GFI MailEssentials: Secure Mail
GFI MailEssentials is well known to many Exchange administrators, especially small and medium-sized companies. It protects Exchange servers or other SMTP-based email systems from spam and malware. For those who are not yet familiar with this product, we will try to briefly tell you what it is and how it can be useful for your organization.
GFI MailEssentials has been famous for many years for providing the highest accuracy of spam filtering. This is achieved through the use of Bayesian analysis methods and other spam identification technologies. According to estimates, GFI MailEssentials blocks more than 99% of spam and at the same time shows a record low level of false positives, which is achieved through the use of automatically updated whitelists, and also provides recognition and filtering of phishing, which uses a special database of phishing resources and search by key according to.
MailEssentials is quickly installed on an enterprise mail server or email gateway and requires virtually no additional configuration. Thus, protection against spam and phishing is implemented at the mail gateway level. Consequently, it is possible to refuse the expensive deployment and maintenance of email protection systems at workstations of the enterprise, there is no need to train users in the specifics of fighting spam and regularly adjusting filtering rules, mail junk will not litter the disk subsystem of the email server.
Moreover, GFI MailEssentials flexibly adapts to the peculiarities of enterprise mail flows without administrator intervention and offers a number of useful server-level message management functions: automatic insertion of text into the message body, monitoring and analysis of the use of the e-mail system, mailing list server, automatic reply and download functions Messages from the provider's multiuser mailbox using the POP3 protocol. For example, the auto answer function along with the usual answer allows you to use custom templates and add an attachment.
Bayesian filtering technology and feature analysis
According to research, Bayesian filtering leads in spam recognition accuracy, provides the highest filtering accuracy - over 98%. It is far ahead of identification methods based on signatures and keywords. It uses probabilistic assessment methods based on the found characteristic features - words and phrases. GFI MailEssentials calculates the likelihood that the message is spam, using a complex formula and uses sets of characteristic features.
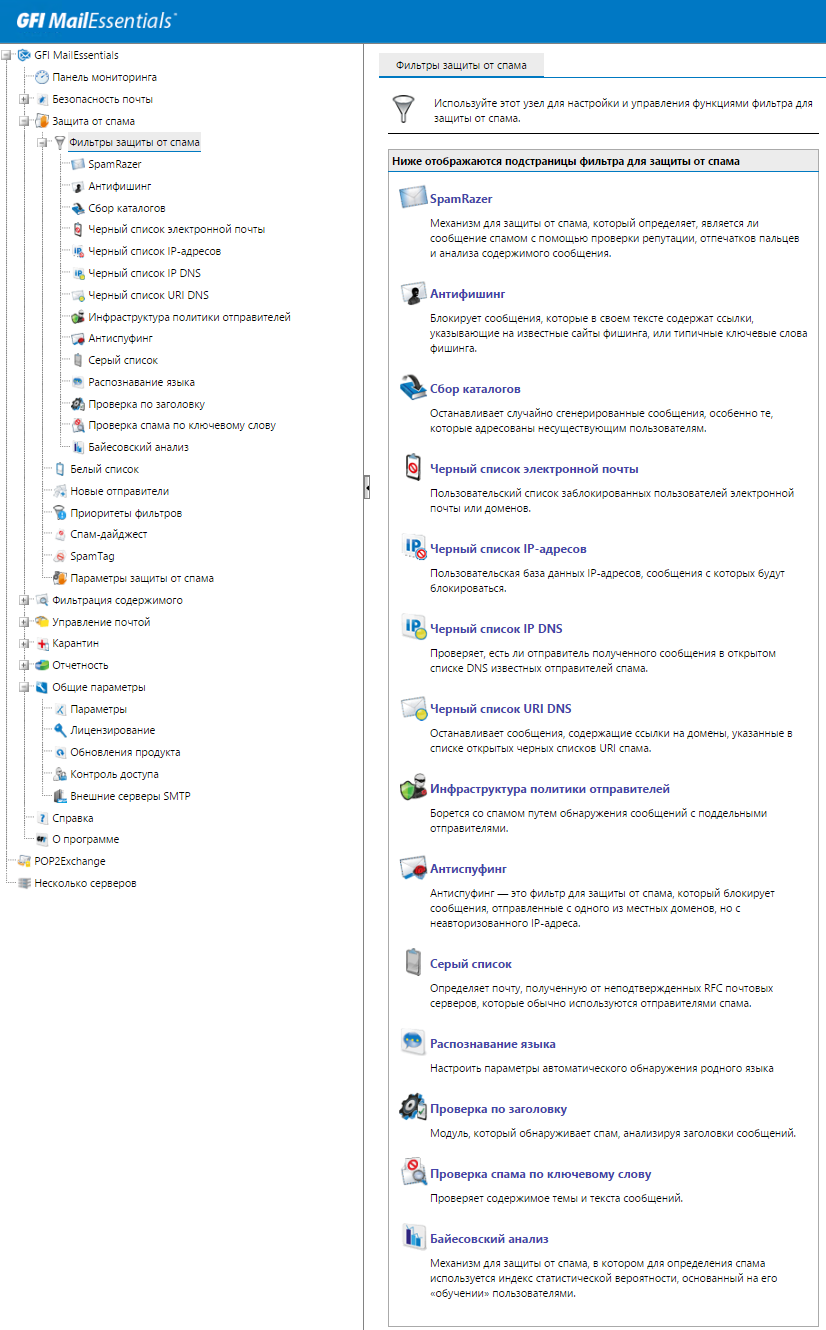
The product includes numerous spam filtering options.
Setting filter rules
Setting actions for filtering mail
The product analyzes in detail the service fields of emails and identifies fake headers, attempts to hide IP addresses, spam mutations, falsified domains and other signs of spam.
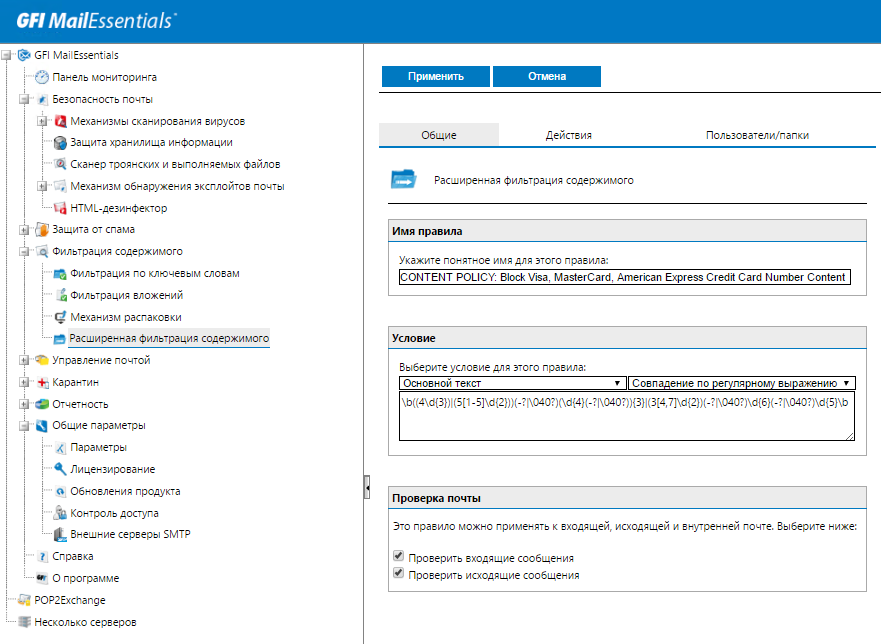
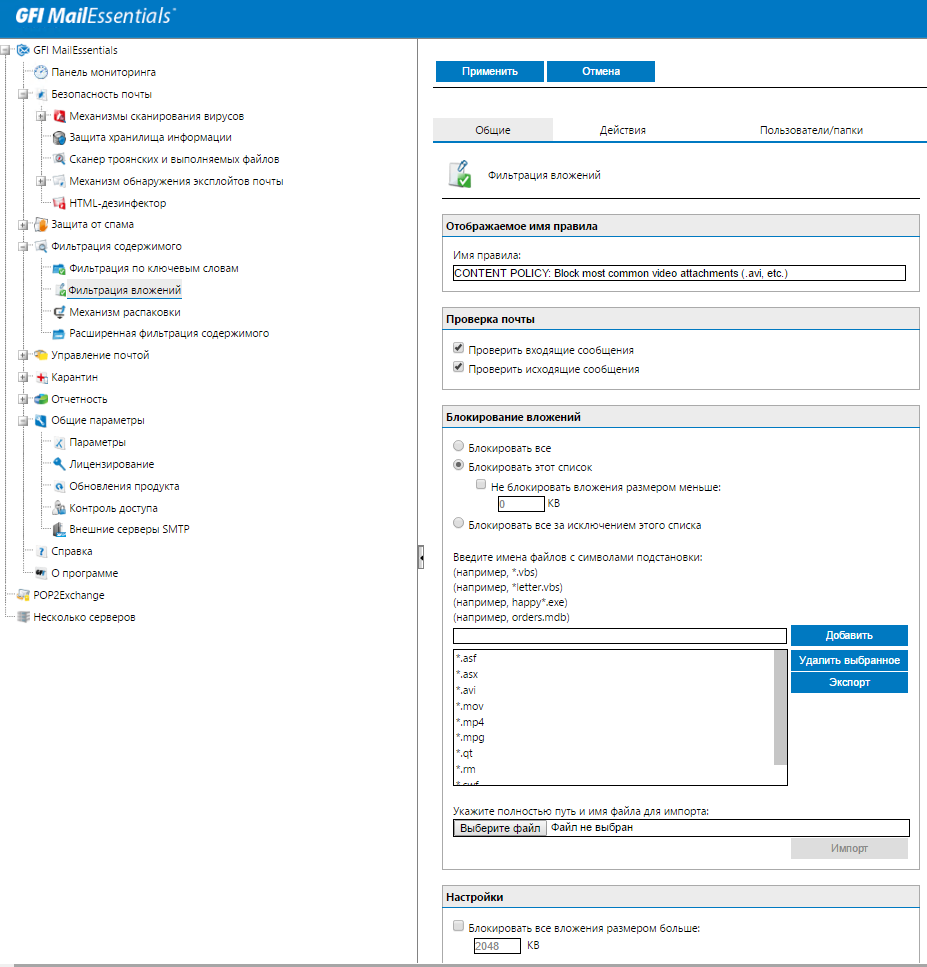
