Tomorrow is March 31st. Please make backups
Recently, security threats have noticeably shook the nerves of the entire IT industry: Wanna Cry, Petya, New Year's surprise Meltdown, etc. These are all large-scale incidents. It is almost impossible to calculate how many small SQL injections, DDoS attacks, hacks, thefts occurred in small and medium-sized businesses. High technology is transforming at an incredible speed: what yesterday was scientific research in university laboratories and in companies, is now actively being introduced into production and used in the commercial field. And the more technology, the higher the likelihood of attacks, and in the most unexpected directions.
Tomorrow is International Backup Day, or Backup Day. One of those dates, which is better not to celebrate, but to work out. Let's see where in the second decade of the XXI century it is worth waiting for attacks.

Entertaining zoology. The arctic fox always sneaks up imperceptibly.
Our company RegionSoft Developer Studio worked in 2011, works in 2018 - and, delivering business solutions and on-premise CRM-system in particular, we face the same security problems of companies in different business fields. Just because for security they’re doing ... nothing. Well, how much can you? Indeed, the dangers are growing literally day by day, and the threats are targeted not at giants with 100,500 levels of protection, but at priceless data from almost any business.
Let's look at two infographics. The first is the number of recorded incidents in the field of information security in 2011, the second is the same, but in 2017. Six years is a fairly short period of time even in conditions of explosive technological growth. Nevertheless, the situation has changed radically, from year to year the number and scale of attacks is growing, they change their vector - from a large number of small incidents to large and damaging a huge amount of data.
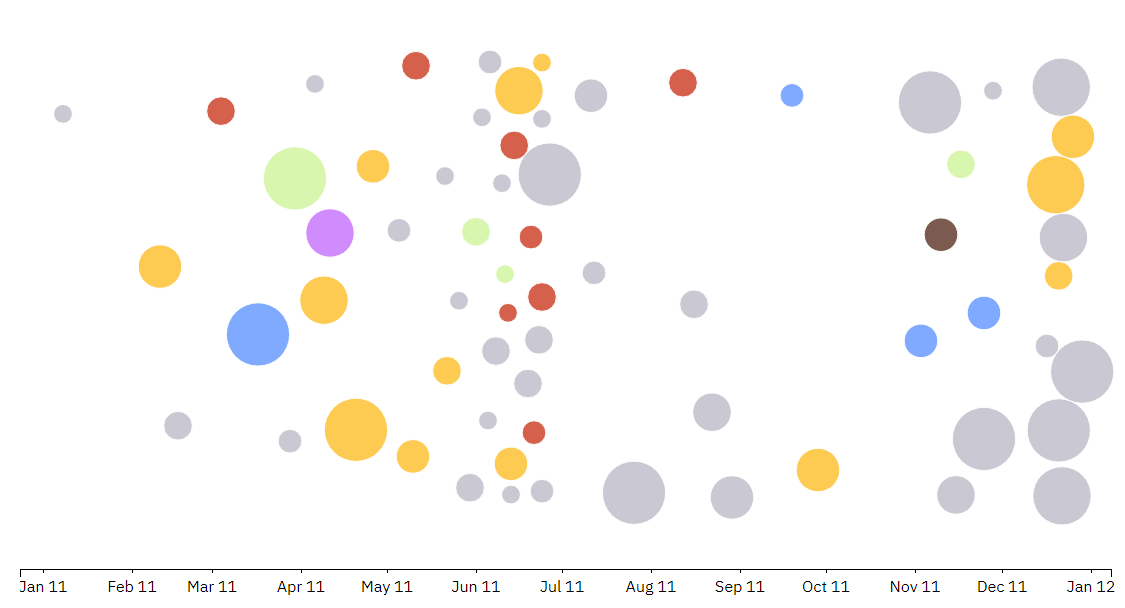 2011
2011
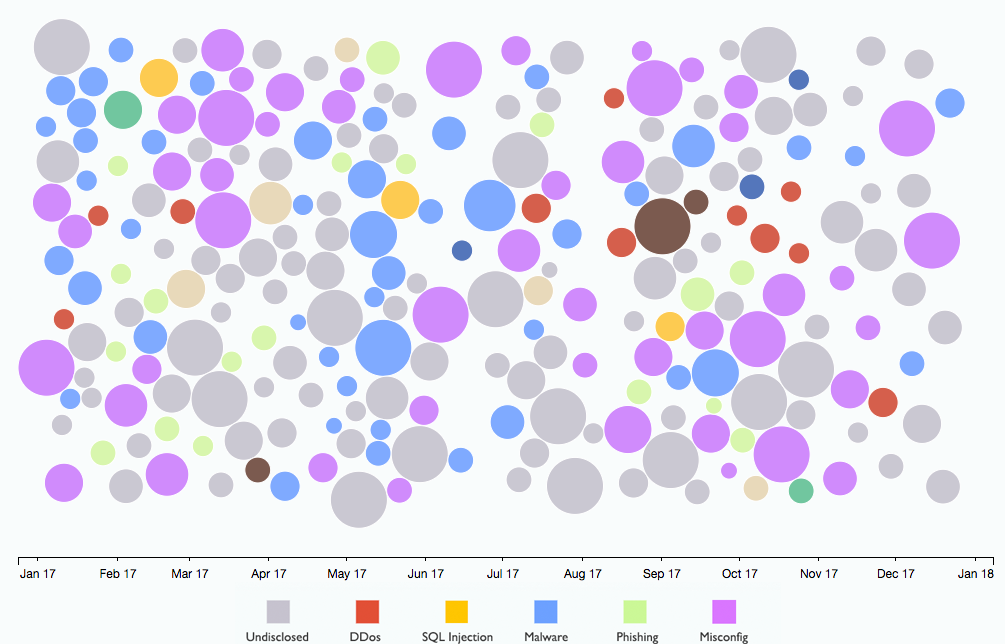
2017 year . Source Securityintelligence . This colorful picture illustrates a not-so-funny security hole. IBM X-Force identified 235 security incidents in 2017 based on 2.8 billion records. As you can see, DDoS has become more modest, but does not disappear, as well as malware. Among the novice leaders are attacks on the Internet of things, misconfig cloud servers and attacks using cryptocurrencies.
