Winter sky for new year holidays
Part of the free time of the New Year holidays should be allocated to the starry sky above us. There, as always, it will be interesting - a parade of planets, a small meteor shower and beautiful non-astronomical phenomena.
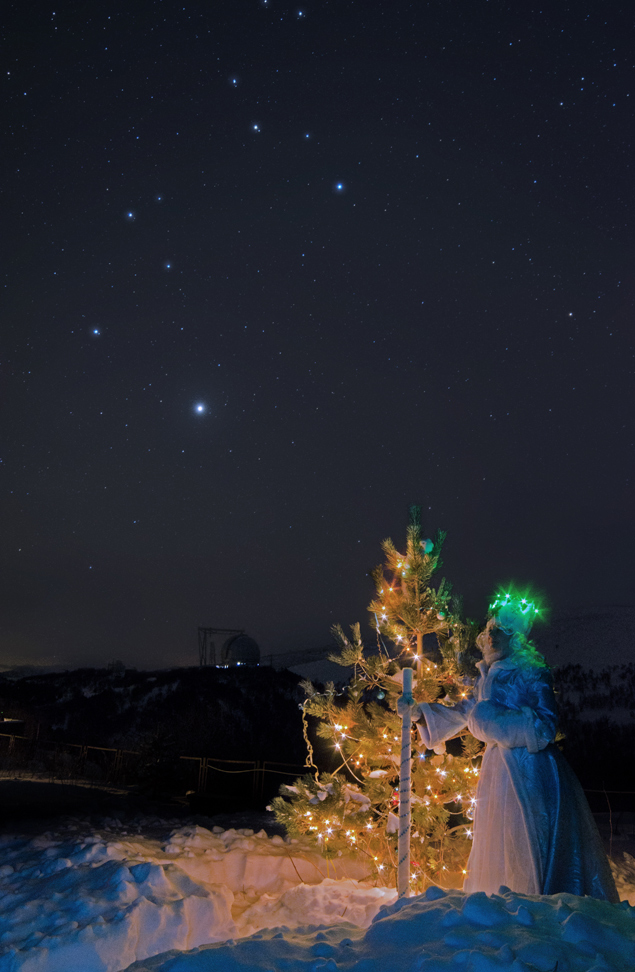

Photo by Upsilon Astroforum
Before you go to the beauties, you will have to disappoint a little. If you think that after the winter solstice the morning already comes earlier, then for the territory of Russia this is not so. Many already managed to get tired of going to work in the dark, but until the very end of December the Sun will rise later. Yes, daylight hours are increasing, but this is due to a later sunset. Here is, for example, a graph for Ufa:
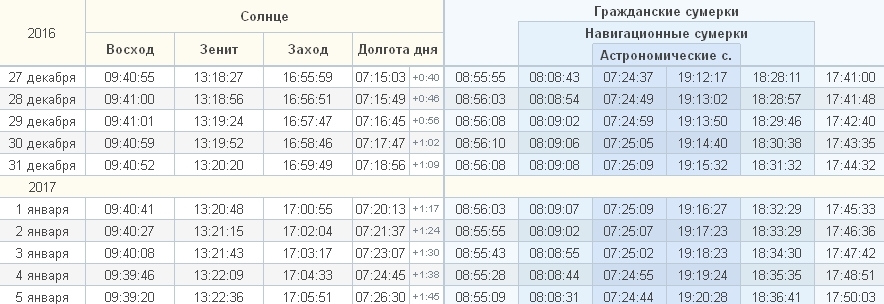
If you play with resources that show the time of sunrise and sunset, you can see that the situation is the opposite in the southern hemisphere - there the Sun begins to rise from the beginning of the month later.
The second paradox is that the Earth passes its pericenter in 2017 in the evening of January 4 and at this moment it will be closest to the Sun. Why is it so cold, you ask, and I will remind you that because of the almost circular orbit, the Earth at perihelion (the point closest to the Sun) receives only 7% more solar energy than at aphelion (the farthest point), and the change of seasons mainly determines the inclination of the axis of rotation of the Earth.
In the evening sky of the end of December, as many as five planets line up, but with the naked eye only two of them can be seen. Venus, Mars, Uranus, Neptune will be over the horizon in December and January evenings, and Mercury will "jump" into the morning sky in the coming days. But without the telescope, Uranus and Neptune you will not see, and the observations of Mercury are complicated by a small distance from the Sun. By the way, Saturn will not be far in the morning sky, and despite the fact that all six planets cannot be seen at the same time, it will be a full-fledged parade of planets in a sector of only 70 °.

