Sound alarm
- Tutorial
- Recovery mode
Sound alarm
This article talks about creating an audible alarm. The project will consist of several parts, one of which is responsible for sound, another for triggering an alarm, and the third for packaging the device in a case.
- Miniature drill, for example proxxon lu-6868.
- Soldering iron, solder, flux.
- Tester and crocodile clamps to it.
- Development board for soldering with leads.
- Solderless breadboard.
- Plastic case for the product.
- Plugs f4, power port.
- A 9-12 volt battery or a power supply of the same rating.
- 1 red, 1 yellow LEDs, one diode 1N4001.
- 8th speaker
- Relay 2 groups of switches (DPDT), 8 contacts, 5 volts direct current tripping.
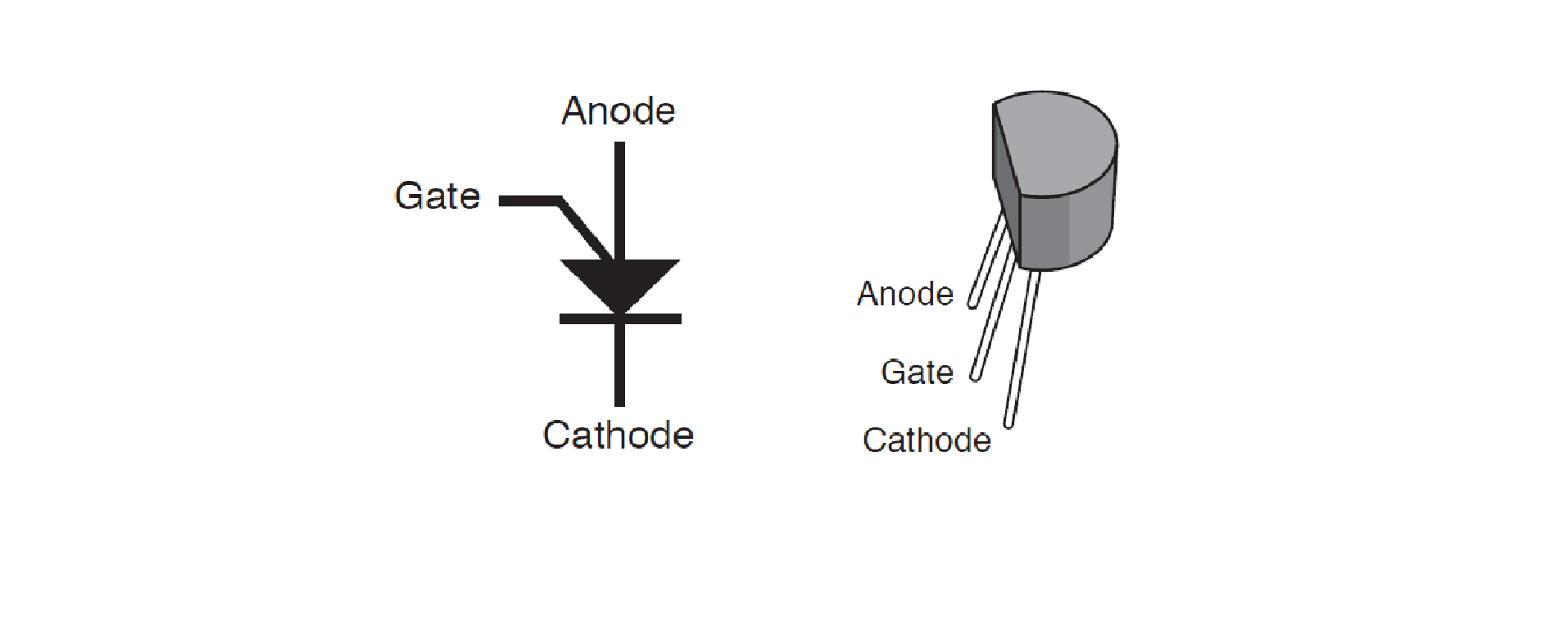
- 2N6027 programmable transistor. Quantity 2.
- Resistors of different ratings, power 0. 250W.
- Electrolytic capacitors of different ratings.
- Ceramic capacitors of different ratings:
- Jumpers - a set.
