Simplify backup and recovery with HPE StoreOnce RMC
How much does one hour of unplanned downtime cost in your organization? According to Gartner research , the industry average cost per minute is $ 5,600. These numbers indicate that your organization’s applications need to be protected and backup plays a key role in building a business without downtime and in maintaining a defined service level agreement (SLA). Otherwise ... Otherwise, expect something white and fluffy :)
What layer of storage under the backup is hidden behind the backup of only 1TB of productive data? In fact, it’s huge: suppose that the data on this 1TB volume is really very important and our backup policy for this volume is as follows:

- We do full backups every day and store them for a week (5 full 1TB backups);
- We store weekly backups for 4 weeks (4 full backups of 1TB);
- store monthly backups for a year (12 full backups of 1TB);
- in order to protect against the failure of the site, we back up to a remote site as a whole (a full copy of the site 1 data).
Total for 2 sites in total we need storage for backups of 42TB! Here the analogy with the tip of the iceberg suggests itself - often we take into account only the visible tip, not taking into account the huge amount hidden from the eyes ...

How can I protect data? First, you can store copies of productive data on tapes. But in this case, it is necessary to constantly check the state of the recorded data, to know where the tapes themselves are stored and be patient when restoring - the speed will rest on the inadequate mechanics of tape drives.
Secondly, you can store copies of data in the form of snapshots on the most productive storage. But in this case, we risk simultaneously losing the productive data and snapshots themselves in the event of a power outage or failure of the storage system.
On the other hand, more and more customers are opting for all-flash arrays to serve the most demanding business applications.
These factors explain the reason for creating a class of specialized disk data backup and disaster recovery systems that meet these challenges - HPE StoreOnce.
HPE StoreOnce systems - hardware systems for data backup with online deduplication at the variable block level. System options cover the full range of customers from the initial to the corporate level: The
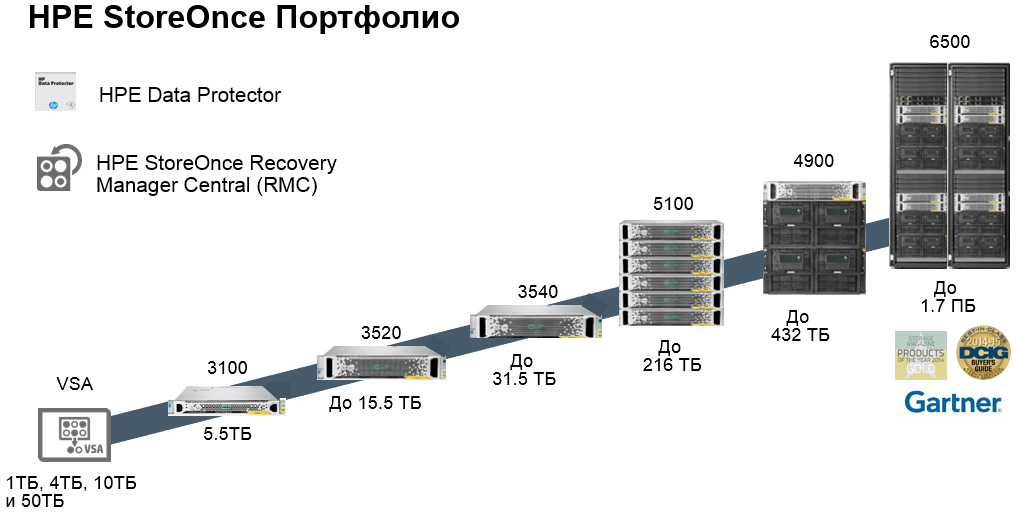
numbers indicate the usable capacity without deduplication.
What are the benefits of HPE StoreOnce backup systems? In brief, the benefits are as follows (expect a detailed description of the benefits in one of the following articles).
Firstly, HPE StoreOnce systems support online deduplication with variable-length blocks, and also allow you to move data between different systems in a compressed form, using even slow WAN channels.
Secondly, in addition to hardware systems, for small sites you can use the StoreOnce VSA virtual system, which can be deployed on any server that supports virtualization. Between the software and hardware complex, the data will also be moved in a compressed form, and you can manage such bundles from one console. A single family architecture allows combining devices of different classes into a common enterprise-level information protection system to provide diverse requirements for service levels and the duration of backup windows of different departments.
Third, older HPE StoreOnce systems support a configuration with 8 controllers, which provides full redundancy at the hardware level and protects against system crashes in the event of a controller failure.
Fourth, any HPE StoreOnce system checks data consistency (integrity) throughout the storage phase - from simple checksum checks that detect block corruption during data transfer, integrity checks at the file system and RAID group level, and to creating high availability configurations .
Fifthly, HPE StoreOnce systems received high marks from world analytical agencies in comparison with competitive offers on the market (links to analyst reports at the end of the article).
Sixth, and we will dwell on this in more detail in this article, the HPE StoreOnce system supports seamless integration with HPE 3PAR productive storage systems - the so-called the mechanism of a flat backup (Flat Backup) through the use of HPE StoreOnce Recovery Manager (RMC).
HPE StoreOnce Recovery Manager is specifically designed to simplify backing up productive data from HPE 3PAR arrays to HPE StoreOnce systems.
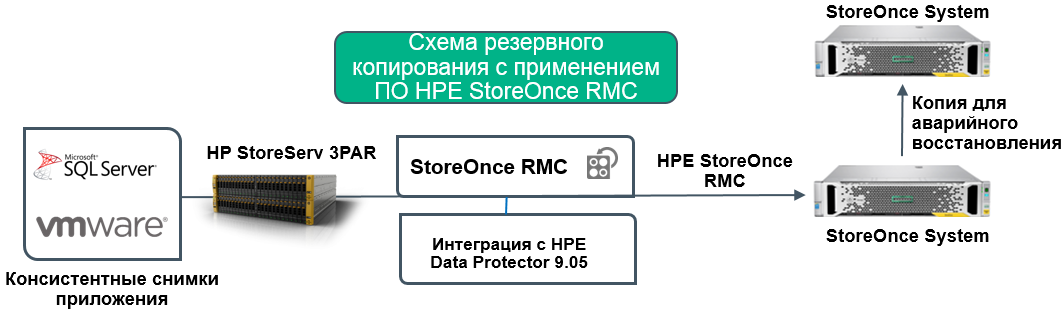
When switching to solid-state drives on productive storage systems, traditional tape backup schemes (with a full copy of all information once a week and daily incremental backups) should be upgraded because the data changes much more often than it did in the era of traditional disk arrays. HPE 3PAR StoreServ technologies allow you to do this in the simplest way - by directly copying “snapshots” of volumes that are consistent from the point of view of business applications to a separate HPE StoreOnce device with deduplication. Administrators of a disk array or virtual environment can run this task without being bound by the traditional backup procedures. Speed and granular recovery, up to individual virtual machine files,
HPE RMC software enables administrators to create hundreds of copies of virtual machine volumes and recover them quickly. VMware administrators have the ability to manage snapshots of productive volumes from a single console.
RMC uses the vCenter plug-in to create consistent snapshots. As soon as the administrator gives a command (or automatically according to the schedule), the virtual machine switches to backup mode and resets the state of the file system and RAM to the storage system. Further, on the storage system side, mechanisms for working with snapshots are enabled. The HPE 3PAR storage system has the ability to control changes at the block level, thanks to the built-in SnapDiff engine. After the data has been written to the array - they are sent as modified blocks to StoreOnce. By combining the 3PAR block change control mechanism with the StoreOnce logical indexing mechanism, RMC controls that only unique blocks are transmitted over data channels. This severely reduces bandwidth requirements.
In addition, the administrator can use the script to create “synthetic full” backups. When the changed blocks are sent from HPE 3PAR to StoreOnce Catalyst, the indexing algorithm creates a data map based on the data already recorded and newly received. In this case, the full backup is updated, and the difference between the backup before the change and after the change is written to disk. Thus, the administrator, in the event of a system crash, restores only one synthetic full backup, instead of restoring the first full “old” backup and several incremental backups in succession, which saves a lot of time.