If you are lucky with the weather on December 31, then a magnificent picture will rotate above your heads. After sunset, the Mars and Venus will be perfectly visible to the naked eye, in January they will rise even higher.
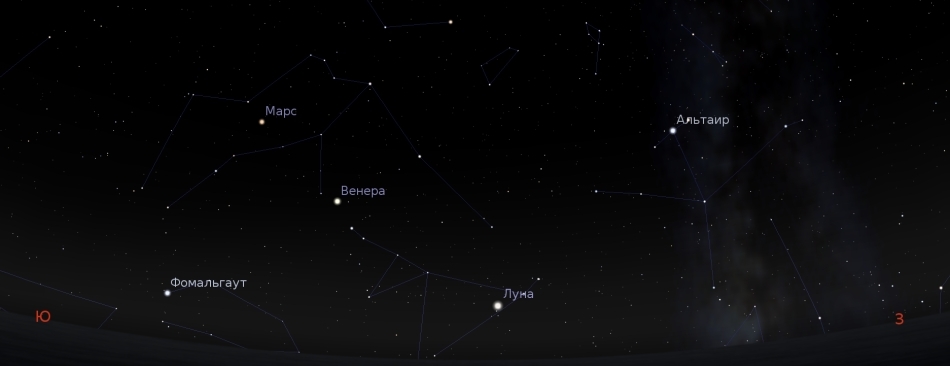
In the north-west, the summer-autumn triangle of Vega, Deneb and Altair will be hidden behind the horizon.
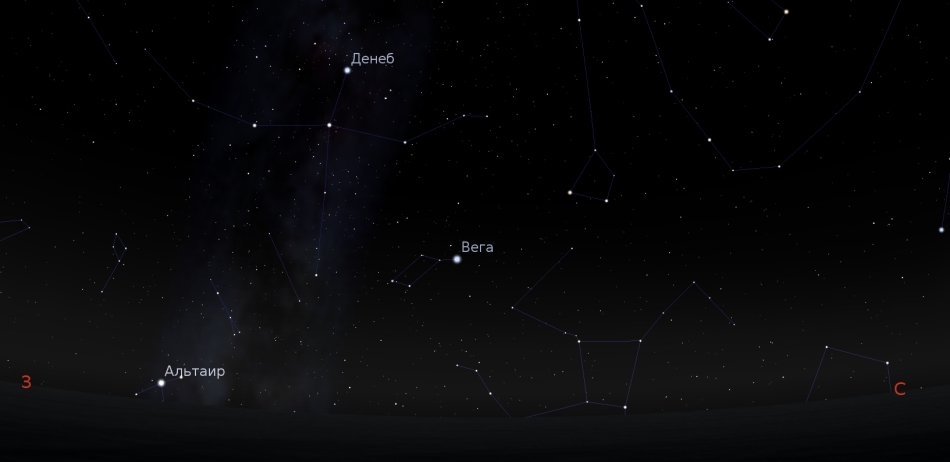
In the north, Ursa Major settles down low above the horizon.
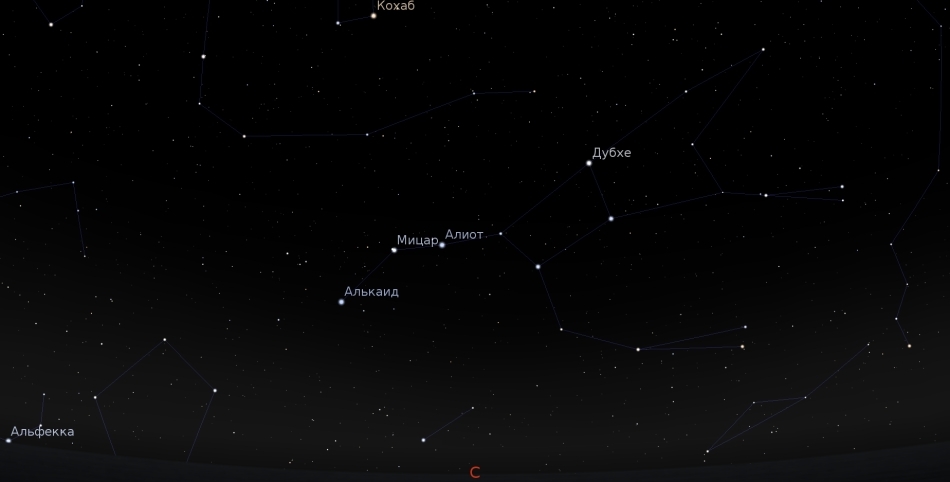

