Choosing a Virtualization Platform: Why VMware
Companies that choose a platform for virtualizing their IT infrastructure, along with VMware products, consider solutions based on other hypervisors, primarily Microsoft Hyper-V and the KVM hypervisor developed as part of OpenSource, as an alternative. To help these companies make the right choice, the Taneja Group analytic agency last year conducted a detailed comparison of several solutions for building software-defined data centers ( SDDC ) and implementing hybrid clouds from three vendors. In this study, we examined the possibilities of using the following packages:
- VMware vCloud Suite 5.5 Enterprise (including vSphere Enterprise Plus and vCenter Server Standard), Virtual SAN and NSX;

- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter (including the basic functionality of Hyper-V plus Hyper-V Replica, Storage Spaces, Hyper-V Network Virtualization, Hyper-V Extensible Switch and other advanced features), System Center 2012 R2 Datacenter;
- Red Hat Cloud Infrastructure (RHCI) consisting of RHEL OpenStack Platform 4.0, RHEV 3.4
(KVM), RHEV-M 3.4, and CloudForms 3.0 IaaS Management. This package of Red Hat is a commercial version of the OpenStack distribution (Cisco and Amazon solutions were also included in the study).
Each package was evaluated by the capabilities of data center virtualization, the implementation of hardware and software infrastructure, automation and operations management, and the implementation of hybrid clouds. And here are the conclusions:
According to the Taneja Group, of these three vendors, VMware offers the most mature, popular and functional platform for implementing virtualization; its solution provides independence from the hardware platform, dynamic allocation of resources based on rules and functions focused on virtual machines and applications.
VMware received the highest marks in the category of “automation and control”, because its solution implements automatic resource allocation, intelligent management of operations.VMware solutions have the most advanced features of hybrid clouds, they are compatible with different types of workloads and support migration between private and public clouds along with synchronization of directories and templates of these clouds. In addition, VMware solutions provide a coordinated framework for high availability and security for private and public clouds.
VMware has the most powerful virtualization features and experience in the enterprise sector since the beginning of the last decade. Although Microsoft has been expanding the capabilities of its virtualization platform in recent years, Hyper-V is still far behind vSphere in popularity in the enterprise sector and in the use of business-critical systems. In mid-2014, Hyper-V supported about 35 guest operating systems, while vSphere has a value of almost a hundred. Several important new Hyper-V features have been added in recent releases of Windows Server 2012 (for example, Extensible Virtual Switch and Replica), but the main drawback of the Hyper-V architecture is still the use of the parent OS, which reduces the security and availability of the hypervisor when installing patches and Maintaining the parent Windows Server. Moreover,
RHEV uses the KVM hypervisor, which runs the vast majority of OpenStack clouds. Now RHEV is very popular with service providers and developers of applications for embedded systems. Like Hyper-V, RHEL is an OS-centric hypervisor (its parent OS is Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)), which impairs security and reduces availability due to the need to install RHEL patches. It supports only 15 guest OSs, significantly inferior to vSphere and Hyper-V in this respect. Red Hat has added a number of new features in recent releases, but it still lacks a virtual distributed switch, storage resource pools, load balancing, and storage and network I / O controls. Corporate customers rarely use RHEV-based OpenStack clouds.
vSphere can scale across multiple host clusters and expand to new clusters and virtual machines as demand grows. As the Taneja Group tests showed, the vSphere architecture supports a larger number of virtual machines per host, and these VMs processed different combinations of business-critical applications. The vcenter Server and vcenter Operations Manager management tools can scale to several thousand and even tens of thousands of VMs.
Due to architecture limitations, Hyper-V cannot scale as efficiently as vSphere - for example, this hypervisor cannot manage logical resource pools (processors, memory, network resources and storage resources), therefore, to ensure stable performance of virtual machines, you need to use dedicated host cluster. RHEV also does not support processor and memory resource pools, which are scalable across multiple cluster hosts and do not provide resource isolation or pool sharing.
VMware vCloud Suite Enterprise provides high availability, resiliency, and disaster recovery capabilities with vSphere HA, vMotion, Storage vMotion, Fault Tolerance, and vCenter Site Recovery Manager. To reduce scheduled shutdowns for servicing servers or storage systems, vMotion and Storage vMotion functions transfer virtual machines and their disks online without stopping applications and users. VSphere Replication supports multiple replication options for vCenter Site Recovery Manager (SRM) to protect against major crashes. SRM provides centralized disaster recovery planning, automatic failover and failback from a backup site or from the vCloud cloud, and disaster recovery testing without disruption to applications.
In Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 with Hyper-V, the HA features implemented using Failover clustering are quite powerful, including fault detection and online migration of VMs and virtual machines. However, failover clustering is not optimized for VM protection.
Red Hat RHEV is capable of detecting host or guest OS failures and supports online migration of VMs and virtual machines, but it does not have built-in backup and replication functions for quick recovery from disasters.