A relatively new area of security is big data and machine learning, which are in service with both large companies and tech startups. Data is collected and aggregated using web applications, internal systems, etc. All of them can be attacked, and dozens of data sources just get out of hand. These data are complex, the collection and processing mechanisms are overloaded, high demands are placed on storage systems - all this colossus requires a lot of time that needs to be spent on creating and deploying a security system. Such systems, due to their complexity, are very vulnerable to hackers and cyber fraudsters. Alas, the majority of companies working with big data provide protection of data flows almost “manually” using software tools of their own design. And it’s not clear what will be the fight against cybercriminals. But such a situation should not slow down the industry, but rather stimulate a developed infrastructure: the development of specialized software, the creation of new ultra-secure storage systems, etc.
 Cybersecurity conference
Cybersecurity conference
On December 20, 2017, an attack on Mongo DB databases began. At first, point incidents occurred, but literally in a week, thousands of Mongo DB servers were completely destroyed (approximately 28,000, which is more than half of all Mongo DB databases accessible via the Internet). Not all the databases were attacked in a row, but those that were accessible through the worldwide network and did not have a password in the DBMS administrator account. Instead of their data, users received a buyback message, moreover, groups of hackers exchanged information and a buyback request could appear a second or third time (at the same time, hackers asked for from $ 150 to $ 500, these are relatively small amounts that companies went with relative ease) . Alas, crackers were not ethical and often forgot to export and save the data of each of the databases, as a result, some companies lost their data forever. By the way, the attack turned out to be so massive because it was not carried out manually as a one-time act, but with the help of automated scripts. And then tell me after that, was it really not clear to developers and system administrators that the DBMS settings by default make the database open for attack and as vulnerable as possible? And where were the backups? Rhetorical questions, a tough lesson, which, by the way, did not teach everyone.
