Botnets and their types: what is known in 2018
- Transfer
We constantly use the Internet to manage our digital devices at work and broadcast life to social networks.
Along with our Internet connection, there is a connection with such side effects as viruses, spam, hacker attacks and digital fraud. The number of phishing sites, malicious emails, destructive viruses has increased worldwide.
Of the various threats that individuals and many companies face today through the Internet, the botnet is the most common.
A botnet is a network of computers that are controlled remotely by hackers.
Botnets are used by criminals to distribute ransomware programs to your laptop, phone, tablet, computer. They may not even be detected by an antivirus, and you may not realize for a long time that your device is part of a botnet.
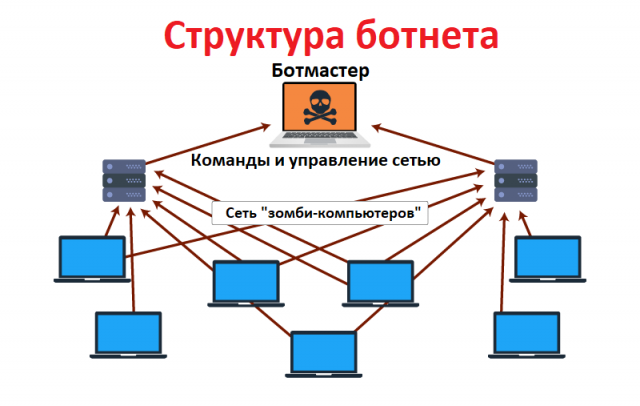
What is a botnet in 2018?
Classical understanding:
The word "botnet" is a combination of the two words "robot" and "network."
Here, the cybercriminal, who acts as a botmaster, uses Trojan viruses to compromise the security of several computers and connect them to the network for malicious purposes. Each computer on the network acts as a “bot” and is controlled by a fraudster to transmit malware, spam, or malicious content to launch an attack. A botnet is sometimes called an "army of zombies" because computers are controlled by someone other than their owner.
The origin of botnets has mainly originated in Internet chat channels (IRC).
In the end, spammers began to exploit the vulnerabilities present in the IRC networks
and developed bots .
This was done specifically to perform malicious actions, such as registration, emulation of “interested client” actions, password theft and much more.
A botnet structure usually takes one of two forms: a client-server model or a peer-to-peer model (P2P, Peer-to-peer).
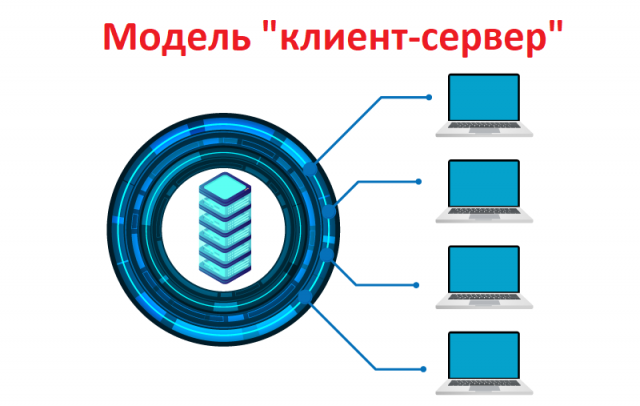
The client-server model In the client-server
botnet structure, a core network is created, in which one server acts as a botmaster. The botmaster controls the transmission of information from each client to set commands and control over client devices.
The client-server model works with the help of special software and allows the botmaster to maintain permanent control over infected devices.
This model has several drawbacks: it can be easily detected, and it has only one control point. In this model, if the server is destroyed, the botnet is killed.
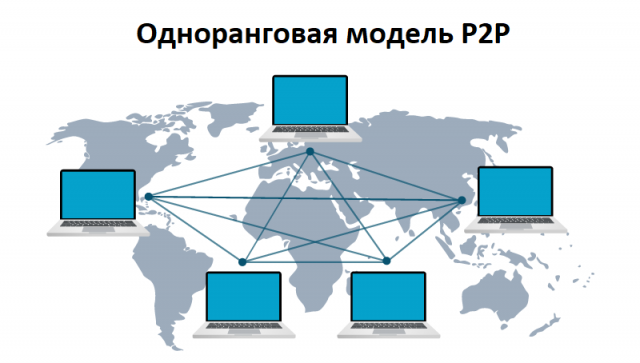
Peer-to-peer model (PTP, Peer-to-peer)
To overcome the disadvantage of using one centralized server, modern type botnets were created. They are interrelated in the form of a peer-to-peer structure.
In the P2P botnet model, each connected device operates independently as a client and as a server, coordinating the update and transmission of information between them.
The structure of the P2P botnet is stronger due to the lack of unified centralized management.
Distributed Denial of Service A
botnet can be used to attack a distributed denial of service (DDoS) to destroy network connections and services.
This is done by overloading computing resources.
The most commonly used attacks are TCP SYN and UDP attacks.
DDoS attacks are not limited to web servers, but can be directed to any service connected to the Internet. The severity of the attack can be increased by using recursive HTTP streams on the victim's website, which means that the bots recursively follow all the links in the HTTP path.
This form is called the "web", and is practiced to increase the load more effectively.