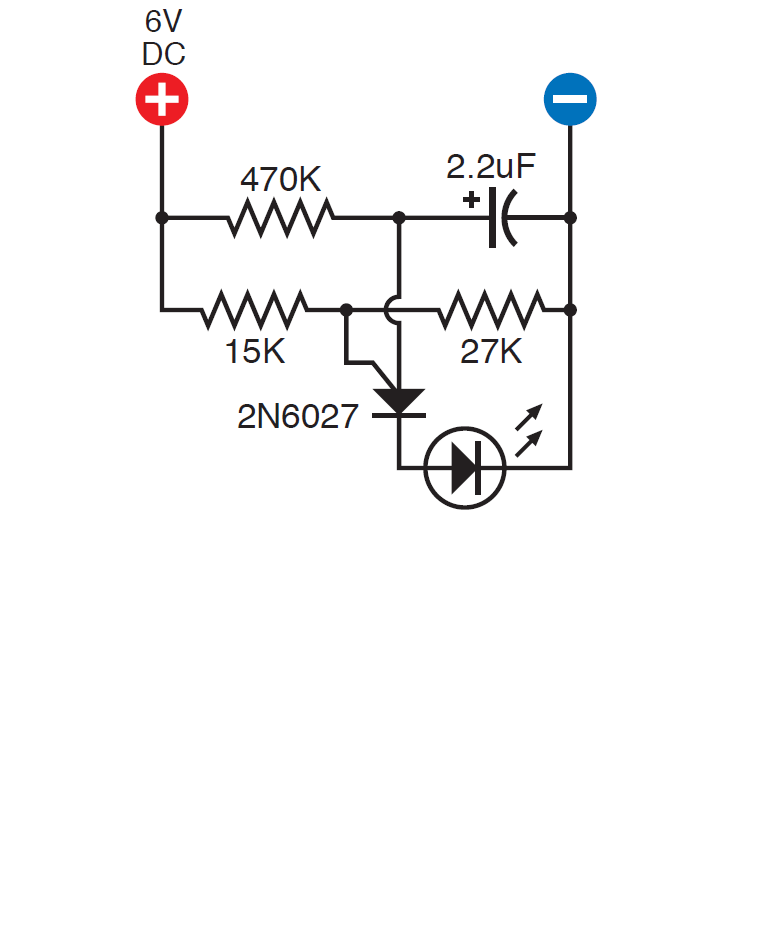
In order to understand how a single-junction transistor works, assemble the circuit on a breadboard.
Click to enlarge.
Click to enlarge.
The LED will blink.
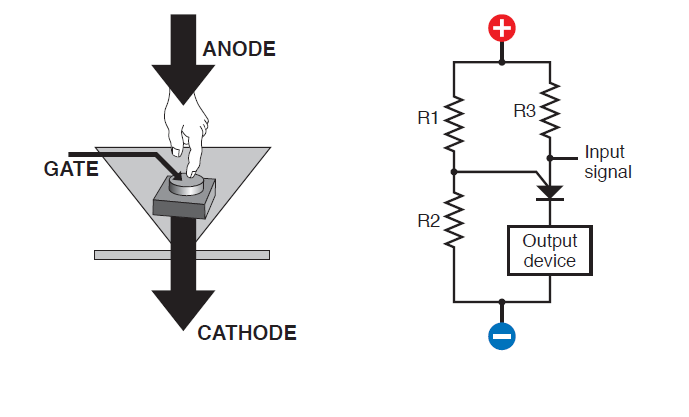
When a certain voltage level is reached, the transistor passes current. If the voltage level drops, the transistor closes. Voltage levels are regulated by a gate.
Click to enlarge.
Click to enlarge.
In the previously assembled circuit, 15 kΩ and 27 kΩ resistors control the voltage at the Gate. A 470 kΩ resistor takes over most of the voltage and therefore the transistor remains closed. The capacitor begins to charge, and at the same time, the voltage between the anode and cathode of the transistor increases. Then the transistor opens (the LED is lit), and the capacitor starts to discharge until the voltage drops and the transistor closes. (LED goes out). And so in a circle.