A study by the Taneja Group came out in mid-2014. Over the past year, vSphere 5.5 first entered the market, then the sixth version of vSphere, and solutions for virtualization of data centers of other vendors, but VMware’s significant technological gap from competitors remains. A report issued this summer report Magic Quadrant for x86 Server Virtualization Infrastructure analytical agency Gartner states that VMware still remains the leader as possible virtualization platform, and to dominate the market, and customers the company is praised features of VMware products and support .
SAFEDATA uses VMware vSphere and other VMware products as a virtualization platform in its Virtual Data Center solution»(Virtual Data Center, VDC), on the basis of which the customer can independently create an IT infrastructure of any complexity, completely similar to the solutions on physical equipment. The HP BladeSystem c-Class blades as well as the NetApp FAS6220 and FAS8060 storage systems are used as the solution hardware platform.
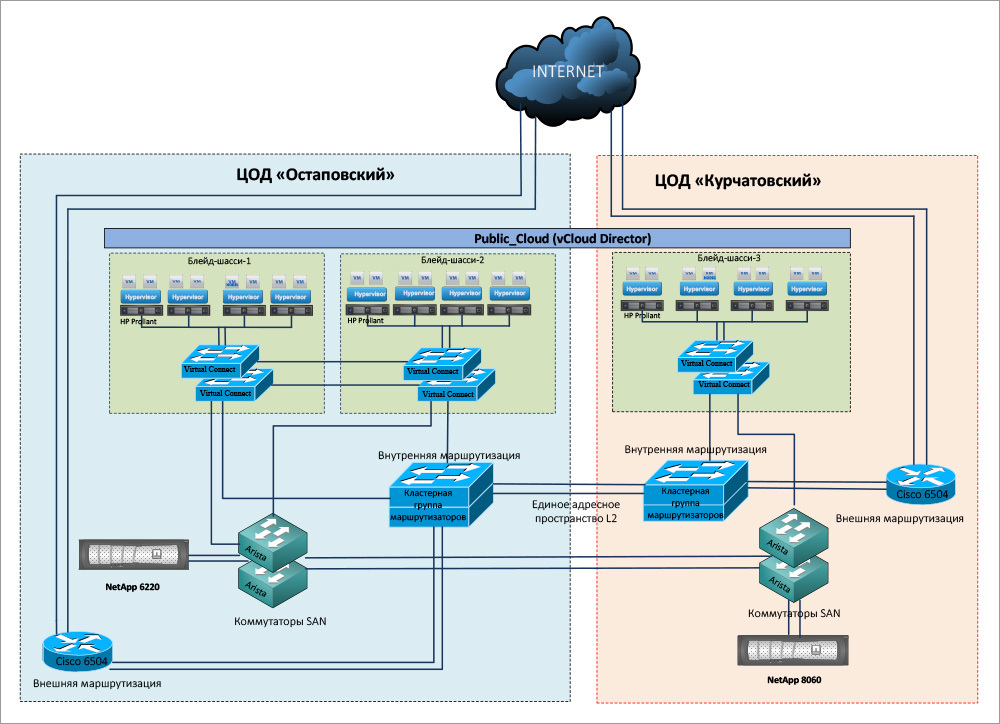
The VDC customer receives computing resources for building a virtual infrastructure from the SFCLOUD cloud located in two geographically distributed data centers. VSphere Node Failure Resilience in SFCLOUD is based on vSphere High Availability (HA) technology. In addition to directly managing this virtual infrastructure using VMware vCloud Director, the customer can flexibly distribute the cloud resources allocated to him between his applications depending on the load change, for example, if at some point the number of requests to one of the applications increases significantly, you can temporarily transfer part of it processors allocated to other applications. In addition, in the process of using the VDC cloud service, the customer can increase or decrease the amount of resources allocated to him, as well as apply various pricing models.
All actions related to managing the service, changing its parameters, monitoring performance, as well as financial documents, are carried out through the web interface of the “Personal Account” of the VDC customer. You can learn more about VDC here .

- Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter (including the basic functionality of Hyper-V plus Hyper-V Replica, Storage Spaces, Hyper-V Network Virtualization, Hyper-V Extensible Switch and other advanced features), System Center 2012 R2 Datacenter;
- Red Hat Cloud Infrastructure (RHCI) consisting of RHEL OpenStack Platform 4.0, RHEV 3.4
(KVM), RHEV-M 3.4, and CloudForms 3.0 IaaS Management. This package of Red Hat is a commercial version of the OpenStack distribution (Cisco and Amazon solutions were also included in the study).
Each package was evaluated by the capabilities of data center virtualization, the implementation of hardware and software infrastructure, automation and operations management, and the implementation of hybrid clouds. And here are the conclusions:
According to the Taneja Group, of these three vendors, VMware offers the most mature, popular and functional platform for implementing virtualization; its solution provides independence from the hardware platform, dynamic allocation of resources based on rules and functions focused on virtual machines and applications.
VMware received the highest marks in the category of “automation and control”, because its solution implements automatic resource allocation, intelligent management of operations.VMware solutions have the most advanced features of hybrid clouds, they are compatible with different types of workloads and support migration between private and public clouds along with synchronization of directories and templates of these clouds. In addition, VMware solutions provide a coordinated framework for high availability and security for private and public clouds.
Data Center Virtualization
VMware has the most powerful virtualization features and experience in the enterprise sector since the beginning of the last decade. Although Microsoft has been expanding the capabilities of its virtualization platform in recent years, Hyper-V is still far behind vSphere in popularity in the enterprise sector and in the use of business-critical systems. In mid-2014, Hyper-V supported about 35 guest operating systems, while vSphere has a value of almost a hundred. Several important new Hyper-V features have been added in recent releases of Windows Server 2012 (for example, Extensible Virtual Switch and Replica), but the main drawback of the Hyper-V architecture is still the use of the parent OS, which reduces the security and availability of the hypervisor when installing patches and Maintaining the parent Windows Server. Moreover,
RHEV uses the KVM hypervisor, which runs the vast majority of OpenStack clouds. Now RHEV is very popular with service providers and developers of applications for embedded systems. Like Hyper-V, RHEL is an OS-centric hypervisor (its parent OS is Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)), which impairs security and reduces availability due to the need to install RHEL patches. It supports only 15 guest OSs, significantly inferior to vSphere and Hyper-V in this respect. Red Hat has added a number of new features in recent releases, but it still lacks a virtual distributed switch, storage resource pools, load balancing, and storage and network I / O controls. Corporate customers rarely use RHEV-based OpenStack clouds.
Scalability
vSphere can scale across multiple host clusters and expand to new clusters and virtual machines as demand grows. As the Taneja Group tests showed, the vSphere architecture supports a larger number of virtual machines per host, and these VMs processed different combinations of business-critical applications. The vcenter Server and vcenter Operations Manager management tools can scale to several thousand and even tens of thousands of VMs.
Due to architecture limitations, Hyper-V cannot scale as efficiently as vSphere - for example, this hypervisor cannot manage logical resource pools (processors, memory, network resources and storage resources), therefore, to ensure stable performance of virtual machines, you need to use dedicated host cluster. RHEV also does not support processor and memory resource pools, which are scalable across multiple cluster hosts and do not provide resource isolation or pool sharing.
Business continuity
VMware vCloud Suite Enterprise provides high availability, resiliency, and disaster recovery capabilities with vSphere HA, vMotion, Storage vMotion, Fault Tolerance, and vCenter Site Recovery Manager. To reduce scheduled shutdowns for servicing servers or storage systems, vMotion and Storage vMotion functions transfer virtual machines and their disks online without stopping applications and users. VSphere Replication supports multiple replication options for vCenter Site Recovery Manager (SRM) to protect against major crashes. SRM provides centralized disaster recovery planning, automatic failover and failback from a backup site or from the vCloud cloud, and disaster recovery testing without disruption to applications.
In Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 with Hyper-V, the HA features implemented using Failover clustering are quite powerful, including fault detection and online migration of VMs and virtual machines. However, failover clustering is not optimized for VM protection.
Red Hat RHEV is capable of detecting host or guest OS failures and supports online migration of VMs and virtual machines, but it does not have built-in backup and replication functions for quick recovery from disasters.
VDC by SAFEDATA
A study by the Taneja Group came out in mid-2014. Over the past year, vSphere 5.5 first entered the market, then the sixth version of vSphere, and solutions for virtualization of data centers of other vendors, but VMware’s significant technological gap from competitors remains. A report issued this summer report Magic Quadrant for x86 Server Virtualization Infrastructure analytical agency Gartner states that VMware still remains the leader as possible virtualization platform, and to dominate the market, and customers the company is praised features of VMware products and support .
SAFEDATA uses VMware vSphere and other VMware products as a virtualization platform in its Virtual Data Center solution»(Virtual Data Center, VDC), on the basis of which the customer can independently create an IT infrastructure of any complexity, completely similar to the solutions on physical equipment. The HP BladeSystem c-Class blades as well as the NetApp FAS6220 and FAS8060 storage systems are used as the solution hardware platform.

The VDC customer receives computing resources for building a virtual infrastructure from the SFCLOUD cloud located in two geographically distributed data centers. VSphere Node Failure Resilience in SFCLOUD is based on vSphere High Availability (HA) technology. In addition to directly managing this virtual infrastructure using VMware vCloud Director, the customer can flexibly distribute the cloud resources allocated to him between his applications depending on the load change, for example, if at some point the number of requests to one of the applications increases significantly, you can temporarily transfer part of it processors allocated to other applications. In addition, in the process of using the VDC cloud service, the customer can increase or decrease the amount of resources allocated to him, as well as apply various pricing models.
All actions related to managing the service, changing its parameters, monitoring performance, as well as financial documents, are carried out through the web interface of the “Personal Account” of the VDC customer. You can learn more about VDC here .
