How to choose a 3D printer, or why you need a heating table and a closed camera
Different models of 3D printers have a maximum temperature for heating the table on which they are printing. In this article, I will talk about different categories of printers for this very important parameter. Indeed, the range of materials that the printer can print depends on the heating of the table. I will also touch on the question of why a closed camera is needed.

Able to print only one type of plastic - PLA. This material is suitable for prototypes, souvenirs, and when heated to 60 ° C it becomes soft and the product loses its shape. With great efforts on such printers, you can try to print with other materials, but the result will not please you. Typically, these are Prusa printers with a movable table, but there are also "cubes".
Problems occur due to shrinkage (reduction in size) of a plastic product after cooling. If the plastic shrinks (and this is almost all plastic, except for PLA), then the edges of the product begin to tear off from the printing table, the geometry of the product irreparably deteriorates or it completely peels off the table, risking damage to the print head, which continues to move.
The plus (or minus?) Of such printers is that manufacturers in them save not only on the table heater, but also on everything else. Therefore, these are cheap printers.
At the same time, in the description of such printers, the lack of table heating may not be indicated at all (be careful!), But the possibility of printing with other plastics other than PLA is indicated, which misleads the buyer. And you will encounter printing problems after purchasing such a printer.
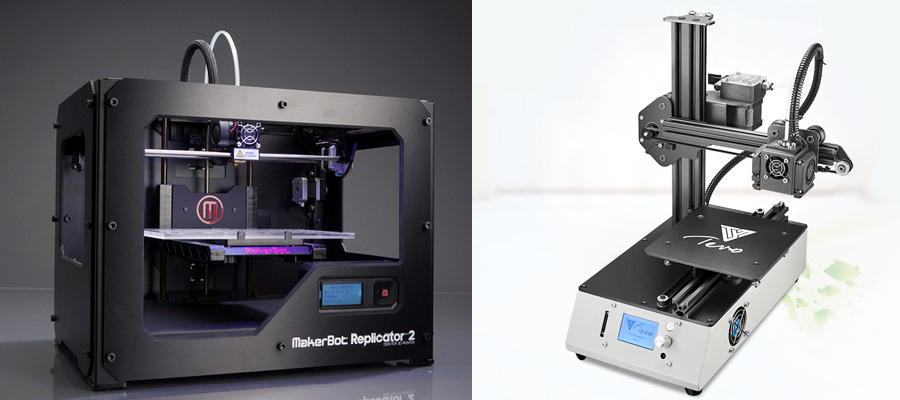
The most famous printer without table heating - Makerbot Replicator 2
Of the Chinese models - TEVO Michelangelo
Further, the story will go about more interesting printers with table heating from 100 ° C to 170 ° C, which are designed for printing with plastic with shrinkage - from classic ABS to Polycarbonate. The higher the maximum temperature of the table, the more plastics you can print, because heating the table prevents damage to the part due to shrinkage during printing. At the same time, the higher the melting temperature of the plastic, the stronger the table should be heated.
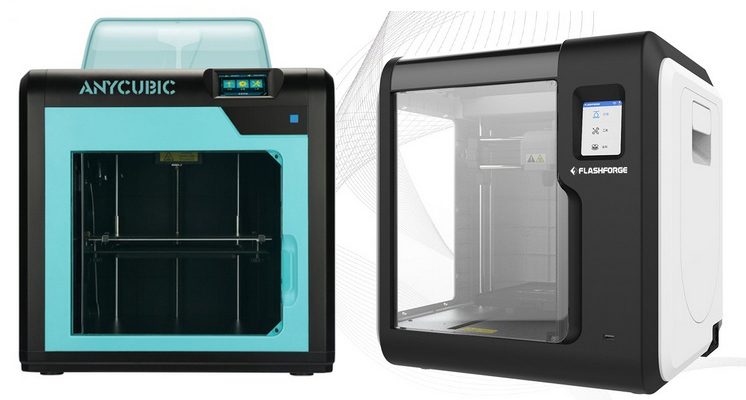
Suitable for printing with many plastics, except for technical ones. At the same time, printing large products with popular ABS plastic at such a low temperature will be problematic. In reality, ABS requires from 110 ° C to 130 ° C on the table, especially for cheap brands with high shrinkage, which are very widely sold. Printing with more interesting technical plastics - nylon, polypropylene, polycarbonate, on such printers will not work at all.
Of the Chinese printers, these are Anycubic, various Flashforge models.

