PHP SQL query
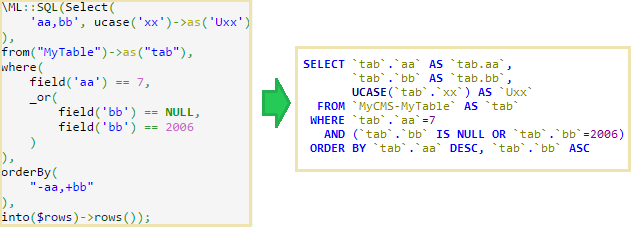
Since ORMs are too heavy for my needs, I usually used DbSimple . However, after meeting with Twig , which compiles templates in php code, the idea periodically arose to write something similar for working with the database. And so I did it. The picture shows a request for PHP, which after compilation generates code to create and execute an SQL query.
In the first implementation, I compiled the request from a syntax similar to DbSimple in PHP code. The idea was to get ready-made code with native functions at the output without any wrappers. At the same time, it was possible to wind up queries of any complexity and the speed of their analysis did not affect the operating time, since after compilation it was normal native code. However, the difficulty in debugging such queries (it was difficult to look for errors in the SQL syntax) and the fact that the parsing time of the query is not so long compared with the execution of the query led to the idea that I refused to use this approach.
Not so long ago I came across a library for parsing PHP code on PHP-Parser tokens . At work, I write code in ABAP, in which commands for working with the database are built into the language itself, so the idea came up "What if we do something like this for PHP"?
The implementation scheme is quite simple and obvious: when the class is autoload, we check its presence in the directory of compiled classes. If there is no compiled class, then we take the source file of the class, replace all special commands in it and write the finished class to the directory of compiled classes. The whole parsing is done by the PHP-Parser library. So that the compiler can understand that this is the command he needs, we wrap everything in the ML namespace ( M acro L anguage). For example, in the code we write like this:
\ML::SQL(Select(
'aa,bb', ucase('xx')->as('Uxx')
),
from("MyTable")->as("tab"),
where(
like('aa','sha%'),
_or(
field('bb') == NULL,
field('bb') == 2006
)
),
orderBy(
"-aa,+bb"
),
into($rows)->rows());and we get the output:
$__driver0 = \ML\SQL::getDriver('c933f3523437d521bf59e9e6077255b9', array('server' => '***', 'database' => '***', 'user' => '***', 'pass' => '***', 'prefix' => 'MyCMS-', 'codepage' => 'utf8'));
$__query1 = new \ML\SQL\Query($__driver0);
$__query1->sql = 'SELECT `tab`.`aa` as `tab.aa`, `tab`.`bb` as `tab.bb`, UCASE(`tab`.`xx`) as `Uxx` FROM `MyCMS-MyTable` as `tab` WHERE `tab`.`aa` LIKE \'sha%\' AND (`tab`.`bb` IS NULL OR `tab`.`bb`=2006) ORDER BY `tab`.`aa` DESC, `tab`.`bb` ASC';
$rows = $__query1->rows();At the same time, we can use the PHP variables directly in the query (which are substituted into the query with protection against SQL injections in PHP and MySQL ) and the function of conditional query generation _if. In particular, the following code:
\ML::SQL(Select(
'aa', _if($mode==1,'bb')
),
from("MyTable")->as("tab"),
where(
field($fname) = $value
),
into($rows)->row());compiles into code like this:
$__driver0 = \ML\SQL::getDriver('c933f3523437d521bf59e9e6077255b9', array('server' => '***', 'database' => '***', 'user' => '***', 'pass' => '***', 'prefix' => 'MyCMS-', 'codepage' => 'utf8'));
$__query1 = new \ML\SQL\Query($__driver0);
$__query1->sql = 'SELECT `tab`.`aa` as `tab.aa`' . ($mode == 1 ? ', `tab`.`bb` as `tab.bb`' : '') . ' FROM `MyCMS-MyTable` as `tab` WHERE ' . $__driver0->getField('tab', $fname, '', '') . '=' . $__driver0->getValue($value);
$rows = $__query1->row();Since the implementation scheme is simple, I decided not to be limited only to SQL. To do this, the code does not look for specific \ ML \ SQL commands, but all calls from the \ ML namespace. If such a call is found, then the presence of the class \ ML \ <class name> is checked. If there is such a class, an object of this class is created and its method <class name> -> compile (...) is called, into which the tokens of the current call are transferred (the root node received from PHP-Parser) + the object of this class itself. This will allow you to use this approach not only to access the database, but also for other needs (have not yet come up with :)). In particular, I plan to make an ORM extension over SQL. Those. I will compile the \ ML \ ORM call into \ ML \ SQL code, which will already be compiled into PHP code. Moreover, since the time of parsing an expression is not important, when parsing an ORM call, you can spend time reading information about entities, their relationships, fields, etc.
PS Although before doing ORM, I will add the JOIN command + UPDATE and DELETE commands.
For those who are interested, a small test site for compiling code . If you find any mistake, write in the comments. So far this is version 0.1 alpha so errors are very likely.
UPD: 2017.02.03 Added more examples of
UPD:Next version