 Trust me it's much easier to do online
Trust me it's much easier to do online
We are the developers of the RegionSoft CRM desktop CRM systemand, of course, every day we are confronted with a business that considers the cloud - the top of the corporate IT infrastructure. Aggressive marketing of providers, cloud service providers and even the largest global corporations does its job - there’s nothing to hide here. But no one excludes the human factor, configuration errors, insider stuffing and outright hacks. Alas, Mongo DB was not the only victim, among the victims of great trouble in the clouds - customers were Salesforce, Amazon S3, Bitrix 24, and in the recent past, Google. And the victims of such cloudy troubles are not only paralyzed and dataless business, but also real corporate monsters. So, in July 2017, the giant telecom operator Verizon was attacked, resulting in more than 14 million hits on the Internet. Records of personal data of subscribers from the USA. It was one of the operator’s service providers, NICE Systems, who accidentally left the data open on the Amazon S3 unprotected cloud server. Leaked data included customer names, mobile phones, PIN-codes - in general, everything that will bypass any form of authentication. It is not known why Verizon trusted the data of an Israeli company, but there is a version that NICE Systems with this information simply controlled the work of call center operators for Verizon. Researchers leak revealed that the grief-supplier is also associated with the French operator Orange. mobile phones, PIN codes - in general, everything that will bypass any form of authentication. It is not known why Verizon trusted the data of an Israeli company, but there is a version that NICE Systems with this information simply controlled the work of call center operators for Verizon. Researchers leak revealed that the grief-supplier is also associated with the French operator Orange. mobile phones, PIN codes - in general, everything that will bypass any form of authentication. It is not known why Verizon trusted the data of an Israeli company, but there is a version that NICE Systems with this information simply controlled the work of call center operators for Verizon. Researchers leak revealed that the grief-supplier is also associated with the French operator Orange.
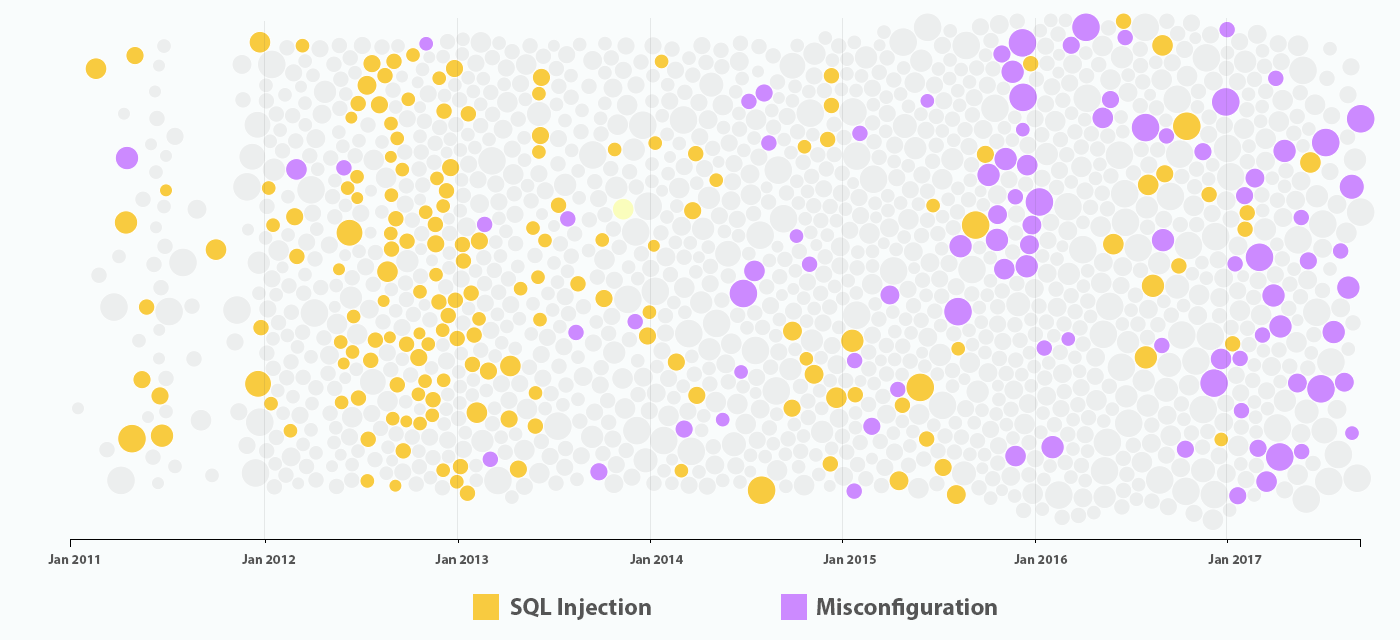 Source Securityintelligence . In 2017, as of September, IBM X-Force tracked over 1.3 billion records from improperly configured servers - a total of 24 incidents. To imagine this in the future, such incorrect configurations account for 71% of the total number of recorded leaks for the period until 2017. Compared to SQL injections, this type of security breach carries much more devastating consequences, since fewer attacks can compromise a thousand times more records (SQL injections compromise millions, not billions, of records).
