The destruction of the wheels of Curiosity is not yet threatening the mission of the rover
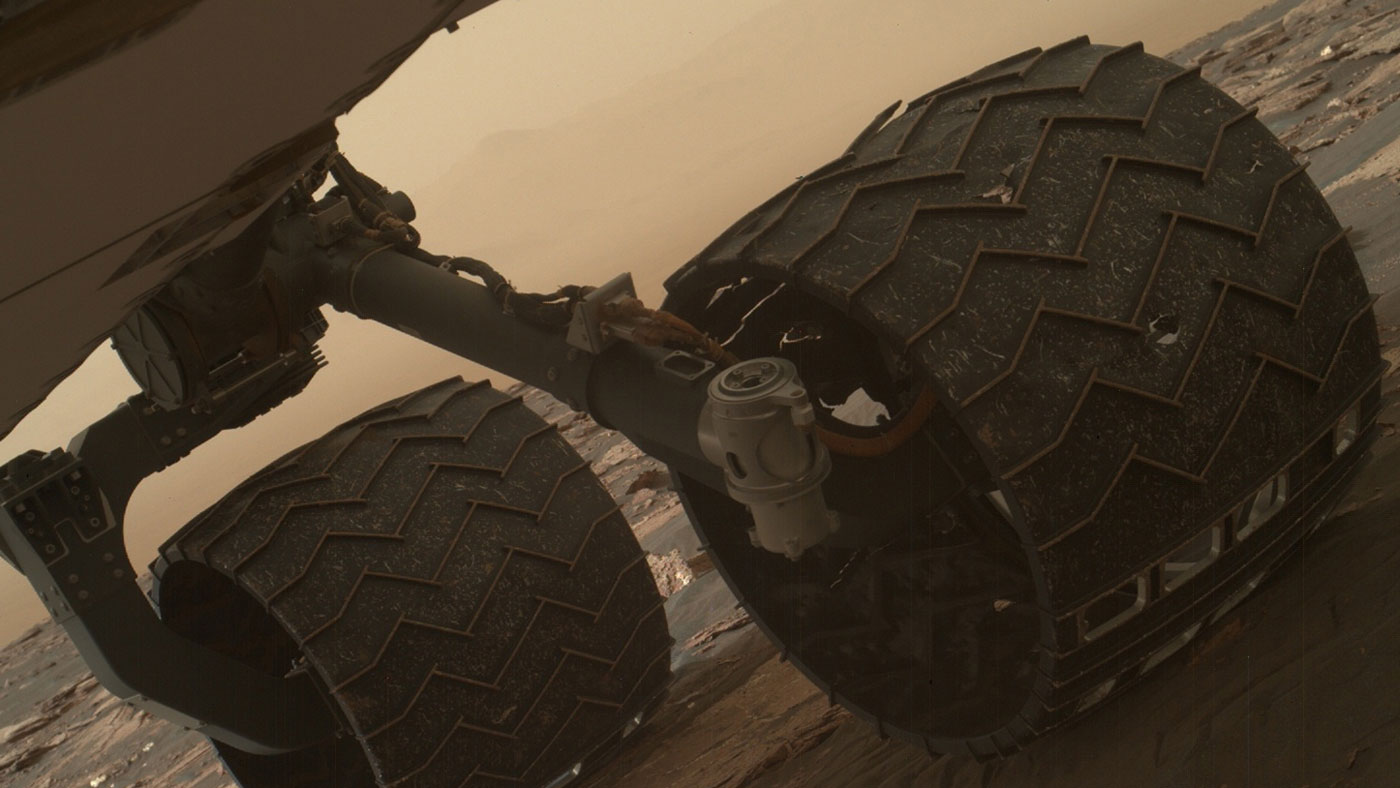

Created by NASA engineers, the Curiosity rover continues to move along a given route on the surface of Mars, studying the features of the atmosphere and lithosphere of a neighboring planet. Now the total distance covered by the device is already 16 kilometers. In general, the rover is in good condition, although the problem with its wheels continues to deteriorate. On aluminum "tires" new cracks, cracks and holes appear.