Synthetic full backups scheme
In addition, such snapshots are completely autonomous and can be restored on any 3PAR array.
Let's see how StoreOnce RMC software is deployed and how the integration of productive storage with the backup system occurs.
1. Deploy the HPE StoreOnce RMC virtual machine in vCenter. Everything is simple here, we won’t dwell in detail (Hosts and Cluster - Action - Deploy from OVF template).
2. We check that the machine is deployed and go to the console:
3. So far, there are no systems, so add. We start with a productive storage system (StoreOnce RMC - Storage Systems - Add Storage System):
4. Enter the IP address of the system, user and password and connect our productive storage:
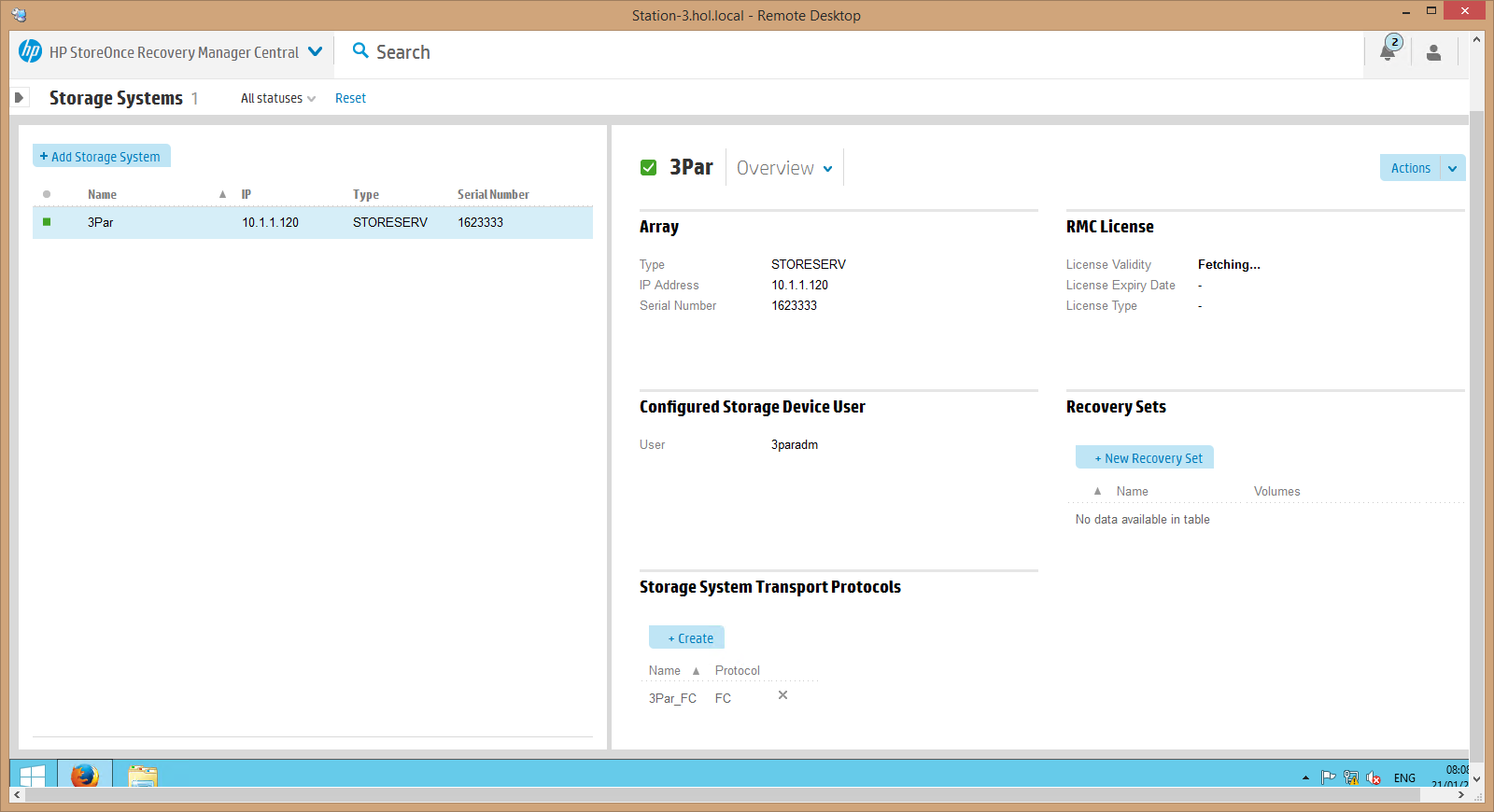
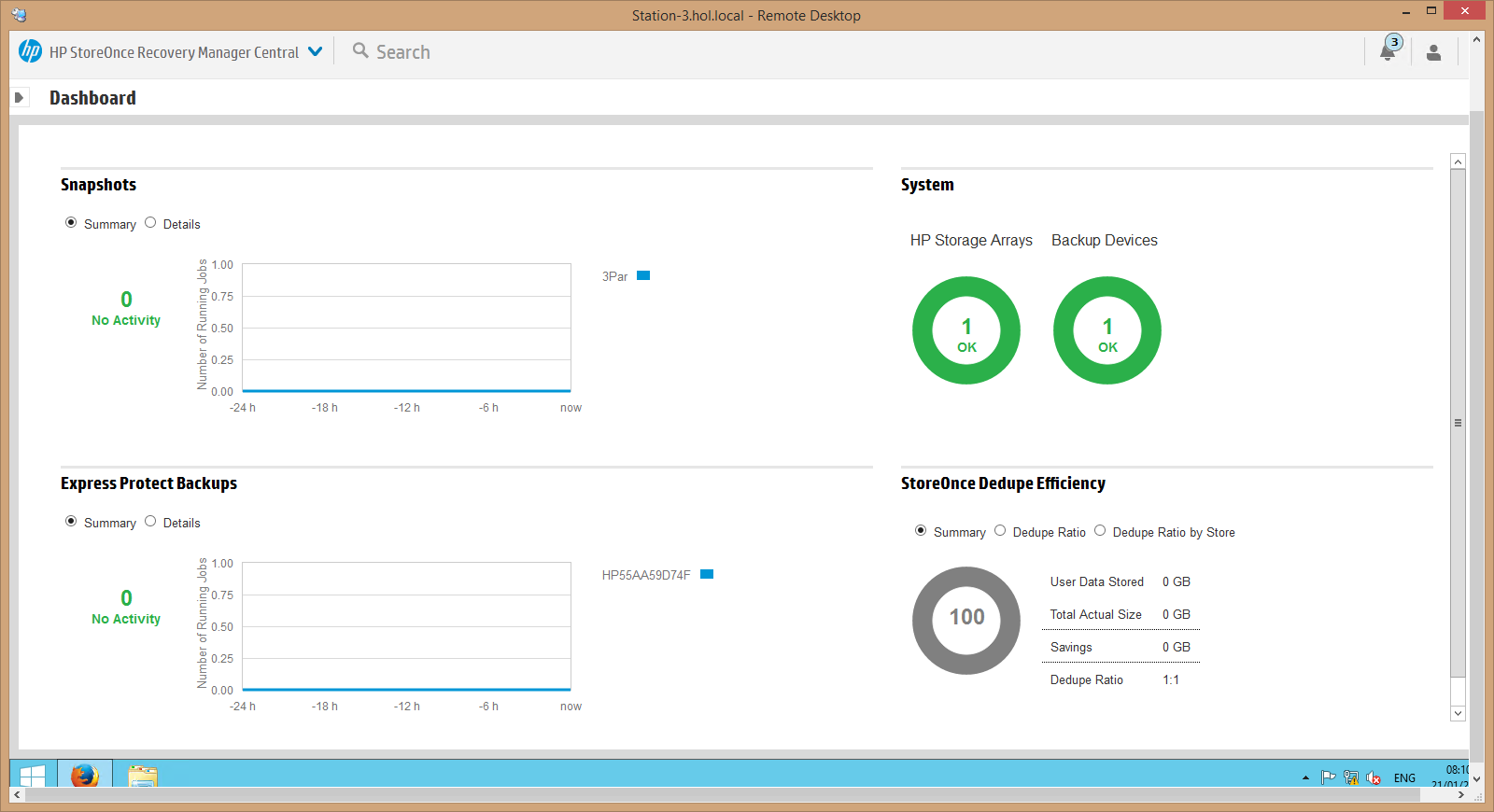
5.Next, we connect our HPE StoreOnce backup system and observe that both systems are connected and working, the Storage Arrays and Backup Devices partitions show the green color (by the way, the HPE RMC software interface resembles HPE OneView software, therefore, for example, server infrastructure administrators will it’s simple and clear to work in the RMC interface):
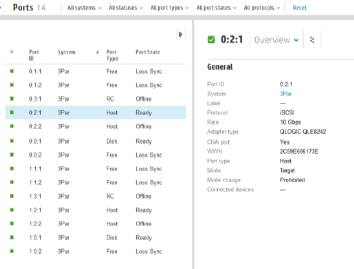
6. Next, configure the ports of the productive storage for backup, for this we launch the SSMC 3PAR console, select Dashboard - Ports and start the configuration, in our case, select the port 0: 2: 1 from the list that is available inter iSCSI:
7.We set up feedback in the HPE StoreOnce RMC console for this, click the Storage Systems green circle in the RMC console and click the + Create button in the Storage System Transport Protocols section and set the iSCSI type:
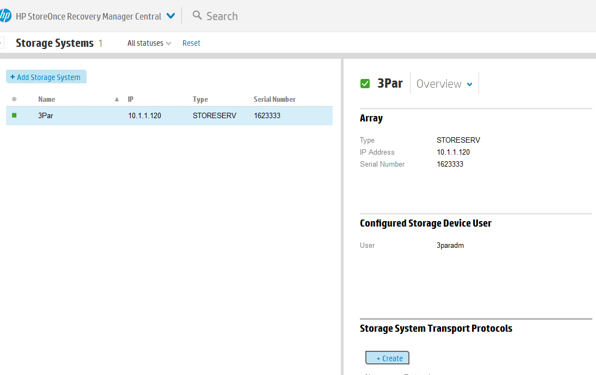
8. After that, create the volume on the productive array that we need to protect, To do this, return to the storage system console, go to the Virtual Volumes section and click + Create Virtual Volumes, set the volume parameters, on which media it will be located and which hosts it will be presented to:
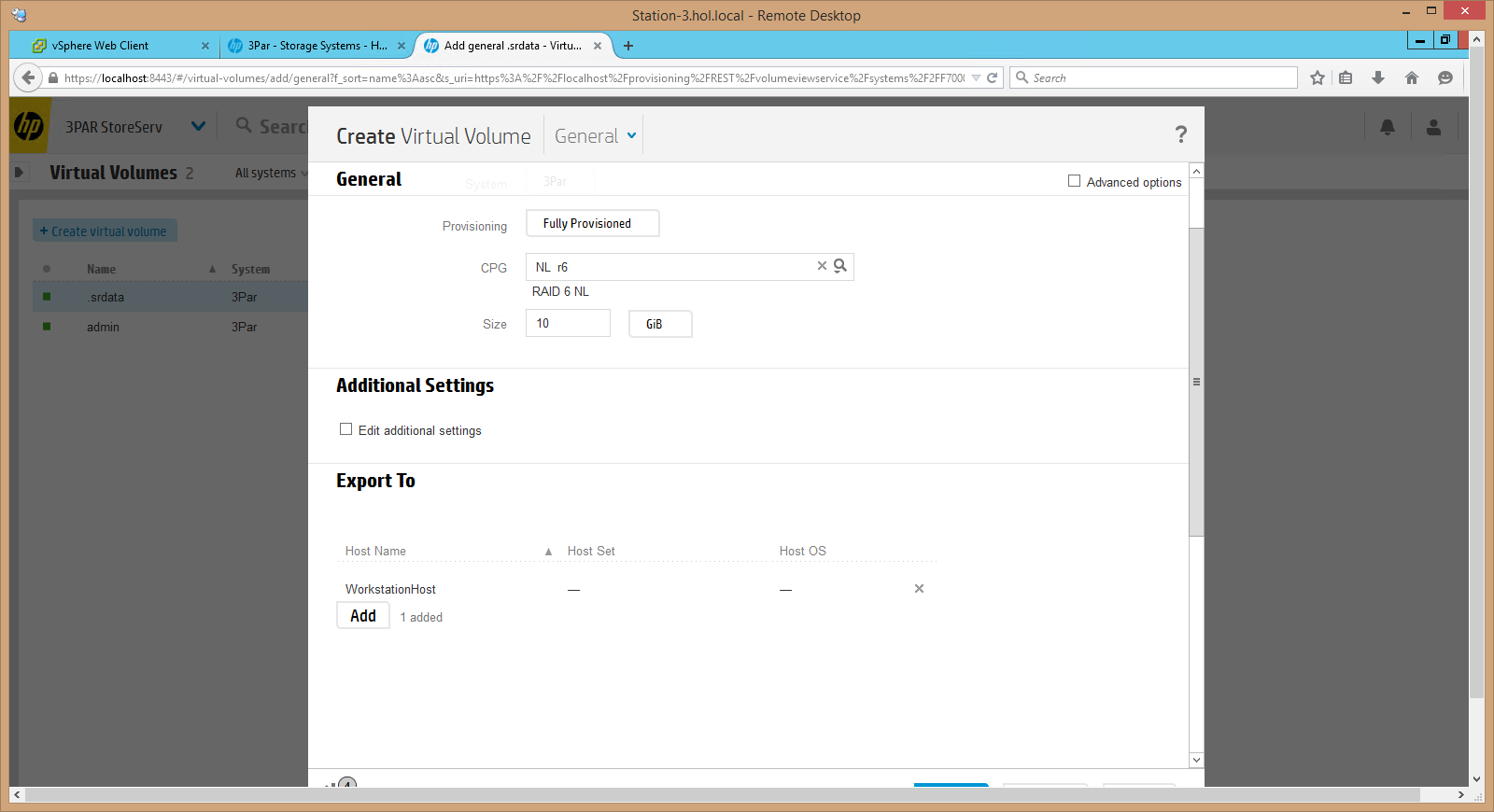
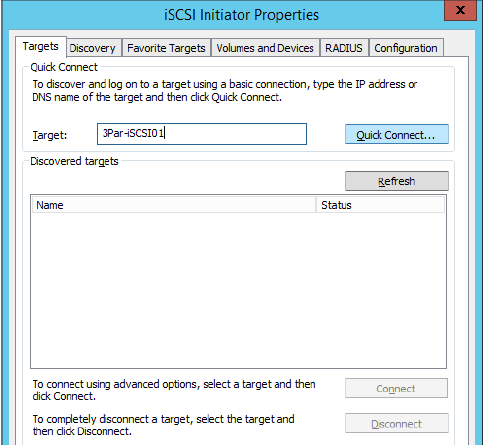
9.Now, on the host that the volume is presented to, you need to connect via iSCSI to 3PAR (for this, in the 3PAR console opposite the port we need, find the iSCSI initiator and connect to the array), then connect the host to the array, initialize and search for new devices and format the new volume. After that, create a document that we will protect:
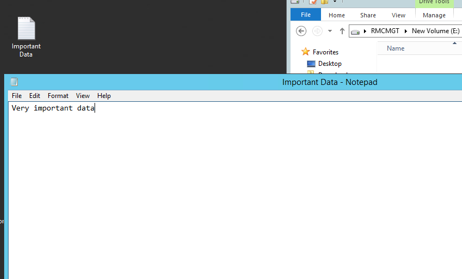
10. Create a very important document on the new drive of our host :)
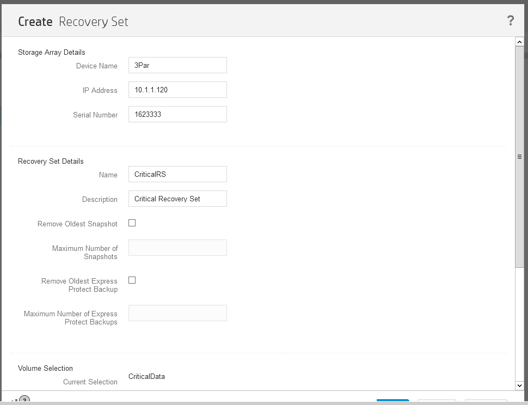
11.After creating the volume and writing important information to it, you need to return to the HPE StoreOnce RMC console and set the backup rules for this volume. To do this, in the RMC console in the Storage Systems section, click + New Recovery Set (here, configure the Remove Oldest Snapshot and Remove Oldest parameters Express Protect Backup, you can flexibly control the depth of attachments of our snapshots and backups), after specifying the name, check that the policy is created for the desired volume, to do this, scroll down the list and click the desired volume in the Volume Selection:
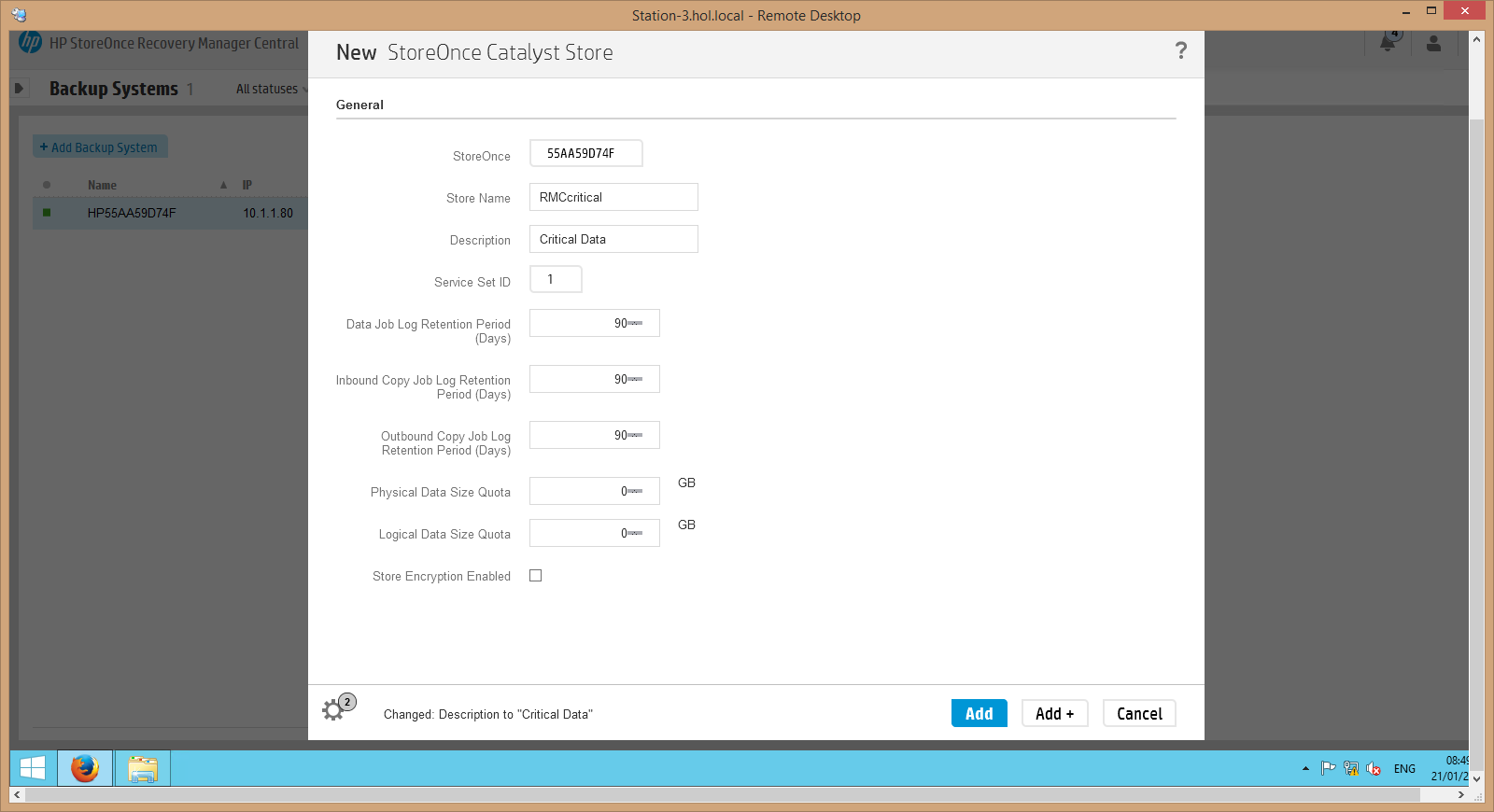
12. Now in the RMC console, go to to configure Backup S ystems, for this, in the backup systems section, select + New Store, drive in the StoreOnce system address, username and password, and configure the backup storage settings:
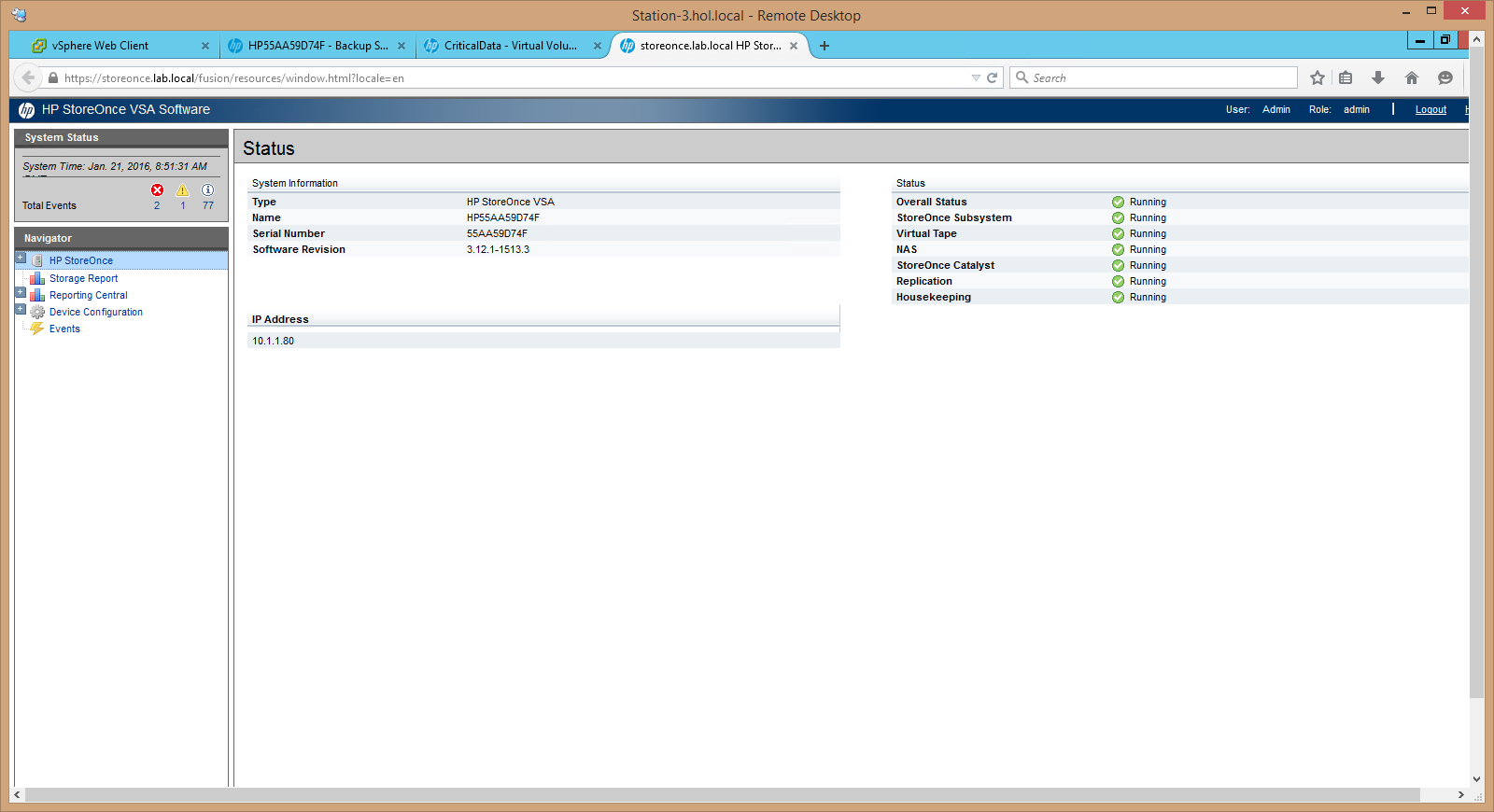
13.Check in the HPE StoreOnce console that RMC created the storage on our backup system:
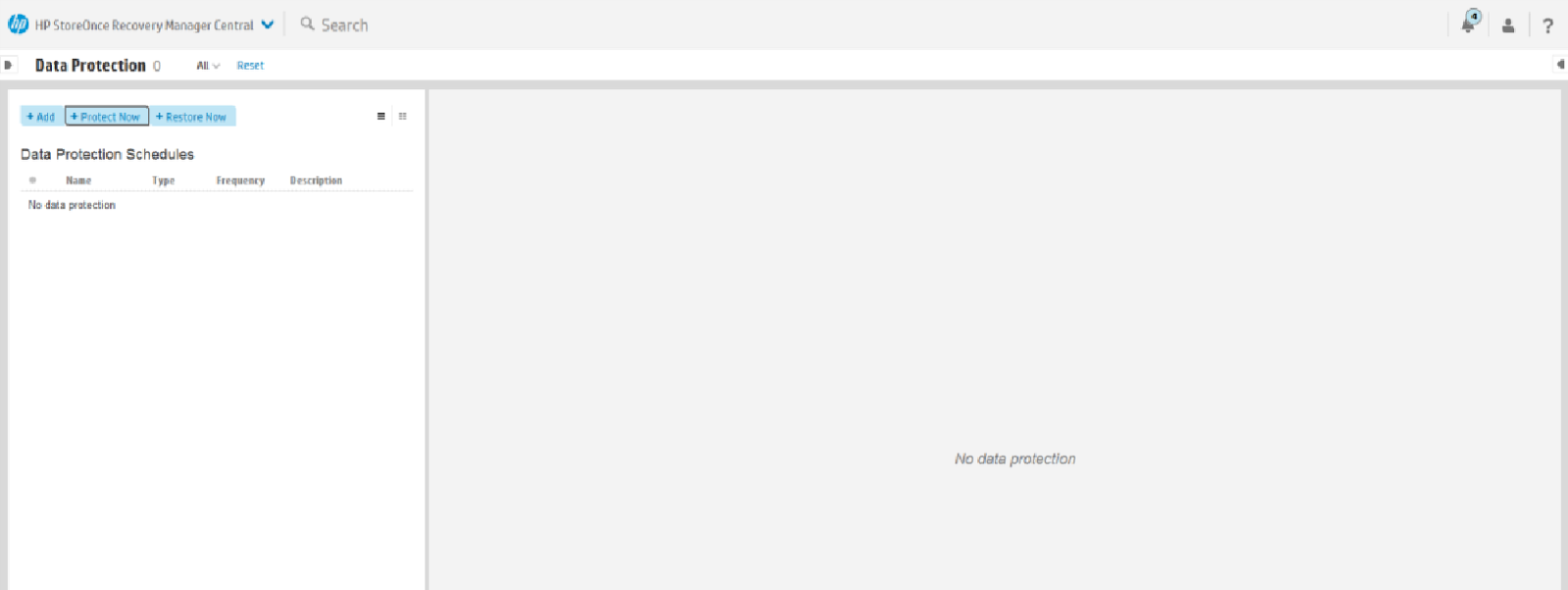
14. Now, in the StoreOnce RMC software console, you can back up our volume and configure scheduled or recovery options, for this, select Data Protection in the console menu and click the + button Protect Now:
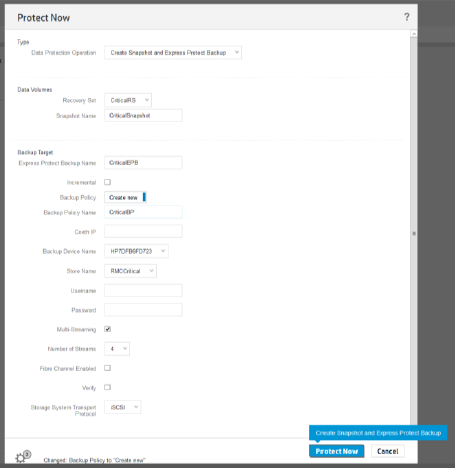
15. Create a snapshot:
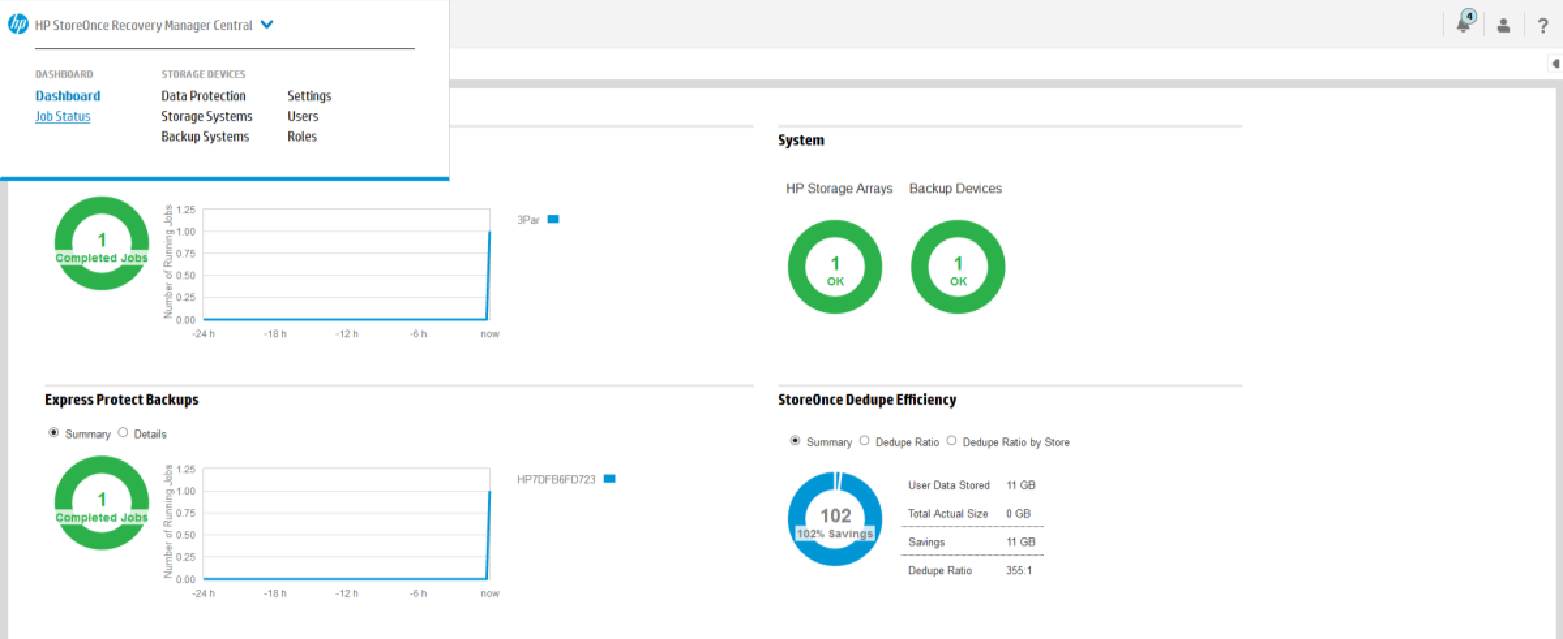
16. After the backup is completed, it will be checked in the HPE StoreOnce RMC console using the Completed Jobs parameter, and we also see the deduplication coefficient on the backup system:
Now our data is reliably protected, and we can test the recovery of a copy in the event of a disaster. To do this, in the Data Protection section, you can select the Restore Now button and restore a copy of our volume to a productive array.
Thus, HPE StoreOnce RMC simplifies the management of the backup process, accelerates the creation and restoration of data backups, and administrators get a single language of communication between productive storage systems and backup systems (so far we are talking only about HPE products).
Material for study:

- We do full backups every day and store them for a week (5 full 1TB backups);
- We store weekly backups for 4 weeks (4 full backups of 1TB);
- store monthly backups for a year (12 full backups of 1TB);
- in order to protect against the failure of the site, we back up to a remote site as a whole (a full copy of the site 1 data).
Total for 2 sites in total we need storage for backups of 42TB! Here the analogy with the tip of the iceberg suggests itself - often we take into account only the visible tip, not taking into account the huge amount hidden from the eyes ...

How can I protect data? First, you can store copies of productive data on tapes. But in this case, it is necessary to constantly check the state of the recorded data, to know where the tapes themselves are stored and be patient when restoring - the speed will rest on the inadequate mechanics of tape drives.
Secondly, you can store copies of data in the form of snapshots on the most productive storage. But in this case, we risk simultaneously losing the productive data and snapshots themselves in the event of a power outage or failure of the storage system.
On the other hand, more and more customers are opting for all-flash arrays to serve the most demanding business applications.
These factors explain the reason for creating a class of specialized disk data backup and disaster recovery systems that meet these challenges - HPE StoreOnce.
HPE StoreOnce About
HPE StoreOnce systems - hardware systems for data backup with online deduplication at the variable block level. System options cover the full range of customers from the initial to the corporate level: The