Photo by pavel S Astroforum
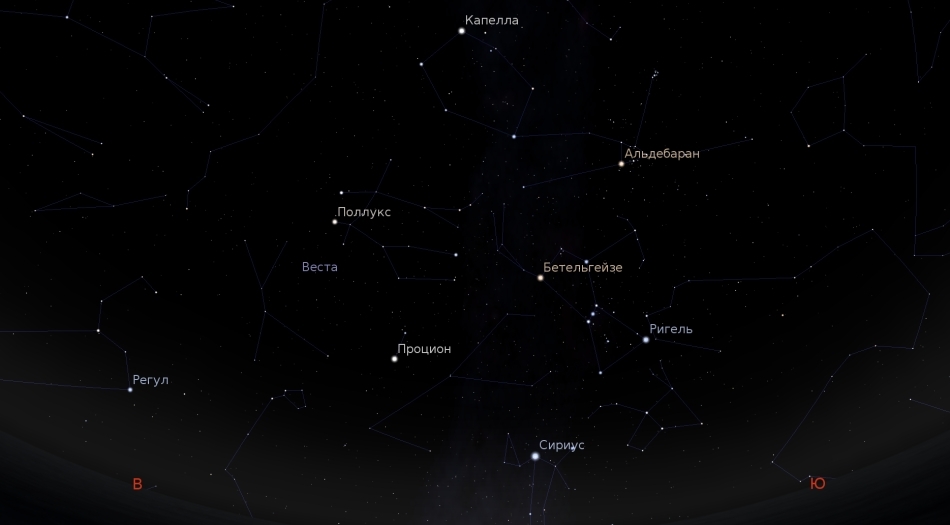
And in the east, the sovereign winter owner - Orion. There are a lot of interesting things around it. Betelgeuse, Procyon and Sirius form a winter triangle, and Sirius, Procyon, Pollux and Castor, Capella, Aldebaran, Rigel - a winter circle. In addition, the Pleiades and slightly more scattered Hyades are clearly visible to the right of Orion.
In the photo it is even more beautiful.
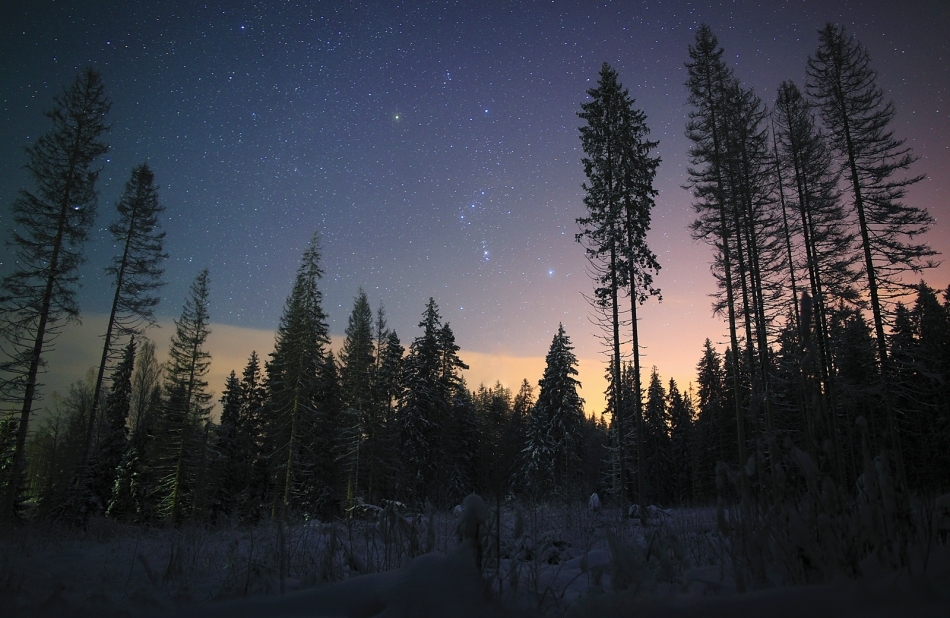