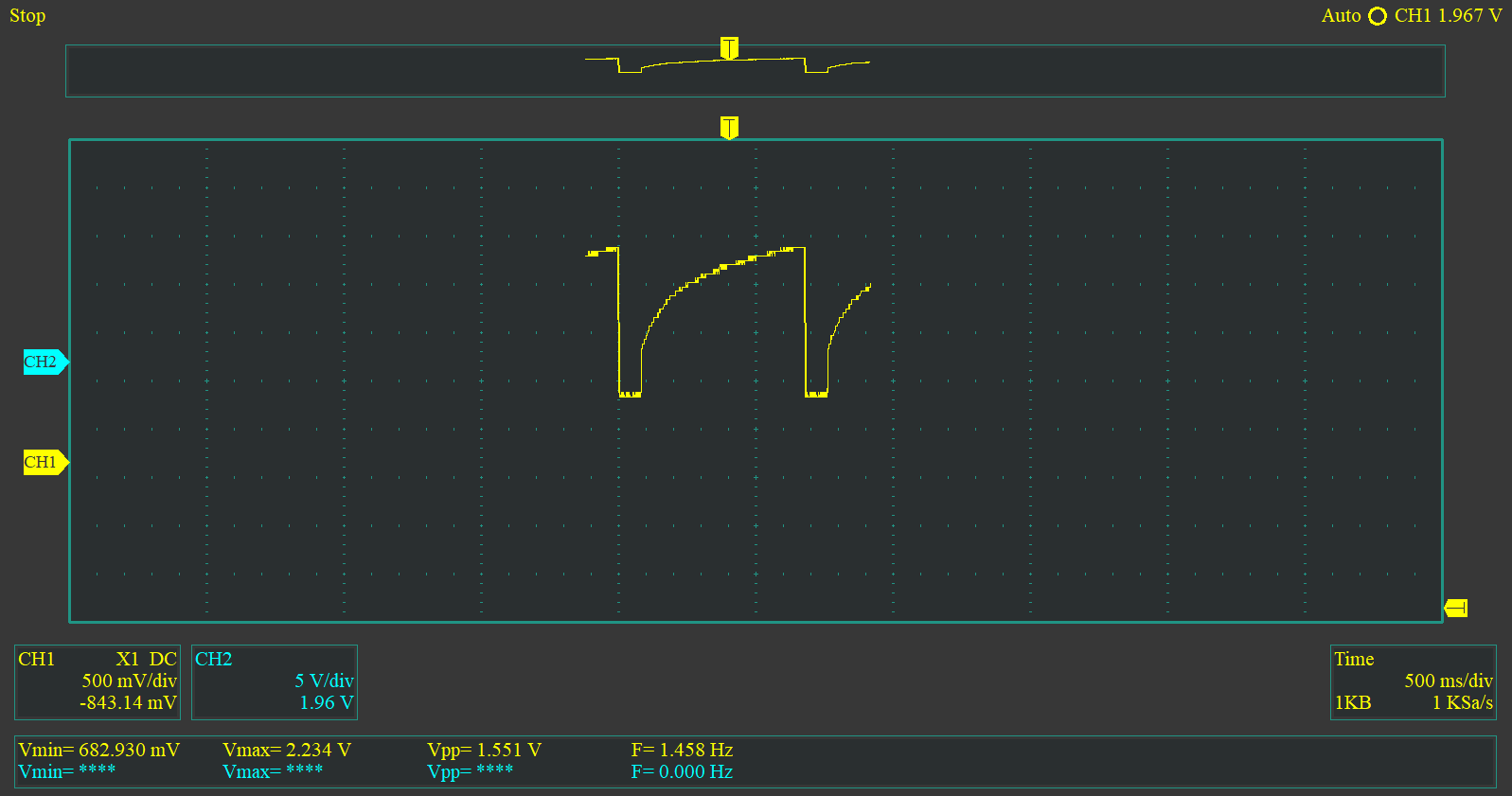
In the following diagram, we add a less capacious capacitor. As is known by the rule of the RC circuit, the smaller the capacitance of the capacitor, the slower it charges. The waveform of the voltage drop on the programmable transistor is shown above.
The human ear can catch a higher frequency of discharge-charge cycles, so we’ll add a different circuit to the speaker.

Click to enlarge.
Holding your ear to the speaker, you will hear a quiet squeak. To amplify the signal, a transistor can be added to the circuit. As you know, the transistor amplifies the current passing through the base.