Checking the condition of the wheels of the device is carried out regularlysince the first dents and scratches were noticed on them. After some time, it turned out that the shell of the wheels collapses faster than the specialists planned. This year, NASA scientists, having studied the condition of the rover wheels, concluded that the wheel part had exhausted its resource by 60%. But the rover is in excellent condition, and can continue to fulfill its mission.
“All six wheels are in more than acceptable condition so that the rover continues to move in any of the planned directions to continue the mission,” said Curioisty Program Manager Jim Erickson. “It was not a surprise to us, but now it’s clear that the left middle wheel is approaching the maximum wear point.” The agency has already stated that wheel wear will not change scientific plans for studying the mineralogy of Mount Sharp.
Now the rover is located on the sandy hills of Murray, studying the geology of the region. In the future, Curiosity is expected to visit the hematite-rich area of the Vera Rubin mountain range. There is a lot of clay, sulfates, and scientists would like more information about this place.
Mars rover gradually climbs higher, studying the younger layers of the Sharp mountain. Scientists are counting on the fact that thanks to the data collected in this area, it will be possible to obtain information about the change in the climate of Mars billions of years ago. Rocks bear traces of these changes, and from them one can judge how the planet as a whole changed. Curiosity has already proven that previously in some areas of Mars, conditions were suitable for life, at least microbial. Higher than now, the temperature made it possible for liquid water to exist on the surface of Mars. According to modern scientists, water is the most important criterion for the existence of life.
It remains to drive another 6 kilometers to the hematite-rich region. Curiosity program participants believe that this distance will be overcome without difficulty - the resource of the rover is sufficient. In addition, over the past four years, scientists have learned how to plan the device’s progress by spotting potentially dangerous places with sharp pieces of sharp rock in order to avoid damage to the wheels of the device.
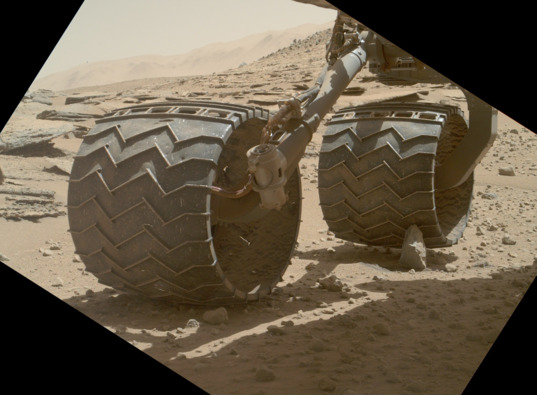
The outer diameter of each of the wheels is 50 centimeters. Tires are made of aluminum. They are not too thick, so most pieces of rock are not able to pierce a layer of aluminum. Damage to the wheels of the rover are divided into several main types. These are holes, scratches, dents and tears of metal.
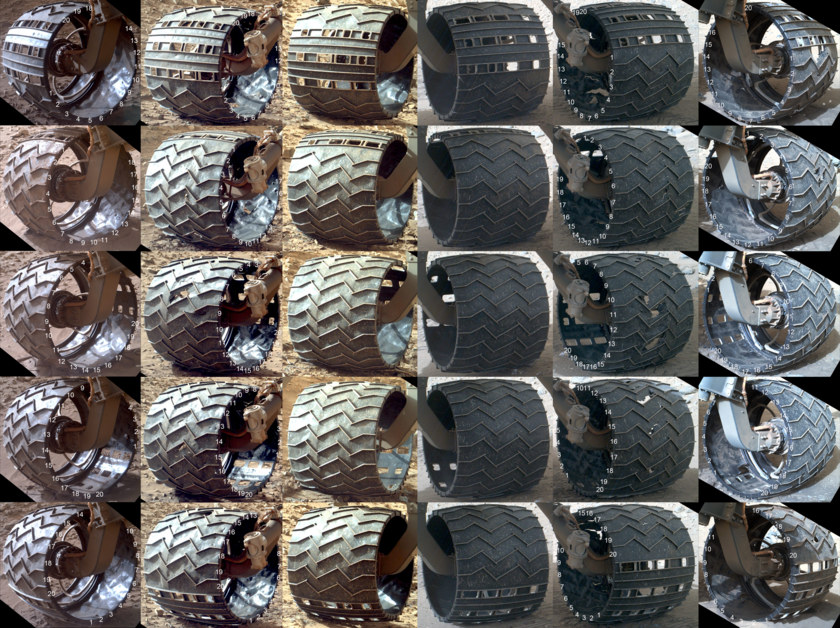

The condition of the wheels of the rover at 708 sol. Photos were taken using the MAHLI camera manipulator. Source: NASA / JPL / MSSS / Emily Lakdawalla The
left central wheel is most damaged. The photo below shows the development of damage from sol 546 to sol 708

Why are the wheels damaged?
