Migrating a physical server to a virtual one - how to manage in 1 day


If you do not want to read the preface and rationale for the rationality of transferring data to a virtual server , you can immediately go to the instructions .
Maintaining your own equipment or its fleet is not a cheap pleasure and almost always has nothing to do with the direct influx of money into the organization. Own server, which can even stand in its own small room in the office - a relic of the past, it is more and more annoying for modern managers.
A business needs a functioning service, not a fleet of equipment and its staff. What problems does small and medium business face when deciding to purchase its own server:
- High cost of initial investment
- Quick depreciation of equipment
- The need to keep a specialist on staff who could assemble, configure and maintain the server in the future
- Constant fears that something will fail while this specialist is not in place
- It is not always possible to quickly get to the place of equipment at night or on a day off to replace components
- You will have to accept the promises of the system administrator on the topic of data security in case of failure of any drive
- If something on the server fails, it will take several days to find out the reasons, purchase a new component and install it. Or in the best case, 1 day if, of course, you store all spare parts in advance in close proximity to the server itself - this is the time while your business and all employees do not work!
- During the operation of a ready-made server, unscrupulous system administrators can simulate the failure of a particular part of the server to replace it and then assign it to a decommissioned
- At the time of purchase of equipment, recommendations from the system administrator at the place of purchase may include his own interest
An attentive reader will ask, why not rent a physical server instead of a virtual one in the cloud? And here are a number of reasons:
- Physical servers (especially those that are often offered for rent) are not fault-tolerant machines; they are essentially home PCs in server enclosures.
- If something fails on such a server, then in the best case, the components will be replaced within 24 hours, and in the worst, you will lose all your data if, for example, the hard drive fails (they just break most often than anything else)
- When something fails on the leased physical server, the one who provides this server for rent can only find out about the problem from you. If it happened at night, you will only find out in the morning that your server has been unavailable for several hours.
- If you decide to rent a server of a professional level, it will be incredibly expensive per month (comparable to the expenses described above when maintaining your own equipment)
- When you finally get tired of being the “owner of the leased iron” and you decide to transfer it to virtual, it can be more difficult to do this from someone else’s equipment, as the provider can create artificial obstacles to this.
- The further you put off the transfer to the cloud infrastructure, the more data you accumulate and the longer the transfer process will take.

Now almost no modern business is complete without its own, albeit minimal, IT infrastructure. This can be a website, a business process management system, any kind of services that require constant stable operation and constant availability: from accounting to exchange trading - this will be provided with the highest degree of fault tolerance by the infrastructure of a cloud service provider, for example, ours.
Why is a virtual server on a foreign infrastructure more reliable than its own physical?
The first thing to understand is not all VPS / VDSservers are equally good, often representatives of the low-cost segment offer a virtual server for reliability no better than what would be at your place under the table. This is precisely because they gather without reserving anything. However, there is also a demand for such servers: there are many tasks for which downtimes of several hours or complete data loss are not critical - these are usually servers for VPNs, proxies, or one-time mailings (most often SPAM).
If we talk about reliability, choosing a segment at least slightly above the minimum bar, then here it is worth counting on:
- 24/7 technical support
- Reservation of communication channels with the outside world and duplication of network equipment inside the data center
- Availability of fault-tolerant data storage systems and regular backup to independent systems
- In case of technical work or failures, the automatic or manual transfer of customer resources to other equipment inside the data center without stopping the operation of client virtual servers
- Constant monitoring of the state of the entire fleet of equipment: its performance and overall workload
- If something fails, you will almost never feel it, and repair work will begin immediately and without your participation
- Elementary responsibility for their reputation in a highly competitive market.
And, of course, you can at any time freely change the configuration of your server, increasing the parameters when necessary and decreasing to save money when large capacities are not needed.
It will be useful to note that all of the above applies to VPS.house
Transferring a physical server to a virtual one is a very simple task and the most ordinary “PC user” can handle it. Most of the time is spent on taking a data image from the current disk and then copying it to the server of the future provider. If there really is a lot of data, then the process can take a day or even more, but you do not have to be at the computer at the same time - you can do any other things in parallel.
1. Create a disk image of the current physical server
To create a disk image, we suggest using the Disk2vhd utility. It does not require installation and can be downloaded directly from the Microsoft website:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/disk2vhd
VHD / VHDX is a disk image format used in Hyper-V hardware virtualization environments . Such an environment is used on the VPS.house service and among many providers who offer rental services for virtual servers running Windows Server.
Unzip the downloaded ZIP-archive and run the disk2vhd.exe file .

Before you start creating the image, make sure that the “Use Vhdx” box is checked, this is important in order to get the disk image in the modern VHDX format that supports the expansion of the volume up to 64TB.
In the file name field, specify the place where you want to save the final image file. Pay attention to the required amount of free space to create an image!
Check only the drives you need to work in the cloud. If you have a large disk for backups in the same server, it may not always be wise to spend time preparing an image and transferring data with it.
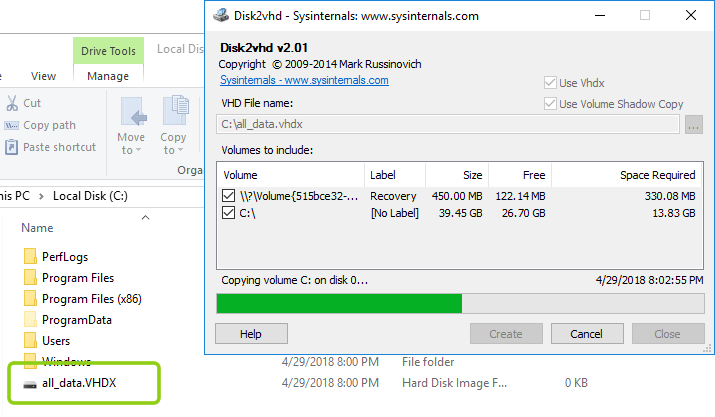
Depending on the amount of data and the speed of your current disk system, the image preparation process can take up to several hours.
Ultimately, you will see your finished image in the chosen place - the most difficult part ends there.
2. Send the disk image to the cloud provider
What features a good cloud service provider should have, we described above, you can choose any one that appeals to you or you can create an account and server automatically in 1-2 minutes on VPS.house When choosing a configuration, pay attention to the size of the hard disk, it should not be less than the file size your image and the volume that you need for normal further work. After creating an account and a virtual server, you need to write a request to the hosting support service with a request to provide data for downloading your disk image - in response, data will be given for accessing an isolated FTP directory where you can copy your image.

Depending on the size of the file and the speed of the communication channels in your current data center or office, the transfer may take several hours. For our part, to download client images, we provide a place on a temporary server that is connected to the network at a constant speed of 2 Gb / s. This speed allows you to transfer, for example, a large file server or database server with a capacity of 1 TB in just an hour and a half .
Once you upload the file, you just need to write a second support request to connect this image to the working hosting architecture - the provider will do the rest for you and turn the server on. It will be immediately available at the new IP address allocated to you, which you will see in your personal account in advance.
PS: this instruction does not only work for transferring a physical server to a virtual one, it is also perfect for moving from one cloud to another .
If you already have a working virtual server , for the setup of which you spent a lot of time and you do not want to repeat everything again in another place, but at the same time you are not completely satisfied with the quality of the services provided or their cost - use the instructions and the identical configured server will work in a new cloud in less than 1 day with minimal effort on your part.
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Please come in.
What infrastructure works in your organization
- 85.8% Own server hardware 73
- 14.1% Everything is in the “cloud” 12
