We collect our OpenWRT on the Tp-Link TL-WR741ND v.4.25 router with vlan, openvpn, provider rotation and blackjack
In this article, I would like to share the experience of building my own openwrt firmware, with the choice of the necessary packages, as well as setting up fault-tolerant Internet access with instant rotation of channels and their simultaneous operation, adding up the speed of providers and, as a result, setting up your favorite vlan-s.
The choice fell on the Tp-Link TL-WR741ND v.4.25 router (price 1150 rubles), which I chose according to the following characteristics:
1) Low price
2) A sufficient amount of memory for the stated requirements
3) The ability to flash USB (for true connoisseurs to pick a piece of iron)
4) Support for OpenWrt Barrier breaker
5) Support for vlan-s
6) Amazing survivability (the router cannot be killed by incorrect firmware, the firmware recovery function by tftpd works like a clock, and more than once helped out during unsuccessful experiments). I will write about recovery methods at the end of the article.
The standard firmware for this router from OpenWrt did not suit. The reason for this was the extra packages that occupied a place in the precious memory of this baby.
It was decided to cut: ppp, support for ipv6, opkg (we will not install anything else).
Add: openvpn-polarssl (takes up less space), luci-mwan3 (I really liked the visual settings and the indication of the channels)
So, let's start:
To get started, update our device to the latest version of the standard tp-link firmware. I don’t see the point of describing this action in detail, everything is quite clear and simple.
We will need a multi-core processor to comfortably create our firmware (I built on i7). But Core2Duo will do, unless it will be longer to collect. OS will fit Ubuntu 15 x86_64.
All further build commands are made from the average user, not from the root!
We go to the "store" for the source. I chose OpenWrt Bariier Breaker for its ease of setup and excellent stability on the previous router (TP-LINK Archer C7).
In the home folder, we will have the wrt folder, where we will build.
Download the sources of additional packages (such as Luci):
Let's configure the platform
A pseudo-graphic menu will appear, where we are interested in the Target System, Subtarget and Target Profile items:
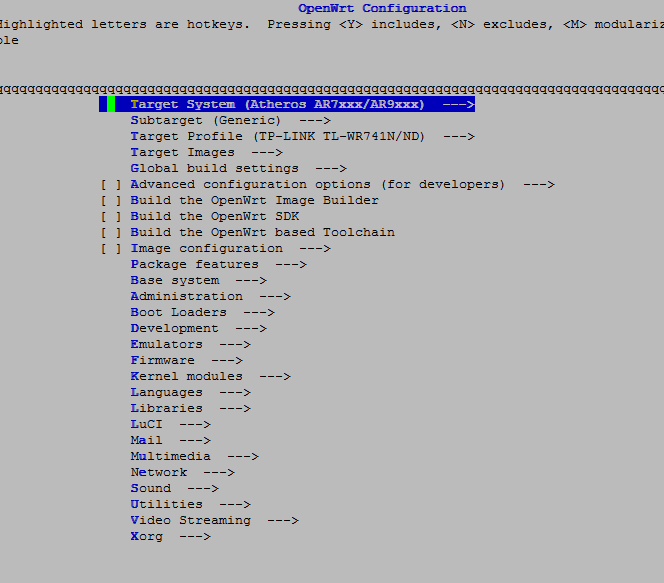
All navigation will be free to select the desired item (by arrows) and press enter, component selection will also be entered, exit from the menu will be Exit. Do not forget to save the config.
We apply standard parameters for the profile:
We modify the set of packages:
Deleted : opkg from (base system)
removed the build option with ipv6 (Global build settings)
ppp (Network) support .
Added by:
Luci
luci-app-mwan3 (Luci-Applications)
openvpn-polarssl (Network-vpn).
Do not forget to save the configuration!
We begin the assembly:
The -j5 parameter indicates the number of cores + 1 thread for quick assembly, and V = s - to display details (if there are errors).
The process will take a long time, 10-15 minutes on the i7 processor, after which our firmware for various versions of the router will appear in the directory / home / user / wrt / bin / ar71xx. If you haven’t appeared, we look at the build logs - for sure, you have exceeded the size of the firmware and you will see the line: “firmware is too big”. You have to do make clean, make distclean and start all over again. (from the step ./scripts/feeds update -a)
We are interested in:
openwrt-ar71xx-generic-tl-wr741nd-v4-squashfs-factory.bin - "factory" firmware.
We transfer it to a computer with a router connected via ethernet (for example, via ftp or winscp).
We go to the address: 192.168.0.1and flashing it with newly-made firmware, we wait for the reboot, then we go to the address: 192.168.1.1
root without a password (we will assign it at the first login - a yellow banner will hang at the top with a warning and a link to change the password).
Well, finally, the hardest part is behind, now we have modern firmware and OUR set of programs.