Source Securityintelligence . In 2017, as of September, IBM X-Force tracked over 1.3 billion records from improperly configured servers - a total of 24 incidents. To imagine this in the future, such incorrect configurations account for 71% of the total number of recorded leaks for the period until 2017. Compared to SQL injections, this type of security breach carries much more devastating consequences, since fewer attacks can compromise a thousand times more records (SQL injections compromise millions, not billions, of records).
Another Amazon Web Services S3 Cloud configuration story happened in October 2017. Due to an error in determining the rights of access to data in the public domain, a consumer data base was found (from personal information to preferences, mortgages, etc.) of 123 million US citizens. Access could be obtained by any authenticated Amazon AWS user - that is, essentially anyone who could register even a fresh account (even with "left" mail). As it turned out, two analytical companies and the Census Bureau were involved in the records.
 Save your personal data here.
Save your personal data here.
So what exactly are these “misconfigurations”? This is an internal problem of the company, and sometimes the provider or service provider, which can lead to easy access to the database without any hacker tricks. Gartner analysts suggest that this type of security breach accounts for between 70 and 99% of all incidents. Anyone can do it on any side of the relationship: admin, developer, and even a testing engineer, who is allowed to live assembly. Good news: these problems can be avoided, if you are a little more careful, do not leave the DBMS without a password, well, avoid the favorite combination of admin / admin and no less than your favorite root / root.
This does not mean that you should abandon the cloud. But it’s better to keep the customer base and important commercial information at home and protect it more reliably.
Cryptocurrency this year will not cease to “please” us with new schemes of fraud, theft and cybercrime. Obviously, there will be a wave of high-profile disappearances (it is difficult for us as a business representative to call these processes bankruptcy) of bitcoin companies that hit the jackpot at the ICO. But it’s much more interesting which cyber fraudsters will find security holes in the blockchain. At the moment, several gigantic acts of theft of bitcoins have already taken place.
Tether cryptocurrency startup lost $ 31 million in tokens. The company immediately stated that it would not redeem tokens from scammers and would completely prevent the crypto-exchanges from accessing this volume. Despite the fact that Tether has already discovered the address where the hacker is holding stolen funds, the attack mechanism could not be understood.
NiceHash Slovenian cryptocurrency exchange recently announced that $ 64 million worth of bitcoins had been stolen. This is about 4,700 BTC, at the time of the theft, each cost $ 13,617. Again, the mechanism of attack is unclear, as, incidentally, the amount of loss is very estimated. There is a version that bitcoins left the wallet of one of the users, and at the time of a sharp increase in the cost of cryptocurrency.
Meanwhile, each such theft dramatically compromises the essence of cryptocurrency and can reduce the rate. When in 2016 almost 120,000 bitcoins worth $ 77 million were stolen from the Bitfinex crypto exchange, the depreciation was 20%. For the exchange rate of any asset, this is simply a colossal fall, in fact, a collapse. Again, the fraud scheme could not be fully disclosed. By the way, for several weeks of that August event, hackers managed to steal Ethereum for $ 50 million.
Cryptocurrency has not really taken root in Russian business, and, it seems, in serious companies it will not take root. But if you suddenly want to attract a new audience and accept payments in bitcoins or something else, remember that you need to pay double attention to security.
In November 2016, the Mirai botnet turned hundreds of thousands of cameras and DVR devices into bots for DDoS attacks. In 2017, he returned and continued his destructive work, using NVR and expanding his geography. Such attacks can lead to the most unpredictable consequences, because the affected devices can be part of the urban infrastructure, an element of physical security of potentially dangerous objects, etc.
In August 2017, the WireX botnet, consisting of tens of thousands of infected Android devices, hit hotels and hotels. It is noteworthy (in fact, sad) that the infection occurred after more than 300 official applications on Google Play, including such harmless programs as file managers and media players.
Another manifestation of IoT threats is the Bluetooth vulnerability called BlueBorn. Without noise and dust, it can be used to compromise systems in the immediate area. This is a very dangerous threat in terms of potential scale: the Bluetooth protocol is used by almost all wearable devices, as well as systems and elements of the smart home system, which are often used in offices, warehouses, and small production rooms for reasons of economy.