The anti-spam engine is complemented by a custom content filtering engine for keywords and attachment types, including the ability to prohibit unpacking ZIP files.
A useful tool is SpamTag, a plug-in for MS Outlook that allows users to participate in the product pre-configuration by marking past spam filters directly from the Outlook interface. It also creates a button in Outlook for user access to quarantine - no need to remember how to get there. He simply presses a button and sees blocked letters sent to him.
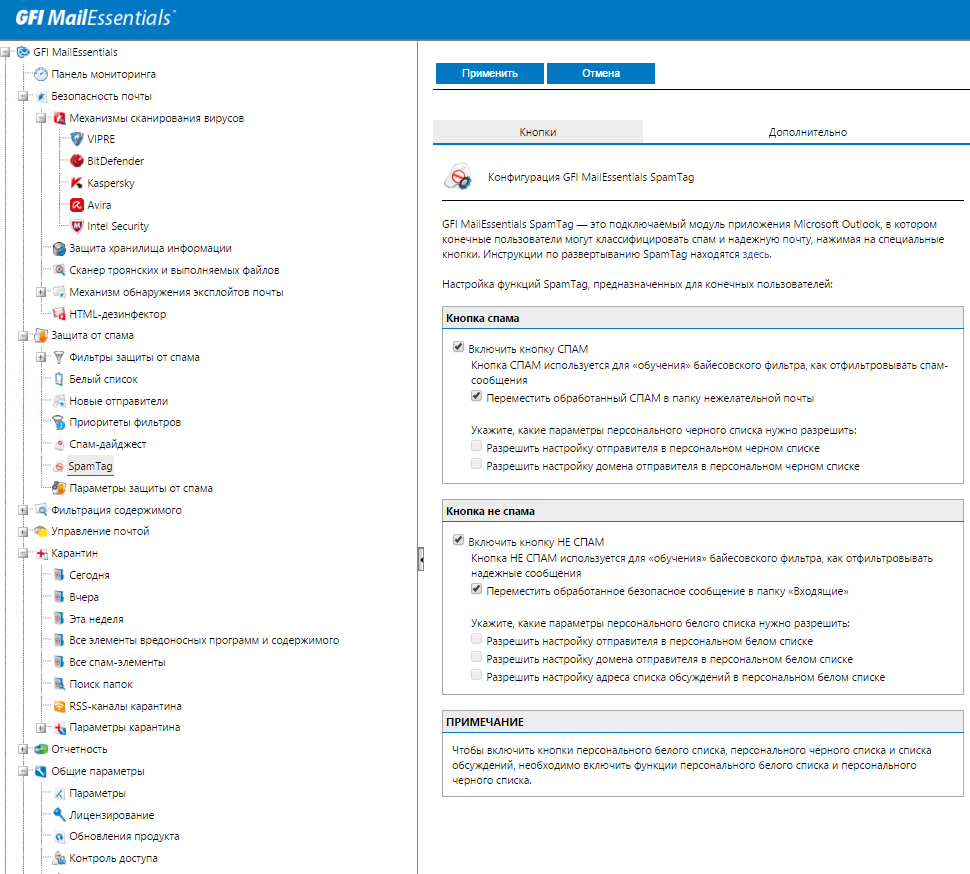
Configuring SpamTag
Among other advanced anti-spam mechanisms is SpamRazor, which uses fingerprints of e-mail messages to detect common spam and DNS URI block lists for checking suspicious messages.
GFI MailEssentials can update the set of characteristic features of spam by accessing the GFI website, which allows you to quickly adapt the system to changing the characteristics of spam distribution and successfully resist the new tricks of mass mailing masters. GFI experts are continuously improving Bayesian databases in collaboration with leading spam collection and research organizations.
A set of "bad" signs are regularly updated by GFI experts and downloaded by GFI MailEssentials from the Internet. The Bayesian GFI MailEssentials filter generates a set of signs of “bad” and “good” messages by analyzing the contents of the corresponding public folders. To increase the accuracy of spam recognition, replenishment of these folders can be performed, along with administrators, by users of the system who are granted the necessary access rights.
Protection against the selection of email addresses
Sometimes spammers send letters to randomly generated email addresses of the enterprise. GFI MailEssentials checks the recipient addresses against the Active Directory database or LDAP directory, and if the number of invalid addresses exceeds the specified value, it is marked as spam.
The analysis of mail messages also involves verifying that a letter received on behalf of an organization was sent from an authorized mail server. This function is performed by the Sender Policy Framework (SPF) module.
White and black lists
Based on white lists, GFI MailEssentials skips mail from specified senders or mail domains. Since these lists are automatically replenished with the addresses of the recipients of outgoing letters, the level of false positives is significantly reduced. Whitelists can also be generated using domain names, individual email addresses, and keywords.
Finally, GFI MailEssentials checks the email addresses contained in the database against databases of spamming sites (Spam URI Realtime Blocklists, SURBL). The administrator can set SURBL servers independently and determine the order of their use. Users can also be involved in the process by giving them access to shared folders, which are used to configure black and white lists in GFI MailEssentials.