It happens in the router menu: network - switch
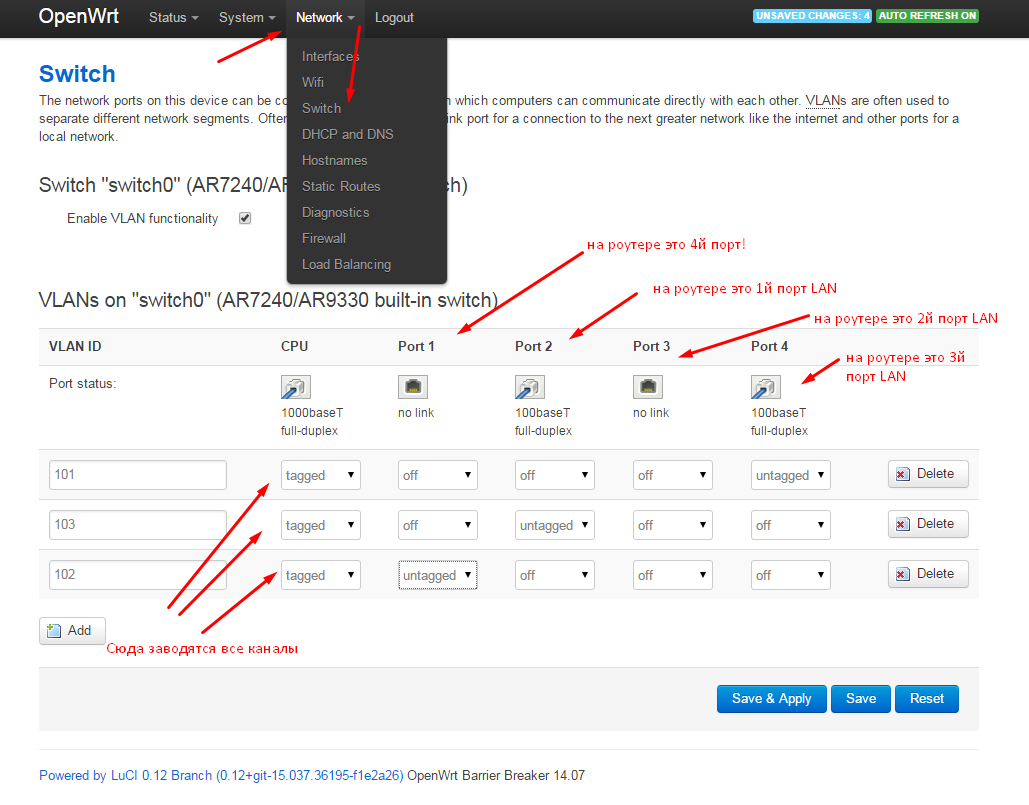
There were some misunderstandings - the port numbers in the router and in the vlan configuration do not match. In the screenshot, I tried to explain how they are changed. The WAN port in the router is not involved in vlan functionality.
Tagged - tagged traffic, packets from each vlan (101, 102, 103) are sent here, which are then distributed on the interfaces wan (primary provider), wan2 (backup provider), eth0.103 (vlan for the local network).
Untagged - untagged port mode (ethernet cable entry point from the desired provider). It is important here not to get lost in the wires: what goes where. I signed the necessary names at the back of the router so that there would be no confusion in the future (provider No. 101, provider No. 102, LAN 103).
Simply put, we let 3 different networks through 3 ports, which are then distributed on the shelves inside the device.
After the changes, click Save, but not Apply! We don’t want to be left without a network during setup?
Now, you need to create the necessary interfaces in Network - Interfaces :
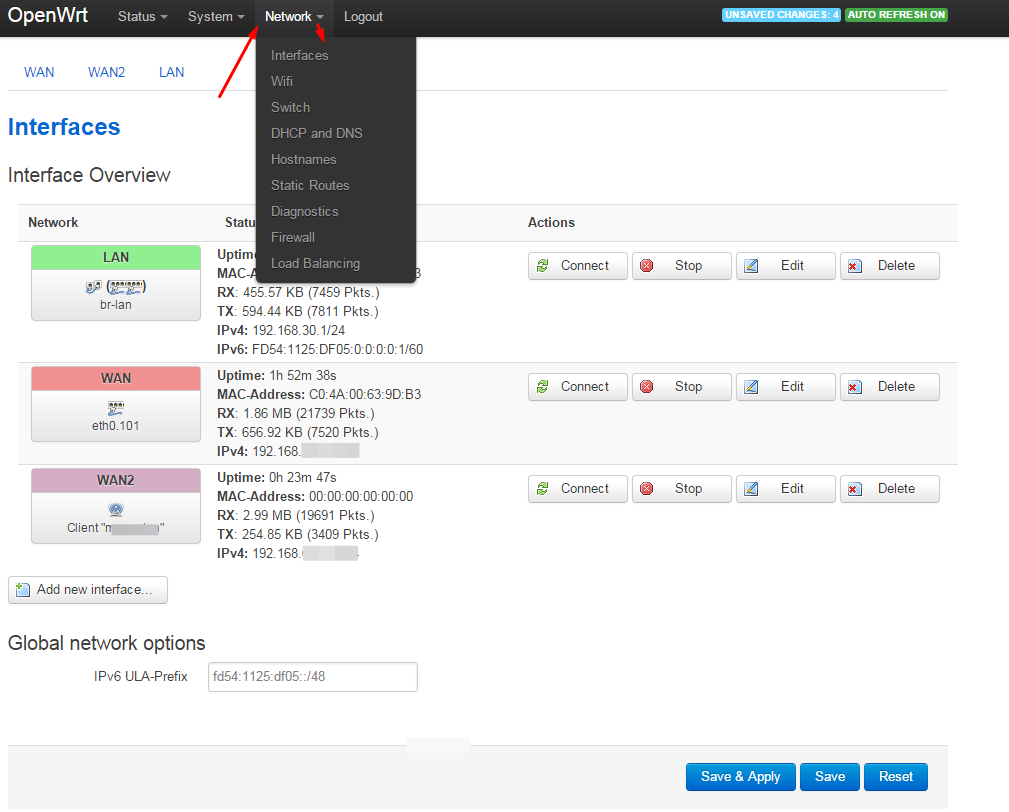
Remove the wan6 interface (we do not use ipv6 in this case).
