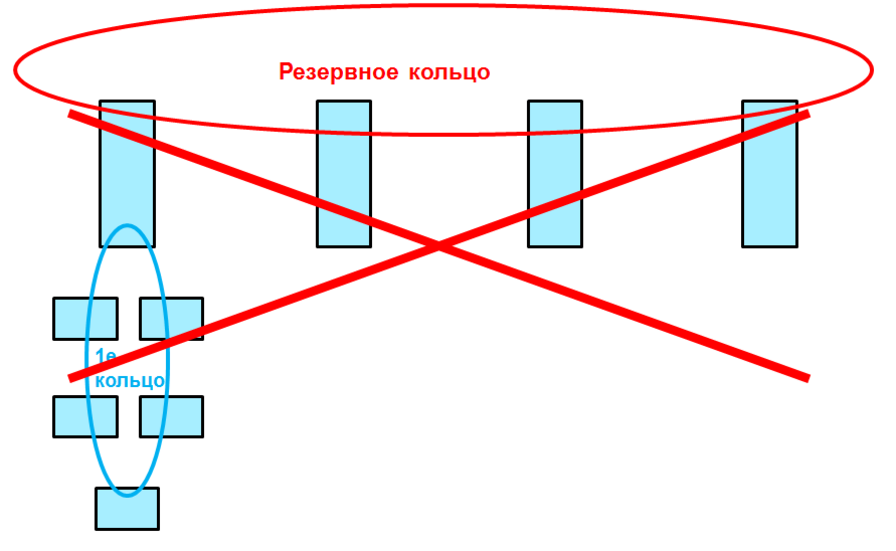
Double Ring Limitations:
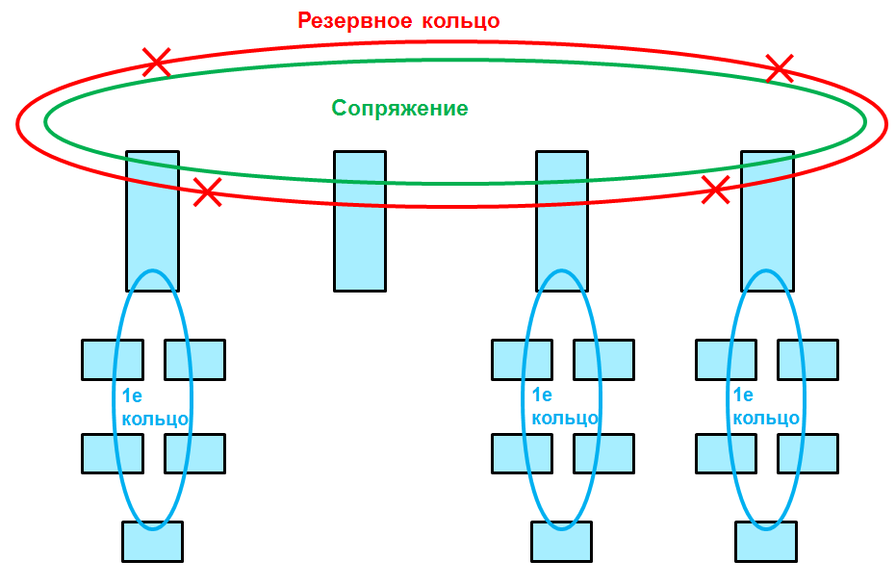
Pairing rings
When pairing in the network can be no more than 200 devices.
Pairing rings implies combining the remaining rings into another ring.
If the ring is connected to the pairing ring through one switch, then this is called pairing the rings through one switch . If two switches from the local ring are connected to the pairing ring, this will be pairing through two switches .
When pairing through one switch on the device, both ports are enabled. The convergence time in this case will be approximately 15-17 ms. With this pairing, the pairing switch will be a point of failure, because having lost this switch, the entire ring is lost immediately. Pairing through two switches avoids this.
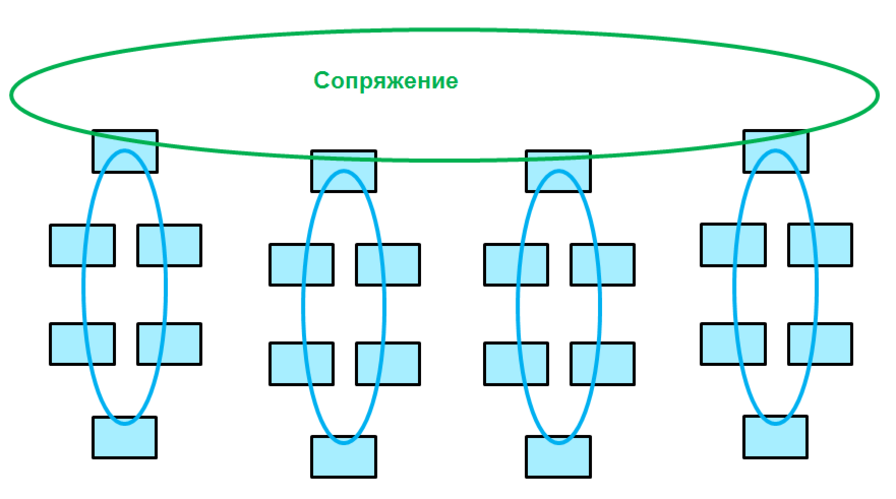

