5 effective opportunities for using process mining technology
What is process mining
I decided to talk about Process mining in simple words: what kind of technology it is and how it is applied in practice, what are its key tasks. Let's start with the definition. Process mining is a technology for visualizing and analyzing business processes based on the study of information system logs. If the company processes are well automated enough, then process mining gives a realistic picture of what is happening. This picture can be very different from the ideal picture (those business processes that were designed).

Example. One of the standard IT outsourcing processes: Incident Management. The business process diagram, according to the standard, looks harmoniously and clearly (figure from the ITIL Service Operation book):

The model of the same business process, but restored from real data and visualized, looks something like this:
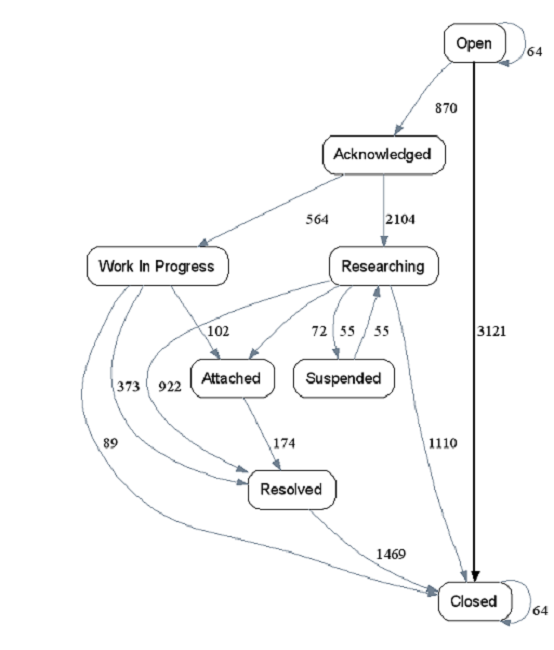
The difference is obvious. And it becomes clear that the theory is quite at odds with practice.
The first figure shows the “ideal” business process diagram, which “ideally” should correspond to all incident processing processes. The process mining technology recreates all business process instances one at a time (the actions for processing each individual incident constitute a separate instance of the real business process) and combines them into a common scheme, shown in the second figure.
There can be many differences between real business processes and planned work:
- strange routes for executing business processes (see the rightmost route: the incident is open and immediately closed);
- significant deviations (omission of mandatory steps, such as approval and confirmation);
- returning the process to the previous steps;
- repetitions, process freezes on one operation, etc.
Process mining provides an opportunity not only to look “inside” the business process, but also to manage it, exploring deviations and bottlenecks and taking steps to eliminate them. The technology has many diverse applications.
Feature 1. Process Audits
Who is useful. Auditors, compliance specialists, and information security specialists.
The bottom line. The restored business processes are compared with the reference ones, special attention is paid to omissions of the required stages of the process (authorization, coordination). Deviations from the standard execution scheme may indicate serious violations, especially in processes related to finances (budgeting, procurement) and in processes that affect security (including information).
Our experience. In our company, process mining is regularly used for internal audits. This is a requirement of ISO standards (9001, 20000, 27001).
Option 2: Continuous Process Improvement
To whom it is useful: to everyone who is involved in process improvements, including:
- teams using various quality management methods (TQM, Lean, Six Sigma, theory of constraints ...);
- business process owners - to optimize “their” processes;
- business consultants - for services to optimize customer business processes.
The bottom line. Process mining technology allows you to visually identify bottlenecks in business processes, collect statistics and analyze in different sections (time ranges, contractors, contractors, etc.). This is the basis for decision making on process optimization.
Our experience. We use Process mining, for example, in the Service Desk teams, to search for trends in incoming calls (incidents) and solve problems. In more detail about application of tools of Lean see in our article on Habr ).
Opportunity 3: customer journeys and usability testing programs
To whom it is useful: to developers of sites and IT systems.
The bottom line. Developers of sites and other information systems can use process mining to verify developed scenarios of user behavior (customer journey), i.e. to observe how users actually interact with the information system (which buttons they use and which ones not, in what order they look at the pages of a website, etc.). Some process mining tools allow you to do this in real time.
Opportunity 4. Selection and preparation of business processes for robotization
Who is useful: consultants, developers of robots for RPA technology, as well as RPA customers.
The bottom line. One of the advanced automation technologies is robot process automation (RPA): the developer writes a robot program that replaces the user in interaction with the information system when performing routine tasks. Process mining helps to find a place in the business process where the use of the robot can have the greatest effect. Some process mining tools allow you to simulate business processes with robotic operations, based on the collected statistics calculating the potential economic effect of connecting the robot.
Our experience.Robots can be launched from employee computers or from a server. A robot running on a company employee’s computer cannot replace it with 100%. He is only capable of performing the tasks that the employee will entrust him. That is, he acts as a digital assistant. At the same time, the robot can significantly unload a person, because the robotization module is installed on the user's computer in addition to the installed applications. And when the task for the robot appears, the person simply launches a program that automatically fulfills the task. However, it must be remembered that at this time the computer is busy with the robot and the user cannot perform other tasks on it. But in the time available, you can make a phone call to the client or discuss a joint project with colleagues.
Opportunity 5. Process mining and data science (data mining)
To whom it is useful: data mining analysts.
The bottom line. The techniques and tools of data science work with data and, as a rule, do not pay attention to the processes as a result of which this data arose. For example, there is a CRM database with detailed information about customers, their contacts with the company and transactions. Using data mining, you can extract useful information about goods and consumers: segment consumers. But if you understand that each transaction is the result of the consumer-company interaction process and, having studied these processes themselves, you can get a deeper understanding of what is happening: information about how clients appear, how they make decisions about working with the company, which affects the company this decision, and, in the end, why customers leave.
Limitations of Process Mining Technology
Although the process mining technology is based on proven mathematical algorithms, it does not have magical properties and will not make the company's business processes work more efficiently. One of the main limitations is the adequacy of the display of the progress of a real business process with the data of the information system logs. If some steps of the business process are performed manually or fixed in the information system after an arbitrary time after execution, the process mining tool can give a distorted picture of what is happening.
The second limitation is the need to interpret the results of the analysis. Deviations of business processes from regulations or bottlenecks in processes should be investigated by the analyst, whether there really are losses for the business or the possibility of increasing efficiency.
Prospects
Despite the obvious technical limitations, process mining is one of the advanced technologies of the fourth industrial revolution , which are already used in large companies with developed IT infrastructure for process management and in the future can become standard technology for leading companies.
* The picture for the announcement is taken from Pikabu .