Change the wan interface for the first provider, specify the necessary data for the connection (for example, the provider gives the Internet via dhcp), and indicate which vlan to use for this interface. This is where the vlan: wire: interface mapping goes.
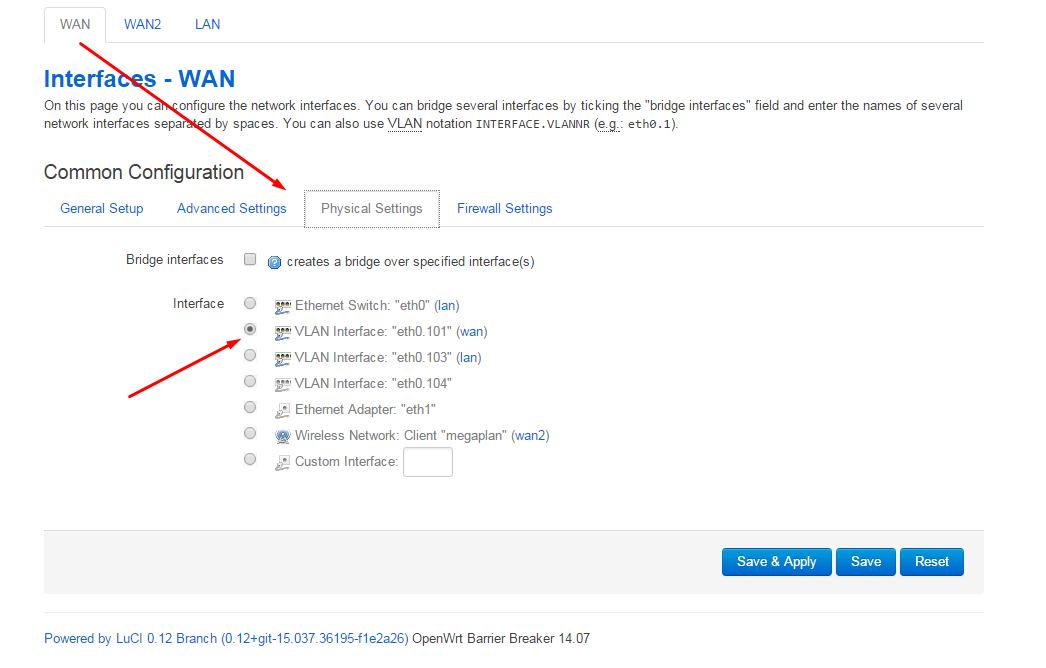
For the second provider wan2, specify eth0.102.
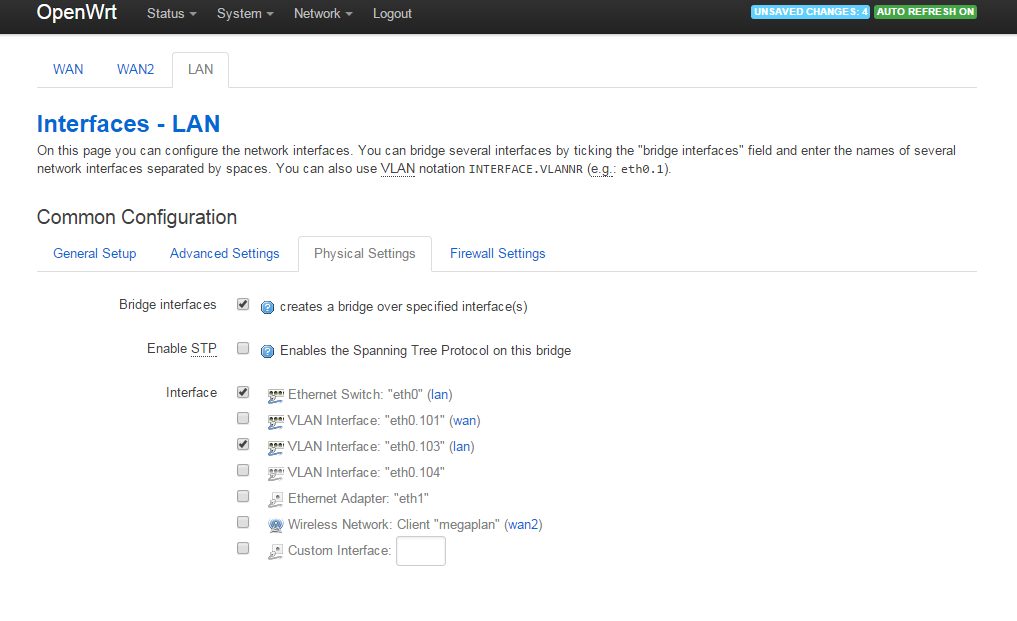
For Lan, we specify the interface to be combined in bridge eth0 and eth0.103:
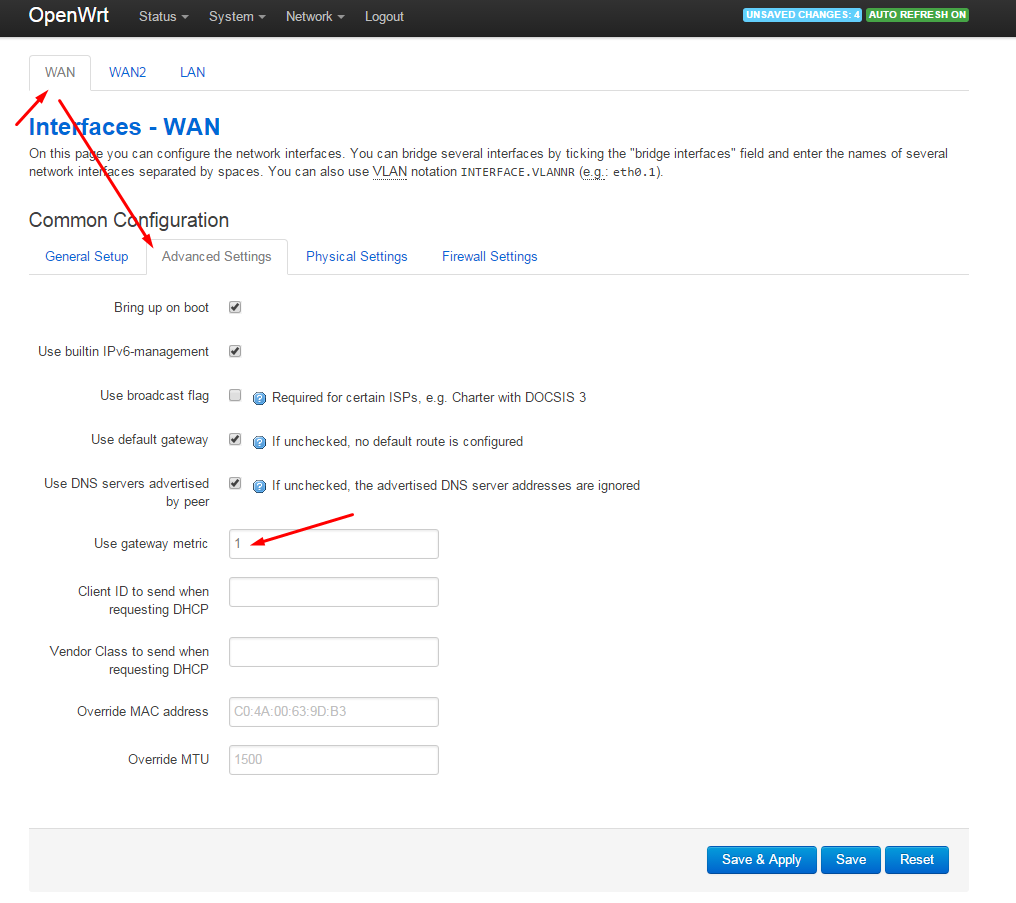
In the settings for the wan and wan2 interfaces, specify the device metric (required for mwan3 to work):
Now you can safely click on Save & Apply and check the entered settings.
It is difficult to underestimate this package, because users will be able to receive the sum of the speed of two Internet channels, the Internet will always be in the office, because it is unlikely that both channels will fall.
For the administrator, there will be a headache in temporarily disconnecting any of the channels, and there is no need to make crutch scripts for switching. I forgot about the problems in the office with the Internet and do not worry when one of them crashes (I get sms for these events).
I know for sure that OpenVPN will switch to the backup channel in 30 seconds (thanks to the multihome parameter), communication with the main office in Moscow will be restored and some users and bosses will not notice this incident.