Perfect for printing with ABS plastic. But, if you need to print large products from ABS, then such a printer also needs a closed print chamber. It is needed to maintain a high air temperature around the printed product, which reduces shrinkage during printing over the entire height of the product. The higher the temperature in the chamber, the better for printing!
And then the fun begins. Those manufacturers who have conventional models with an "open camera", cover them with a plastic transparent "aquarium" on top, and sellers offer them under the guise of printers with a closed camera! Of course, such a solution is cheap, but the larger the volume of the chamber, the more difficult it is to maintain a high temperature, and in this case, the volume increases significantly. This means that in such printers the temperature in the camera will be lower than necessary for high-quality printing.
Even more interesting is the situation when the printer is closed on the sides, but completely open at the top and generally has no lid. At the same time, sellers give them out for printers with a closed camera (be careful!).
The question is, why not close any printer from above completely without increasing the volume of the "aquarium"? Yes, because all simple models are designed so that a bundle of wires rises vertically up from the extruder (printhead), as well as the tube through which the thread with plastic is fed (look carefully when choosing a printer photo from all sides). All this sticks out from the top of the printer and does not allow it to close normally. This is especially true for printers with remote Bowden plastic feed, where the motor pushing the plastic thread is carried out on the printer body.
It would seem, and so what? Well, turn the wires to the side of the extruder so that they do not stick up and do not interfere ... However, for this you need to apply design solutions with a horizontal arrangement of wires and tubes suitable for the extruder, and design the printer initially, taking into account the closed camera.
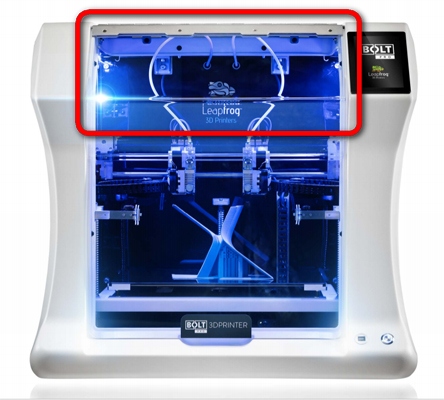

Interestingly, even some expensive closed imported printers have a large height and increased clearance inside the chamber between the extruder and the top cover, because in them, the designers could not (did not want to) rotate the plastic feed tube horizontally. This means that in them the volume of the camera is more than necessary.
Most of both imported and domestic printers fall into this category.
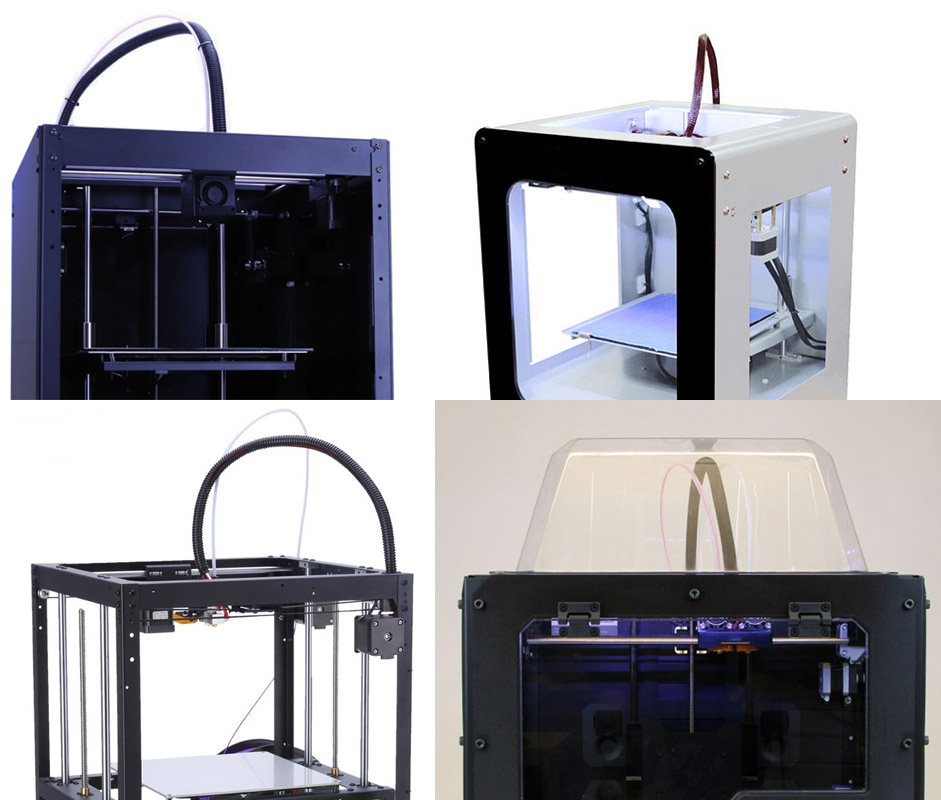

These printers are already quite well designed by the designers. Most of these printers really have a well-heated closed chamber with lateral arrangement of wires and tubes of the extruder. They can print both large products from ABS plastic and small products from technical plastics - nylon, polypropylene, polycarbonate.
Among domestic printers in this category, we note Picaso3D and PrintBox3D.