It is possible to match duplicate rings.

Path Control

The Path Control function allows you to configure the ports through which data will be transmitted in normal operation. If the channel fails and the network is rebuilt to the backup topology, then after the restoration of the channel, the network is rebuilt back to the specified topology.
This feature saves on redundant cable. Moreover, the topology used for Troubleshoot will always be known.
The main topology switches to backup in 15 ms. Reverse switching during network recovery will take about 30 ms.
Limitations:
The principle of operation

The principle of operation of ERR
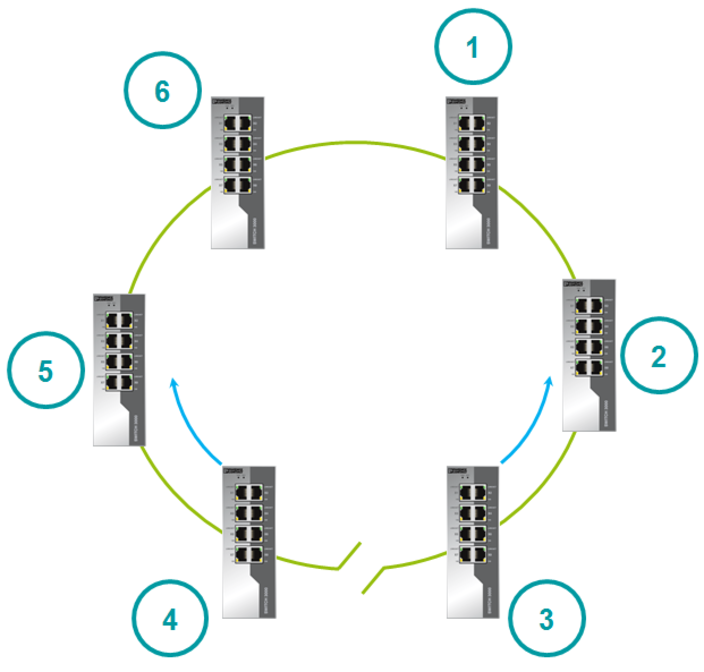
For example, consider six switches - 1-6. The switches are ringed together. Each switch uses two ports to connect to the ring and stores their statuses. Switches forward port statuses to each other. This device data is used to set the initial state of the ports.