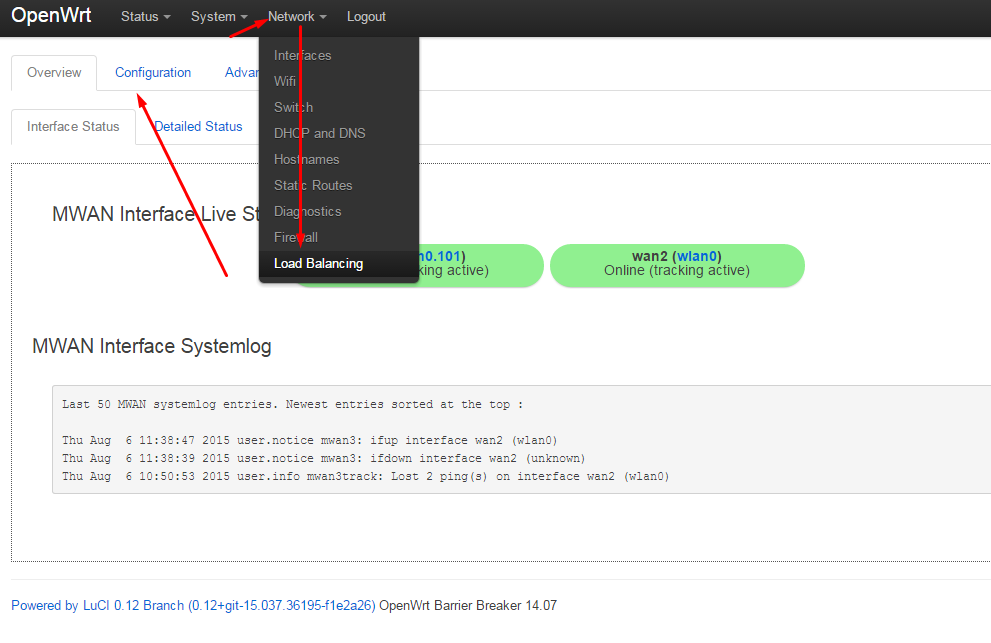
Let's
start : Let's go to network - load balancing - configuration:
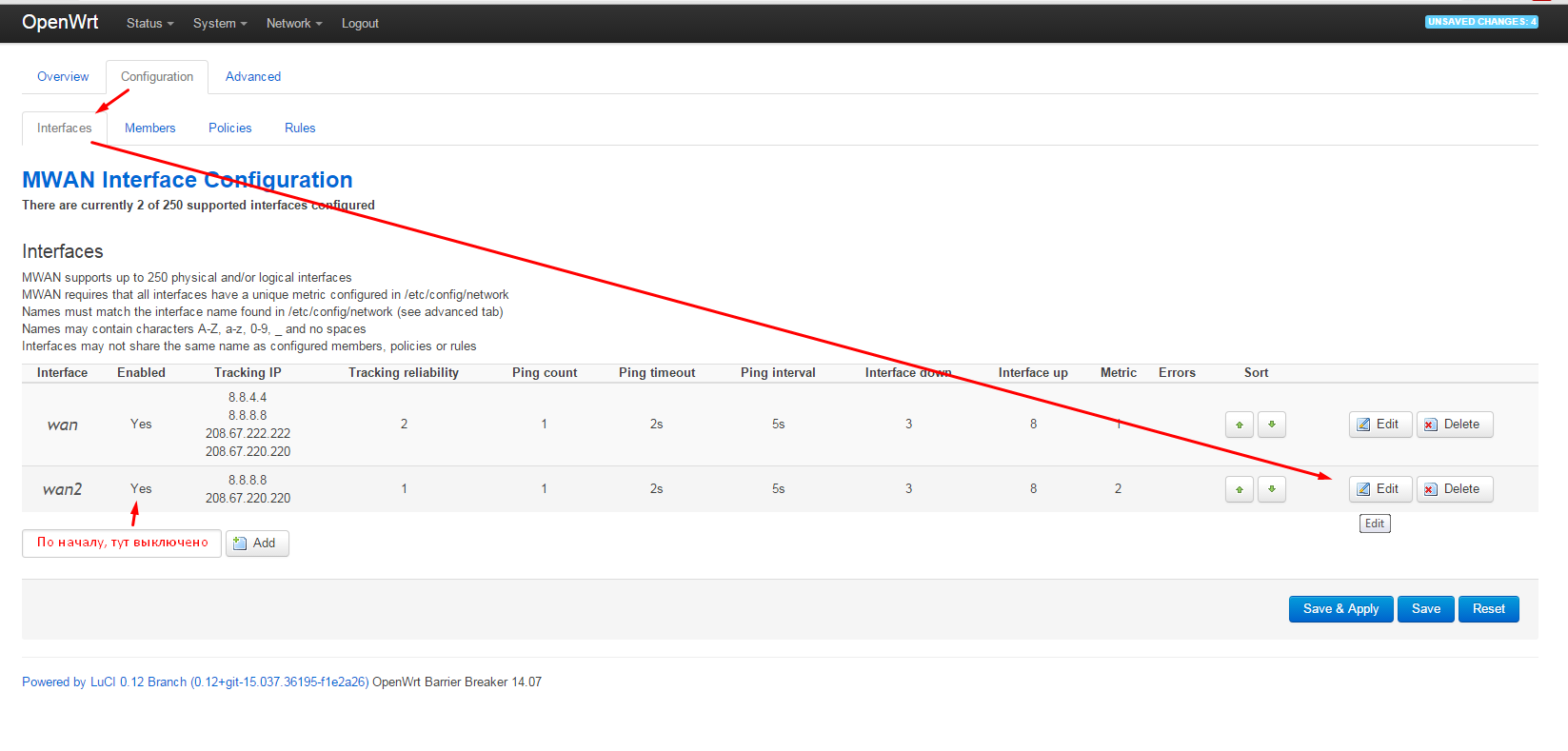
and turn wan2 into work:
Next, we will configure the rules for the operation of channels:
1) Balanced - Channels add up, speed increases, there is fault tolerance (switching). Recommend.