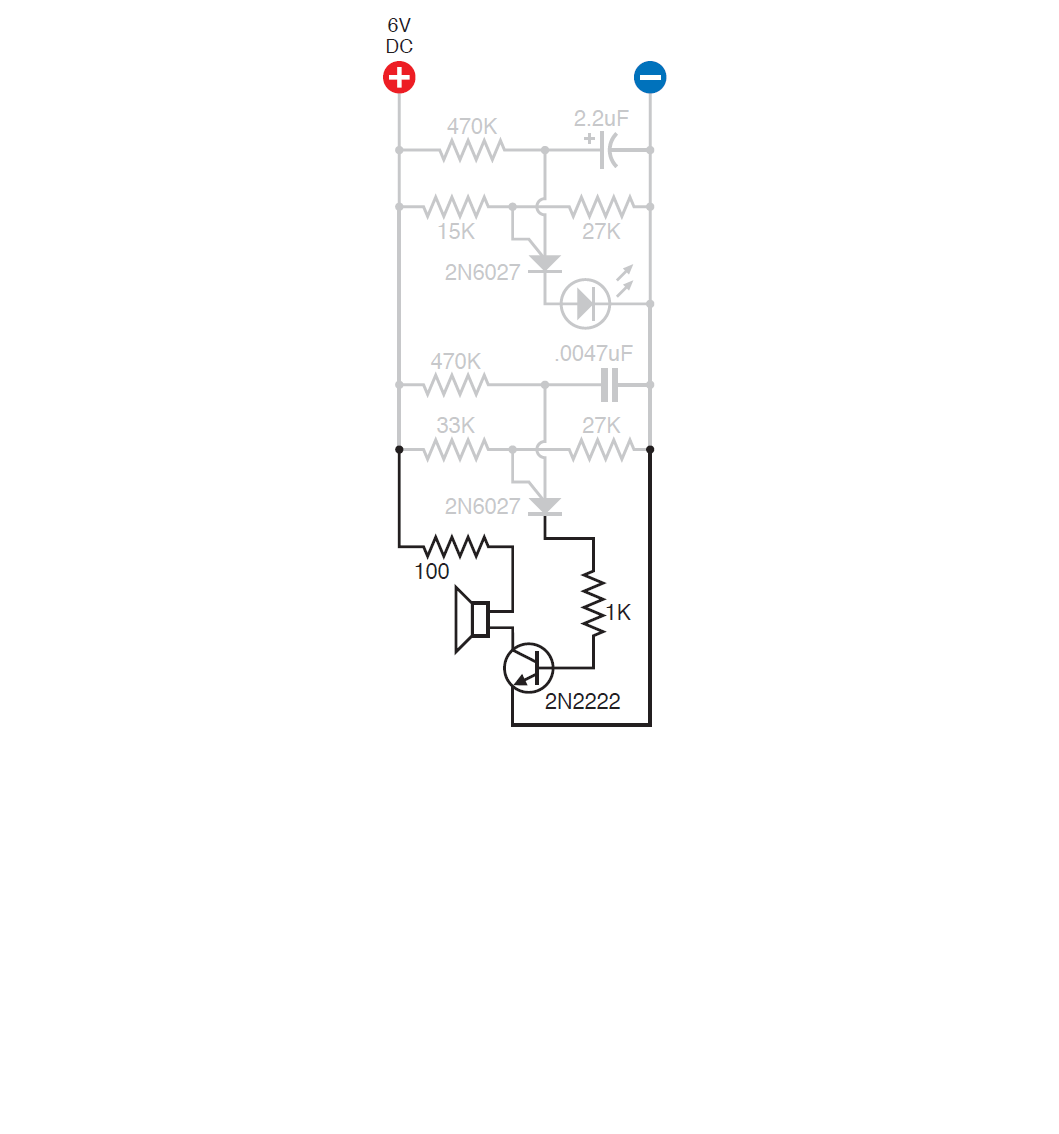
Click to enlarge.
Add another transistor.
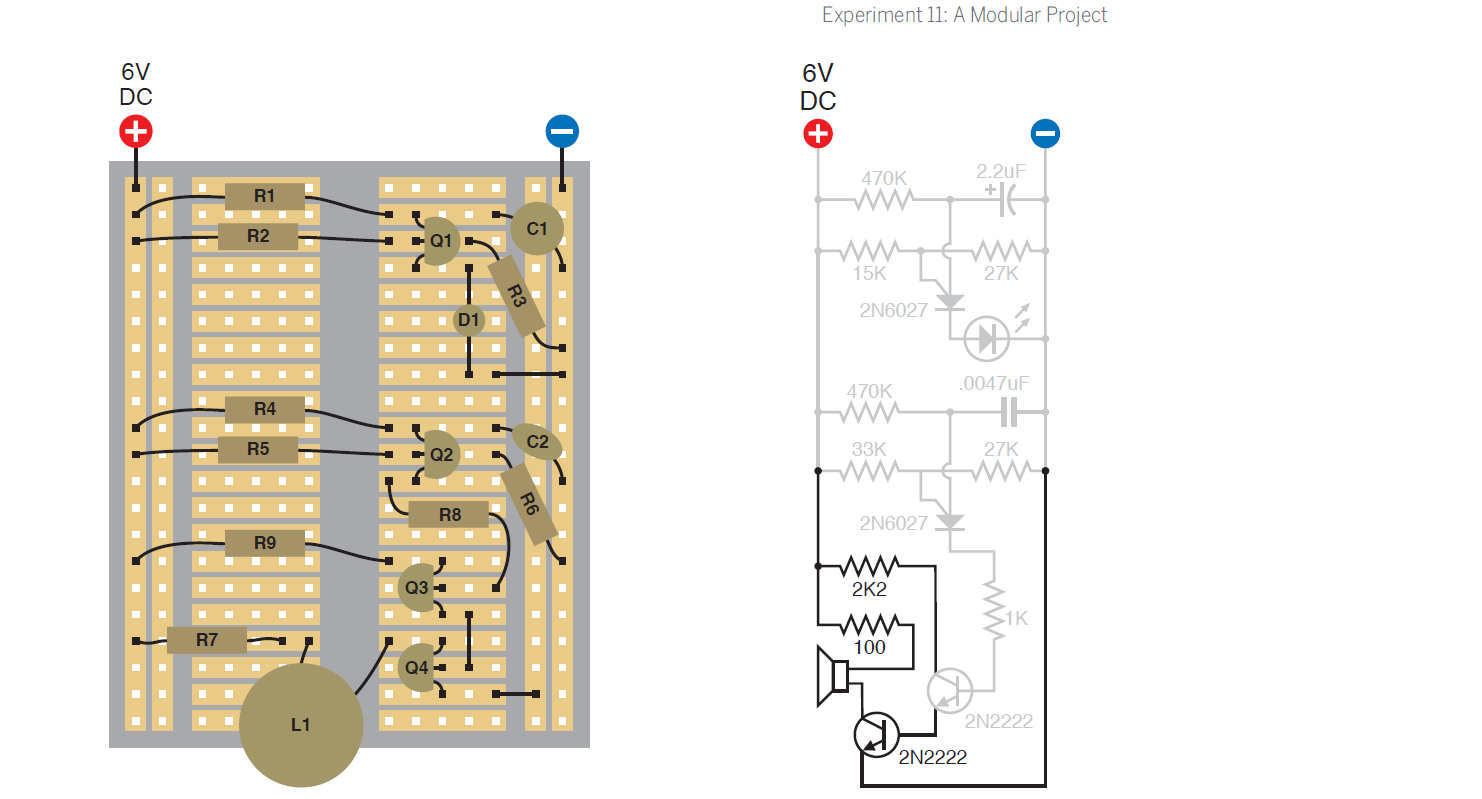
Click to enlarge.
Now audibility has improved significantly.
In order to make the sound look like an alarm, it is necessary to connect