Elbrus: from the past to the future
Under the proud name "Elbrus" a series of supercomputers was released, which was developed by the Soviet scientist Vsevolod Sergeyevich Burtsev (70-80s). These computers have made a number of innovations in the theory of computers, such as superscalarity (processing more than one instruction per cycle), the implementation of secure programming with hardware data types, parallel processing of several instructions. But the main feature of Soviet supercomputers was their orientation to high-level languages. Soviet-American scientist Vladimir Mstislavovich Pentkovsky, who participated in the development of "Elbrus", created a high-level programming language El-76.
In addition to improving the sphere of Soviet computers, the computer became the basis for the creation of 64-bit universal microprocessors Elbrus 4-S and the next generation Elbrus 8-C. They diluted the market for American manufacturers Intel, AMD and IBM. Local development and production of processors was due to the need to find their own solutions for the defense industry, where the use of domestic devices is more desirable.
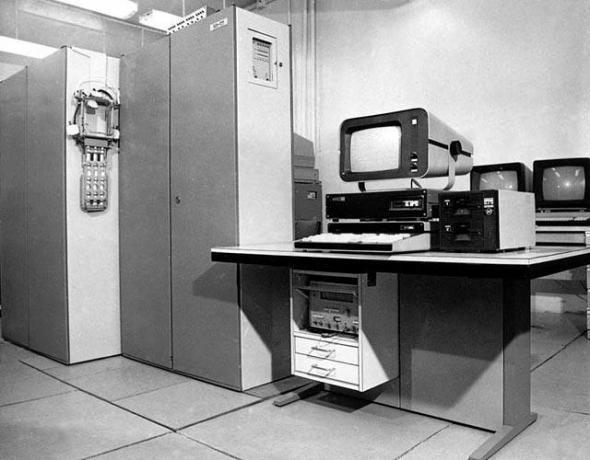

Supercomputer "Elbrus"
The development of the computer architecture "Elbrus" began in the 70s at ITMiVT named after Lebedev. The developers were faced with the task of creating a computing system with a capacity of 100 million op / s. Burtsev was engaged in a computer control and design system and became the chief designer of the project.
In 1980, Elbrus-1 with a total capacity of 15 million op / s successfully passed state tests. It was the first computer in the Soviet Union, built on the basis of TTL-microcircuits. A feature of the machine was the scalable architecture, which supported the simultaneous operation of up to 10 processors. RAM reached 64 MB (2 20 machine words). The organization of the transfer of data streams between peripheral devices and RAM was carried out using special input-output processors. There could be about 4 such processors in the system and they had their own memory, working in parallel with the central processor.
"Elbrus-1" was used in many military systems - missile defense, the Space Control Center, etc.
The next step in the development of the Elbrus computer was the transfer of the architecture of the first model to a new element base. Thus, Elbrus-2 arose, which was based on the basis of ELS integrated circuits. Its productivity reached 125 million op / s. The amount of RAM has increased - up to 144 MB. The clock frequency reached 20 MHz.
In 1985, Elbrus-2 was launched into serial production. It was used in areas where large computations were required. Also, the computer was actively used in the defense industry, in the Space Flight Control Center and in nuclear research centers (in Arzamas-16, in Chelyabinsk-70). Since 1991, the computer has been operating in the A-135 missile defense system and at other military facilities.