2) wan_only - only provider
# 1 3) wan2_only - only provider # 2
configuration - rules
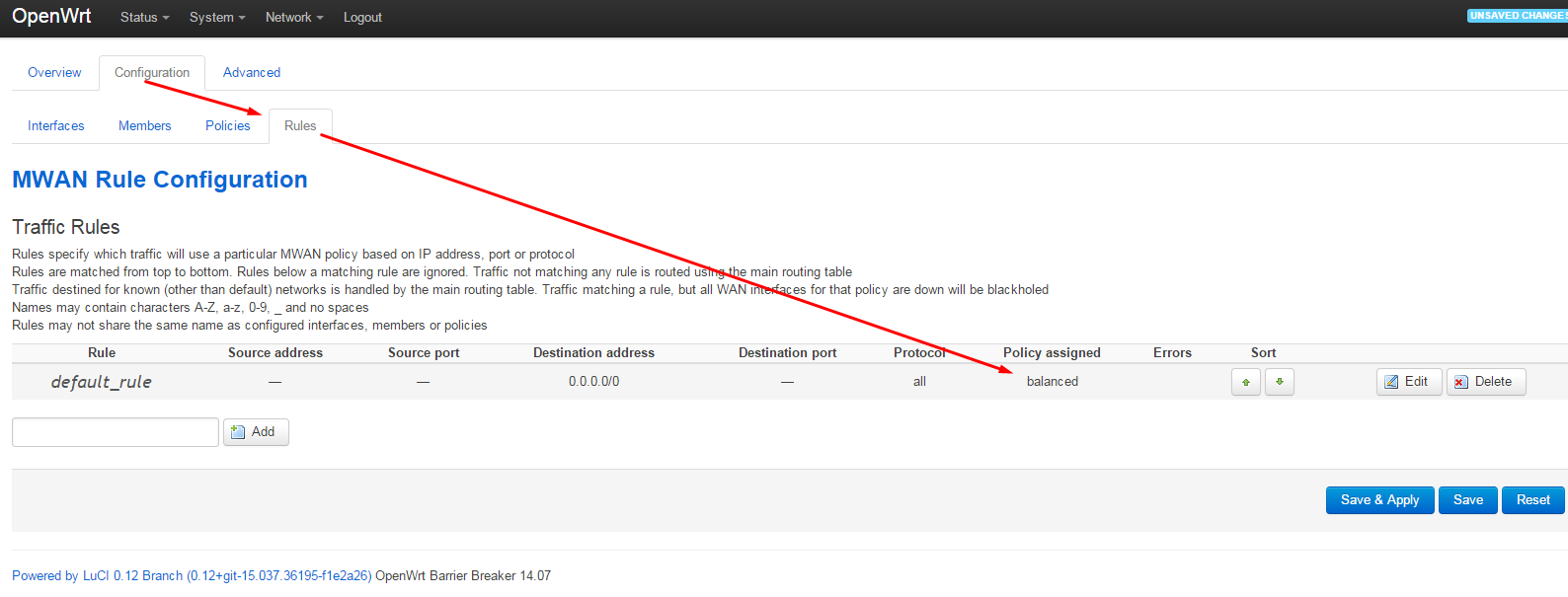
The rest of the rules can be deleted or another rule can be left.
I won’t dwell on mwan3 in detail - I’ll just say that it is possible to send traffic to a specific resource through one of the channels if there is an IP binding on this resource.
Ok, we’ve set up the Internet, now you need to connect 2 offices together.
Will go by static key. Key generation can be done on the client side:
The key must be placed in / etc / openvpn / keys / (server, client).
OpenVPN is already installed on the router and we will start editing the config. To do this, go to TP-Link via ssh.
In the config header we change:
Save, exit. Here we included a custom config in /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf - for me personally it is somehow more familiar.
Next, the config itself:
On the router we have the server side openvpn. We bring a config to a look:
Save, then:
Now the client:
An example config looks like this:
Save the config, apply:
We watch ifconfig, logs and enjoy the reliable channel.
Of course, you will kill your router more than once with unsuccessful firmware, taking the trouble to remove the necessary components of the base system.
But no big deal!
The easiest way to reanimate the router is to fail safe in openwrt:
1) Assign the network adapter on the computer the IP address 192.168.1.2
2) Mask 255.255.255.0
3) The ethernet cable to LAN1
4) Turn off the router
5) Turn on and wait until the icon lights up gears
6) Hold the QSS router button for 1-2 seconds - the gear will flash very quickly
7) Run the telnet client and connect to the address 192.168.1.1
8) Paste the default encryption for your model into tmp router, for example, via the mini-web server tinyweb
9) Run:
The router eats the firmware and reboots.
Chef, it's all gone!
Yes, that's exactly what I thought when I killed the router even harder. The gear did not burn, and the router cyclically rebooted without stopping.
We use a wonderful function in the tp-link firmware - downloading the firmware via tftp:
1) Assign the network adapter on the computer IP address 192.168.0.66
2) Mask 255.255.255.0
3) Ethernet cable - to LAN1 port
4) Start the tftp server with default firmware in a folder called “wr741ndv4_tp_recovery.bin” (you need to rename the firmware file)
4) Turn off the router
5) Take a sharp and thin object (pen)
6) Take the router in your hands, turn it to the ports, hold the handle in your free hand
7) Turn on the router and immediately hold the QSS with the finger of one hand + reset with the handle in the other hand. Practice and it will work out.
8) Hold down these 2 buttons for 4-8 seconds until the firmware download to the router starts in the tftp client. And she will go, do not worry.
Once the firmware has loaded (2-3 sec), release the buttons. Exhale, the router is saved.