numbers indicate the usable capacity without deduplication.
What are the benefits of HPE StoreOnce backup systems? In brief, the benefits are as follows (expect a detailed description of the benefits in one of the following articles).
Firstly, HPE StoreOnce systems support online deduplication with variable-length blocks, and also allow you to move data between different systems in a compressed form, using even slow WAN channels.
Secondly, in addition to hardware systems, for small sites you can use the StoreOnce VSA virtual system, which can be deployed on any server that supports virtualization. Between the software and hardware complex, the data will also be moved in a compressed form, and you can manage such bundles from one console. A single family architecture allows combining devices of different classes into a common enterprise-level information protection system to provide diverse requirements for service levels and the duration of backup windows of different departments.
Third, older HPE StoreOnce systems support a configuration with 8 controllers, which provides full redundancy at the hardware level and protects against system crashes in the event of a controller failure.
Fourth, any HPE StoreOnce system checks data consistency (integrity) throughout the storage phase - from simple checksum checks that detect block corruption during data transfer, integrity checks at the file system and RAID group level, and to creating high availability configurations .
Fifthly, HPE StoreOnce systems received high marks from world analytical agencies in comparison with competitive offers on the market (links to analyst reports at the end of the article).
Sixth, and we will dwell on this in more detail in this article, the HPE StoreOnce system supports seamless integration with HPE 3PAR productive storage systems - the so-called the mechanism of a flat backup (Flat Backup) through the use of HPE StoreOnce Recovery Manager (RMC).
HPE StoreOnce RMC
HPE StoreOnce Recovery Manager is specifically designed to simplify backing up productive data from HPE 3PAR arrays to HPE StoreOnce systems.