A photoby Dolph1n Astroforum User
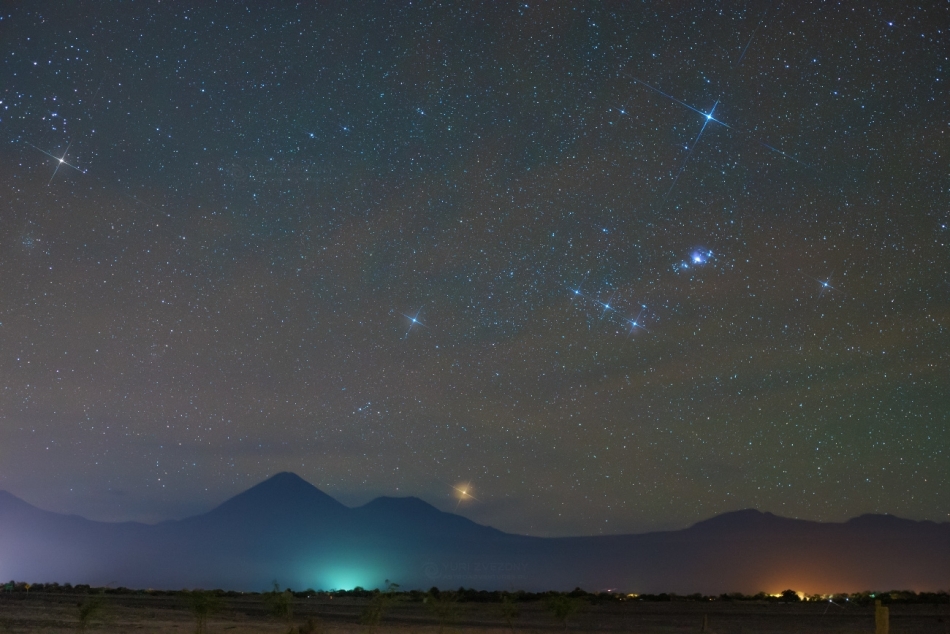

photo Citizen of the Universe Astroforum

Photo by Upsilon Astroforum
And in the morning Jupiter will rise.
On the night of January 3 to 4 there will be a maximum of the Quadrantida meteor shower. Last year, activity was so-so, but suddenly who is lucky?
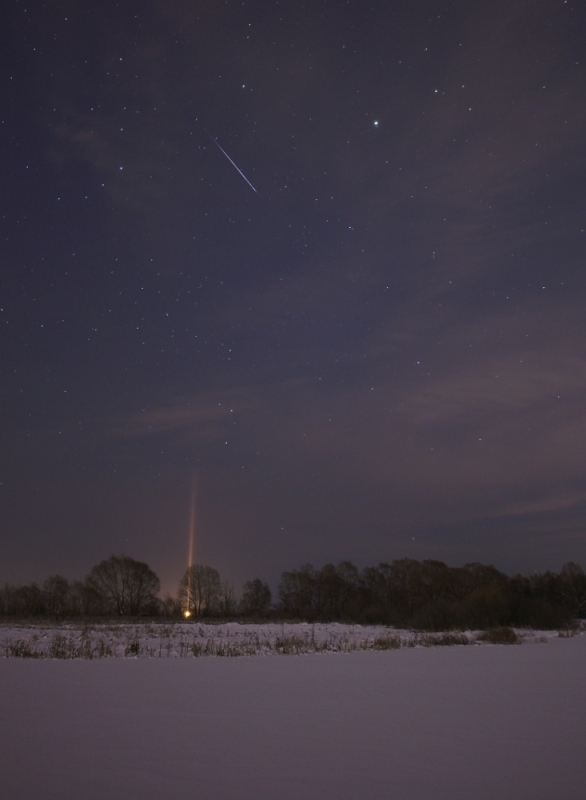

Photo by VLANN Astroforum
Now in the sky there is not a single comet visible to the eye. But you can see the comet 45P / Honda-Mrkos-Paydushakova through the telescope.