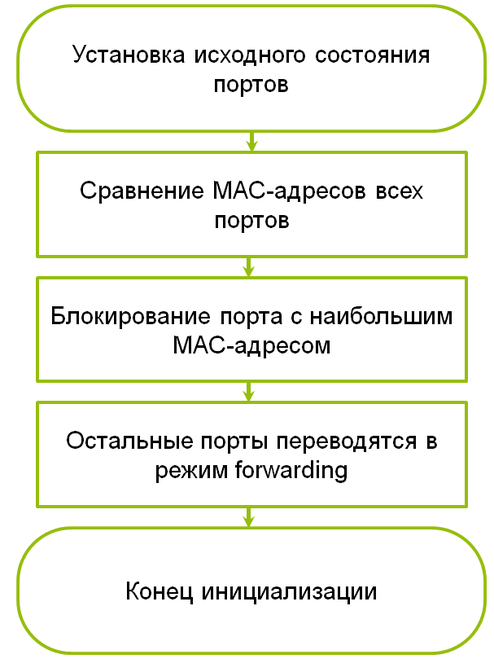
Ports have only two roles - Blocked and Forwarding .
The switch with the highest MAC address blocks the port. All other ports in the ring transmit data.
If the Blocked port stops working, then the next port with the largest MAC address becomes Blocked.
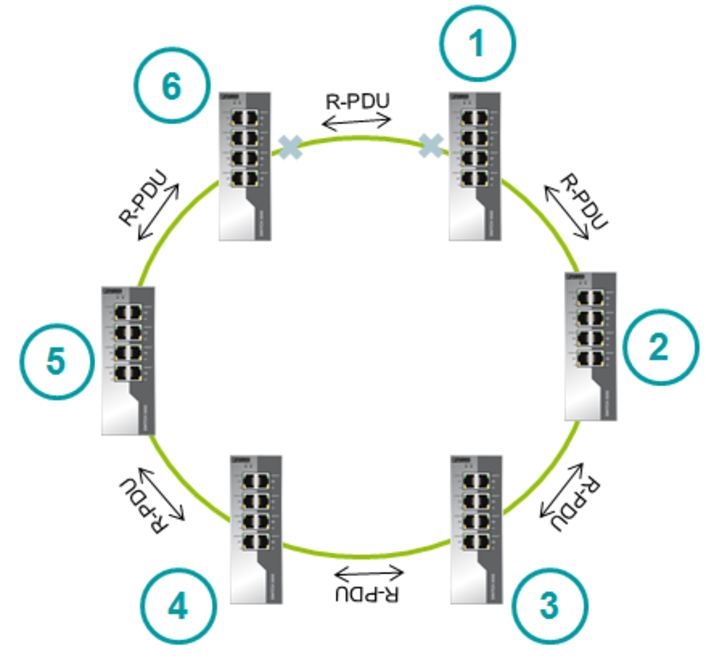
After booting, the switches begin to send the Ring Protocol Data Unit (R-PDU). R-PDU is transmitted using multicast. The R-PDU is a service message, like the BPDUs in RSTP. The R-PDU contains the port statuses of the switch and its MAC address.
Channel Failure Algorithm
When a channel fails, the switches send an R-PDU to notify them of port status changes.
Channel recovery algorithm
When a failed channel is put into operation, the switches send an R-PDU to notify them of a change in port status.
The switch with the highest MAC address becomes the new root switch.