After scientists learned that the wheels of the rover are badly damaged in the process of moving the device, they began to look for the cause. It was not revealed immediately. When developing the rover, scientists provided for possible holes and damage, but not in such quantity.

Moreover, the size of the damage was more than calculated. “When we saw the photos of the wheels, we realized that one of the holes is much larger than we expected. This did not happen in any of the tests passed. We did not know what was the reason. We did not know whether this would continue, ”says one of the operators of the rover, Matt Heverly. “This was the moment when we realized that the way of movement needed to be radically changed. But how? This could not be said before the new tests. ”
Tests were carried out for a whole year - both on Earth and on Mars, in the field. It turned out that one of the reasons that leads to damage to the aluminum tires of the rover is material fatigue. Wheels constantly pass on rough terrain. Thin aluminum undergoes deformation and eventually bursts. A good illustration of what happened can be a breakdown of an ordinary paper clip, which is constantly bent in different directions in the same place. The wheels were designed in such a way that in the event of a collision with a stone to deform with a return to normal condition. But, as you know, the planned service life of the rover is several tens of times less than the current life of Curiosity. The tests to which the wheels were subjected showed that they should last an estimated service life.
As for the holes, they are left by the sharp edges of the rock found in many regions of Mars.
It is clear that the presence of such debris on Mars is not at all a surprise for the crew of the rover. The designers knew very well that there were a lot of such stones on the surface of the planet, but did not expect that some of them would be stronger than the calculated parameters. In tests on Earth, the device rode through fragments of various sizes and acuity, but there were no special problems. Metal on wheels is designed for frequent impacts on stones of various sizes, so the fact of impact on a sharp piece of rock does not mean a hole. The reason here is different.
As it turned out, the reason is the mechanical wheel balancing system during the trip. A wheel when hitting a stone can withstand about 1/6 of the mass of the device. In some cases, for example, when moving along a steep slope, the main load goes to the left or right row of wheels. When hitting a sharp stone, the load increases even more, and the design features of Curiosity lead to the fact that the middle wheel is loaded as much as possible. As a result, it simply does not withstand almost the full weight of Curiosity and sometimes metal pierces with stone.
True, not every sharp stone that the rover has piled on with the whole mass will certainly pierce the wheel. The calculation was based on the fact that during a collision a heavy apparatus will simply knock a stone, so that the sharp end will not threaten the wheel. But on the rover's path, very hard, motionless, sharp stones are sometimes found. It is a strong rock that has been weathering for millions or even tens of millions of years. It is they who pose a special danger. One of the engineers on the team demonstrated the problem by hitting a copy of Curiosity on Earth at the tip of a spear top. The tip pierced the aluminum tire of the rover without any problems. Scientists, examining the surface of Mars before the rover went there, did not find particularly sharp stones, the tip of which is directed exactly up. Unfortunately, it turned out that they are relatively common. In November 2014, the rover drove through a region with many fragments of this type.
How long are the wheels designed for, and what happens after?