GFI MailEssentials also maintains blacklists of third-party organizations and communities such as ORDB, SpamHaus and Spamcop. In addition, the administrator can independently specify the servers that provide blacklist services.
Setting up lists
Gray lists
Another method of protection against spam is the so-called gray lists. It is especially effective because it assumes that the spammer software does not follow the same rules that apply to a regular email server. The engine tells the mail server to “try again”. On the second attempt, the message will be accepted, and the engine will skip subsequent mail messages from this sender. In general, this does not affect the time of email delivery, but it can significantly help protect against spam.
What to do with spam?
GFI MailEssentials offers the flexibility to handle suspicious messages classified as spam. You can choose to automatically delete such messages, move them to a special public folder, forward them to the specified email address, or transfer them to the folder for suspicious messages in the recipient's mailbox in order to avoid the loss of emails mistakenly classified as spam. At the same time, actions can be set individually for each filter.
Finally, GFI MailEssentials creates a special New Senders folder in the user's mailbox and puts messages in it that do not fall into the spam category, but are received from correspondents that the user has not previously contacted.
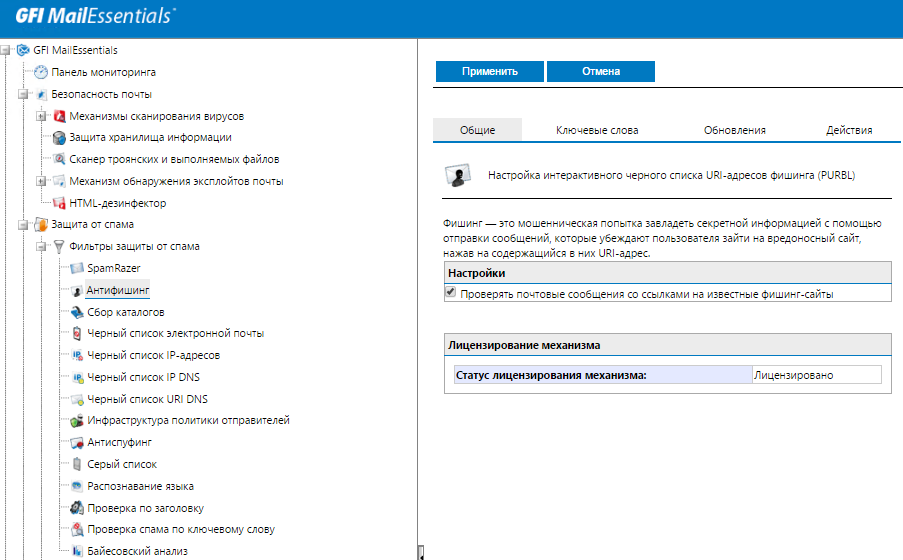
To protect against phishing attacks, GFI MailEssentials contains links to websites in the email message using the PURBL phishing resource database (Phishing URI Realtime Blocklist). In case of coincidence, the letter is blocked.
The anti-phishing module in GFI MailEssentials detects and blocks threats not only by the database of phishing URLs, which are constantly updated: for additional protection, each email message is checked for compliance with keywords.
To protect against spyware and viruses, GFI MailEssentials uses a whole arsenal of technologies, including several anti-virus engines, as well as other tools designed specifically to protect against attacks through email systems, such as exploit analysis, Trojan and executable file scanner and HTML cleaning to remove dangerous content like javascript.
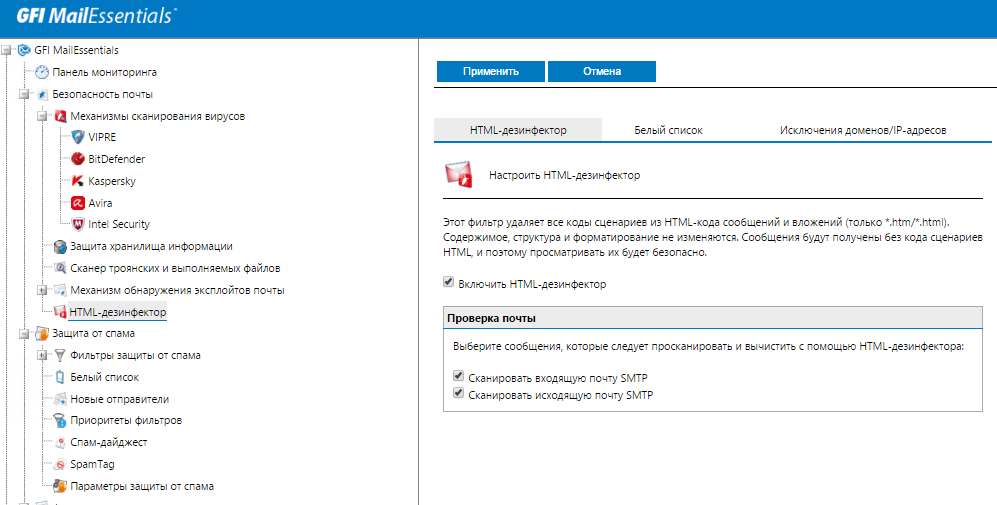
HTML cleanup
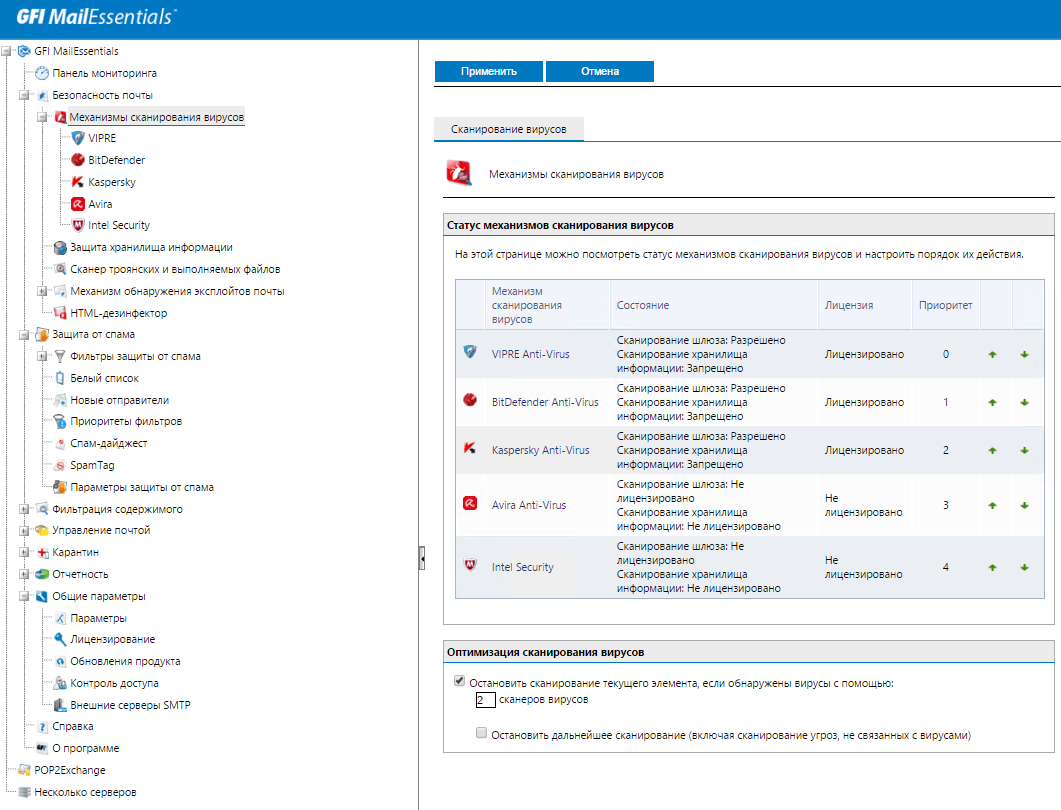
Configure antivirus engines
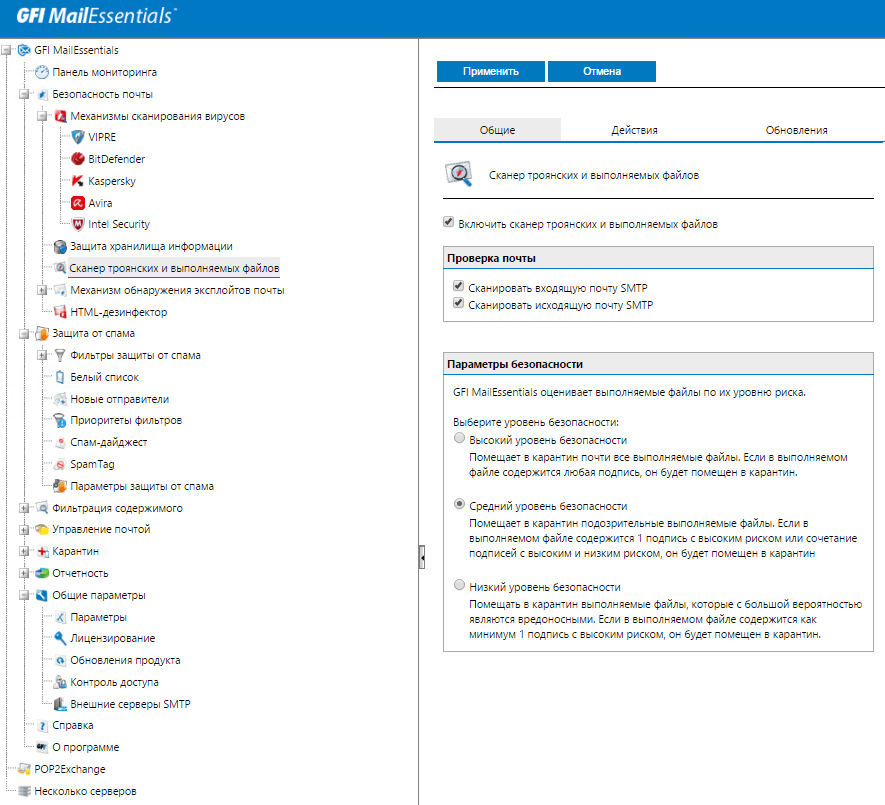
Configuring anti-virus scanning policies for mail
MailEssentials includes five anti-virus engines: VIPRE, BitDefender, Kaspersky, Avira and McAfee. Each of them is automatically updated. In the standard configuration, GFI MailEssentials comes with VIPRE and BitDefender engines, the rest can be added if necessary. For example, optionally GFI MailEssentials allows you to check mail with Kaspersky anti-virus engine with a built-in database of signatures of adware and spyware, known trojans.
As practice shows, different anti-virus kernels protect against different threats. This is clearly seen in the screenshots of one of the Russian users of the product:
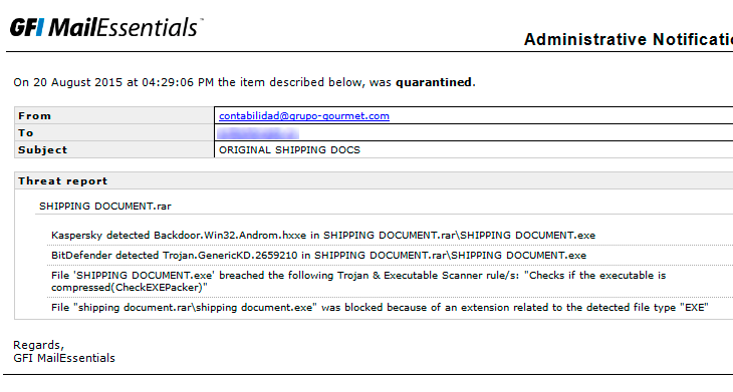
The Trojan was caught by Kaspersky and BitDefender engines
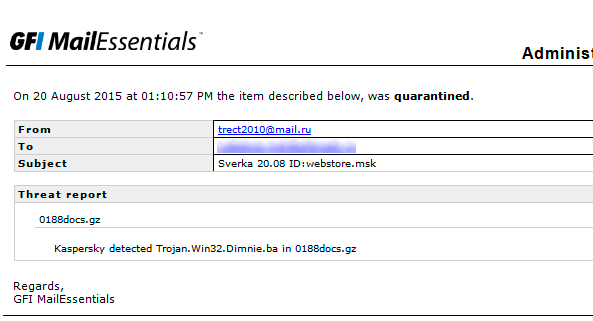
Troyan was a floodplain Kaspersky engine
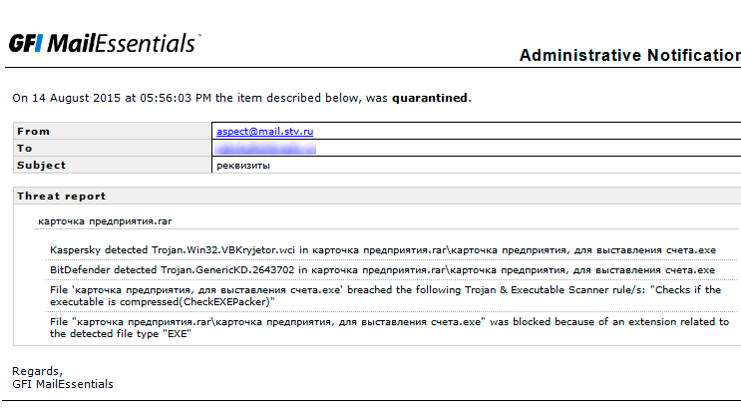
The Trojan was caught by Kaspersky and BitDefender engines
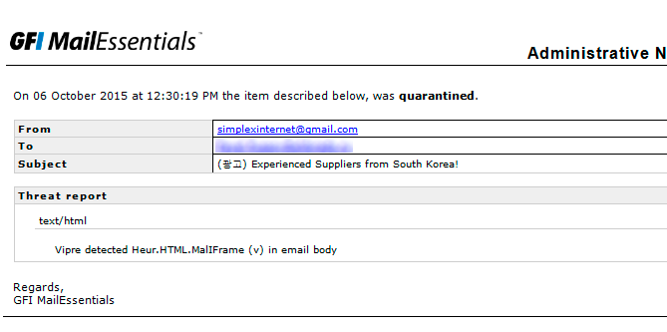
Vipre caught an HTML exploit The
quarantine is configured quite thinly, you can give access to individual quarantine for each user. In the case of a distributed installation of the product on the network, quarantine is synchronized between copies of the product.
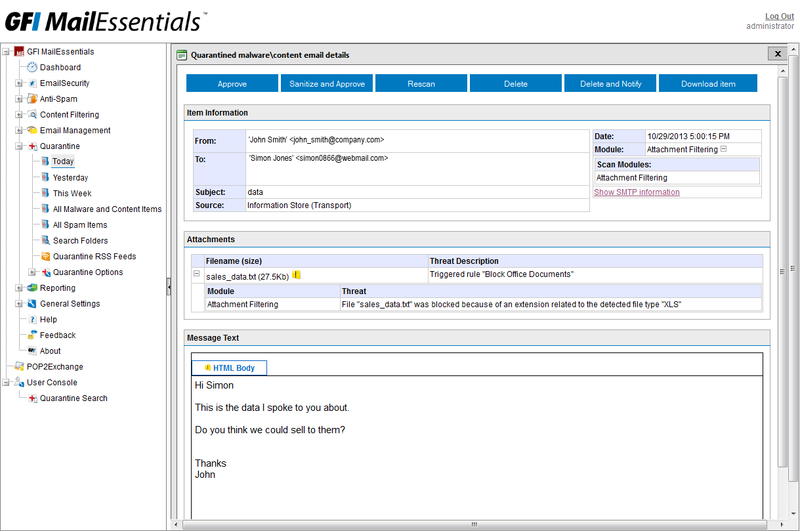
Configuring malware quarantine
Built-in reporting tools will allow you to analyze the intensity and nature of the use of corporate e-mail, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of the spam filtering system.
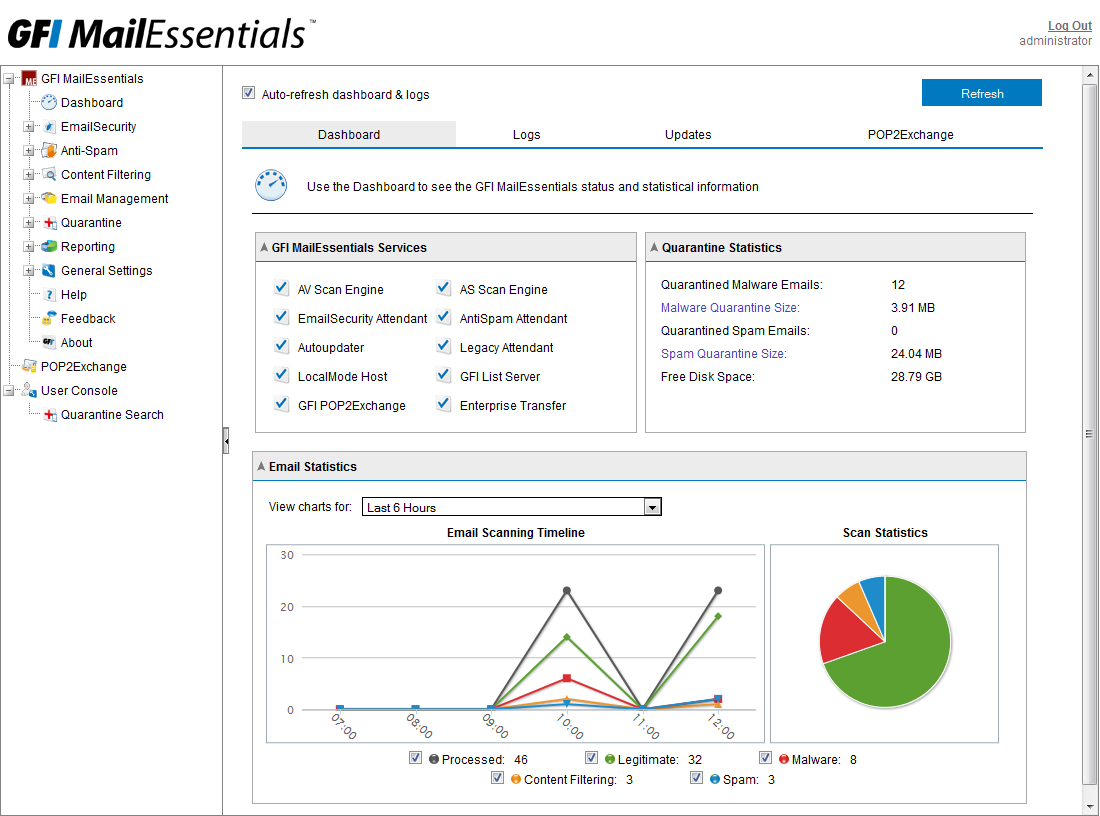
GFI MailEssentials Reports
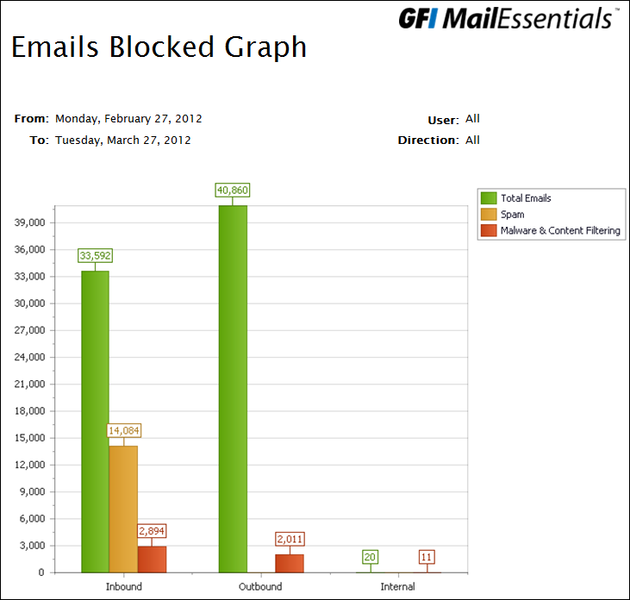
Blocked Mail Summary Statistics
A typical installation of GFI MailEssentials is a Windows Server server with SMTP and MailEssentials service, or an Exchange server with MailEssentials. The latest version of MailEssentials is aimed at medium and large organizations: the deployable configuration can be “clustered” with the ability to replicate and centralized reporting. This option is suitable for customers with multiple Exchange servers who do not want to use anti-spam cloud services, or this is contrary to corporate policy.
When installed on a Microsoft Exchange server, GFI MailEssentials automatically imports the SMTP service settings. Additional configuration of the mail gateway is not required. Using the SMTP protocol provides support for standard SMTP / POP3 mail servers.
An Exchange server is also integrated with the Exchange server with the functions of registration and cancellation of a subscription (in accordance with the requirements of anti-spam legislation). It can use Microsoft Access or Microsoft SQL Server as a storage of information.
The 2015 version is aimed at multi-server installations and has new simple configuration settings that allow you to use general configuration settings, quarantine and centralized reports. The product integrates well with the current version of Exchange.
Although the product installation includes more than 20 steps, including preparation, installation itself and the final stage, this is a very simple process. You just need to make sure that the system requirements are satisfied .
Installing MailEssentials on an Exchange server is actually a two-step process. First you need to select several options for integrating the product with Active Directory and Exchange. The User Mode selection determines how many users MailEssentials will recognize. On Exchange Server, it makes sense to join an Active Directory domain. Next, the website for the MailEssentials control panel is installed. You can select multiple sites for different roles. After that, MailEssentials installs the various components. Upon completion of the process, MailEssentials enables you to complete the final configuration and integrate the software with the underlying Exchange platform.
