SpiderTest: use the power of CI

This article is a continuation of SpiderTest: DIY do-it-yourself tests . However, the first part of the review for this application was more focused on the desktop interface. In the same I would like to talk about exotics: the connection of tests with CI-server and GitHub.
The question may arise: “Why do we need all this? We wrote a test, ran it in the necessary browsers and it’s enough for us, ”and in general it’s pretty reasonable! Indeed, for routine testing, running autotests from the SpiderTest application itself in most cases is enough. But what if we want to run tests in different versions of IE9-11, Opera, FireFox and Google Chrome? It is impossible to do this on one machine, but creating a bunch of virtual machines and launching each in turn is tedious (and in general it’s a crutch).
And if we want to conduct smoke testing? Or do we want to run tests not only in different browsers, but also in different operating systems (Windows OS, Linux OS)?
The best answer to the above questions is to use a continuous integration server. In this article, I will discuss how to configure SpiderTest and Jenkins. In fairness, it’s worth saying that you can run tests on both bamboo and teamcity, but Jenkins is simple and free, so consider it.
Configuring Jenkins for Windows OS and Linux OS.
Before you begin, you need to install the Jenkins distribution , download the Apache Maven Project , JDK 7 and Git and write them in system variables.
Now you are ready to configure Jenkins. And the first thing to start with is to install the necessary plugins.

To do this, go to “Configure Jenkins” (1), and then to “Manage plugins” (2).
• GitHub plugin - plugin for working with GitHub
• JUnit Plugin - plugin for running unit tests
• Allure Jenkins Plugin - Yandex plugin for creating reports.
After installation, you need to restart the server, this can be done by entering localhost : 8080 / restart in the address bar.
Then go to "System Configuration" (3). In the window that opens, fill in the "Git", "Jenkins Location" and "Allure Plugin" blocks.
Two “Git installations” for WindowsOS and LinuxOS should be specified, it is better to do as in the screenshot.

It is also not superfluous to register “Jenkins Location” so that you can enter Jenkins from the outside.

And finally, fill in the “Allure Plugin”.

After configuration, you need to restart the server again.
Git version control system
For testing to be very serious, like for severe programmers, it is not superfluous for the tester team to use version control system. It’s not for me to explain that “the version control system takes a little time, but there’s a whole carriage of its benefits” (c) Koroviev “Master and Margarita”.
In general, we create a profile on the github and drop the following files from those that are in the SpiderTest folder:
• Config - the folder in which the settings are indicated, lists of steps and elements are stored
• Data - a folder with class templates, methods of the maven project
• Lib - a folder with the SpiderTestCILib.jar library
• Add-lib.bat - an executable file that adds libraries to the local maven repository
• Add-lib.sh - the same, but for LinuxOS.
• SpiderTestCI.jar - Jar nickname that creates the maven project.
• Start-test.bat - the executable file that runs SpiderTestCI.jar.
• Start-test.sh is the same, but for LinuxOS.
• TestKit - folder with autotests.
Here about SpiderTestCI.jar I would like to say a few words separately, but a little later.
Creating a test build plan
After Jenkins CI is configured, you can begin to create a build plan.

The assembly plan consists of the steps that need to be taken during assembly. First we describe the project, so that it is clear why it was created, and indicate where to get the files with tests (profile on github).

Git executable will choose the "default" Windows. And start adding build steps.



The first step in creating a build plan is to add the library to the local maven repository by running add-lib.bat (or add-lib.sh on LinuxOS).
The second step is to create a maven build project and run the tests. To do this, run start-test.bat [arg] (or start-test.sh [arg]), where [arg] is the path to the file or the path to the test folder.

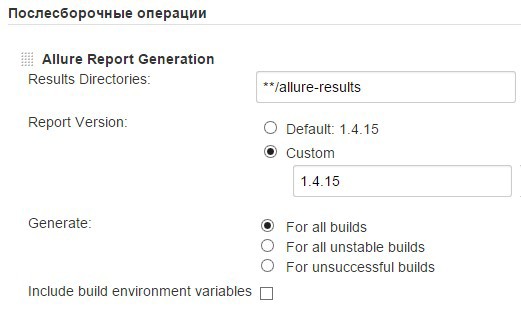
And finally, add the post-assembly step of the Allure Jenkins Plugin with the report version.
Now all that remains is to complete the assembly by clicking "Build Now."
The first build will be quite long, due to the downloading of project dependencies. Assembly history and report can be found here.

Sponsored report has become a beautiful plugin Yandeksovsky Allure Plugin more written about him in detail here

algorithm works SpiderTestCI.jar
Performing start-test.bat, SpiderTestCI.jar checks that it was passed as an argument: a file or a folder with files. If the folder has been transferred, then it looks for files with the extension .sff in it (the folder should contain only test files in the extension .sff otherwise the dzharnik will swear). So, SpiderTestCI.jar reads the test file, finds frequently used steps and elements and pulls them from config \ namespaces \, then from the config \ config.cfg file reads the path to browsers (if specified), then looks at the variables (if they are indicated), then it reads the maven project templates from the data folder and, finally, we get a maven project with tests ready to run, which consists of three objects:
• environment.xml
• pom.xml
• src directory
Configuring the collector on LinuxOS
Now set up another slave collector to run tests on LinuxOS.
Before you begin to configure another collector, you need to make some presets on the Linux machine. Namely:
• JDK7 - to perceive Jar-nicknames.
• Git - so that Linux can take source from github.
sudo apt-get install git
It will be useful to verify that git is registered in the system variables for this you need to enter git on the command line. Did you get a lot of text? Great)
• An SSH client so that Jenkins can connect to its collector via ssh.
sudo apt-get install openssh-client
sudo apt-get install openssh-server
• slave.jar - jar nickname launched by Jenkins on the “slave” machine. You
can download it by entering localhost : 8080 / jnlpJars / slave.jar
Then drop it into a folder, for example, \ home \ user \ slave and give all rights to the folder like
chmod –R 777
And only now you can configure a new node in Jenkins.

Enter ssh access settings. You should make sure that you can connect to the virtual machine from the outside, for example, using Putty. By the way, it is worth giving an adequate name to the collector, so that when switching from one to another, it is correctly identified.

Then turn on the slave node to the master. The new collector will be included for the first time as long as the "master". It's all about the same maven libraries.

To start the assembly on LinuxOS you need to do the following:
1. In the build plan settings, select the executor (the machine on which Jenkins - master is deployed, and set the names of all assemblers yourself).

2. Switch between collectors in the "Source Control" block.

3. Correct the command in the assembly plan so that Linux executable files are involved:

And restart the assembly. It will not be superfluous to mention that all browsers that we use in tests must be installed on virtual machines and the drivers of these browsers are registered in system variables.
This article completes the review of the SpiderTest tool, but this does not mean that it will stop in its development. We need more people who will use SpiderTest to take the app to the next level. Subscribe to new versions, comment, suggest.
PS Since the release of the previous article, 3 versions of SpiderTest have already been released. The latest version 1.1.1 is already available for download. The next release is just around the corner and there will be additions that you add in the comments.
PPS practice has shown that you need to use lists of steps and elements very consciously. They are saved in a special folder “config / namespaces” and if you delete / transfer or somehow modify files from the namespaces folder, then the tests using them will not be executed. So please be careful.