Supercomputer "Elbrus-2"
Together with supercomputers, the general-purpose computer Elbrus 1-KB (1988) was also produced. These machines replaced the BESM-6 with which they had full backward software compatibility. It was supplemented with a new mode of operation with increased capacity for numbers and addresses.
Comparative characteristics of BESM-6 and Elbrus 1-KB
The next was released "Elbrus-3", in which the developers for the first time implemented a "post-superscalar" approach. This computer was developed from 1986 to 1994. ITM&VT staff led by Soviet scientist Boris Artashesovich Babayan.
Elbrus-3 was not put into mass production, but its architecture became the basis for the development of microprocessors Elbrus 2000 and Elbrus-3M1.
The Elbrus series was appreciated by the Soviet leadership. Developers Babayan, Burtsev, Bardizh received prizes and orders. The remaining participants in the work were also awarded state prizes.
The Russian company MCST was founded in 1992 on the basis of the Elbrus-3 development team. She became the assignee of the Moscow Center for SPARC Technologies LLP (hence the name ICST). The abbreviation SPARC came from the main partner of the MCST of the American corporation Sun Microsystems, which promotes computers with the SPARC architecture.
The MCST produced microprocessors with the SPARC architecture (MTsST-R100, MTsST-R150, MTsST-R500 and MTsST-R500S) and created computer systems based on them. But in 2007, the Elbrus processor of the same name was released. The peak performance of the device in 64-bit mode reached 2.4 GFLOPS. The operating clock frequency was 300 MHz. The processor had 75.8 million transistors. Power dissipation 6 watts.
Elbrus processor
Based on the processor, the Elbrus-3M1 computing complex was developed, which was used for the defense industry. This complex was provided with a secure operating system MSVS-E (Mobile system of the Armed Forces), based on Linux version 2.6.14. Elbrus-3M1 was backward compatible with the first and second Elbrus.
The computer complex had two design options - the server one, which could be used both as a desktop and as a CompactPCI (system bus). The server version was based on the device of the UV 3M1 calculator. In the case of CompactPCI, Elbrus-3M1 occupied two modules of the Euromechanics format 6U. The execution equipment of both versions was equipped with network equipment for ultra-high-speed exchanges with similar computing systems.
In 2010, at the ChipEXPO-2010 and Softool exhibitions, the public was presented with the Elbrus-S crystal system. The number of transistors in this processor has increased - up to 218 million. Also, the clock frequency has increased up to 500 MHz and peak performance has increased: up to 4 GFLOPS in 64-bit and up to 8 GFLOPS in 32-bit modes.
Together with "Elbrus-S" the controller of peripheral interfaces (KPI) was presented.

Elbrus-S processor
In 2011, the MCST presented the next-generation dual-core processor Elbrus-2C +. In addition to the 2 main cores (Elbrus architecture) operating at a clock frequency of 500 MHz, the model also had an additional 4 cores of the built-in digital signal processor (Multicore architecture). An I / O channel was added to the processor, with which it is possible to connect another KPI. Elbrus-2C + also added support for DDR2 memory with an effective frequency of 800 MHz. Processor performance has increased - up to 28 GFLOPS in 32-bit mode. The number of transistors reached 368 million.
The developers implemented a version of the C language compiler to reproduce the code for DSP cores and to establish effective interaction between the main program on the CPU cores and actions on the DSP.
According to the creators, Elbrus-2C + was to be used in digital intelligent signal processing systems (radars, image analyzers, etc.). But the processors were better adapted to civilian tasks. For example, Kraftway launched a test series of monoblock computers based on Elbrus-2C + crystals.

Elbrus-2C + processor
In April 2014, the company introduced the improved quad-core Elbrus-4C processors.
Specifications "Elbrus-4C"
First of all, it is worth paying attention to the transition of processor production to a 65 nm process. Also, the clock frequency and the bandwidth of the RAM channels have also increased. These and other improvements have significantly affected the performance growth of new processors. Each core in one cycle is capable of performing up to 23 operations. In floating point operations, the peak theoretical performance of four cores is about 50 GFLOPS single precision and 25 GFLOPS double precision. Compared with the previous Elbrus-2C + model, in 64-bit mode this is more than three times higher. In the new processor, a more complex crystal, which contains 986 million transistors, has a useful area of 380 mm 2 .