Photo taken from the AstroAlert Observational Astronomy page .
There is little hope for comets with comets in February, when the same comet 45P / Honda-Mrkos-Paydushakova passes just 0.08 astronomical units (12 million kilometers) from Earth and, with any luck, can become visible through binoculars or even with the naked eye.
In winter, long nights, this purely statistically increases the likelihood of seeing the northern lights. Yes, they rarely reach medium latitudes, but the radiance of spring and summer 2015 is teased by constantly chances to fall.
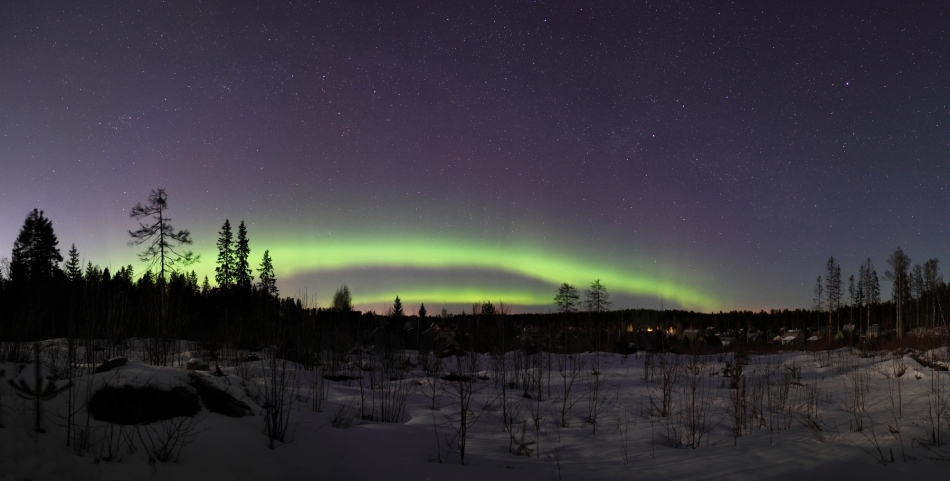

Photo by Dolph1n Astroforum
In winter, ice crystals are more common in the atmosphere, which can refract light and create halo, false suns and solar poles. Here is a general outline.

In reality, the chances are small that there will be all types of ice crystals in the atmosphere, and usually one or two types fall out.

Photos User Mirasun Astroforuma
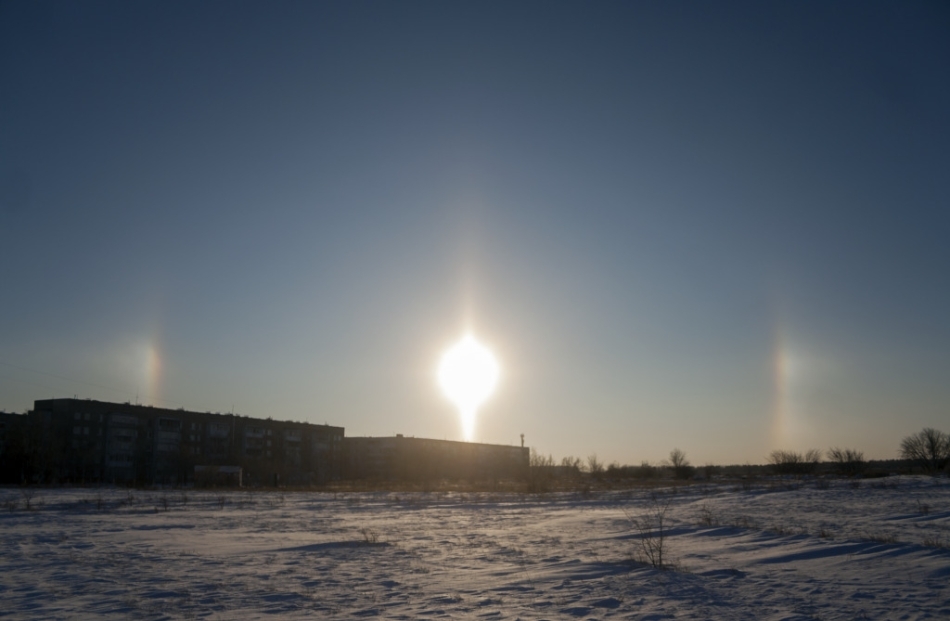

photo user granat Astroforuma

photo User Anatoly Belkin Astroforuma
Halo may be lunar.