Articles used:
wiki.openwrt.org/en/doc/howto/build
openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/documentation/miscellaneous/78-static-key-mini-howto.html
denisyuriev.ru/linux/openwrt -linux / openwrt-sborka-iz-isxodnikov
habrahabr.ru/post/186760
wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/OpenVPN
wiki.openwrt.org/doc/howto/mwan3
wiki.openwrt.org/en/doc/howto/generic .uninstall
The choice fell on the Tp-Link TL-WR741ND v.4.25 router (price 1150 rubles), which I chose according to the following characteristics:
1) Low price
2) A sufficient amount of memory for the stated requirements
3) The ability to flash USB (for true connoisseurs to pick a piece of iron)
4) Support for OpenWrt Barrier breaker
5) Support for vlan-s
6) Amazing survivability (the router cannot be killed by incorrect firmware, the firmware recovery function by tftpd works like a clock, and more than once helped out during unsuccessful experiments). I will write about recovery methods at the end of the article.
The standard firmware for this router from OpenWrt did not suit. The reason for this was the extra packages that occupied a place in the precious memory of this baby.
It was decided to cut: ppp, support for ipv6, opkg (we will not install anything else).
Add: openvpn-polarssl (takes up less space), luci-mwan3 (I really liked the visual settings and the indication of the channels)
So, let's start:
1) Preparation of the device
To get started, update our device to the latest version of the standard tp-link firmware. I don’t see the point of describing this action in detail, everything is quite clear and simple.
2) Collecting firmware
We will need a multi-core processor to comfortably create our firmware (I built on i7). But Core2Duo will do, unless it will be longer to collect. OS will fit Ubuntu 15 x86_64.
Installing the necessary packages:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
sudo apt-get install subversion git g++ libncurses5-dev zlib1g-dev gawk -y
All further build commands are made from the average user, not from the root!
We go to the "store" for the source. I chose OpenWrt Bariier Breaker for its ease of setup and excellent stability on the previous router (TP-LINK Archer C7).
svn co svn://svn.openwrt.org/openwrt/branches/barrier_breaker wrt
cd ~/wrt
svn update
In the home folder, we will have the wrt folder, where we will build.
Download the sources of additional packages (such as Luci):
./scripts/feeds update -a
./scripts/feeds install -a
Let's configure the platform
make menuconfig
A pseudo-graphic menu will appear, where we are interested in the Target System, Subtarget and Target Profile items:

All navigation will be free to select the desired item (by arrows) and press enter, component selection will also be entered, exit from the menu will be Exit. Do not forget to save the config.
We apply standard parameters for the profile:
make defconfig
We modify the set of packages:
make menuconfig
Deleted : opkg from (base system)
removed the build option with ipv6 (Global build settings)
ppp (Network) support .
Added by:
Luci
luci-app-mwan3 (Luci-Applications)
openvpn-polarssl (Network-vpn).
Do not forget to save the configuration!
We begin the assembly:
make -j5 V=s
The -j5 parameter indicates the number of cores + 1 thread for quick assembly, and V = s - to display details (if there are errors).
The process will take a long time, 10-15 minutes on the i7 processor, after which our firmware for various versions of the router will appear in the directory / home / user / wrt / bin / ar71xx. If you haven’t appeared, we look at the build logs - for sure, you have exceeded the size of the firmware and you will see the line: “firmware is too big”. You have to do make clean, make distclean and start all over again. (from the step ./scripts/feeds update -a)
We are interested in:
openwrt-ar71xx-generic-tl-wr741nd-v4-squashfs-factory.bin - "factory" firmware.
We transfer it to a computer with a router connected via ethernet (for example, via ftp or winscp).
We go to the address: 192.168.0.1and flashing it with newly-made firmware, we wait for the reboot, then we go to the address: 192.168.1.1
root without a password (we will assign it at the first login - a yellow banner will hang at the top with a warning and a link to change the password).
Well, finally, the hardest part is behind, now we have modern firmware and OUR set of programs.
3) Configuring vlan:
It happens in the router menu: network - switch

There were some misunderstandings - the port numbers in the router and in the vlan configuration do not match. In the screenshot, I tried to explain how they are changed. The WAN port in the router is not involved in vlan functionality.
Tagged - tagged traffic, packets from each vlan (101, 102, 103) are sent here, which are then distributed on the interfaces wan (primary provider), wan2 (backup provider), eth0.103 (vlan for the local network).
Untagged - untagged port mode (ethernet cable entry point from the desired provider). It is important here not to get lost in the wires: what goes where. I signed the necessary names at the back of the router so that there would be no confusion in the future (provider No. 101, provider No. 102, LAN 103).
Simply put, we let 3 different networks through 3 ports, which are then distributed on the shelves inside the device.
After the changes, click Save, but not Apply! We don’t want to be left without a network during setup?
Now, you need to create the necessary interfaces in Network - Interfaces :

Remove the wan6 interface (we do not use ipv6 in this case).
Change the wan interface for the first provider, specify the necessary data for the connection (for example, the provider gives the Internet via dhcp), and indicate which vlan to use for this interface. This is where the vlan: wire: interface mapping goes.

For the second provider wan2, specify eth0.102.
For Lan, we specify the interface to be combined in bridge eth0 and eth0.103:

In the settings for the wan and wan2 interfaces, specify the device metric (required for mwan3 to work):

Now you can safely click on Save & Apply and check the entered settings.
4) mwan3 or cool admin admin
It is difficult to underestimate this package, because users will be able to receive the sum of the speed of two Internet channels, the Internet will always be in the office, because it is unlikely that both channels will fall.
