Wearable miniature sensors help control diet
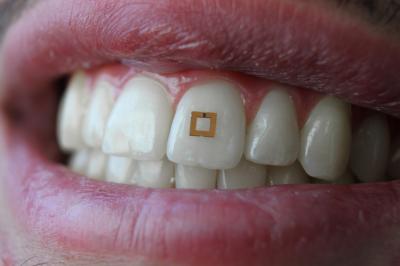 Technology is constantly evolving, and medical systems are no exception. They become more and more perfect, in many cases - tiny, for the convenience of those who will use them. The other day it became known about a tiny sensor that is attached to a person’s tooth. This sensor allows you to control the power mode.
Technology is constantly evolving, and medical systems are no exception. They become more and more perfect, in many cases - tiny, for the convenience of those who will use them. The other day it became known about a tiny sensor that is attached to a person’s tooth. This sensor allows you to control the power mode. It was created by biomedicine specialist Fiorenzo Omenetto from Tufts University . According to the developer, in the near future, such devices will become common, and will help to monitor compliance with the proper diet, as well as the state of the human body.
Development results have been publishedin Advanced Materials. The Omenetto team has been working for a long time to create all kinds of sensors - both for application to the skin, teeth, and for implantation in the brain or surgical implants. As for the oral cavity, here you can place various sensors that can constantly monitor certain indicators.
The working prototype of the sensor is small, its size is 2 * 2 mm. The thickness is minimal; it is a film with electronic components. Sensors are placed between two gold-plated resonators, so that the active medium of the oral cavity does not damage the device. The sensor reacts to the presence of various substances with the help of specialized enzymes or antibodies. They help determine the presence of specific molecules. Bioactive sensors respond to changes in the composition of the medium, and give a signal.
Resonators act like antennas, transmitting radio waves generated by the device itself when the chemical composition changes among. These waves are captured by a special device connected to a tablet or mobile phone. Each detectable substance corresponds to a radio wave of a certain frequency. The application installed on the connected device analyzes the signal and gives the result.
So far, the list of connections to which the sensor can respond is not too extensive. These are sugar, salt and alcohol. In principle, even this is enough to control the human diet, but, of course, the developers do not plan to stop there, especially since the sensor is not able to determine the amount of food eaten, and this is a major drawback of the system. In the future, developers plan to ensure that the application shows - "you consumed foods with a calorie content of 358.2 kcal."
Generally speaking, thin film sensors are not a new idea. Last year, for example, miniature temperature sensors were reported that are attached directly to food. Moreover, these sensors are "edible", they completely dissolve under the action of gastric juice, without emitting any harmful substances in the process. Their thickness is less than the thickness of a human hair, only about 100 micrometers.
In 2016, the pages of Geektimes reported the creation of a wearable device for the automatic diagnosis and correction of glucose in the blood of diabetics. It was proposed by an integrated team of scientists from South Korea and the United States. The progress report is published in the authoritative publication Nature. The device itself is a compact bracelet worn on the brush with active elements from graphene. It connects to the smartphone wirelessly.
And there are sensors designed to analyze the state of the human brain. They are being introducedto the brain, where they work for some time, transmitting important data (temperature, electrical activity, etc.). Then the sensor dissolves without a trace, without emitting harmful substances. So far, these systems are being tested on rats. After - clinical trials will begin, but this stage will follow only after a few years. The approval of new systems by regulators from medicine is a very quick affair.
In general, such systems are becoming more common. Over time, we can expect the appearance of similar IoT sensors, which transmit information constantly, keeping under control the state of many human organs. And this is not at all such a distant future, as is commonly believed.