A failed channel becomes a backup.
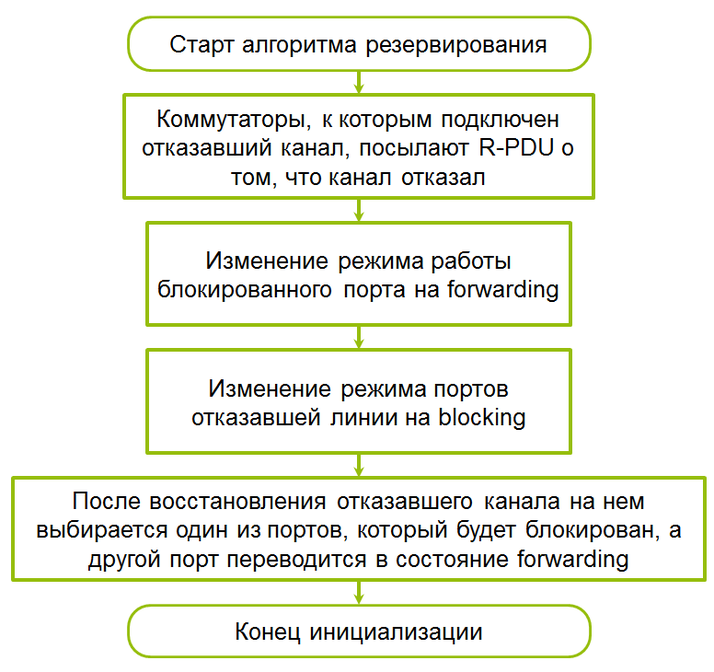
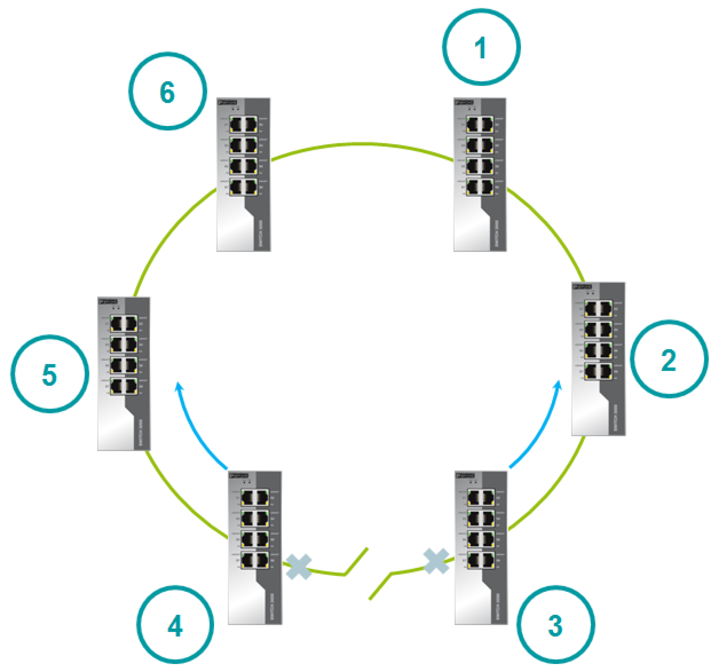
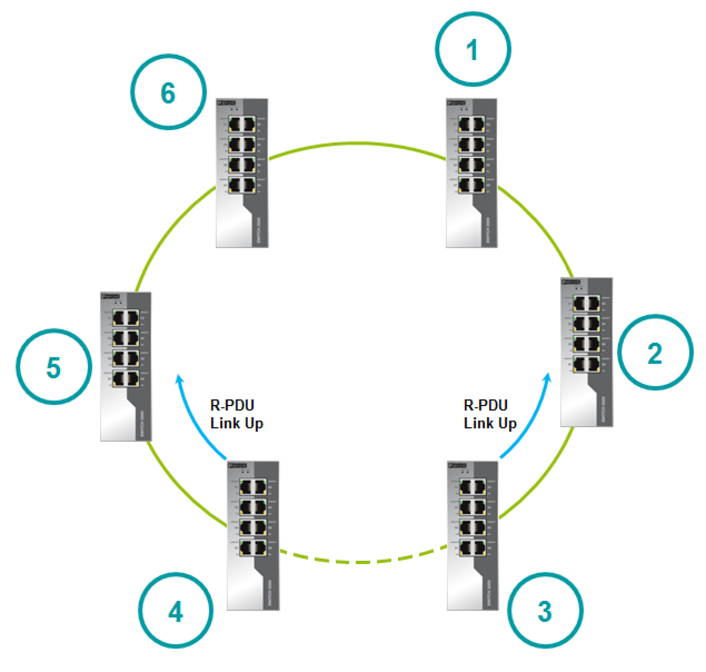
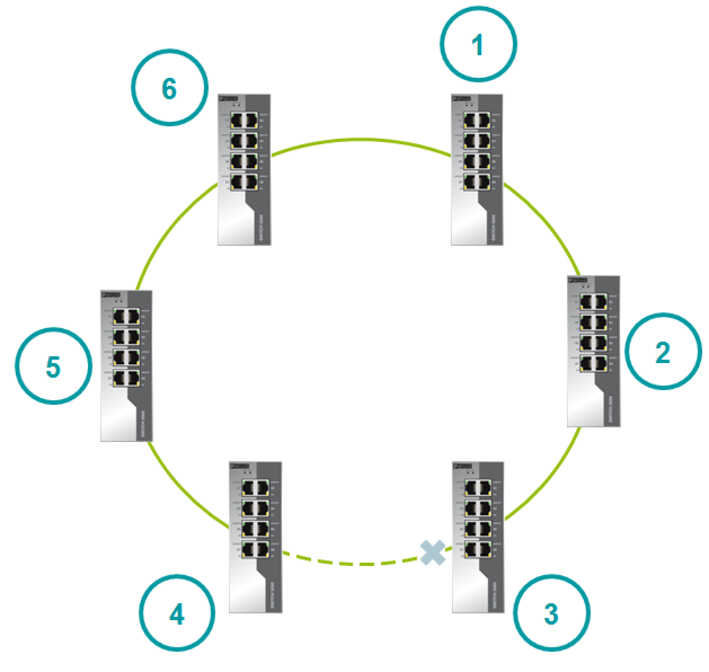
After recovery, one of the channel ports remains blocked, and the second is put into forwarding state. A blocked port becomes the port with the highest speed. If the speeds are equal, then the switch port with the highest MAC address will become blocked. This principle allows you to block a port that goes from blocked to forwarding at maximum speed.
The maximum number of devices on the network The
maximum number of switches in the ERR ring is 200.
Interaction of ERR and RSTP
RSTP can be used in combination with ERR. But the RSTP ring and the ERR ring must cross only through one switch.
Summary
ERR is great for organizing typical topologies. For example, a ring or a duplicated ring.
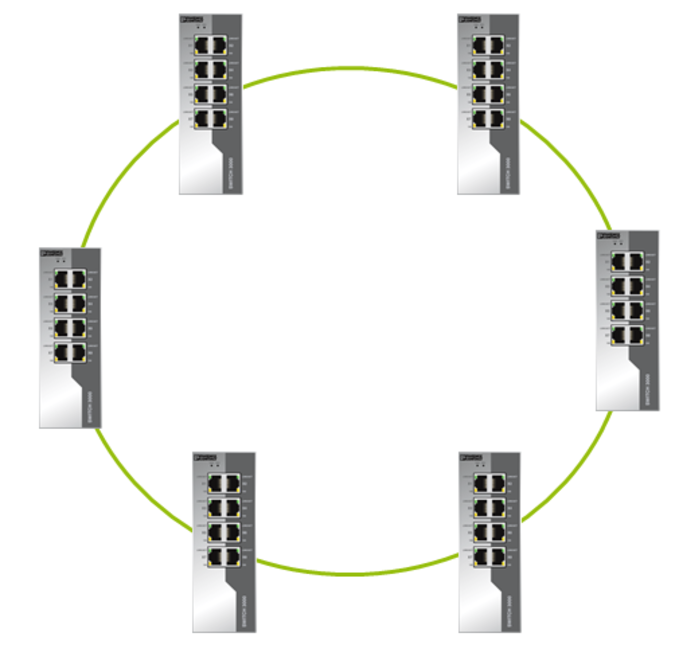