For integration, several software agents are installed that intercept messages at the transport level. At the final stage, an account is created to access the mailboxes.
After installation on the first server, MailEssentials will be available on the Exchange Server at http: // servername / MailEssentials . Active Directory is used for login.
A browser interface is used to work with MailEssentials. Administrators can manage both Exchange and MailEssentials without additional tools.
In the tree menu, you can configure anti-malware protection, anti-spam, content filtering, use the mail system management tools, set the quarantine folder and select general settings.
In the Multi-Server section, you can define a “cluster” of MailEssentials. One server is defined as the primary, the other as the slave. You can add new, additional servers to the latter.
After that, you can configure black and white lists, keywords and content filtering rules. When installed on multiple servers, GFI MailEssentials automatically synchronizes configuration and settings between them, including filtering rules, keywords, and black / white lists. All these settings are replicated between servers. You can also select specific servers for quarantine and reporting.
In May 2016, a new version of the product was released - 20.1, in which a number of functions were improved and the identified errors were fixed . In conclusion, we list the main features of version 20, introduced in January 2015.
Spam and malware protection products are widely used today and are used in organizations of various profiles and sizes. Among them are Sophos, McAfee, Barracuda and IronPort. E-mail systems deployed locally or in the cloud offer similar features. GFI MailEssentials is a worthy alternative to Forefront Protection for Exchange, offering additional functionality. The product has earned a good reputation and received four VBSpam + awards.
MailEssentials is a useful, multifunctional tool for a mail server, supplementing it not only with anti-spam and malware protection tools, but also offering a number of other functions that are usually implemented by stand-alone products.
As the name Essentials implies, the product includes features that are very important to many organizations that have not yet been implemented by Microsoft in Exchange. And this is the reason for his more than 15 years of commercial success.
You can download a free full-featured version (demo, 30 days) here:
gfi-software.ru/downloads/gfi-mailessentials
For the time of use, technical support in Russian is provided in accordance with the policy:
gfi-software.ru/support/policy
Post 1 - GFI LanGuard - virtual security consultant >>
Post 2 - GFI Archiver: storage for mail >>