Elbrus-4C processor
ICST specialists created their own Elbrus operating system specifically for the released processor. The OS is based on the Linux kernel version 2.6.33. It consists of over 3000 software packages (from the Debian 5.0 distribution) and there is a package manager. A full set of developer tools is included, including optimization compilers for the high-level programming languages C, C ++, Fortran-77 and Fortran-9.
Elbrus OS was certified for the second class of protection against unauthorized access and the second level of control over undeclared capabilities. But computers based on Elbrus-4C processors also work with versions of the Windows OS.
One of the company's projects was the development of the first Russian desktop computer based on the Elbrus-4C processor. It received the name "Workstation Elbrus-401" (where the workstation stands for an automated workstation). The model is designed for an office in a MiniTower standard enclosure. But it can be used in various fields with increased requirements for information security.
The computer has a 65 nm process technology with a clock frequency of 800 Hz, SATA-2 and USB 2.0 ports, a pre-installed 120 GB SSD with mSATA interface and support for DDR3-1600 with ECC. The basic configuration is offered 24 GB of RAM (expandable up to 96 GB). Among the architectural features of the "Workstation Elbrus-401" can be identified as follows: the presence of 6 parallel channels of arithmetic-logic devices; register file of 256 84-bit registers; hardware loop support; support for speculative computing and single-bit predicates; a command that can set up to 23 operations in a single measure with maximum filling. An AMD Radeon 6000 series video card is also installed in the computer.

Computer “Workstation Elbrus-401”
The Elstrus-8S processor is being developed by the MCST company with the participation of the Institute of Electronic Control Machines (INEUM) named after I.S. Brooke. The architecture, circuitry and topology of the microprocessor were created by Russian specialists. The processor has eight cores with an improved 64-bit Elbrus architecture. The clock frequency reaches 1.3 GHz, the cache volume of the second and third levels is 4 and 16 MB. Estimated performance reaches 250 GFLOPS.
Specifications "Elbrus-8C"
The computer has its own Elbrus architecture, which was developed at ZAO MTsST. Vector command system accelerators help make encryption and signal processing faster.
The interaction of the hardware with the OS occurs through its own BIOS microcode. The processor is compatible with Linux, FreeBSD, QNX, Windows XP distributions, but the recommended Elbrus operating system is based on the Linux 2.6.33 kernel. The use of specialized development tools (optimizing compilers from C and C ++, Fortran, Java, etc.) makes it possible to optimize the program code taking into account the Elbrus architecture.
Elbrus-8C processor
The company is already developing utilities and auxiliary components optimized for working on processors. This is all - tools for working with the network and peripherals (utilities, general purpose libraries, services, database support, graphics subsystem).
Elbrus-8S should be paired with KPI 2 - the controller of peripheral interfaces of Russian production.
By tradition, there is a bit of advertising in the basement, where it will not hurt anyone. We remind you that due to the fact that the total network capacity of the Dutch data center in which we provide services has reached 5 Tbps (58 points of presence, inclusion in 36 exchange points, in more than 20 countries and 4,213 peer-to-peer inclusions ), we offer dedicated servers for rent at incredibly low prices, only a week! .
In addition to improving the sphere of Soviet computers, the computer became the basis for the creation of 64-bit universal microprocessors Elbrus 4-S and the next generation Elbrus 8-C. They diluted the market for American manufacturers Intel, AMD and IBM. Local development and production of processors was due to the need to find their own solutions for the defense industry, where the use of domestic devices is more desirable.

Supercomputer "Elbrus"
History of development
The development of the computer architecture "Elbrus" began in the 70s at ITMiVT named after Lebedev. The developers were faced with the task of creating a computing system with a capacity of 100 million op / s. Burtsev was engaged in a computer control and design system and became the chief designer of the project.
Autobiographical information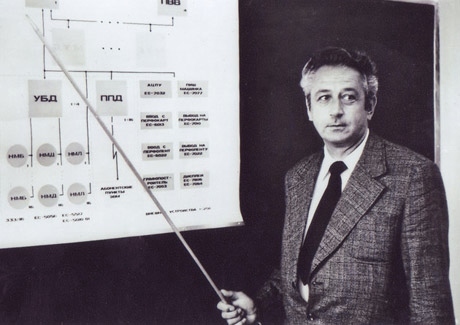
Vsevolod Sergeevich Burtsev (1927-2005) - Soviet academician, scientist in the field of control systems and the theory of designing universal computers, chief designer of the first Soviet supercomputers and computer complexes.
Burtsev went from a simple engineer to the director of the Institute of Precision Mechanics and Computer Engineering of the USSR Academy of Sciences. Leading developer of the first high-speed electronic computing machine. The scientist owns about 200 scientific papers. For successes and achievements in the field of science, engineering, he received many state awards (Lenin and State Prizes of the USSR, orders of Lenin, October Revolution and the Red Banner of Labor).
The scientist made an invaluable contribution to the development of high-performance Soviet and Russian computers, as well as to the implementation of multiprocessor computing systems. Burtsev also became famous as a deputy chief designer of computers Diana-1, Diana-2, M-40, M-60, 5E92, 5E92b, 5E51 and directly as chief designer of Elbrus computers, which were used to create various systems and special-purpose equipment.