If you use IoT, you can theoretically get a huge network of bots that will be able to permanently "put" hundreds of thousands of infrastructure and collect the most valuable data (about preferences, movements, health, etc.).
 Listen, have we done a backup?
Listen, have we done a backup?
We have already given stories related to data leakage from partners and employees, but we will repeat again. If the reasons we talked about above often do not depend on us, and attacks are difficult to detect, then in the case of the business ecosystem, you yourself can harm yourself. These are untested and unreliable employees, business trainers and consultants whom you trust your data yourself, naively believing that they are like doctors of your business. They are also partners, contractors and other companies that do something for you or have a relationship with you. When it comes to benefits, they won’t be stopped by any signed NDA. Firstly, not everyone will go to court, secondly, they will still need to be found, and thirdly, even if the problems are resolved in the legal field, the damage will still remain. The advice here is one and quite universal - think with your head.
 In the right corner of the ring we have a firewall, encryption, antivirus and other cybersecurity. And in the left corner of the ring we have ... Vasya (human factor).
In the right corner of the ring we have a firewall, encryption, antivirus and other cybersecurity. And in the left corner of the ring we have ... Vasya (human factor).
We will not engage in moralizing and ship you with detailed tips on protecting corporate information (we will write about this separately soon). Just remember one thing. Here is the list:
There is nothing particularly complicated and unusual about it. But the implementation of these points will already make your company several times more secure. Pay particular attention to the last three points - we still do not understand why they are not often made so much. Maybe someone will reveal the secret in the comments.
Well, for that matter, today is Friday, the evening of which, by tradition, may turn out to be interesting. Here is another warning:

Our site with absolutely desktop business software and our flagship RegionSoft CRM.
 Our Telegram channel BizBreeze . Anything about CRM and business, wisely, without copy-paste and 90% without advertising. Join in disordered ranks.
Our Telegram channel BizBreeze . Anything about CRM and business, wisely, without copy-paste and 90% without advertising. Join in disordered ranks.
Tomorrow is International Backup Day, or Backup Day. One of those dates, which is better not to celebrate, but to work out. Let's see where in the second decade of the XXI century it is worth waiting for attacks.

Entertaining zoology. The arctic fox always sneaks up imperceptibly.
Our company RegionSoft Developer Studio worked in 2011, works in 2018 - and, delivering business solutions and on-premise CRM-system in particular, we face the same security problems of companies in different business fields. Just because for security they’re doing ... nothing. Well, how much can you? Indeed, the dangers are growing literally day by day, and the threats are targeted not at giants with 100,500 levels of protection, but at priceless data from almost any business.
Let's look at two infographics. The first is the number of recorded incidents in the field of information security in 2011, the second is the same, but in 2017. Six years is a fairly short period of time even in conditions of explosive technological growth. Nevertheless, the situation has changed radically, from year to year the number and scale of attacks is growing, they change their vector - from a large number of small incidents to large and damaging a huge amount of data.


2017 year . Source Securityintelligence . This colorful picture illustrates a not-so-funny security hole. IBM X-Force identified 235 security incidents in 2017 based on 2.8 billion records. As you can see, DDoS has become more modest, but does not disappear, as well as malware. Among the novice leaders are attacks on the Internet of things, misconfig cloud servers and attacks using cryptocurrencies.
Where were the main "punctures" of the last two years?
Machine Learning and Big Data
A relatively new area of security is big data and machine learning, which are in service with both large companies and tech startups. Data is collected and aggregated using web applications, internal systems, etc. All of them can be attacked, and dozens of data sources just get out of hand. These data are complex, the collection and processing mechanisms are overloaded, high demands are placed on storage systems - all this colossus requires a lot of time that needs to be spent on creating and deploying a security system. Such systems, due to their complexity, are very vulnerable to hackers and cyber fraudsters. Alas, the majority of companies working with big data provide protection of data flows almost “manually” using software tools of their own design. And it’s not clear what will be the fight against cybercriminals. But such a situation should not slow down the industry, but rather stimulate a developed infrastructure: the development of specialized software, the creation of new ultra-secure storage systems, etc.

