Windows Server 2019
The history of Windows Server has more than 25 years: Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server was released on July 27, 1993. In October 2018, three years after the previous major release, Windows Server 2019 was released. Windows Server 2019 develops and improves the capabilities inherent in previous releases. Details about this - under the cut!

Starting with Windows Server 2016, a new release cycle has been adopted. Now there are two distribution channels: LTSC (Long-term servicing channel) - release coming out in 2-3 years, with 5-year main and 5-year extended support, and also Semi-Annual Channel - releases that go every six months, have a main support cycle for 6 months and extended support for 18 months. Why are these two channels necessary? Microsoft is actively innovating its Azure cloud platform. This support for Linux virtual machines, containers with Linux and Windows, and many other technologies.
Customers using these technologies in the cloud also want to use them in their data centers. Semi-Annual Channel reduces the gap in capabilities between Azure and local data centers. Semiannual releases are intended for dynamic companies in the development that have moved to a flexible service model for providing IT services to businesses. LTSC releases are designed for companies that use well-established applications with a long support cycle, for example, Exchange Server, SharePoint Server, SQL Server, as well as infrastructure roles, software-defined data centers and hyper-convergent infrastructure.
Windows Server 2019 is exactly the release in the LTSC channel. It includes all the functionality updates from Windows Server 2016 and subsequent semi-annual releases.
The main efforts of the developers of Windows Server 2019 were focused on four key areas:
Windows Admin Center (WAC) is a new server administration tool. It is installed locally in the infrastructure and allows you to administer local and cloud-based instances of Windows Server, Windows 10 computers, clusters, and hyper-convergent infrastructure.
WAC complements, rather than replaces, existing administrative tools, such as mmc and Server Manager consoles. Connecting to the WAC is done from the browser.

