Mobile Security Fears
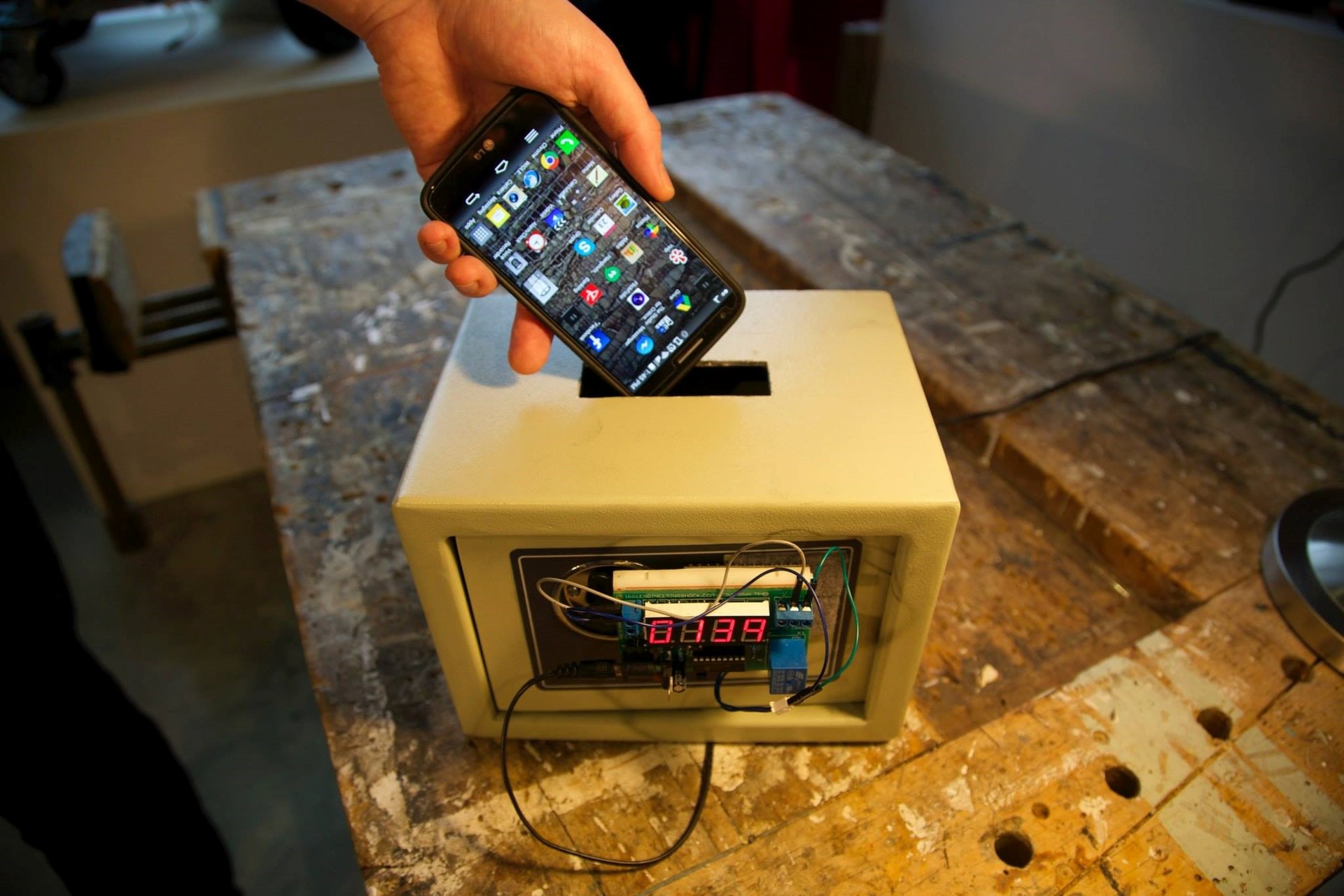

Gernet Hertz, a researcher at the University of California, proposed a way to ensure mobile security: a safe with a slot for a mobile phone at the top. The safe allows you to set the time during which the phone will be locked inside. It cannot be reached, and there is no way to reduce the set time. While the phone is in a locked box and you are not using it, your data is safe. With her installation, Hertz shows that the main vulnerability lies in the user himself. Is this so, we argue under the cut.