Databases - keep an eye out for protection
On December 20, 2017, an attack on Mongo DB databases began. At first, point incidents occurred, but literally in a week, thousands of Mongo DB servers were completely destroyed (approximately 28,000, which is more than half of all Mongo DB databases accessible via the Internet). Not all the databases were attacked in a row, but those that were accessible through the worldwide network and did not have a password in the DBMS administrator account. Instead of their data, users received a buyback message, moreover, groups of hackers exchanged information and a buyback request could appear a second or third time (at the same time, hackers asked for from $ 150 to $ 500, these are relatively small amounts that companies went with relative ease) . Alas, crackers were not ethical and often forgot to export and save the data of each of the databases, as a result, some companies lost their data forever. By the way, the attack turned out to be so massive because it was not carried out manually as a one-time act, but with the help of automated scripts. And then tell me after that, was it really not clear to developers and system administrators that the DBMS settings by default make the database open for attack and as vulnerable as possible? And where were the backups? Rhetorical questions, a tough lesson, which, by the way, did not teach everyone.

Cloud systems and services - data rain
We are the developers of the RegionSoft CRM desktop CRM systemand, of course, every day we are confronted with a business that considers the cloud - the top of the corporate IT infrastructure. Aggressive marketing of providers, cloud service providers and even the largest global corporations does its job - there’s nothing to hide here. But no one excludes the human factor, configuration errors, insider stuffing and outright hacks. Alas, Mongo DB was not the only victim, among the victims of great trouble in the clouds - customers were Salesforce, Amazon S3, Bitrix 24, and in the recent past, Google. And the victims of such cloudy troubles are not only paralyzed and dataless business, but also real corporate monsters. So, in July 2017, the giant telecom operator Verizon was attacked, resulting in more than 14 million hits on the Internet. Records of personal data of subscribers from the USA. It was one of the operator’s service providers, NICE Systems, who accidentally left the data open on the Amazon S3 unprotected cloud server. Leaked data included customer names, mobile phones, PIN-codes - in general, everything that will bypass any form of authentication. It is not known why Verizon trusted the data of an Israeli company, but there is a version that NICE Systems with this information simply controlled the work of call center operators for Verizon. Researchers leak revealed that the grief-supplier is also associated with the French operator Orange. mobile phones, PIN codes - in general, everything that will bypass any form of authentication. It is not known why Verizon trusted the data of an Israeli company, but there is a version that NICE Systems with this information simply controlled the work of call center operators for Verizon. Researchers leak revealed that the grief-supplier is also associated with the French operator Orange. mobile phones, PIN codes - in general, everything that will bypass any form of authentication. It is not known why Verizon trusted the data of an Israeli company, but there is a version that NICE Systems with this information simply controlled the work of call center operators for Verizon. Researchers leak revealed that the grief-supplier is also associated with the French operator Orange.

Another Amazon Web Services S3 Cloud configuration story happened in October 2017. Due to an error in determining the rights of access to data in the public domain, a consumer data base was found (from personal information to preferences, mortgages, etc.) of 123 million US citizens. Access could be obtained by any authenticated Amazon AWS user - that is, essentially anyone who could register even a fresh account (even with "left" mail). As it turned out, two analytical companies and the Census Bureau were involved in the records.

So what exactly are these “misconfigurations”? This is an internal problem of the company, and sometimes the provider or service provider, which can lead to easy access to the database without any hacker tricks. Gartner analysts suggest that this type of security breach accounts for between 70 and 99% of all incidents. Anyone can do it on any side of the relationship: admin, developer, and even a testing engineer, who is allowed to live assembly. Good news: these problems can be avoided, if you are a little more careful, do not leave the DBMS without a password, well, avoid the favorite combination of admin / admin and no less than your favorite root / root.
This does not mean that you should abandon the cloud. But it’s better to keep the customer base and important commercial information at home and protect it more reliably.
Yesterday exotic, today threat: cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency this year will not cease to “please” us with new schemes of fraud, theft and cybercrime. Obviously, there will be a wave of high-profile disappearances (it is difficult for us as a business representative to call these processes bankruptcy) of bitcoin companies that hit the jackpot at the ICO. But it’s much more interesting which cyber fraudsters will find security holes in the blockchain. At the moment, several gigantic acts of theft of bitcoins have already taken place.
Tether cryptocurrency startup lost $ 31 million in tokens. The company immediately stated that it would not redeem tokens from scammers and would completely prevent the crypto-exchanges from accessing this volume. Despite the fact that Tether has already discovered the address where the hacker is holding stolen funds, the attack mechanism could not be understood.