Similar topologies are often used for redundancy in industrial facilities.
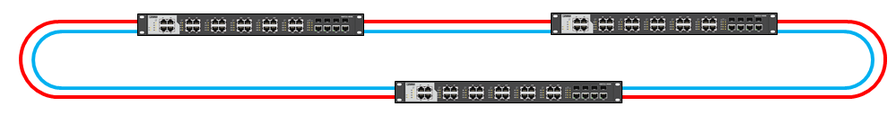
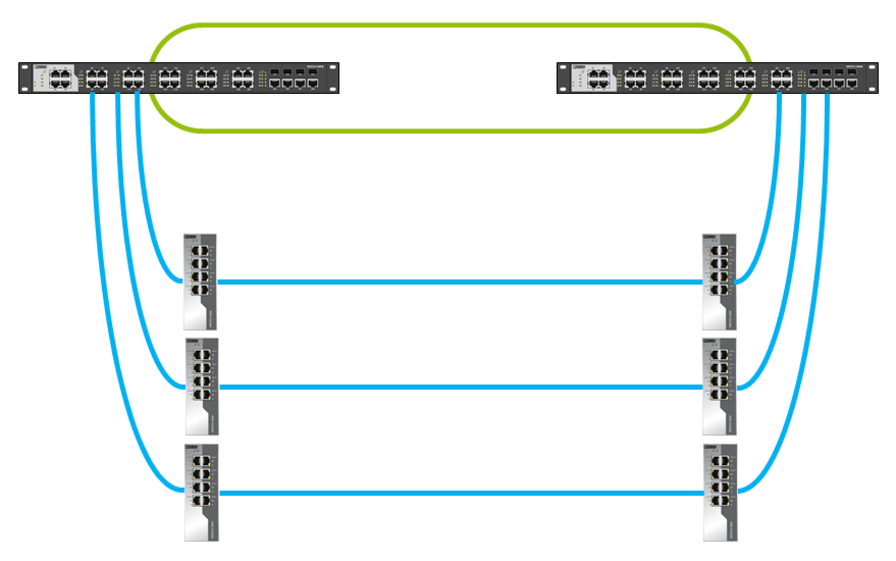
Moreover, with the help of ERR, the second topology can be implemented less reliably, but more budgetally. This can be done using a duplicated ring.
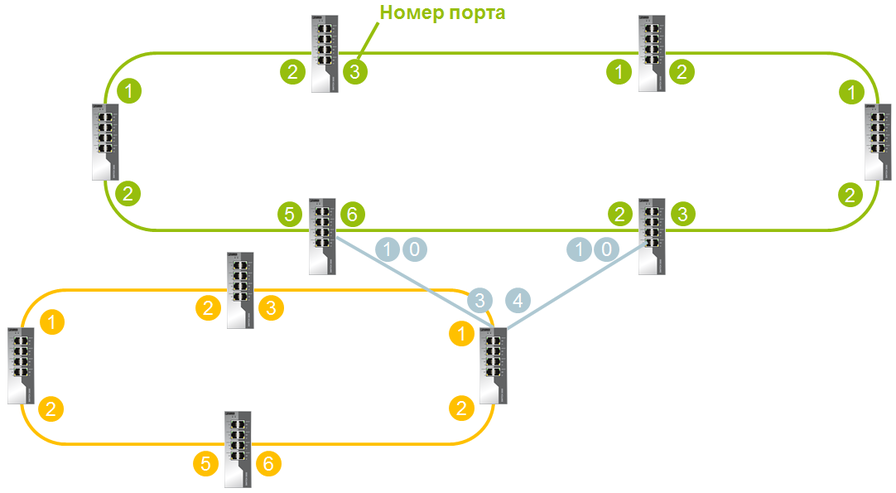
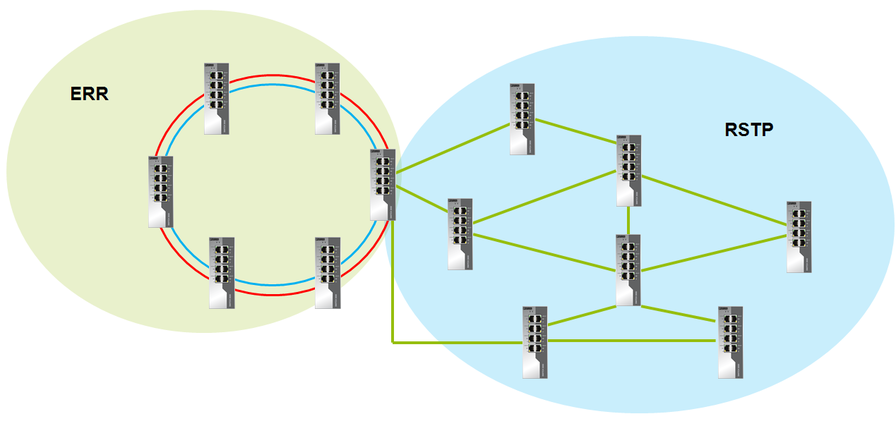
But it is not always possible to apply ERR. There are quite exotic schemes. With one of our customers, we tested the following topology.
In this case, ERR is not possible to apply. For such a scheme, we used RSTP. The customer had a strict convergence time requirement of less than 3 s. To achieve this time, it was necessary to clearly identify the root switches (primary and backup), as well as the cost of ports in manual mode.
As a result, ERR noticeably wins in convergence time, but does not provide the flexibility that RSTP provides.
RSTP Implementation Details
General Information
Convergence Time - 1-10 c
Possible Topologies - Any
It is widely believed that RSTP allows you to combine switches only in a ring:

But RSTP allows you to connect switches arbitrarily. For example, RSTP can handle this topology.

The principle of operation of
RSTP reduces any topology to a tree. One of the switches becomes the center of the topology - the root switch. The root switch passes most of the data through itself.
The principle of operation of RSTP is as follows:
- power is supplied to the switches;
- the root switch is selected;
- other switches determine the fastest path to the root switch;
- the remaining channels are blocked and become redundant.
Choosing a Root Switch
RSTP switches exchange BPDU packets. BPDU is a service package that contains RSTP information. BPDUs come in two types:
- Configuration BPDU.
- Topology Change Notification.
Configuration BPDU is used to build the topology. Only the root switch sends it. Configuration BPDU contains:
- Sender ID (Bridge ID);
- Root Bridge ID
- identifier of the port from which the packet was sent (Port ID);
- the cost of the route to the root switch (Root Path Cost).
Topology Change Notification can be sent by any switch. They are sent when the topology changes.
After switching on, all switches consider themselves root. They begin to transmit BPDU packets. As soon as the switch receives a BPDU with a smaller Bridge ID than its own, it ceases to consider itself root.
Bridge ID consists of two values - MAC address and Bridge Priority. We can’t change the MAC address. Bridge Priority is 32768 by default. If you do not change Bridge Priority, the switch with the lowest MAC address will become the root. The switch with the lowest MAC address is the oldest and perhaps not the most productive. It is recommended that you manually determine the topology root switch. To do this, you need to configure a small Bridge Priority on the root switch (for example, 0). You can also define a backup root switch by giving it a slightly larger Bridge Priority (for example, 4096).