Listening and user reaction
There are already more phones than people, and a reliable way to protect information for them has not yet been created. Demand for mobile devices has overtaken the pace of development of protective equipment. Although every self-respecting antivirus company has released mobile versions of its products, these solutions are not well received by users.
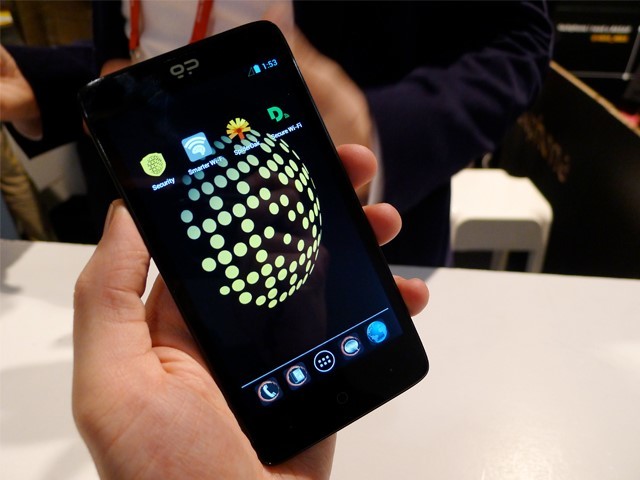

This is a Blackphone - an ordinary Chinese Android smartphone, which was positioned by Silent Circle as a device for encrypted communications. Data encryption provides a modified version of Android - PrivatOS. Inside there is a set of specific applications: VoIP-client Silent Phone, cross-platform program for encrypting voice traffic Silent World (used to communicate with subscribers who do not have Silent Phone), Silent Contacts address book, Silent Text messenger and browser. All traffic goes through the VPN as part of a proprietary paid service.
Google has given the company the opportunity to seriously modify Android. Even terrorist organizations recommendedthese phones to their supporters, but many questions remained. How much does the Silent Circle learn about us? According to the company itself, it can block a client smartphone, "if it really goes about life and death." That is, we are not talking about absolute protection. Add to this information from Azimuth Security about vulnerabilities found in the first version of Blackphone.
Users took this device cool. The Blackphone failed in sales, and Silent Circle was in debt. Reality has shown that people are not very concerned about the protection of their data. The smartphone was convenient, but it turned out to be of no interest to anyone.

Blackberry is experiencing similar problems. Carl Wiese, head of global sales, admitted that making smartphones is no longer profitable. At the same time, despite the skepticism of analysts, software development is seen by the company as the most promising direction. Blackberry continues to create software in the field of data encryption, but only a narrow segment of politicians and businessmen can use their services.
Perhaps the reason for the indifference of users is that a smartphone that looks simple is a priori perceived to be vulnerable. Blackphone did not provide any hardware protection, while many security methods are not very convenient for mass products. For example, two encryption devices that connect to existing phones - the signal to the phone is transmitted in encrypted form, and even in the case of interception, the attacker will not receive valuable information. In this case, the keys of the encryption algorithm are distributed among subscribers using a special device connected to the computer. Not the best solution if you value convenience and simplicity.
SMS hacking
SMS hacking has existed for about the same number of years as the communication standard itself has been living: you receive a message from one number, but in fact it was sent from another. Thus, it is possible to scroll through various types of fraudulent schemes: to find out credit card information, appearing to be a bank, send links to viruses, in the end - just to lure a subscriber out of the apartment.
SMS is often used to activate vulnerabilities in mobile OS. For example, a line composed of certain Unicode characters sent as an SMS to any Apple device causes the operating system to crash .
It is surprising that news about new hacks via SMS is returned year after year. Even at the beginning of the “zero” it was known: phones do not check the source of service messages, which allows you to send them to anyone and from anyone.
In 2010, there were messages of anti-virus companies about the first infected by malicious mobile applications, send SMS messages to premium rate numbers are short.