To perform tasks, WinRM, WMI, and PowerShell scripts are used.
You can publish WAC and administer servers from outside the organization's perimeter. Azure AD's multi-factor authentication and proxy services help protect such access from the outside, and using Microsoft Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) solution will allow or deny access depending on the device’s compliance with policies, risks, location and other factors. Using a web application instead of accessing a remote worker for administration, in my opinion, is the right strategy for security.
Windows Server 2019 has become smarter. With the help of the new System Insights feature, predictive analytics is implemented, which allows you to switch from reactive to proactive server fleet management. The machine learning model takes into account performance counters and events to accurately predict problems with free space on the disk subsystem, determine trends for processor computing, network interaction, and storage performance.
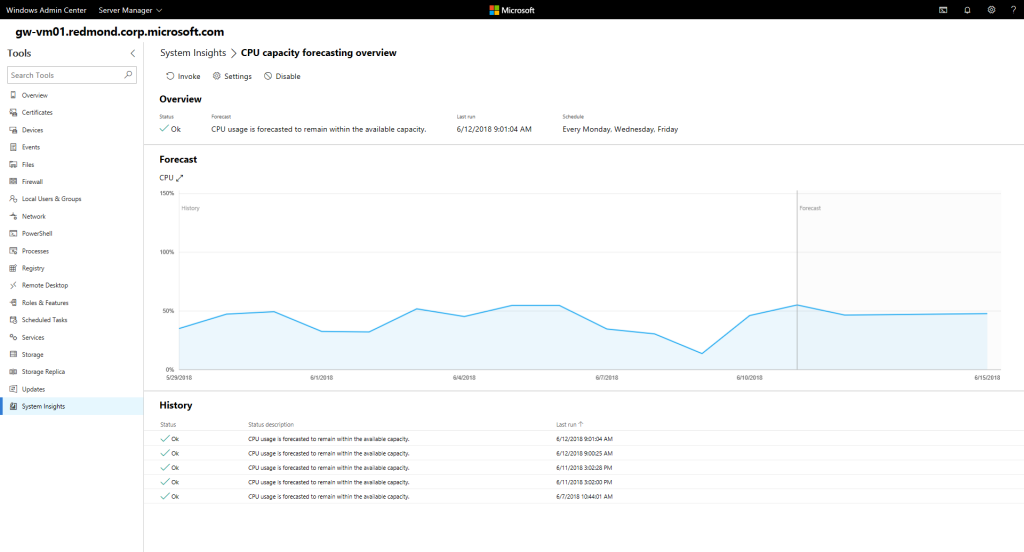
In Windows Server 2019, there is a new technology for migrating data from old servers to new ones - the Storage Migration Service.
Migration occurs in several stages:
Manage migration processes using the Windows Admin Center.
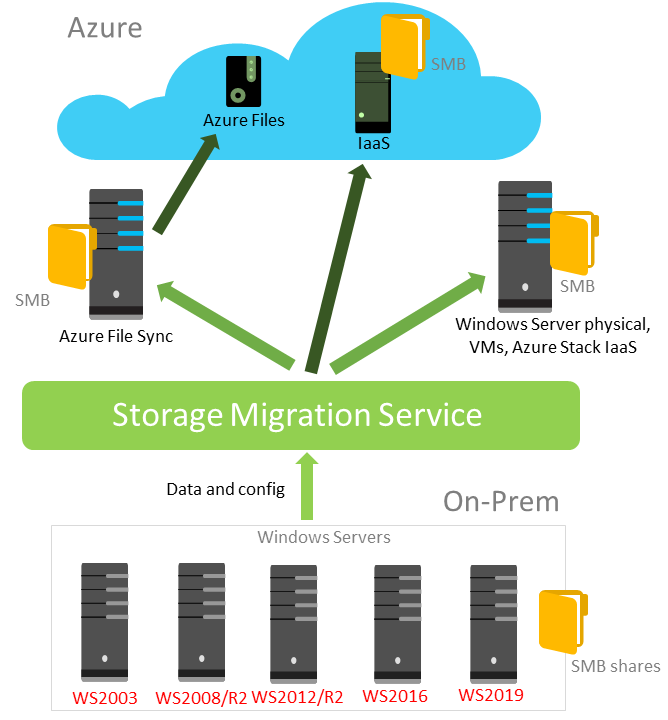
Azure File Sync transforms traditional file servers and expands storage to virtually unattainable volumes in real life. Data is divided into several levels: hot cache is data stored on file server disks and accessible at maximum speed for users. As it cools down, the data moves imperceptibly into Azure. Azure File Sync can be used in conjunction with any protocol to access files: SMB, NFS and FTPS.
This disaster protection technology first appeared in Windows Server 2016. In version 2019, there was limited support for the Windows Server Standard edition. Now even small companies can make an automatic copy (replica) of storage in Azure virtual machines, if the company’s infrastructure does not have a second remote data center.
Local disk spaces are a necessary component for building a hyperconvergent infrastructure and a scalable file server. In Windows Server 2019, there is built-in support for non-volatile memory, improved deduplication algorithms, including on volumes with the ReFS file system, scalability up to 4PB per cluster, and performance improvements.
Cluster sets appeared, increasing the scalability to hundreds of nodes.
To ensure a quorum in clusters with an even number of nodes, a special resource is used - a disk witness. In the days of Windows Server 2012 R2, it was necessary for a witness disk to allocate a disk to storage, in Windows Server 2016 it became possible to use a network folder or a cloud witness disk. Improvements in Windows Server 2019 are associated with reduced infrastructure requirements for small businesses. A USB witness, for example, connected to a router, can act as a witness disk.
There was a migration of clusters between domains and other improvements in the service of failover clustering.
Now you can run Windows and Linux based containers on the same container node using the same Docker control program. This allows you to work in a heterogeneous container node environment and give developers the flexibility to create applications.
Containers have improved application compatibility, the size of Server Core and Nano Server images has been significantly reduced, and performance has improved.
Windows Server 2019 received many other improvements. You can learn more about them in the Windows Server section of the official documentation site docs.microsoft.com.
The documentation describes the minimum installation requirements for Windows Server 2019. It should be understood that, depending on the roles and components, running applications, server requirements may be increased.
Minimum RAM requirements:
Storage Requirements:
Windows Server 2019 does not support ATA / PATA / IDE and EIDE for booting, a paging file, or data disks. The minimum amount is 32 GB.
Network adapters:
Windows Server 2019 comes in two editions: Standard and Datacenter.
The editors for data centers have advanced features: support for hyper-converged infrastructure, local disk spaces, extended license rights when using virtualization.