Here we come to closed printers with a very high table temperature. These printers are designed by designers taking into account the trends in 3D printing to increase operating temperatures, which means that they can be printed with more durable, heat-resistant plastics. There are few such printers; they are expensive, with rare exceptions.
Why warm the table so much? The fact is that the higher the melting temperature of the plastic, the stronger the table and the surrounding air in the chamber should heat up, otherwise the product will detach from the table when printing and the printing will be interrupted. So, for polycarbonate, the extruder print temperature can reach 310 ° C. If small parts can be printed at a table temperature of 130 ° C, then medium ones are already from 150 ° C, while large ones will be kept on the table only at 170 ° C.
In addition, such printers have the potential for printing and other refractory plastics. For example, at an extruder temperature of 400 ° C, PEEK (polyetheretherketone) can be printed. This refractory and durable plastic is used in aviation, space technology.
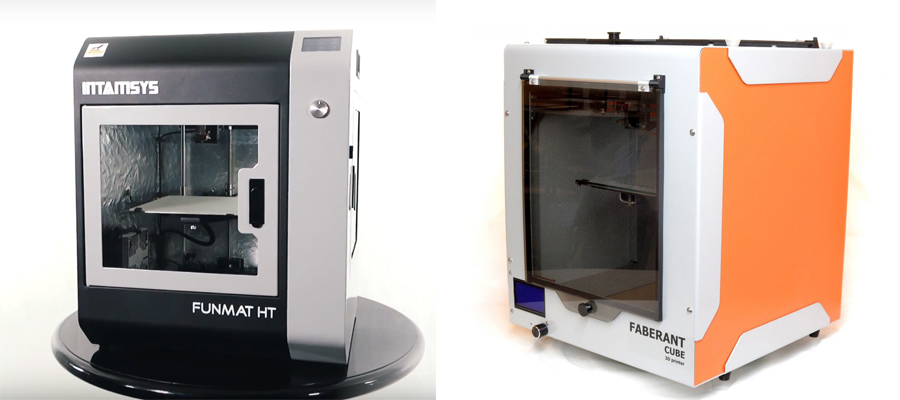
In this high-temperature category, we note the Intamsys FUNMAT HT Chinese printer with an extruder temperature of up to 450 ° C, a table - up to 160 ° C.
From domestic, we cannot but mention the Faberant Cube 3D printer
with an extruder temperature of up to 340 ° C, of a table - up to 170 ° C.

If you want to print with various plastics, and not just with one PLA, then the 3D printer must have a heated table. If you plan to print large products from ABS, then you need a real closed chamber, without a “tank” on top. The higher the maximum temperature of the table, the greater the range of materials that you can use in your printer. For printers with table heating up to 170 ° C, this spectrum is very large, up to polycarbonate and PEEK, if the extruder allows heating.
In the following articles, the story will go into more detail about the maximum temperature of the extruder, kinematics and other things.

Printers without table heating
Able to print only one type of plastic - PLA. This material is suitable for prototypes, souvenirs, and when heated to 60 ° C it becomes soft and the product loses its shape. With great efforts on such printers, you can try to print with other materials, but the result will not please you. Typically, these are Prusa printers with a movable table, but there are also "cubes".
Problems occur due to shrinkage (reduction in size) of a plastic product after cooling. If the plastic shrinks (and this is almost all plastic, except for PLA), then the edges of the product begin to tear off from the printing table, the geometry of the product irreparably deteriorates or it completely peels off the table, risking damage to the print head, which continues to move.
The plus (or minus?) Of such printers is that manufacturers in them save not only on the table heater, but also on everything else. Therefore, these are cheap printers.
At the same time, in the description of such printers, the lack of table heating may not be indicated at all (be careful!), But the possibility of printing with other plastics other than PLA is indicated, which misleads the buyer. And you will encounter printing problems after purchasing such a printer.
The most famous printer without table heating - Makerbot Replicator 2
Of the Chinese models - TEVO Michelangelo