Choosing a path to the root switch
The root switch sends BPDU packets to all active ports. BPDU has a Path Cost field. Path Cost means the cost of the path. The higher the cost of the path, the longer the packet is transmitted over it. When the BPDU passes through the port, the cost is added to the Path Cost field. The added number is called Port Cost.

Adds a specific value to Path Cost when a BPDU passes through a port. The value that adds is called the Port Cost and can be determined either manually or automatically. Port Cost can be determined both manually and automatically.
When a non-root switch has several alternative paths to the root, it chooses the fastest. He compares the path cost of these paths. The port from which the BPDU came with the lowest Path Cost becomes the root (Root Port).



The cost of the ports that are assigned automatically can be found in the table:
| Port Data Rate | Port cost |
|---|---|
| 10 Mb / s | 2,000,000 |
| 100 Mb / s | 200,000 |
| 1 Gb / s | 20,000 |
| 10 Gb / s | 2,000 |
Port Roles and Statuses
Switch ports have several port statuses and roles.
Port Statuses (for STP):
- Disabled - Inactive.
- Blocking - listens to BPDU, but does not transmit. Does not transmit data.
- Listening - listens and transmits BPDU. Does not transmit data.
- Learning - listens and transmits BPDU. Prepares for data transfer - fills in the MAC address table.
- Forwarding - transmits data, listens and transmits BPDU.
STP convergence time is 30-50 seconds. After the switch is turned on, all ports go through all the statuses. In each status, the port is a few seconds. Because of this operating principle, STP has such a long convergence time. RSTP has fewer port statuses.
Port Statuses (for RSTP):
- Discarding - Inactive.
- Discarding - listens to BPDU, but does not transmit. Does not transmit data.
- Discarding - listens and transmits BPDU. Does not transmit data.
- Learning - listens and transmits BPDU. Prepares for data transfer - fills in the MAC address table.
- Forwarding - transmits data, listens and transmits BPDU.
- In RSTP, the Disabled, Blocking and Listening statuses are combined into one - Discarding.
Port Roles:
- Root port - port through which data is transmitted. It serves as the fastest route to the root switch.
- Designated port - port through which data is transmitted. Defined for each LAN segment.
- Alternate port - port through which data is not transmitted. It is an alternative path to the root switch.
- Backup port - port through which data is not transmitted. It is the backup path for a segment where one port with RSTP support is already connected. Backup port is used if two channels of the switch are connected to the same segment (read the hub).
- Disabled port - RSTP is disabled on this port.
Root Port selection is described above. How is Designated port selected?
First of all, let's define what a LAN segment is. The LAN segment is a collision domain. For a switch or router, each port forms a separate collision domain. LAN segment - a channel between switches or routers. If we talk about the hub, then the hub all the ports are in the same collision domain.
Only one Designated Port is assigned to one segment.
In the case of segments where there are already Root Ports, everything is clear. The second port of the segment becomes Designated Port.

But there are backup channels where there will be one Designated Port and one Alternate Port. How will they be chosen? Designated Port will become the port with the smallest Path Cost to the root switch. If the Path Costs are equal, then the Designated Port will be the port that resides on the switch with the lowest Bridge ID. If Bridge ID are equal, then Designated Port becomes the port with the lowest number. The second port will be Alternate.