When switching to solid-state drives on productive storage systems, traditional tape backup schemes (with a full copy of all information once a week and daily incremental backups) should be upgraded because the data changes much more often than it did in the era of traditional disk arrays. HPE 3PAR StoreServ technologies allow you to do this in the simplest way - by directly copying “snapshots” of volumes that are consistent from the point of view of business applications to a separate HPE StoreOnce device with deduplication. Administrators of a disk array or virtual environment can run this task without being bound by the traditional backup procedures. Speed and granular recovery, up to individual virtual machine files,
HPE RMC software enables administrators to create hundreds of copies of virtual machine volumes and recover them quickly. VMware administrators have the ability to manage snapshots of productive volumes from a single console.
A little bit about snapshots
RMC uses the vCenter plug-in to create consistent snapshots. As soon as the administrator gives a command (or automatically according to the schedule), the virtual machine switches to backup mode and resets the state of the file system and RAM to the storage system. Further, on the storage system side, mechanisms for working with snapshots are enabled. The HPE 3PAR storage system has the ability to control changes at the block level, thanks to the built-in SnapDiff engine. After the data has been written to the array - they are sent as modified blocks to StoreOnce. By combining the 3PAR block change control mechanism with the StoreOnce logical indexing mechanism, RMC controls that only unique blocks are transmitted over data channels. This severely reduces bandwidth requirements.
In addition, the administrator can use the script to create “synthetic full” backups. When the changed blocks are sent from HPE 3PAR to StoreOnce Catalyst, the indexing algorithm creates a data map based on the data already recorded and newly received. In this case, the full backup is updated, and the difference between the backup before the change and after the change is written to disk. Thus, the administrator, in the event of a system crash, restores only one synthetic full backup, instead of restoring the first full “old” backup and several incremental backups in succession, which saves a lot of time.