For the administrator, there will be a headache in temporarily disconnecting any of the channels, and there is no need to make crutch scripts for switching. I forgot about the problems in the office with the Internet and do not worry when one of them crashes (I get sms for these events).
I know for sure that OpenVPN will switch to the backup channel in 30 seconds (thanks to the multihome parameter), communication with the main office in Moscow will be restored and some users and bosses will not notice this incident.
Let's
start : Let's go to network - load balancing - configuration:

and turn wan2 into work:

Next, we will configure the rules for the operation of channels:
1) Balanced - Channels add up, speed increases, there is fault tolerance (switching). Recommend.
2) wan_only - only provider
# 1 3) wan2_only - only provider # 2
configuration - rules

The rest of the rules can be deleted or another rule can be left.
I won’t dwell on mwan3 in detail - I’ll just say that it is possible to send traffic to a specific resource through one of the channels if there is an IP binding on this resource.
5) Office friendship or openvpn
Ok, we’ve set up the Internet, now you need to connect 2 offices together.
Will go by static key. Key generation can be done on the client side:
sudo openvpn --genkey --secret office2.key
The key must be placed in / etc / openvpn / keys / (server, client).
OpenVPN is already installed on the router and we will start editing the config. To do this, go to TP-Link via ssh.
vi /etc/config/openvpn
In the config header we change:
package openvpn
#################################################
# Sample to include a custom config file. #
#################################################
config openvpn custom_config
# Set to 1 to enable this instance:
option enabled 1
# Include OpenVPN configuration
option config /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf
Save, exit. Here we included a custom config in /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf - for me personally it is somehow more familiar.
Next, the config itself:
mkdir /etc/openvpn
mkdir /etc/openvpn/keys
vi /etc/openvpn/openvpn.conf
On the router we have the server side openvpn. We bring a config to a look:
port 1194 #порт сервера
proto udp
dev tun-office2 #обзовем интерфейс
multihome #слушаем подключения на wan и wan2
ifconfig 10.0.0.2 10.0.0.3 #IP-шники окончания туннелей
secret /etc/openvpn/keys/office2.key #ключик
keepalive 5 30 #переподключение через 30 сек.
user nobody
group nogroup
persist-tun
persist-key
status /tmp/office2.status
log /tmp/office2.log #логи
verb 3
Save, then:
/etc/init.d/openvpn restart
Now the client:
An example config looks like this:
remote wan.office2.ru #стучимся сначала сюда
remote wan2.office2.ru #потом сюда (по очереди)
port 1194
proto udp
dev tun-office1
ifconfig 10.0.0.3 10.0.0.2 # наоборот как на сервере
route 192.168.30.0 255.255.255.0 #пропишем роут для включения офисной подсети роутера в главный офис
secret /etc/openvpn/keys/office2.key #клон ключа с сервера
keepalive 5 30 #передергиваем туннель при плохом поведении одного из каналов
user nobody
group nogroup
persist-tun
persist-key
status /var/log/openvpn/office.status
log /var/log/openvpn/office.log
verb 3
Save the config, apply:
/etc/init.d/openvpn restart
We watch ifconfig, logs and enjoy the reliable channel.
Conclusion:
Of course, you will kill your router more than once with unsuccessful firmware, taking the trouble to remove the necessary components of the base system.
But no big deal!
The easiest way to reanimate the router is to fail safe in openwrt:
1) Assign the network adapter on the computer the IP address 192.168.1.2
2) Mask 255.255.255.0
3) The ethernet cable to LAN1
4) Turn off the router
5) Turn on and wait until the icon lights up gears
6) Hold the QSS router button for 1-2 seconds - the gear will flash very quickly
7) Run the telnet client and connect to the address 192.168.1.1
8) Paste the default encryption for your model into tmp router, for example, via the mini-web server tinyweb
9) Run:
mtd -r write /tmp/имяпрошивки.bin firmware
The router eats the firmware and reboots.
Chef, it's all gone!
Yes, that's exactly what I thought when I killed the router even harder. The gear did not burn, and the router cyclically rebooted without stopping.
We use a wonderful function in the tp-link firmware - downloading the firmware via tftp:
1) Assign the network adapter on the computer IP address 192.168.0.66
2) Mask 255.255.255.0
3) Ethernet cable - to LAN1 port
4) Start the tftp server with default firmware in a folder called “wr741ndv4_tp_recovery.bin” (you need to rename the firmware file)
4) Turn off the router
5) Take a sharp and thin object (pen)
6) Take the router in your hands, turn it to the ports, hold the handle in your free hand
7) Turn on the router and immediately hold the QSS with the finger of one hand + reset with the handle in the other hand. Practice and it will work out.
8) Hold down these 2 buttons for 4-8 seconds until the firmware download to the router starts in the tftp client. And she will go, do not worry.
Once the firmware has loaded (2-3 sec), release the buttons. Exhale, the router is saved.
Articles used:
wiki.openwrt.org/en/doc/howto/build
openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/documentation/miscellaneous/78-static-key-mini-howto.html
denisyuriev.ru/linux/openwrt -linux / openwrt-sborka-iz-isxodnikov
habrahabr.ru/post/186760
wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/OpenVPN
wiki.openwrt.org/doc/howto/mwan3
wiki.openwrt.org/en/doc/howto/generic .uninstall