GFI MailEssentials has been famous for many years for providing the highest accuracy of spam filtering. This is achieved through the use of Bayesian analysis methods and other spam identification technologies. According to estimates, GFI MailEssentials blocks more than 99% of spam and at the same time shows a record low level of false positives, which is achieved through the use of automatically updated whitelists, and also provides recognition and filtering of phishing, which uses a special database of phishing resources and search by key according to.
MailEssentials is quickly installed on an enterprise mail server or email gateway and requires virtually no additional configuration. Thus, protection against spam and phishing is implemented at the mail gateway level. Consequently, it is possible to refuse the expensive deployment and maintenance of email protection systems at workstations of the enterprise, there is no need to train users in the specifics of fighting spam and regularly adjusting filtering rules, mail junk will not litter the disk subsystem of the email server.
Moreover, GFI MailEssentials flexibly adapts to the peculiarities of enterprise mail flows without administrator intervention and offers a number of useful server-level message management functions: automatic insertion of text into the message body, monitoring and analysis of the use of the e-mail system, mailing list server, automatic reply and download functions Messages from the provider's multiuser mailbox using the POP3 protocol. For example, the auto answer function along with the usual answer allows you to use custom templates and add an attachment.
SPAM PROTECTION MECHANISMS
Bayesian filtering technology and feature analysis
According to research, Bayesian filtering leads in spam recognition accuracy, provides the highest filtering accuracy - over 98%. It is far ahead of identification methods based on signatures and keywords. It uses probabilistic assessment methods based on the found characteristic features - words and phrases. GFI MailEssentials calculates the likelihood that the message is spam, using a complex formula and uses sets of characteristic features.