Vsevolod Sergeevich Burtsev (1927-2005) - Soviet academician, scientist in the field of control systems and the theory of designing universal computers, chief designer of the first Soviet supercomputers and computer complexes.
Burtsev went from a simple engineer to the director of the Institute of Precision Mechanics and Computer Engineering of the USSR Academy of Sciences. Leading developer of the first high-speed electronic computing machine. The scientist owns about 200 scientific papers. For successes and achievements in the field of science, engineering, he received many state awards (Lenin and State Prizes of the USSR, orders of Lenin, October Revolution and the Red Banner of Labor).
The scientist made an invaluable contribution to the development of high-performance Soviet and Russian computers, as well as to the implementation of multiprocessor computing systems. Burtsev also became famous as a deputy chief designer of computers Diana-1, Diana-2, M-40, M-60, 5E92, 5E92b, 5E51 and directly as chief designer of Elbrus computers, which were used to create various systems and special-purpose equipment.
In 1980, Elbrus-1 with a total capacity of 15 million op / s successfully passed state tests. It was the first computer in the Soviet Union, built on the basis of TTL-microcircuits. A feature of the machine was the scalable architecture, which supported the simultaneous operation of up to 10 processors. RAM reached 64 MB (2 20 machine words). The organization of the transfer of data streams between peripheral devices and RAM was carried out using special input-output processors. There could be about 4 such processors in the system and they had their own memory, working in parallel with the central processor.
"Elbrus-1" was used in many military systems - missile defense, the Space Control Center, etc.
The next step in the development of the Elbrus computer was the transfer of the architecture of the first model to a new element base. Thus, Elbrus-2 arose, which was based on the basis of ELS integrated circuits. Its productivity reached 125 million op / s. The amount of RAM has increased - up to 144 MB. The clock frequency reached 20 MHz.
In 1985, Elbrus-2 was launched into serial production. It was used in areas where large computations were required. Also, the computer was actively used in the defense industry, in the Space Flight Control Center and in nuclear research centers (in Arzamas-16, in Chelyabinsk-70). Since 1991, the computer has been operating in the A-135 missile defense system and at other military facilities.

Supercomputer "Elbrus-2"
Together with supercomputers, the general-purpose computer Elbrus 1-KB (1988) was also produced. These machines replaced the BESM-6 with which they had full backward software compatibility. It was supplemented with a new mode of operation with increased capacity for numbers and addresses.
Comparative characteristics of BESM-6 and Elbrus 1-KB
| Characteristic | BESM-6 | Elbrus 1-KB |
| Productivity (mln op / s) | 1 | 2,5 - 3 |
| Frequency, MHz | 10 | 20 |
| Bit depth | 48 | 48 |
| RAM address resolution, bit | fifteen | fifteen |
| The amount of RAM, MB | 0.032-0.128 | 0.77 |
| The amount of disk memory, MB | 116 | 58 |
| Occupied area, m 2 | 150-200 | 250 |
| Power consumption kW | thirty | 105 |
| Total released | 355 | 60 |
The next was released "Elbrus-3", in which the developers for the first time implemented a "post-superscalar" approach. This computer was developed from 1986 to 1994. ITM&VT staff led by Soviet scientist Boris Artashesovich Babayan.
Elbrus-3 was not put into mass production, but its architecture became the basis for the development of microprocessors Elbrus 2000 and Elbrus-3M1.
The Elbrus series was appreciated by the Soviet leadership. Developers Babayan, Burtsev, Bardizh received prizes and orders. The remaining participants in the work were also awarded state prizes.
MCST processor era
The Russian company MCST was founded in 1992 on the basis of the Elbrus-3 development team. She became the assignee of the Moscow Center for SPARC Technologies LLP (hence the name ICST). The abbreviation SPARC came from the main partner of the MCST of the American corporation Sun Microsystems, which promotes computers with the SPARC architecture.
The MCST produced microprocessors with the SPARC architecture (MTsST-R100, MTsST-R150, MTsST-R500 and MTsST-R500S) and created computer systems based on them. But in 2007, the Elbrus processor of the same name was released. The peak performance of the device in 64-bit mode reached 2.4 GFLOPS. The operating clock frequency was 300 MHz. The processor had 75.8 million transistors. Power dissipation 6 watts.