the cathode of the first programmable transistor to the Gate of the second transistor. Its oscillations on the Gate will change the pass voltage of the second transistor dynamically, creating a sound of two tones. It is also necessary to add a resistor, and a capacitor in order to smooth the signal.
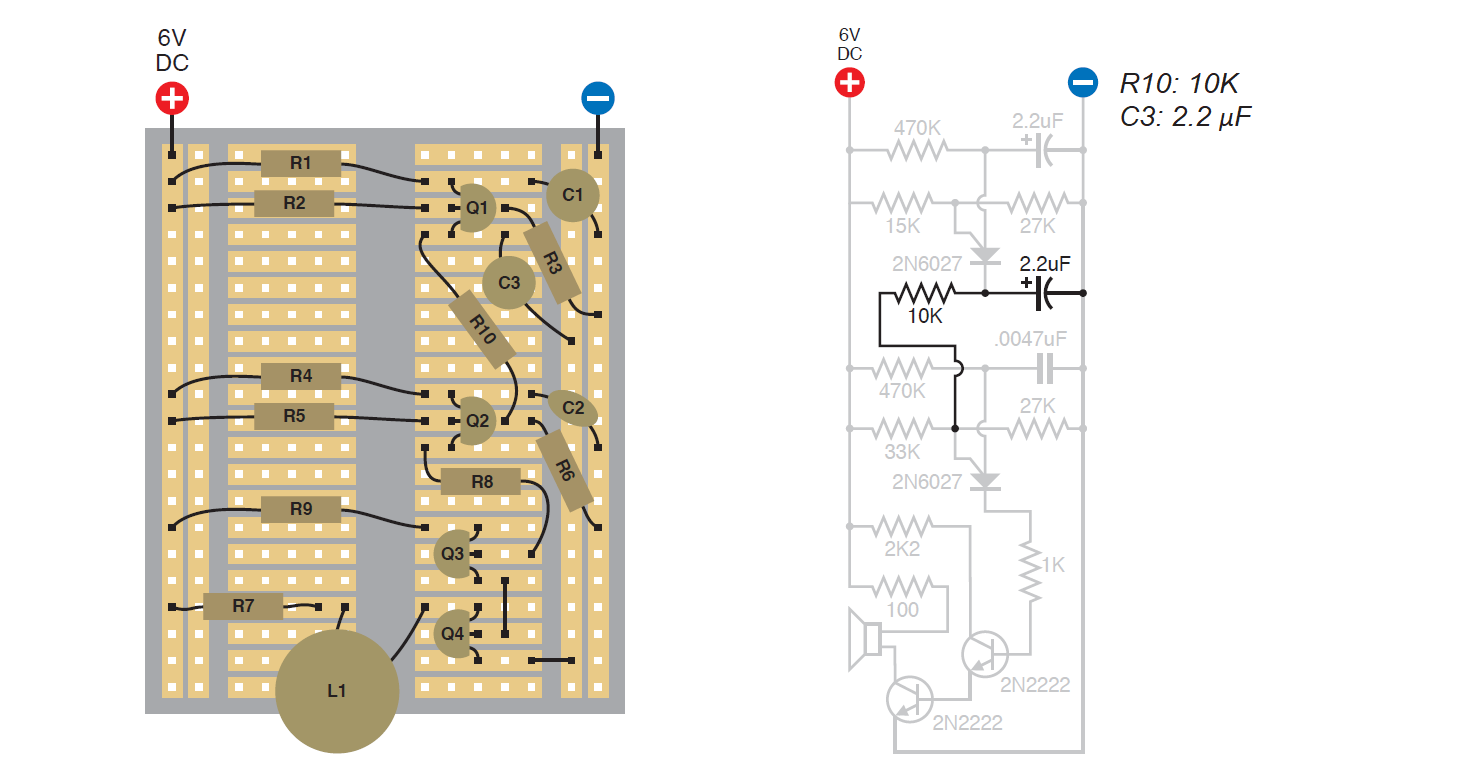
Click to enlarge.
The alarm circuitry is shown below.

Click to enlarge.
The device is activated by magnetic sensors.
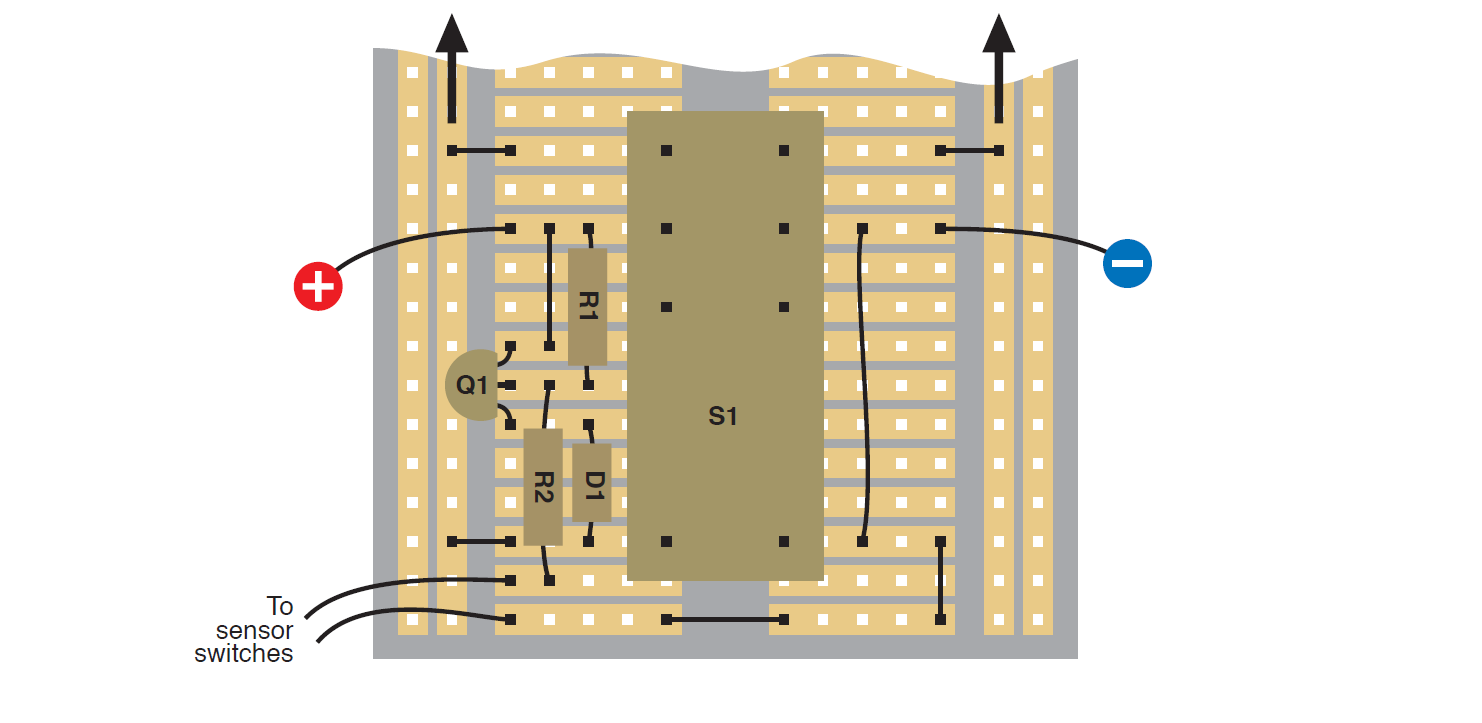
Click to enlarge.
