In Japan, began broadcasting in 8K format
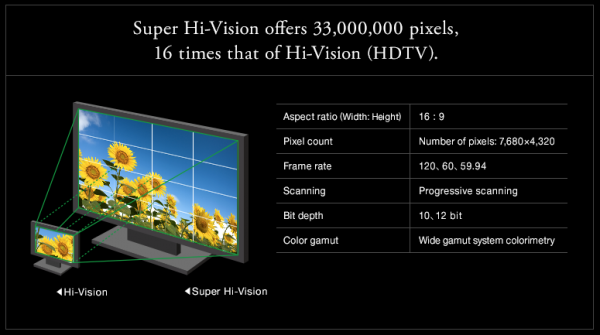
The 8K frame is 16 times larger in size than the HDTV frame, that is, “high definition” television with a resolution of 1080 lines The
Japanese broadcasting company NHK yesterday (December 1) started a permanent television broadcast in 8K format , that is, at a resolution of 7680 × 4320 pixels. According to the broadcaster, this means “a new era of full-scale ultra-high resolution television” (Super Hi-Vision) and is a stage of preparation for the 2020 Olympic Games in Tokyo, which are not too long to go.
Television 8K NHK is broadcast daily on a special channel between 10 am and 10 pm. As shown in the illustration above, the image quality in such programs is 16 times higher than in HD. The sound is transmitted in multichannel mode. 22.2. NHK will broadcast with a frame rate of 59.94, as well as 60 and 120P.
Currently, a very limited number of programs are broadcast on the NHK Super High Resolution Channel. They are repeated several times during the day.
To watch 8K television, you need not only an 8K TV, but also a special satellite dish for receiving broadcasts. NHK also says that viewers may need to replace receiving equipment, such as amplifiers and distributors. The diagram below shows approximately what equipment should be installed in the house (signatures in Japanese).
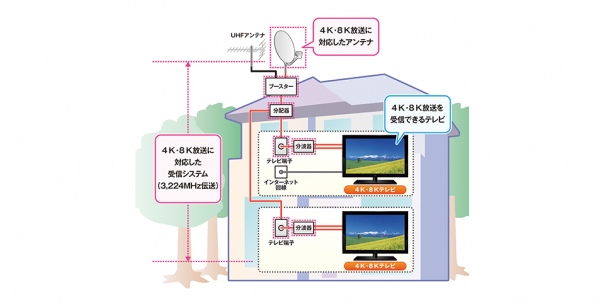
Currently in Japan for viewing 4K programs only a decoder is needed (it costs from $ 800 to $ 1000 equivalent). Broadcasting 4K and 8K via satellite. NHK has no specific plans for organizing 4K / 8K terrestrial digital broadcasting. In this case, viewers could save substantial amounts on the equipment for receiving the 8K signal.
Four years ago, NHK successfully tested 8K image transmissions in the country's largest cable television network. In the same 2014, they carried out an experimental survey using the 8K Super Hi-Vision camera at a frame rate of 120 Hz, that is, 120 frames per second.
Despite the fact that high-definition television advertising is increasingly common in Japan, even the 4K format is still not widespread. Most Japanese still watch regular HD broadcasts on high-definition television, which transmits a picture 16 times smaller in size. It is even surprising that NHK is actively promoting 8K, if even in 4K resolution, it now lacks content to fill the broadcasting network.
At present, even 8K TVs on the market are quite small, and they cost a lot of money. For example, the 70 "SHARP LC-70X500 in Japan costs ¥ 646,290, that is, $ 5,705 equivalent. The cheapest 8K TV you can currently buy in Japan is the 60-inch Sharp 8T-C60AW1, which sells for 498 000 yen ($ 4,395).
It seems obvious that the future belongs to higher resolution formats, and after the appearance of a large number of films and programs in such a resolution, as well as after the organization of terrestrial digital broadcasting, the 8K format has every chance of being popular. However, migration to 8K will not be so easy. In fact, broadcasters will need to change the entire infrastructure, and viewers will need to buy new televisions, which are so far unavailable for the majority of the population, even in Western countries, not to mention Russia. So the transition to 8K will be long and difficult.
However, for companies that operate in the industry, there are no options. They are absolutely confident in the bright prospects of 8K and strongly put pressure on the promotion of this format. At the latest technology exhibitions everywhere you can see the equipment of this format: these are not only TVs and displays, but also 8K video cameras, and at one of the exhibitions recently showed IP video broadcasting in the 5G mobile network. The Japanese telecommunications giant Docomo also transmitted 8K content in a test mode on its experimental 5G network, which has not yet been introduced to the market.
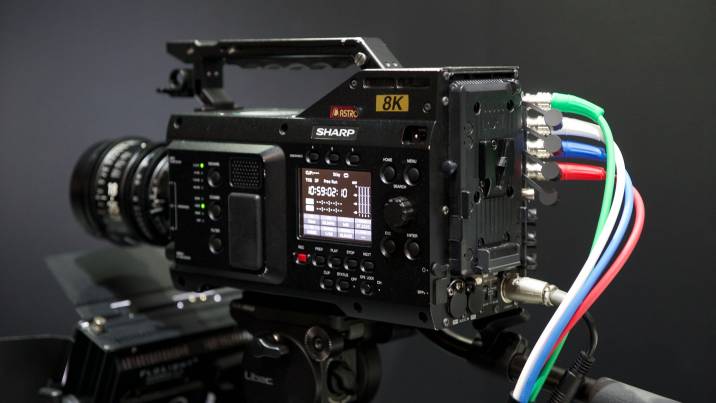

Sharp camcorder in 8K format
If this is not enough, then some companies already show 16K TVs!

16K TV. Photo: Matthew Allard
One way or another, but with the start of NHK’s standard television broadcasting and with the upcoming Olympic Games in Tokyo in 2020, there are great chances that high-definition television will receive a big boost for development in Japan: not only content will appear in this resolution, but the technology itself will become more accessible and cheaper for consumers.