NiceHash Slovenian cryptocurrency exchange recently announced that $ 64 million worth of bitcoins had been stolen. This is about 4,700 BTC, at the time of the theft, each cost $ 13,617. Again, the mechanism of attack is unclear, as, incidentally, the amount of loss is very estimated. There is a version that bitcoins left the wallet of one of the users, and at the time of a sharp increase in the cost of cryptocurrency.
Meanwhile, each such theft dramatically compromises the essence of cryptocurrency and can reduce the rate. When in 2016 almost 120,000 bitcoins worth $ 77 million were stolen from the Bitfinex crypto exchange, the depreciation was 20%. For the exchange rate of any asset, this is simply a colossal fall, in fact, a collapse. Again, the fraud scheme could not be fully disclosed. By the way, for several weeks of that August event, hackers managed to steal Ethereum for $ 50 million.
Cryptocurrency has not really taken root in Russian business, and, it seems, in serious companies it will not take root. But if you suddenly want to attract a new audience and accept payments in bitcoins or something else, remember that you need to pay double attention to security.
IoT: they themselves will take away clothes and a motorcycle
In November 2016, the Mirai botnet turned hundreds of thousands of cameras and DVR devices into bots for DDoS attacks. In 2017, he returned and continued his destructive work, using NVR and expanding his geography. Such attacks can lead to the most unpredictable consequences, because the affected devices can be part of the urban infrastructure, an element of physical security of potentially dangerous objects, etc.
In August 2017, the WireX botnet, consisting of tens of thousands of infected Android devices, hit hotels and hotels. It is noteworthy (in fact, sad) that the infection occurred after more than 300 official applications on Google Play, including such harmless programs as file managers and media players.
Another manifestation of IoT threats is the Bluetooth vulnerability called BlueBorn. Without noise and dust, it can be used to compromise systems in the immediate area. This is a very dangerous threat in terms of potential scale: the Bluetooth protocol is used by almost all wearable devices, as well as systems and elements of the smart home system, which are often used in offices, warehouses, and small production rooms for reasons of economy.
If you use IoT, you can theoretically get a huge network of bots that will be able to permanently "put" hundreds of thousands of infrastructure and collect the most valuable data (about preferences, movements, health, etc.).

Their merge
We have already given stories related to data leakage from partners and employees, but we will repeat again. If the reasons we talked about above often do not depend on us, and attacks are difficult to detect, then in the case of the business ecosystem, you yourself can harm yourself. These are untested and unreliable employees, business trainers and consultants whom you trust your data yourself, naively believing that they are like doctors of your business. They are also partners, contractors and other companies that do something for you or have a relationship with you. When it comes to benefits, they won’t be stopped by any signed NDA. Firstly, not everyone will go to court, secondly, they will still need to be found, and thirdly, even if the problems are resolved in the legal field, the damage will still remain. The advice here is one and quite universal - think with your head.

We will not engage in moralizing and ship you with detailed tips on protecting corporate information (we will write about this separately soon). Just remember one thing. Here is the list:
- set complex passwords on the DBMS
- change default settings
- pursue ITAM and ITSM strategy
- don't trust newcomers
- do not disclose data to business coaches
- put minimal protection on the site
- to train employees in safe work with information
- upgrade to the latest enterprise software and OS
- make backups
- make backups
- make backups.
There is nothing particularly complicated and unusual about it. But the implementation of these points will already make your company several times more secure. Pay particular attention to the last three points - we still do not understand why they are not often made so much. Maybe someone will reveal the secret in the comments.
Well, for that matter, today is Friday, the evening of which, by tradition, may turn out to be interesting. Here is another warning:

Our site with absolutely desktop business software and our flagship RegionSoft CRM.
Interesting links:
In preparing the article most of us are pleased with the IBM blog materials on safety Securityintelligence , we recommend you read everything - security honest, interesting and, most importantly, fairly reasonable English.
→ By the way, if you want to get to know security incidents more closely, IBM has a cool interactive map . With her, the rest of Friday will pass unnoticed. Scroll through the year on the right in the block of text - and you will see that 2011 is very different from 2017. Incidents have become more widespread in terms of coverage (more circles - this is more data covered).
→ By the way, if you want to get to know security incidents more closely, IBM has a cool interactive map . With her, the rest of Friday will pass unnoticed. Scroll through the year on the right in the block of text - and you will see that 2011 is very different from 2017. Incidents have become more widespread in terms of coverage (more circles - this is more data covered).