Transfer the entire circuit to the solder board with the leads and create the product.
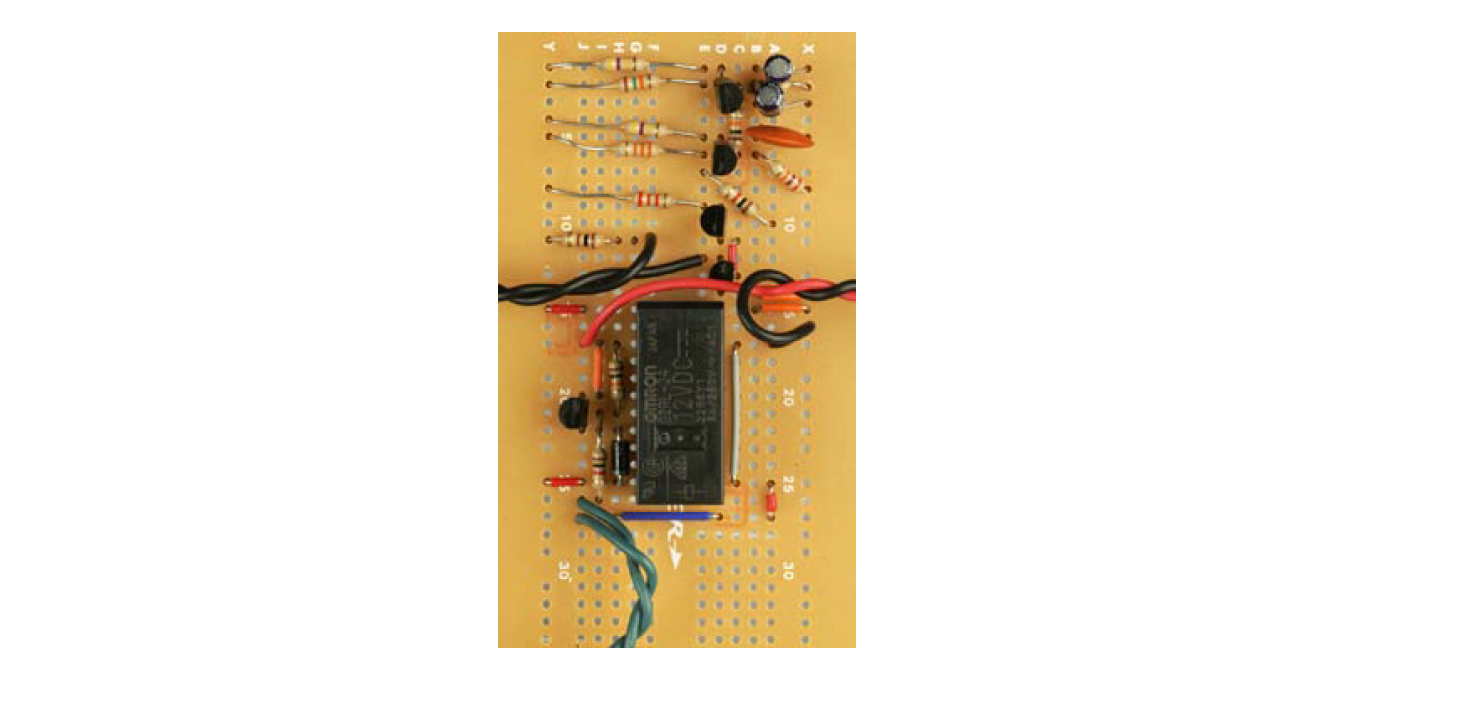
Click to enlarge.
If everything works correctly, in the case of hinged mounting, assemble the following diagram.