Elbrus processor
Based on the processor, the Elbrus-3M1 computing complex was developed, which was used for the defense industry. This complex was provided with a secure operating system MSVS-E (Mobile system of the Armed Forces), based on Linux version 2.6.14. Elbrus-3M1 was backward compatible with the first and second Elbrus.
The computer complex had two design options - the server one, which could be used both as a desktop and as a CompactPCI (system bus). The server version was based on the device of the UV 3M1 calculator. In the case of CompactPCI, Elbrus-3M1 occupied two modules of the Euromechanics format 6U. The execution equipment of both versions was equipped with network equipment for ultra-high-speed exchanges with similar computing systems.
In 2010, at the ChipEXPO-2010 and Softool exhibitions, the public was presented with the Elbrus-S crystal system. The number of transistors in this processor has increased - up to 218 million. Also, the clock frequency has increased up to 500 MHz and peak performance has increased: up to 4 GFLOPS in 64-bit and up to 8 GFLOPS in 32-bit modes.
Together with "Elbrus-S" the controller of peripheral interfaces (KPI) was presented.

Elbrus-S processor
In 2011, the MCST presented the next-generation dual-core processor Elbrus-2C +. In addition to the 2 main cores (Elbrus architecture) operating at a clock frequency of 500 MHz, the model also had an additional 4 cores of the built-in digital signal processor (Multicore architecture). An I / O channel was added to the processor, with which it is possible to connect another KPI. Elbrus-2C + also added support for DDR2 memory with an effective frequency of 800 MHz. Processor performance has increased - up to 28 GFLOPS in 32-bit mode. The number of transistors reached 368 million.
The developers implemented a version of the C language compiler to reproduce the code for DSP cores and to establish effective interaction between the main program on the CPU cores and actions on the DSP.
According to the creators, Elbrus-2C + was to be used in digital intelligent signal processing systems (radars, image analyzers, etc.). But the processors were better adapted to civilian tasks. For example, Kraftway launched a test series of monoblock computers based on Elbrus-2C + crystals.

Elbrus-2C + processor
Elbrus-4C processor
In April 2014, the company introduced the improved quad-core Elbrus-4C processors.
Specifications "Elbrus-4C"
| Technological process | 65 nm |
| The number of architecture cores | 4 |
| Clock frequency | 800 MHz |
| Peak performance | 64 bits - 25 GFLOPS 32 bits - 50 GFLOPS |
| Level 1 Command Cache | 128 kb |
| Level 1 Data Cache | 64 kb |
| Level 2 Cache | 8 MB |
| RAM organization | Up to 3 channels DDR3-1600 ECC |
| RAM bandwidth | 38.4 GB / s |
| Power dissipation | Up to 60 watts |
| Number of transistors | 986 million |
First of all, it is worth paying attention to the transition of processor production to a 65 nm process. Also, the clock frequency and the bandwidth of the RAM channels have also increased. These and other improvements have significantly affected the performance growth of new processors. Each core in one cycle is capable of performing up to 23 operations. In floating point operations, the peak theoretical performance of four cores is about 50 GFLOPS single precision and 25 GFLOPS double precision. Compared with the previous Elbrus-2C + model, in 64-bit mode this is more than three times higher. In the new processor, a more complex crystal, which contains 986 million transistors, has a useful area of 380 mm 2 .