The last moment remains: when is the backup role assigned to the port? As already mentioned above, Backup port is used only when two channels of the switch are connected to one segment, that is, to the hub. In this case, the Designated Port is selected exactly according to the same criteria:
- Least Path Cost to the root switch.
- Least Bridge ID.
- Least Port ID.
Maximum number of devices on a network
The IEEE 802.1D standard does not impose strict requirements on the number of devices on a LAN with RSTP. But the standard recommends using no more than 7 switches in one branch (no more than 7 hop), i.e. no more than 15 in the ring. If this value is exceeded, the network convergence time begins to increase.
Details of the implementation of ERR.
General information
Convergence
time ERR convergence time - 15 ms. With the maximum number of switches in the ring and the presence of pairing rings - 18 ms.
Possible topologies
ERR does not allow devices to be freely combined as RSTP. ERR has clear topologies that you can use:
- Ring
- Duplicated ring
- Pair up to three rings

Ring

When ERR combines all the switches in one ring, then on each switch it is necessary to configure the ports that will participate in the construction of the ring.
Double ring

Switches can be combined into a double ring, which greatly increases the reliability of the ring.
Double Ring Limitations:
- A double ring cannot be used to pair switches with other rings. To do this, use Ring Coupling.
- A double ring cannot be used for a pairing ring.


Pairing rings

When pairing in the network can be no more than 200 devices.
Pairing rings implies combining the remaining rings into another ring.
If the ring is connected to the pairing ring through one switch, then this is called pairing the rings through one switch . If two switches from the local ring are connected to the pairing ring, this will be pairing through two switches .
When pairing through one switch on the device, both ports are enabled. The convergence time in this case will be approximately 15-17 ms. With this pairing, the pairing switch will be a point of failure, because having lost this switch, the entire ring is lost immediately. Pairing through two switches avoids this.


It is possible to match duplicate rings.

Path Control

The Path Control function allows you to configure the ports through which data will be transmitted in normal operation. If the channel fails and the network is rebuilt to the backup topology, then after the restoration of the channel, the network is rebuilt back to the specified topology.
This feature saves on redundant cable. Moreover, the topology used for Troubleshoot will always be known.
The main topology switches to backup in 15 ms. Reverse switching during network recovery will take about 30 ms.
Limitations:
- Cannot be used with Dual Ring.
- The function must be enabled on all switches in the network.
- One of the switches is configured as a Path Control wizard.
- The automatic transition to the main topology after recovery is carried out after 1 second by default (this parameter can be changed using SNMP in the range from 0 s to 99 s).
The principle of operation

The principle of operation of ERR
For example, consider six switches - 1-6. The switches are ringed together. Each switch uses two ports to connect to the ring and stores their statuses. Switches forward port statuses to each other. This device data is used to set the initial state of the ports.

Ports have only two roles - Blocked and Forwarding .
The switch with the highest MAC address blocks the port. All other ports in the ring transmit data.
If the Blocked port stops working, then the next port with the largest MAC address becomes Blocked.
After booting, the switches begin to send the Ring Protocol Data Unit (R-PDU). R-PDU is transmitted using multicast. The R-PDU is a service message, like the BPDUs in RSTP. The R-PDU contains the port statuses of the switch and its MAC address.
Channel Failure Algorithm
When a channel fails, the switches send an R-PDU to notify them of port status changes.
Channel recovery algorithm
When a failed channel is put into operation, the switches send an R-PDU to notify them of a change in port status.
The switch with the highest MAC address becomes the new root switch.
A failed channel becomes a backup.





After recovery, one of the channel ports remains blocked, and the second is put into forwarding state. A blocked port becomes the port with the highest speed. If the speeds are equal, then the switch port with the highest MAC address will become blocked. This principle allows you to block a port that goes from blocked to forwarding at maximum speed.

The maximum number of devices on the network The
maximum number of switches in the ERR ring is 200.
Interaction of ERR and RSTP
RSTP can be used in combination with ERR. But the RSTP ring and the ERR ring must cross only through one switch.

Summary
ERR is great for organizing typical topologies. For example, a ring or a duplicated ring.


Similar topologies are often used for redundancy in industrial facilities.
Moreover, with the help of ERR, the second topology can be implemented less reliably, but more budgetally. This can be done using a duplicated ring.

But it is not always possible to apply ERR. There are quite exotic schemes. With one of our customers, we tested the following topology.

In this case, ERR is not possible to apply. For such a scheme, we used RSTP. The customer had a strict convergence time requirement of less than 3 s. To achieve this time, it was necessary to clearly identify the root switches (primary and backup), as well as the cost of ports in manual mode.
As a result, ERR noticeably wins in convergence time, but does not provide the flexibility that RSTP provides.