The product includes numerous spam filtering options.

Setting filter rules

Setting actions for filtering mail
The product analyzes in detail the service fields of emails and identifies fake headers, attempts to hide IP addresses, spam mutations, falsified domains and other signs of spam.
The anti-spam engine is complemented by a custom content filtering engine for keywords and attachment types, including the ability to prohibit unpacking ZIP files.
A useful tool is SpamTag, a plug-in for MS Outlook that allows users to participate in the product pre-configuration by marking past spam filters directly from the Outlook interface. It also creates a button in Outlook for user access to quarantine - no need to remember how to get there. He simply presses a button and sees blocked letters sent to him.

Configuring SpamTag
Among other advanced anti-spam mechanisms is SpamRazor, which uses fingerprints of e-mail messages to detect common spam and DNS URI block lists for checking suspicious messages.
GFI MailEssentials can update the set of characteristic features of spam by accessing the GFI website, which allows you to quickly adapt the system to changing the characteristics of spam distribution and successfully resist the new tricks of mass mailing masters. GFI experts are continuously improving Bayesian databases in collaboration with leading spam collection and research organizations.
A set of "bad" signs are regularly updated by GFI experts and downloaded by GFI MailEssentials from the Internet. The Bayesian GFI MailEssentials filter generates a set of signs of “bad” and “good” messages by analyzing the contents of the corresponding public folders. To increase the accuracy of spam recognition, replenishment of these folders can be performed, along with administrators, by users of the system who are granted the necessary access rights.
Protection against the selection of email addresses
Sometimes spammers send letters to randomly generated email addresses of the enterprise. GFI MailEssentials checks the recipient addresses against the Active Directory database or LDAP directory, and if the number of invalid addresses exceeds the specified value, it is marked as spam.
The analysis of mail messages also involves verifying that a letter received on behalf of an organization was sent from an authorized mail server. This function is performed by the Sender Policy Framework (SPF) module.
White and black lists
Based on white lists, GFI MailEssentials skips mail from specified senders or mail domains. Since these lists are automatically replenished with the addresses of the recipients of outgoing letters, the level of false positives is significantly reduced. Whitelists can also be generated using domain names, individual email addresses, and keywords.
Finally, GFI MailEssentials checks the email addresses contained in the database against databases of spamming sites (Spam URI Realtime Blocklists, SURBL). The administrator can set SURBL servers independently and determine the order of their use. Users can also be involved in the process by giving them access to shared folders, which are used to configure black and white lists in GFI MailEssentials.
GFI MailEssentials also maintains blacklists of third-party organizations and communities such as ORDB, SpamHaus and Spamcop. In addition, the administrator can independently specify the servers that provide blacklist services.

Setting up lists
Gray lists
Another method of protection against spam is the so-called gray lists. It is especially effective because it assumes that the spammer software does not follow the same rules that apply to a regular email server. The engine tells the mail server to “try again”. On the second attempt, the message will be accepted, and the engine will skip subsequent mail messages from this sender. In general, this does not affect the time of email delivery, but it can significantly help protect against spam.
What to do with spam?
GFI MailEssentials offers the flexibility to handle suspicious messages classified as spam. You can choose to automatically delete such messages, move them to a special public folder, forward them to the specified email address, or transfer them to the folder for suspicious messages in the recipient's mailbox in order to avoid the loss of emails mistakenly classified as spam. At the same time, actions can be set individually for each filter.
Finally, GFI MailEssentials creates a special New Senders folder in the user's mailbox and puts messages in it that do not fall into the spam category, but are received from correspondents that the user has not previously contacted.
PROTECTION AGAINST PHISHING
To protect against phishing attacks, GFI MailEssentials contains links to websites in the email message using the PURBL phishing resource database (Phishing URI Realtime Blocklist). In case of coincidence, the letter is blocked.
The anti-phishing module in GFI MailEssentials detects and blocks threats not only by the database of phishing URLs, which are constantly updated: for additional protection, each email message is checked for compliance with keywords.
PROTECTION AGAINST Malicious programs
To protect against spyware and viruses, GFI MailEssentials uses a whole arsenal of technologies, including several anti-virus engines, as well as other tools designed specifically to protect against attacks through email systems, such as exploit analysis, Trojan and executable file scanner and HTML cleaning to remove dangerous content like javascript.