Further, the story will go about more interesting printers with table heating from 100 ° C to 170 ° C, which are designed for printing with plastic with shrinkage - from classic ABS to Polycarbonate. The higher the maximum temperature of the table, the more plastics you can print, because heating the table prevents damage to the part due to shrinkage during printing. At the same time, the higher the melting temperature of the plastic, the stronger the table should be heated.
Printers with table heating up to 100 ° С
Suitable for printing with many plastics, except for technical ones. At the same time, printing large products with popular ABS plastic at such a low temperature will be problematic. In reality, ABS requires from 110 ° C to 130 ° C on the table, especially for cheap brands with high shrinkage, which are very widely sold. Printing with more interesting technical plastics - nylon, polypropylene, polycarbonate, on such printers will not work at all.
Of the Chinese printers, these are Anycubic, various Flashforge models.

Printers with table heating up to 120 ° С
Perfect for printing with ABS plastic. But, if you need to print large products from ABS, then such a printer also needs a closed print chamber. It is needed to maintain a high air temperature around the printed product, which reduces shrinkage during printing over the entire height of the product. The higher the temperature in the chamber, the better for printing!
And then the fun begins. Those manufacturers who have conventional models with an "open camera", cover them with a plastic transparent "aquarium" on top, and sellers offer them under the guise of printers with a closed camera! Of course, such a solution is cheap, but the larger the volume of the chamber, the more difficult it is to maintain a high temperature, and in this case, the volume increases significantly. This means that in such printers the temperature in the camera will be lower than necessary for high-quality printing.
Even more interesting is the situation when the printer is closed on the sides, but completely open at the top and generally has no lid. At the same time, sellers give them out for printers with a closed camera (be careful!).
The question is, why not close any printer from above completely without increasing the volume of the "aquarium"? Yes, because all simple models are designed so that a bundle of wires rises vertically up from the extruder (printhead), as well as the tube through which the thread with plastic is fed (look carefully when choosing a printer photo from all sides). All this sticks out from the top of the printer and does not allow it to close normally. This is especially true for printers with remote Bowden plastic feed, where the motor pushing the plastic thread is carried out on the printer body.
It would seem, and so what? Well, turn the wires to the side of the extruder so that they do not stick up and do not interfere ... However, for this you need to apply design solutions with a horizontal arrangement of wires and tubes suitable for the extruder, and design the printer initially, taking into account the closed camera.

Interestingly, even some expensive closed imported printers have a large height and increased clearance inside the chamber between the extruder and the top cover, because in them, the designers could not (did not want to) rotate the plastic feed tube horizontally. This means that in them the volume of the camera is more than necessary.
Most of both imported and domestic printers fall into this category.

Printers with table heating from 130 ° C to 150 ° C
These printers are already quite well designed by the designers. Most of these printers really have a well-heated closed chamber with lateral arrangement of wires and tubes of the extruder. They can print both large products from ABS plastic and small products from technical plastics - nylon, polypropylene, polycarbonate.
Among domestic printers in this category, we note Picaso3D and PrintBox3D.

Printers with table heating up to 170 ° С
Here we come to closed printers with a very high table temperature. These printers are designed by designers taking into account the trends in 3D printing to increase operating temperatures, which means that they can be printed with more durable, heat-resistant plastics. There are few such printers; they are expensive, with rare exceptions.
Why warm the table so much? The fact is that the higher the melting temperature of the plastic, the stronger the table and the surrounding air in the chamber should heat up, otherwise the product will detach from the table when printing and the printing will be interrupted. So, for polycarbonate, the extruder print temperature can reach 310 ° C. If small parts can be printed at a table temperature of 130 ° C, then medium ones are already from 150 ° C, while large ones will be kept on the table only at 170 ° C.
In addition, such printers have the potential for printing and other refractory plastics. For example, at an extruder temperature of 400 ° C, PEEK (polyetheretherketone) can be printed. This refractory and durable plastic is used in aviation, space technology.
In this high-temperature category, we note the Intamsys FUNMAT HT Chinese printer with an extruder temperature of up to 450 ° C, a table - up to 160 ° C.
From domestic, we cannot but mention the Faberant Cube 3D printer
with an extruder temperature of up to 340 ° C, of a table - up to 170 ° C.

conclusions
If you want to print with various plastics, and not just with one PLA, then the 3D printer must have a heated table. If you plan to print large products from ABS, then you need a real closed chamber, without a “tank” on top. The higher the maximum temperature of the table, the greater the range of materials that you can use in your printer. For printers with table heating up to 170 ° C, this spectrum is very large, up to polycarbonate and PEEK, if the extruder allows heating.
In the following articles, the story will go into more detail about the maximum temperature of the extruder, kinematics and other things.