One of the largest botnet DDoS attacks in 2018 was associatedwith IoT and used the Mirai botnet virus.
The virus was designed for tens of thousands of less protected Internet devices and controlled them, turning them into bots to launch a DDoS attack.
Mirai spawned many derivative queries and continued to expand, making the attack more difficult.
This forever changed the threat landscape in terms of the methods used.
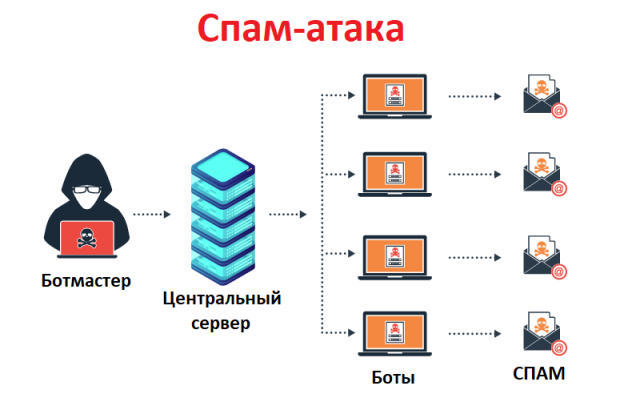
Spam and traffic monitoring
Bots can be used as an analyzer to detect the presence of sensitive data on infected machines or zombie computers. They can also find a competitor's botnets (if installed on the same machine), and can be hacked in a timely manner. Some bots offer to open a SOCKS v4 / v5 proxy (universal proxy protocol for a TCP / IP based network). When the SOCKS proxy is enabled on a compromised machine, it can be used for various purposes, for example, to send spam.
Bots use a packet sniffer to track information or data transmitted by a compromised machine. The sniffer can obtain sensitive information such as username and password.
Keylogging
With the help of the keylogger, the botmaster can easily obtain confidential information and steal user data. Using the keylogger program, an attacker can collect only those keys that are typed in a sequence of klyuev words, such as PayPal, Yahoo and more.
A variety of spyware identified as OSX / XSLCmd, migrated from Windows to OS X, includes the ability to blog and capture screen.
Mass Identity Theft
Various types of bots can interact to carry out large-scale identity theft, which is one of the fastest growing crimes. With the help of bots, you can disguise yourself as a well-known brand and ask the user to provide personal data, such as bank account password, credit card data, tax data.
Mass identity theft can be accomplished using phishing emails that force victims to enter their login credentials to websites like eBay, Amazon, or even well-known commercial banks.
Pay Per Click Abuse
The Google Ads program allows websites to show Google ads and make money from them. Google pays money to website owners based on the number of clicks received from ads. Compromised machines are used to automatically click on links, increasing the number of fake clicks.
Adware
Adware is used to attract users by advertising on web pages or in applications. They appear on computers without the knowledge or permission of users, and the original advertisement is replaced with fraudulent adware that infects the system of any users who click on it.
Adware looks like a harmless advertisement, but uses spyware to collect browser data.
Along with our Internet connection, there is a connection with such side effects as viruses, spam, hacker attacks and digital fraud. The number of phishing sites, malicious emails, destructive viruses has increased worldwide.
Of the various threats that individuals and many companies face today through the Internet, the botnet is the most common.
A botnet is a network of computers that are controlled remotely by hackers.
Botnets are used by criminals to distribute ransomware programs to your laptop, phone, tablet, computer. They may not even be detected by an antivirus, and you may not realize for a long time that your device is part of a botnet.