HTML cleanup

Configure antivirus engines

Configuring anti-virus scanning policies for mail
MailEssentials includes five anti-virus engines: VIPRE, BitDefender, Kaspersky, Avira and McAfee. Each of them is automatically updated. In the standard configuration, GFI MailEssentials comes with VIPRE and BitDefender engines, the rest can be added if necessary. For example, optionally GFI MailEssentials allows you to check mail with Kaspersky anti-virus engine with a built-in database of signatures of adware and spyware, known trojans.
As practice shows, different anti-virus kernels protect against different threats. This is clearly seen in the screenshots of one of the Russian users of the product:

The Trojan was caught by Kaspersky and BitDefender engines

Troyan was a floodplain Kaspersky engine

The Trojan was caught by Kaspersky and BitDefender engines

Vipre caught an HTML exploit The
quarantine is configured quite thinly, you can give access to individual quarantine for each user. In the case of a distributed installation of the product on the network, quarantine is synchronized between copies of the product.

Configuring malware quarantine
REPORTS
Built-in reporting tools will allow you to analyze the intensity and nature of the use of corporate e-mail, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of the spam filtering system.

GFI MailEssentials Reports

Blocked Mail Summary Statistics
INSTALLATION AND INTEGRATION WITH MICROSOFT EXCHANGE SERVER
A typical installation of GFI MailEssentials is a Windows Server server with SMTP and MailEssentials service, or an Exchange server with MailEssentials. The latest version of MailEssentials is aimed at medium and large organizations: the deployable configuration can be “clustered” with the ability to replicate and centralized reporting. This option is suitable for customers with multiple Exchange servers who do not want to use anti-spam cloud services, or this is contrary to corporate policy.
When installed on a Microsoft Exchange server, GFI MailEssentials automatically imports the SMTP service settings. Additional configuration of the mail gateway is not required. Using the SMTP protocol provides support for standard SMTP / POP3 mail servers.
An Exchange server is also integrated with the Exchange server with the functions of registration and cancellation of a subscription (in accordance with the requirements of anti-spam legislation). It can use Microsoft Access or Microsoft SQL Server as a storage of information.
The 2015 version is aimed at multi-server installations and has new simple configuration settings that allow you to use general configuration settings, quarantine and centralized reports. The product integrates well with the current version of Exchange.
Although the product installation includes more than 20 steps, including preparation, installation itself and the final stage, this is a very simple process. You just need to make sure that the system requirements are satisfied .
Installing MailEssentials on an Exchange server is actually a two-step process. First you need to select several options for integrating the product with Active Directory and Exchange. The User Mode selection determines how many users MailEssentials will recognize. On Exchange Server, it makes sense to join an Active Directory domain. Next, the website for the MailEssentials control panel is installed. You can select multiple sites for different roles. After that, MailEssentials installs the various components. Upon completion of the process, MailEssentials enables you to complete the final configuration and integrate the software with the underlying Exchange platform.
For integration, several software agents are installed that intercept messages at the transport level. At the final stage, an account is created to access the mailboxes.
After installation on the first server, MailEssentials will be available on the Exchange Server at http: // servername / MailEssentials . Active Directory is used for login.
A browser interface is used to work with MailEssentials. Administrators can manage both Exchange and MailEssentials without additional tools.
In the tree menu, you can configure anti-malware protection, anti-spam, content filtering, use the mail system management tools, set the quarantine folder and select general settings.
In the Multi-Server section, you can define a “cluster” of MailEssentials. One server is defined as the primary, the other as the slave. You can add new, additional servers to the latter.
After that, you can configure black and white lists, keywords and content filtering rules. When installed on multiple servers, GFI MailEssentials automatically synchronizes configuration and settings between them, including filtering rules, keywords, and black / white lists. All these settings are replicated between servers. You can also select specific servers for quarantine and reporting.
GFI MAILESSENTIALS 20: WHAT'S NEW?
In May 2016, a new version of the product was released - 20.1, in which a number of functions were improved and the identified errors were fixed . In conclusion, we list the main features of version 20, introduced in January 2015.
- Multi-threaded spam protection to increase the throughput of the e-mail system on systems with multiple processors or multi-core CPUs, as well as in cluster configurations.
- Support for 64-bit systems, which allows GFI MailEssentials to more efficiently handle large volumes of email.
- Remote Active Directory (AD) support enables you to install GFI MailEssentials on non-AD systems, such as IIS SMTP or Edge servers. At the same time, Active Directory will still be used, despite the lack of local access to it.
- Support for scanning Exchange 2013 and older vaults for malware using Exchange Web Services.
- Support for Exchange 2016, Windows 10, and Office 2016.
CONCLUSIONS
Spam and malware protection products are widely used today and are used in organizations of various profiles and sizes. Among them are Sophos, McAfee, Barracuda and IronPort. E-mail systems deployed locally or in the cloud offer similar features. GFI MailEssentials is a worthy alternative to Forefront Protection for Exchange, offering additional functionality. The product has earned a good reputation and received four VBSpam + awards.
MailEssentials is a useful, multifunctional tool for a mail server, supplementing it not only with anti-spam and malware protection tools, but also offering a number of other functions that are usually implemented by stand-alone products.
As the name Essentials implies, the product includes features that are very important to many organizations that have not yet been implemented by Microsoft in Exchange. And this is the reason for his more than 15 years of commercial success.
You can download a free full-featured version (demo, 30 days) here:
gfi-software.ru/downloads/gfi-mailessentials
For the time of use, technical support in Russian is provided in accordance with the policy:
gfi-software.ru/support/policy
Post 1 - GFI LanGuard - virtual security consultant >>
Post 2 - GFI Archiver: storage for mail >>