A photoby Marat (Kukuksumushu) of Astroforum
And the abundance of artificial light sources in winter often creates a forest of light poles, which are formed according to the same principle.
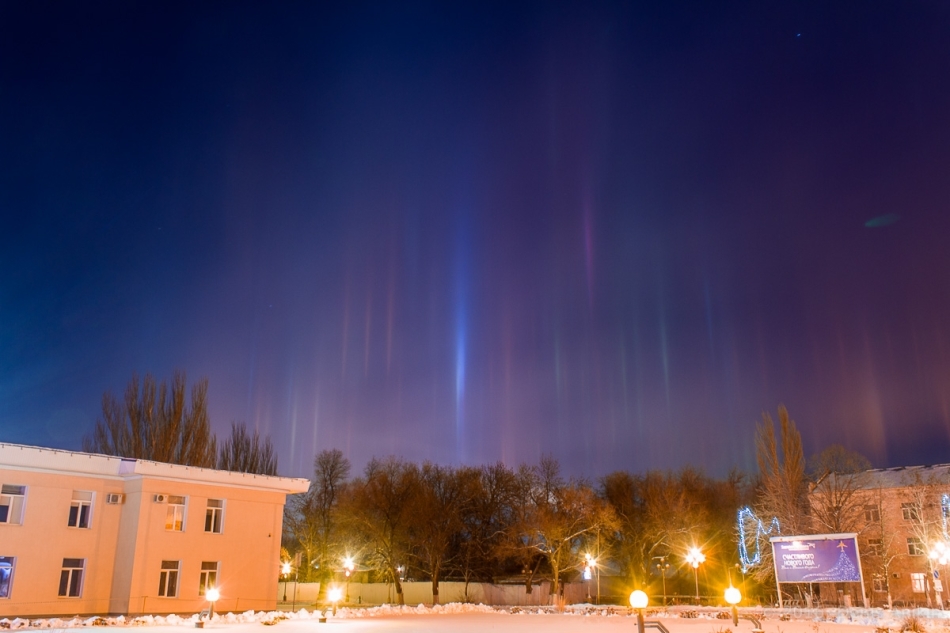


Both photos of LJ user denisanikin
And here the surface inversion bends the smoke from the pipes. The earth is calm, but starting at a certain height, wind appears and the smoke turns beautifully. This phenomenon is also more common in winter.
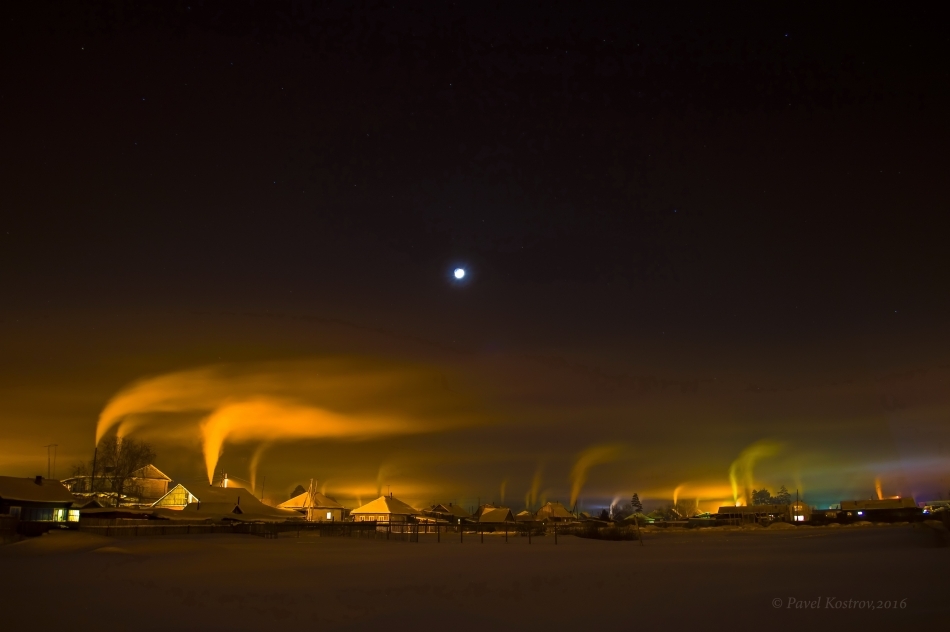

Photo by Oleg1774 Astroforum
There are a lot of beauty in the sky of a very different nature. Do not yawn.