Synthetic full backups scheme
In addition, such snapshots are completely autonomous and can be restored on any 3PAR array.
Let's see how StoreOnce RMC software is deployed and how the integration of productive storage with the backup system occurs.
HPE StoreOnce RMC Software Deployment Steps
1. Deploy the HPE StoreOnce RMC virtual machine in vCenter. Everything is simple here, we won’t dwell in detail (Hosts and Cluster - Action - Deploy from OVF template).

2. We check that the machine is deployed and go to the console:

3. So far, there are no systems, so add. We start with a productive storage system (StoreOnce RMC - Storage Systems - Add Storage System):

4. Enter the IP address of the system, user and password and connect our productive storage:

5.Next, we connect our HPE StoreOnce backup system and observe that both systems are connected and working, the Storage Arrays and Backup Devices partitions show the green color (by the way, the HPE RMC software interface resembles HPE OneView software, therefore, for example, server infrastructure administrators will it’s simple and clear to work in the RMC interface):

6. Next, configure the ports of the productive storage for backup, for this we launch the SSMC 3PAR console, select Dashboard - Ports and start the configuration, in our case, select the port 0: 2: 1 from the list that is available inter iSCSI:

7.We set up feedback in the HPE StoreOnce RMC console for this, click the Storage Systems green circle in the RMC console and click the + Create button in the Storage System Transport Protocols section and set the iSCSI type:

8. After that, create the volume on the productive array that we need to protect, To do this, return to the storage system console, go to the Virtual Volumes section and click + Create Virtual Volumes, set the volume parameters, on which media it will be located and which hosts it will be presented to:

9.Now, on the host that the volume is presented to, you need to connect via iSCSI to 3PAR (for this, in the 3PAR console opposite the port we need, find the iSCSI initiator and connect to the array), then connect the host to the array, initialize and search for new devices and format the new volume. After that, create a document that we will protect:

10. Create a very important document on the new drive of our host :)

11.After creating the volume and writing important information to it, you need to return to the HPE StoreOnce RMC console and set the backup rules for this volume. To do this, in the RMC console in the Storage Systems section, click + New Recovery Set (here, configure the Remove Oldest Snapshot and Remove Oldest parameters Express Protect Backup, you can flexibly control the depth of attachments of our snapshots and backups), after specifying the name, check that the policy is created for the desired volume, to do this, scroll down the list and click the desired volume in the Volume Selection:

12. Now in the RMC console, go to to configure Backup S ystems, for this, in the backup systems section, select + New Store, drive in the StoreOnce system address, username and password, and configure the backup storage settings:

13.Check in the HPE StoreOnce console that RMC created the storage on our backup system:

14. Now, in the StoreOnce RMC software console, you can back up our volume and configure scheduled or recovery options, for this, select Data Protection in the console menu and click the + button Protect Now:

15. Create a snapshot:

16. After the backup is completed, it will be checked in the HPE StoreOnce RMC console using the Completed Jobs parameter, and we also see the deduplication coefficient on the backup system:

Now our data is reliably protected, and we can test the recovery of a copy in the event of a disaster. To do this, in the Data Protection section, you can select the Restore Now button and restore a copy of our volume to a productive array.
Thus, HPE StoreOnce RMC simplifies the management of the backup process, accelerates the creation and restoration of data backups, and administrators get a single language of communication between productive storage systems and backup systems (so far we are talking only about HPE products).
Material for study:
