Cognitive computing - work faster than thought

Cognitive computing is a trend of the past few years. These are technologies that many experts are developing at a very fast pace and help people cope with a huge flow of information. Moreover, this stream is very deep and wide, figuratively speaking, this is the entire stream of information generated by humanity. The human brain is a powerful system that can analyze unstructured data arrays, process them and “sort them out”. But even this tool does not cope with the information flows of our time, therefore, man has put computers at his service, both ordinary personal and superproductive systems. But here a problem arose of a different nature, namely, the need to structure the data that is being processed. Every day, humanity generates about 2, 5 quintillion bytes of data, and 80% of them are unstructured. And this means that these 80% are invisible to modern computer systems created using conventional technology.
Cognitive calculations, technologies that partially repeat the features of the human brain and are able to work many times more effective than their organic forerunner come to the rescue. Here it is worth mentioning that we are talking only about a small part of the brain functions responsible for processing and analyzing information coming from outside. You can also talk about the system’s self-training, with certain assumptions. But, nevertheless, cognitive technologies are capable of much, simplifying the life of both an individual person and business structures.
Such systems can be used in a huge variety of different areas and areas, including banks, materials science, business optimization, urban infrastructure management, environmental assessment, research in various fields of science and medicine. The main task of cognitive technologies is to give a person the opportunity to work with unstructured data in a convenient way.
At the same time, a new type of system is gradually being created that not only follows a given algorithm, but is able to take into account many third-party factors during operation, self-study, use the results of past calculations and third-party resources (Internet, as an example). The architecture of the new systems will be different from the architecture of von Neumann.

John von Neumann
As you know, the principles of von Neumannread as follows:
The principle of homogeneity of memory. Commands and data are stored in the same memory and are externally indistinguishable in memory. They can only be recognized by the way they are used; that is, the same value in the memory cell can be used both as data, and as a command, and as an address, depending only on the way it is accessed. This allows you to perform the same operations on commands as on numbers, and, accordingly, opens up a number of possibilities. So, cyclically changing the address part of the command, you can provide access to the sequential elements of the data array. This technique is called a modification of commands and from the standpoint of modern programming is not welcome. More useful is another consequence of the principle of homogeneity, when the commands of one program can be obtained as a result of the execution of another program.
The principle of targeting . Structurally, the main memory consists of numbered cells, and any cell is available to the processor at any time. The binary codes of commands and data are divided into units of information called words and stored in memory cells, and the numbers of the corresponding cells — addresses — are used to access them.
The principle of program management. All calculations provided by the algorithm for solving the problem should be presented in the form of a program consisting of a sequence of control words - commands. Each of which prescribes a certain operation from a set of operations implemented by a computer. Program commands are stored in sequential memory cells of a computer and are executed in a natural sequence, that is, in the order of their position in the program. If necessary, using special commands, this sequence can be changed. The decision to change the order of execution of program instructions is made either based on an analysis of the results of previous calculations, or unconditionally.
Binary coding principle. According to this principle, all information, both data and commands, is encoded with binary digits 0 and 1. Each type of information is represented by a binary sequence and has its own format. A sequence of bits in a format that makes sense is called a field. In numerical information, a sign field and a field of significant digits are usually distinguished. In the command format, two fields can be distinguished: the operation code field and the address field.
The following are the main elements of a cognitive computing system (IBM Redbook - Rob High - “The Age of Cognitive Systems”):
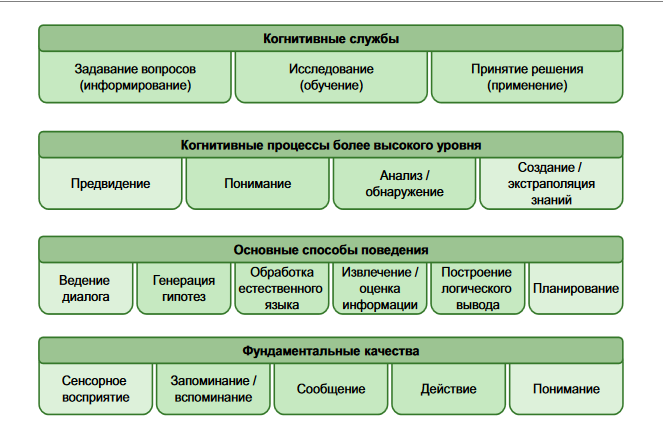
In order to meet its purpose (simplifying a person’s work with his information environment), cognitive systems should be:
- Adaptive . It is necessary to study changes in the information environment, including changing goals and objectives. Also, when analyzing information, unpredictable factors must be taken into account. Cognitive systems should be able to process dynamic data and provide a result in real time or close to it.
- Interactive . They should interact with the user in such a way that he, the user, feels comfortable getting the desired result. Also, such systems should be able to work with other systems, devices, cloud services and people.
- Self-learning . The work of cognitive systems should be based not only on new data, but also on the results of their work in the past. They should “remember” previous iterations and access this information if necessary.
- Contextual . They need to understand, identify, and highlight contextual elements such as value, time, location, user profile, goal, process, and task. Be able to access multiple sources of information, including structured and unstructured data, as well as input devices.
Cognitive systems can also be integrated or use existing information systems (including systems with von Neumann architecture), be able to work with various interfaces and tools.
The scope of cognitive systems is very extensive:
In business, cognitive systems allow you to detect problem areas in the infrastructure, daily routine of the enterprise and other elements. As a result of the elimination of “bottlenecks”, the labor productivity of workers and the efficiency of entire departments increase. Significant savings and time are saved for employees, as well as machine time.
Cognitive technology can come in handy in a business in many cases, including the following:
- Involvement: understanding the aspects of each specific person, the cognitive system can carry out individual interaction with users, customers.
- Expertise: the cognitive system can be used to audit the activities of the enterprise, including financial matters. As a result, the company takes an individual approach to the client.
- Products and services: the same systems help to constantly improve the services of some companies, showing weaknesses that could be improved and improved.
- Discoveries: yes, in scientific research conducted by corporations or individual scientists, cognitive technologies can be of great benefit, since the most implicit data can be taken to the surface, studied and recorded.
- Decision making: identifying an increasing number of dependencies in any information, working with this data, the system can improve decision making in a single company or its division.

Application of IBM Watson cognitive system capabilities - study of trends
In healthcare, cognitive systems help to gradually move towards such a goal as an individual approach to patient treatment. This is especially true in complex cases, for example, with cancer. Analysis of human DNA and a comparison of additional factors (place of residence, load, etc.) helps to treat much more effectively than before. By studying the genotype and characteristics of the body of a particular person, doctors can prescribe the most effective drugs and procedures in a given case.
In cooking, cognitive systems can offer something completely unexpected, open up a new field, add new product combinations. Already, some cognitive systems (for example, Watson) can make recipes for various dishes based on a predefined list of products.
In sports, cognitive computing helps in real-time to evaluate the training of various athletes, as well as to recruit teams of players with the characteristics that a trainer needs.
And all this is only a small fraction of what cognitive systems are capable of. We will talk more about this topic in one of the following articles.
Many organizations and governments of different countries are working on the creation of cognitive systems. But at the moment, the most perfect and complete cognitive system, including a huge number of subsystems and elements, is IBM Watson. The IBM blog has written about this system more than once, and we plan to continue talking about it, because every day the system develops and improves. This is an attempt to operate with categories of the future, not just thinking, but thinking ahead of the curve.
Source: IBM Materials.