You can learn more about the features of Windows Server 2019, usage scenarios, licensing options at the “Windows Server 2019 for a modern data center” webinar.
Speaker - Dmitry Uzlov , certified expert in Microsoft solutions with many years of experience.
Cybersecurity expert, Microsoft Gold Partner Project Manager Technopolis
Webinar will be held on December 6 at 11.00, after the webinar you can do practical work on deploying a virtual infrastructure of Windows Server and setting up typical hybrid data center scenarios. Successfully coped with the tasks of practical work will receive an electronic certificate of completion of the training.
Record webinar can be viewed at the link .

Starting with Windows Server 2016, a new release cycle has been adopted. Now there are two distribution channels: LTSC (Long-term servicing channel) - release coming out in 2-3 years, with 5-year main and 5-year extended support, and also Semi-Annual Channel - releases that go every six months, have a main support cycle for 6 months and extended support for 18 months. Why are these two channels necessary? Microsoft is actively innovating its Azure cloud platform. This support for Linux virtual machines, containers with Linux and Windows, and many other technologies.
Customers using these technologies in the cloud also want to use them in their data centers. Semi-Annual Channel reduces the gap in capabilities between Azure and local data centers. Semiannual releases are intended for dynamic companies in the development that have moved to a flexible service model for providing IT services to businesses. LTSC releases are designed for companies that use well-established applications with a long support cycle, for example, Exchange Server, SharePoint Server, SQL Server, as well as infrastructure roles, software-defined data centers and hyper-convergent infrastructure.
Windows Server 2019 is exactly the release in the LTSC channel. It includes all the functionality updates from Windows Server 2016 and subsequent semi-annual releases.
The main efforts of the developers of Windows Server 2019 were focused on four key areas:
- Hybrid cloud - Windows Server 2019 and Windows Admin Center make it easy to use Azure cloud services with the server operating system: Azure Backup, Azure Site Recovery, Azure Update Management, Azure AD Authentication, and others.
- Security is one of the most important priorities for customers. Windows Server 2019 has built-in features to make it difficult for attackers to penetrate and gain a foothold in the system. These are the Defender ATP and Defender Exploit Guard technologies known on Windows 10.
- Application Platform - Containers are becoming a modern trend for packaging and delivering applications to various systems. At the same time, Windows Server can run not only native Windows applications, but also Linux applications. To do this, there are Linux containers in Windows Server 2019, a Windows subsystem for Linux (WSL), and the size of container images is significantly reduced.
- Hyper-converged infrastructure - allows you to combine within the same server, the standard architecture and computing, and storage. This approach significantly reduces the cost of infrastructure, while providing excellent performance and scalability.
Windows Admin Center
Windows Admin Center (WAC) is a new server administration tool. It is installed locally in the infrastructure and allows you to administer local and cloud-based instances of Windows Server, Windows 10 computers, clusters, and hyper-convergent infrastructure.
WAC complements, rather than replaces, existing administrative tools, such as mmc and Server Manager consoles. Connecting to the WAC is done from the browser.

To perform tasks, WinRM, WMI, and PowerShell scripts are used.
You can publish WAC and administer servers from outside the organization's perimeter. Azure AD's multi-factor authentication and proxy services help protect such access from the outside, and using Microsoft Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) solution will allow or deny access depending on the device’s compliance with policies, risks, location and other factors. Using a web application instead of accessing a remote worker for administration, in my opinion, is the right strategy for security.

System analytics
Windows Server 2019 has become smarter. With the help of the new System Insights feature, predictive analytics is implemented, which allows you to switch from reactive to proactive server fleet management. The machine learning model takes into account performance counters and events to accurately predict problems with free space on the disk subsystem, determine trends for processor computing, network interaction, and storage performance.