Elbrus-4C processor
ICST specialists created their own Elbrus operating system specifically for the released processor. The OS is based on the Linux kernel version 2.6.33. It consists of over 3000 software packages (from the Debian 5.0 distribution) and there is a package manager. A full set of developer tools is included, including optimization compilers for the high-level programming languages C, C ++, Fortran-77 and Fortran-9.
Elbrus OS was certified for the second class of protection against unauthorized access and the second level of control over undeclared capabilities. But computers based on Elbrus-4C processors also work with versions of the Windows OS.
Tandem processor and desktop
One of the company's projects was the development of the first Russian desktop computer based on the Elbrus-4C processor. It received the name "Workstation Elbrus-401" (where the workstation stands for an automated workstation). The model is designed for an office in a MiniTower standard enclosure. But it can be used in various fields with increased requirements for information security.
The computer has a 65 nm process technology with a clock frequency of 800 Hz, SATA-2 and USB 2.0 ports, a pre-installed 120 GB SSD with mSATA interface and support for DDR3-1600 with ECC. The basic configuration is offered 24 GB of RAM (expandable up to 96 GB). Among the architectural features of the "Workstation Elbrus-401" can be identified as follows: the presence of 6 parallel channels of arithmetic-logic devices; register file of 256 84-bit registers; hardware loop support; support for speculative computing and single-bit predicates; a command that can set up to 23 operations in a single measure with maximum filling. An AMD Radeon 6000 series video card is also installed in the computer.

Computer “Workstation Elbrus-401”
The processor of the new generation - "Elbrus-8C"
The Elstrus-8S processor is being developed by the MCST company with the participation of the Institute of Electronic Control Machines (INEUM) named after I.S. Brooke. The architecture, circuitry and topology of the microprocessor were created by Russian specialists. The processor has eight cores with an improved 64-bit Elbrus architecture. The clock frequency reaches 1.3 GHz, the cache volume of the second and third levels is 4 and 16 MB. Estimated performance reaches 250 GFLOPS.
Specifications "Elbrus-8C"
| Technological process | 65 nm |
| The number of architecture cores | 8 |
| Clock frequency | 1.3 GHz |
| Peak performance | 64 bits - 125 GFLOPS 32 bits - 250 GFLOPS |
| Level 2 Cache | 512 kb |
| Level 3 Cache | 16 MB |
| Number of memory controllers | 4 |
| RAM organization | DDR3-1600 ECC |
| Bandwidth of each interprocessor channel | 8 GB / s |
| Power dissipation | 60 - 90 W |
| Crystal area | 350 mm 2 |
The computer has its own Elbrus architecture, which was developed at ZAO MTsST. Vector command system accelerators help make encryption and signal processing faster.
The interaction of the hardware with the OS occurs through its own BIOS microcode. The processor is compatible with Linux, FreeBSD, QNX, Windows XP distributions, but the recommended Elbrus operating system is based on the Linux 2.6.33 kernel. The use of specialized development tools (optimizing compilers from C and C ++, Fortran, Java, etc.) makes it possible to optimize the program code taking into account the Elbrus architecture.

Elbrus-8C processor
The company is already developing utilities and auxiliary components optimized for working on processors. This is all - tools for working with the network and peripherals (utilities, general purpose libraries, services, database support, graphics subsystem).
Elbrus-8S should be paired with KPI 2 - the controller of peripheral interfaces of Russian production.
By tradition, there is a bit of advertising in the basement, where it will not hurt anyone. We remind you that due to the fact that the total network capacity of the Dutch data center in which we provide services has reached 5 Tbps (58 points of presence, inclusion in 36 exchange points, in more than 20 countries and 4,213 peer-to-peer inclusions ), we offer dedicated servers for rent at incredibly low prices, only a week! .