What is a botnet in 2018?
Classical understanding:
The word "botnet" is a combination of the two words "robot" and "network."
Here, the cybercriminal, who acts as a botmaster, uses Trojan viruses to compromise the security of several computers and connect them to the network for malicious purposes. Each computer on the network acts as a “bot” and is controlled by a fraudster to transmit malware, spam, or malicious content to launch an attack. A botnet is sometimes called an "army of zombies" because computers are controlled by someone other than their owner.
The origin of botnets has mainly originated in Internet chat channels (IRC).
In the end, spammers began to exploit the vulnerabilities present in the IRC networks
and developed bots .
This was done specifically to perform malicious actions, such as registration, emulation of “interested client” actions, password theft and much more.
A botnet structure usually takes one of two forms: a client-server model or a peer-to-peer model (P2P, Peer-to-peer).
The client-server model In the client-server
botnet structure, a core network is created, in which one server acts as a botmaster. The botmaster controls the transmission of information from each client to set commands and control over client devices.
The client-server model works with the help of special software and allows the botmaster to maintain permanent control over infected devices.
This model has several drawbacks: it can be easily detected, and it has only one control point. In this model, if the server is destroyed, the botnet is killed.

Peer-to-peer model (PTP, Peer-to-peer)
To overcome the disadvantage of using one centralized server, modern type botnets were created. They are interrelated in the form of a peer-to-peer structure.
In the P2P botnet model, each connected device operates independently as a client and as a server, coordinating the update and transmission of information between them.
The structure of the P2P botnet is stronger due to the lack of unified centralized management.

Types of botnet attacks
Distributed Denial of Service A
botnet can be used to attack a distributed denial of service (DDoS) to destroy network connections and services.
This is done by overloading computing resources.
The most commonly used attacks are TCP SYN and UDP attacks.
DDoS attacks are not limited to web servers, but can be directed to any service connected to the Internet. The severity of the attack can be increased by using recursive HTTP streams on the victim's website, which means that the bots recursively follow all the links in the HTTP path.
This form is called the "web", and is practiced to increase the load more effectively.

One of the largest botnet DDoS attacks in 2018 was associatedwith IoT and used the Mirai botnet virus.
The virus was designed for tens of thousands of less protected Internet devices and controlled them, turning them into bots to launch a DDoS attack.
Mirai spawned many derivative queries and continued to expand, making the attack more difficult.
This forever changed the threat landscape in terms of the methods used.
Spam and traffic monitoring
Bots can be used as an analyzer to detect the presence of sensitive data on infected machines or zombie computers. They can also find a competitor's botnets (if installed on the same machine), and can be hacked in a timely manner. Some bots offer to open a SOCKS v4 / v5 proxy (universal proxy protocol for a TCP / IP based network). When the SOCKS proxy is enabled on a compromised machine, it can be used for various purposes, for example, to send spam.
Bots use a packet sniffer to track information or data transmitted by a compromised machine. The sniffer can obtain sensitive information such as username and password.

Keylogging
With the help of the keylogger, the botmaster can easily obtain confidential information and steal user data. Using the keylogger program, an attacker can collect only those keys that are typed in a sequence of klyuev words, such as PayPal, Yahoo and more.
A variety of spyware identified as OSX / XSLCmd, migrated from Windows to OS X, includes the ability to blog and capture screen.
Mass Identity Theft
Various types of bots can interact to carry out large-scale identity theft, which is one of the fastest growing crimes. With the help of bots, you can disguise yourself as a well-known brand and ask the user to provide personal data, such as bank account password, credit card data, tax data.
Mass identity theft can be accomplished using phishing emails that force victims to enter their login credentials to websites like eBay, Amazon, or even well-known commercial banks.
Pay Per Click Abuse
The Google Ads program allows websites to show Google ads and make money from them. Google pays money to website owners based on the number of clicks received from ads. Compromised machines are used to automatically click on links, increasing the number of fake clicks.
Adware
Adware is used to attract users by advertising on web pages or in applications. They appear on computers without the knowledge or permission of users, and the original advertisement is replaced with fraudulent adware that infects the system of any users who click on it.
Adware looks like a harmless advertisement, but uses spyware to collect browser data.
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Sign in , please.