Imagine that there is a small application on the SIM card that receives a message from the service provider and displays it on the screen of your Android device. Through the SIM Toolkit on Android 5.1, it was possible to emulate and intercept SIM commands.
There are a lot of news of this kind, and the conclusion can be made unequivocal: if someone wants to read your SMS, he has many ways to do this.
Hacking the networks themselves
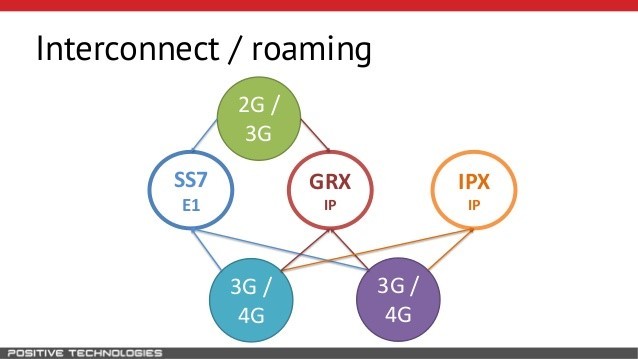
GRX (GPRS roaming exchange) is used to route commercial roaming traffic between visited and home operators. Mostly, 2.5G and 3G networks used GRX for data roaming.
IP exchange (IPX) - a model of telecommunication interaction for the exchange of IP traffic between clients of individual mobile and fixed operators, through IP based on the gateway.
The process of establishing voice calls in mobile networks is based on SS7 technology, the development of which began back in the 70s of the last century. SS7 (Signaling System No. 7) is a digital network and a set of technical protocols that control data exchange. Now SS7 is often used for roaming, and thanks to this technology, you can receive / make calls and send SMS where your mobile operator does not work.
Forty years ago, no one thought about software protection. As a result, the entire pile of security problems safely reached our days. The vulnerability of networks based on SS7 technology allows revealing a subscriber’s location, disrupting its availability, intercepting SMS messages, forging USSD requests and transferring funds with them, redirecting voice calls, eavesdropping on conversations. When making an attack does not require special equipment or special knowledge. Completely prepared instructions for attacking SS7 a few years ago could simply be downloaded from the Internet - even a schoolboy could deal with this type of hacking. More details about attacks can be found in this study .
In short, the essence of the problem is this: all applications that authenticate via SMS are vulnerable. Vulnerabilities are affected not only by the SS7 network, but also by air interface encryption algorithms. There is only one protection from users in this situation: the use of two-factor authentication (one password will need to be remembered and not written down anywhere). Protection from mobile operators: constantly testing their networks for possible, impossible and incredible vulnerabilities.
Do not forget about modern achievements. InfoWatch
toldthat is going to intercept (legally) telephone calls, integrating with the core of the operator’s network and creating a trusted base station. Then this base station will intercept voice traffic from mobile phones in the coverage area.
How to protect yourself
The good news is that most of these risks can be minimized if the user himself is not lazy and takes a number of steps to ensure his own mobile security.
First you need to come to terms with the idea that the phone knows everything about the user. Moreover, he even knows what the user has already forgotten. Old contacts, notes made a few years ago, ancient photos, videos, SMS (which you were planning to delete for a long time), access to cloud storages, a password bank or just passwords to your bank recorded in notes.
A phone that is more than a year old often lives its own life: one day you will be surprised to find that you see programs in it that you did not install. As mentioned above, use two-factor authentication to access various services whenever possible. Make backups where you can’t access from your phone. It is much easier to turn on the cloud on the device itself, but the chance to lose all data with the phone increases many times over.
Now almost every stall has its own mobile application. If you order a taxi through it, nothing bad will happen. It is more difficult if you use a mobile bank. An infected smartphone with direct access to an account is a huge problem. And the confirmation of the operation, which comes in the form of SMS to this smartphone, only exacerbates the situation. The solution for users who are seriously concerned about their security, in this case, only one thing: a second phone, designed only for receiving authorization SMS.
Unfortunately, many people forget about even simpler defense methods. Use different passwords on your smartphone and in applications, do not forget to make them more difficult. And wherever possible, use data encryption.