New in the storage subsystem
Storage Migration Service
In Windows Server 2019, there is a new technology for migrating data from old servers to new ones - the Storage Migration Service.
Migration occurs in several stages:
- Inventory data on various servers
- Fast transfer of files, network folders and security configurations from source servers
- Capturing control and replacing server ID and network settings from the old server to the new one
Manage migration processes using the Windows Admin Center.

Azure File Sync
Azure File Sync transforms traditional file servers and expands storage to virtually unattainable volumes in real life. Data is divided into several levels: hot cache is data stored on file server disks and accessible at maximum speed for users. As it cools down, the data moves imperceptibly into Azure. Azure File Sync can be used in conjunction with any protocol to access files: SMB, NFS and FTPS.
Storage replica
This disaster protection technology first appeared in Windows Server 2016. In version 2019, there was limited support for the Windows Server Standard edition. Now even small companies can make an automatic copy (replica) of storage in Azure virtual machines, if the company’s infrastructure does not have a second remote data center.
Storage space direct
Local disk spaces are a necessary component for building a hyperconvergent infrastructure and a scalable file server. In Windows Server 2019, there is built-in support for non-volatile memory, improved deduplication algorithms, including on volumes with the ReFS file system, scalability up to 4PB per cluster, and performance improvements.
Failover Clustering Changes
Cluster sets appeared, increasing the scalability to hundreds of nodes.
To ensure a quorum in clusters with an even number of nodes, a special resource is used - a disk witness. In the days of Windows Server 2012 R2, it was necessary for a witness disk to allocate a disk to storage, in Windows Server 2016 it became possible to use a network folder or a cloud witness disk. Improvements in Windows Server 2019 are associated with reduced infrastructure requirements for small businesses. A USB witness, for example, connected to a router, can act as a witness disk.
There was a migration of clusters between domains and other improvements in the service of failover clustering.
What's new in the application platform
Now you can run Windows and Linux based containers on the same container node using the same Docker control program. This allows you to work in a heterogeneous container node environment and give developers the flexibility to create applications.
Containers have improved application compatibility, the size of Server Core and Nano Server images has been significantly reduced, and performance has improved.
Windows Server 2019 received many other improvements. You can learn more about them in the Windows Server section of the official documentation site docs.microsoft.com.
System requirements
The documentation describes the minimum installation requirements for Windows Server 2019. It should be understood that, depending on the roles and components, running applications, server requirements may be increased.
- 1.4-GHz 64-bit processor
- Compatible with x64 architecture instruction set
- NX and DEP technology support
- Support CMPXCHG16b, LAHF / SAHF and PrefetchW
- Support for second level address translation (EPT or NPT)
Minimum RAM requirements:
- 512MB (2GB for the “Server with Desktop” installation option)
Storage Requirements:
Windows Server 2019 does not support ATA / PATA / IDE and EIDE for booting, a paging file, or data disks. The minimum amount is 32 GB.
Network adapters:
- Ethernet adapter with a bandwidth of at least 1GB.
- Compliant with PCI Express Architecture Specification.
- Supports PXE remote boot protocol.
Compare Windows Server 2019 Standard and Datacenter Editions
Windows Server 2019 comes in two editions: Standard and Datacenter.
The editors for data centers have advanced features: support for hyper-converged infrastructure, local disk spaces, extended license rights when using virtualization.
Webinar Invitation

You can learn more about the features of Windows Server 2019, usage scenarios, licensing options at the “Windows Server 2019 for a modern data center” webinar.
Speaker - Dmitry Uzlov , certified expert in Microsoft solutions with many years of experience.
- Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert: Cloud Platform and Infrastructure
- Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert: Productivity
Cybersecurity expert, Microsoft Gold Partner Project Manager Technopolis
Webinar will be held on December 6 at 11.00, after the webinar you can do practical work on deploying a virtual infrastructure of Windows Server and setting up typical hybrid data center scenarios. Successfully coped with the tasks of practical work will receive an electronic certificate of completion of the training.
Record webinar can be viewed at the link .