According to experts from NASA, in order for the wheels to completely collapse, it is enough to drive only 8 km through the rock, the type of which is described above. What exactly is meant by “wheel failure”?
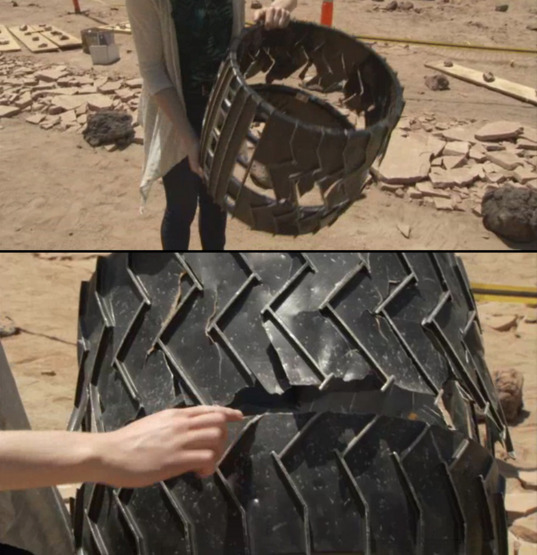

As you can see, for the most part, the damage is concentrated in the center. This is what can happen on Mars - a wheel can simply be cut in half. If stiffeners are broken, the wheel may fail. Fortunately, the situation is not so complicated so far. The wheels work, although some of them are badly damaged.
The good news is that Curiosity is now out of the area with rock debris. As already mentioned, he rides along the slopes of sandy hills.
NASA experts have calculated how much the rover can travel on surfaces of various types until the wheels break down:
- Sharp and hard stones: 8 km;
- A large number of ordinary stones: 13-14 km;
- Sandstone: 30-40 kilometers or more;
- Ordinary hard surface or sand with a small amount of stones: probably not determined, tens or even hundreds of kilometers.
How can I extend the life of the wheels?
Of course, Curiosity has already exceeded its scientific program, but if it is in good condition, why abandon its operation? Therefore, scientists are thinking about how to extend the life of the wheels. Here are a few ways suggested by NASA.
Drive the rover more carefully . Try to check every point that is in front, look around, avoid sharp stones and especially problematic terraces with such stones.
Plan a route to places with a flat surface or sand. One of the best ways is to get directions through places covered with soft material with a minimum of stones. Over the past few months, scientists have been trying to plan the path of the rover, checking photos of exceptionally high resolution. Such photos are obtained using the CRISM tool from the MRO apparatus ( Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter ). Experts compare images from orbit with photos of the surface, which were obtained by the rover itself.
Modification of the rover software, in order to “teach” the device to determine the load on the wheels. This part has not yet been implemented, although it has already begun to be implemented. The point is that when the rover moves, all data on the various parameters of its elements are analyzed by specialized software. In this case, it will be possible to avoid situations with strong pressure of sharp stones on the wheels of the rover.
NASA is far from the first time going to change the software on a remote device. At the same time, the rover is much more perfect, on board is a relatively modern computer with modern software. So updating should not be a problem. On the other hand, mission participants are concerned that the software is rather complicated. “The more complex the software, the more likely it is that something will go wrong. You will get surprises both during the tests and when performing various operations, ”said one of the mission’s representatives. However, scientists hope that everything goes well.
As for the Curiosity heir, the Mars 2020 rover, then NASA has already announced that they will take into account the mistakes of the previous mission. In this case, most likely, the wheels will not significantly modify. Instead, scientists will simply reduce the possible path that the rover needs to travel. If in the case of Curiosity, he first sat down, and then he began to look for interesting goals, then Mars 2020 is planned to be planted near the goals of interest to scientists. The fact is that several orbital probes are now operating in orbit, capable of receiving high-resolution photographs of the surface of Mars. And this makes it easier to choose a goal to study. The new rover is designed for astrobiological studies of the ancient environment on Mars, the surface of the planet, geological processes and history, including the assessment of the past habitability of the planet and the search for evidence of life within available geological materials.