Photo by Upsilon Astroforum
Two astronomical paradoxes
Before you go to the beauties, you will have to disappoint a little. If you think that after the winter solstice the morning already comes earlier, then for the territory of Russia this is not so. Many already managed to get tired of going to work in the dark, but until the very end of December the Sun will rise later. Yes, daylight hours are increasing, but this is due to a later sunset. Here is, for example, a graph for Ufa:

If you play with resources that show the time of sunrise and sunset, you can see that the situation is the opposite in the southern hemisphere - there the Sun begins to rise from the beginning of the month later.
The second paradox is that the Earth passes its pericenter in 2017 in the evening of January 4 and at this moment it will be closest to the Sun. Why is it so cold, you ask, and I will remind you that because of the almost circular orbit, the Earth at perihelion (the point closest to the Sun) receives only 7% more solar energy than at aphelion (the farthest point), and the change of seasons mainly determines the inclination of the axis of rotation of the Earth.
Parade of planets
In the evening sky of the end of December, as many as five planets line up, but with the naked eye only two of them can be seen. Venus, Mars, Uranus, Neptune will be over the horizon in December and January evenings, and Mercury will "jump" into the morning sky in the coming days. But without the telescope, Uranus and Neptune you will not see, and the observations of Mercury are complicated by a small distance from the Sun. By the way, Saturn will not be far in the morning sky, and despite the fact that all six planets cannot be seen at the same time, it will be a full-fledged parade of planets in a sector of only 70 °.

For those who will not sleep
If you are lucky with the weather on December 31, then a magnificent picture will rotate above your heads. After sunset, the Mars and Venus will be perfectly visible to the naked eye, in January they will rise even higher.

In the north-west, the summer-autumn triangle of Vega, Deneb and Altair will be hidden behind the horizon.

In the north, Ursa Major settles down low above the horizon.


Photo by pavel S Astroforum
And in the east, the sovereign winter owner - Orion. There are a lot of interesting things around it. Betelgeuse, Procyon and Sirius form a winter triangle, and Sirius, Procyon, Pollux and Castor, Capella, Aldebaran, Rigel - a winter circle. In addition, the Pleiades and slightly more scattered Hyades are clearly visible to the right of Orion.

In the photo it is even more beautiful.

A photoby Dolph1n Astroforum User

photo Citizen of the Universe Astroforum

Photo by Upsilon Astroforum
And in the morning Jupiter will rise.

Meteor showers
On the night of January 3 to 4 there will be a maximum of the Quadrantida meteor shower. Last year, activity was so-so, but suddenly who is lucky?

Photo by VLANN Astroforum
Comets
Now in the sky there is not a single comet visible to the eye. But you can see the comet 45P / Honda-Mrkos-Paydushakova through the telescope.

Photo taken from the AstroAlert Observational Astronomy page .
There is little hope for comets with comets in February, when the same comet 45P / Honda-Mrkos-Paydushakova passes just 0.08 astronomical units (12 million kilometers) from Earth and, with any luck, can become visible through binoculars or even with the naked eye.
Non-astronomical phenomena
In winter, long nights, this purely statistically increases the likelihood of seeing the northern lights. Yes, they rarely reach medium latitudes, but the radiance of spring and summer 2015 is teased by constantly chances to fall.

Photo by Dolph1n Astroforum
In winter, ice crystals are more common in the atmosphere, which can refract light and create halo, false suns and solar poles. Here is a general outline.

In reality, the chances are small that there will be all types of ice crystals in the atmosphere, and usually one or two types fall out.

Photos User Mirasun Astroforuma

photo user granat Astroforuma

photo User Anatoly Belkin Astroforuma
Halo may be lunar.

A photoby Marat (Kukuksumushu) of Astroforum
And the abundance of artificial light sources in winter often creates a forest of light poles, which are formed according to the same principle.


Both photos of LJ user denisanikin
And here the surface inversion bends the smoke from the pipes. The earth is calm, but starting at a certain height, wind appears and the smoke turns beautifully. This phenomenon is also more common in winter.
Photo by Oleg1774 Astroforum
There are a lot of beauty in the sky of a very different nature. Do not yawn.