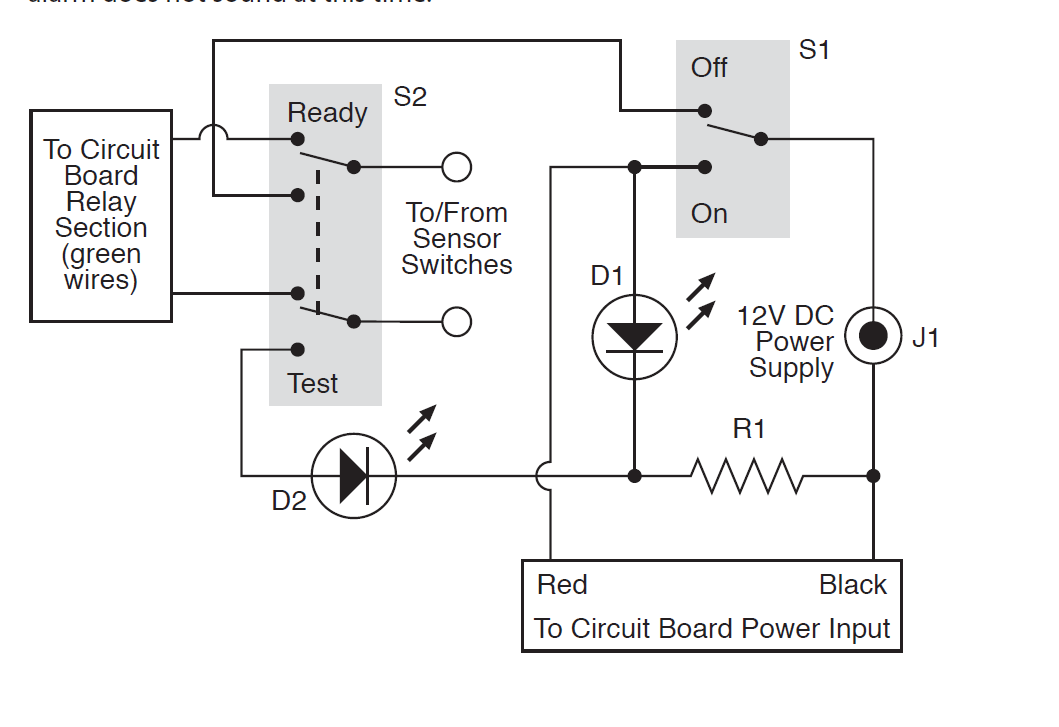
Click to enlarge.
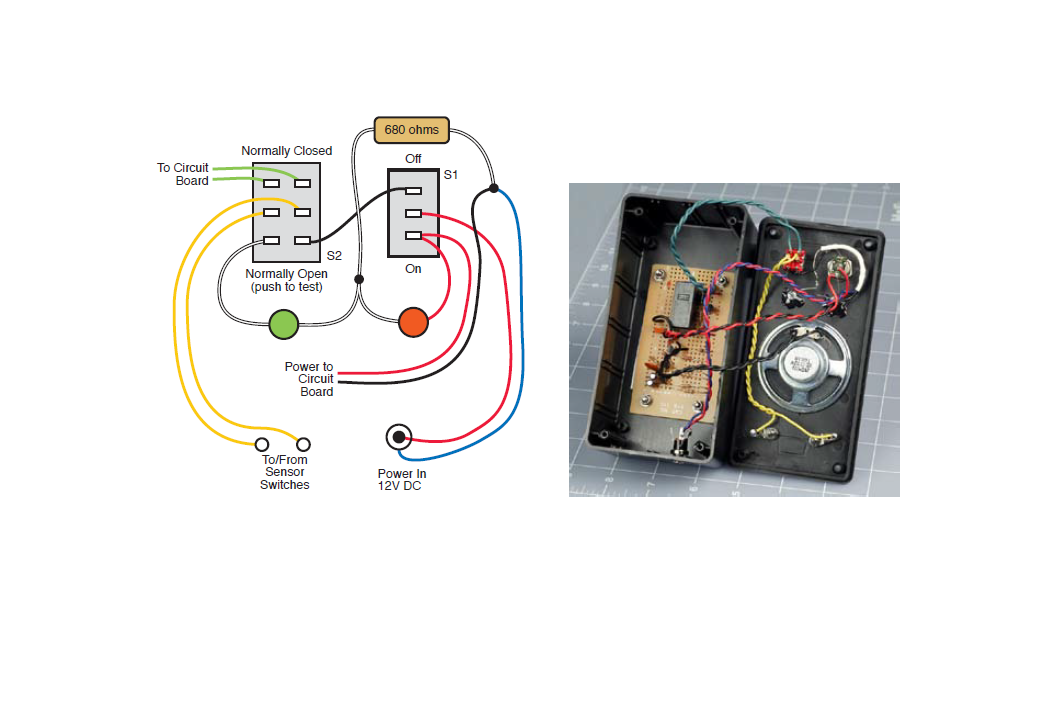
Click to enlarge.
When the button is pressed while the switch is on, the green LED will glow when the sensors are connected. When the switch is in the “on” position, the red LED will glow. When the switches open, an alarm will sound. It also works at the touch of a button. The final result is in the video with my cat Masha.
