Seven Steps to Business Continuity
Currently, there are a huge number of business continuity management techniques that help in planning, improving the availability of critical business processes of the company. But these techniques contain the theoretical foundations of business continuity and do not answer the question "How to implement such a project?" This article describes the sequence of actions that will give you an idea of how the business continuity management system is implemented and what results you will get at each stage.

Business Continuity Management Life Cycle
Managing a company's business continuity is a cyclical process that should take into account possible changes in business, IT, legislation and other areas that affect the organization’s activities, as well as help it adapt to these changes. In other words, business continuity management is a process of continuous improvement, which, in turn, increases the company's confidence in the reliability of business continuity plans.
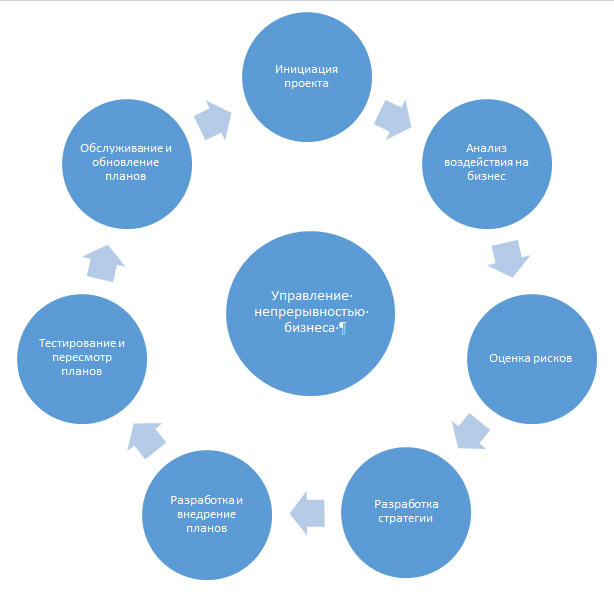
The life cycle of the business continuity management process includes 7 stages, each of which determines the sequence of steps and the result (the list of stages was built on the basis of the BCM Institute cycle [8]).
Initiating a project A
project is an activity aimed at creating a unique product, service or result.
Project Management Plan - A document describing how a project will be implemented, how it will be monitored and controlled.
PMBOK Handbook - Fifth Edition
At this stage, the content of the business continuity project is determined and a step-by-step plan is developed. It determines how the project will be executed, how it will be monitored, controlled and closed, and also defines the boundaries of the project, the roles of members of the project team and the objectives of the project.
In addition to the above actions, it is necessary to determine the need for the project. For some companies, business continuity is ensuring the effectiveness of critical business functions, as well as demonstrating the sustainability of the business to customers. But we must not forget that there are requirements of regulatory legal acts and regulatory bodies for business continuity. The table below lists and describes the standards / regulatory legal acts (NLA) that are widely used in the Russian Federation, as well as a number of requirements that these standards / NLA have for the business continuity system.
After the project plan is finally formed and developed, it must be sent to the company management for approval. Work on the plan should only begin after agreement with management.
Note! In some companies, the project sponsor does not pay enough attention to it, and the responsibility lies with the middle manager. This can lead to communication problems among stakeholders and reduced support for senior management. This problem can be solved by creating a project committee, which will include representatives of all interested parties. The committee should periodically meet, solve problems and discuss the progress of the project.
Business Impact Analysis
Business impact analysis - a method that allows you to investigate the impact of incidents on key activities and processes of the company.
At this stage, a detailed study of the company's processes is provided. To do this, the consultant conducts interviews with the management of departments within the project area. During the conversation, information is requested about the activities of the department and a list of processes / functions that it performs is compiled. Further, for a detailed study of processes / functions, process owners are interviewed and the type of impact on the business (material, reputation) and the degree of dependence of the process on IT and external services are determined. And then the Maximum Allowable Outage is determined.
Maximum Allowable Outage - the period of time after which there is a threat of the final loss of the organization's viability in the event that the supply of products and / or the provision of services is not resumed.
GOST R ISO / IEC 31010—2011 “Risk management. Risk assessment methods ”
After the owner of the process / function has been determined by the MAO, the IT department (based on the MAO) determines the indicators RTO, RPO, SDO.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) . The time during which the restoration of a business function or resource should occur during an emergency.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) The recovery target point determines the amount of allowable data loss in case of interruption of operations. For example, if the RPO is 15 minutes, data loss over the past 15 minutes is allowed.
- Service Delivery Objective (SDO) . The level of service availability at a particular point in time.
The figure shows how the above metrics are determined.
The result of a business impact analysis is:
- a list of critical processes ranked by priority and the corresponding interdependencies;
- recorded economic and industrial impacts caused by the violation of critical processes;
- supporting resources needed for identified critical processes;
- Possible periods of downtime and recovery of critical processes and interconnected information technologies.
Note! Often, business process owners intentionally or unconsciously overestimate the target value of recovery standards, which contributes to the distortion of the analysis and entails unreasonable costs. To avoid this problem, it is necessary, together with the project team, as well as with interested parties, to consider the value of the business function in the context of the incident that affected the entire company. This approach will make it possible to objectively determine recovery standards.
Risk Assessment
Risk is the effect of uncertainty on goals.
Deviation: this article does not address the details of risk assessment.
Risk assessment is a process that includes risk identification, risk analysis and risk assessment.
ISO 73: 2009 “Risk management. Dictionary »
The purpose of risk assessment in the framework of business continuity management is to identify events that may lead to disruption of the company, as well as their consequences (damage).
Risk assessment provides:
- an understanding of potential hazards and the impact of their consequences on the achievement of the company's goals;
- understanding of threats and their sources;
- identification of key risk factors; vulnerabilities of the company and its systems;
- selection of risk treatment methods;
- compliance with the requirements of standards.
The risk assessment process consists of:
- Risk identification - the process of identifying risk elements, describing each of them, and compiling a list of them. The purpose of risk identification is to compile a list of sources of risk and threats that may affect the achievement of each of the established goals of the company;
- Risk analysis - the process of researching risk information. Risk analysis provides input to the overall risk assessment process, helps in making decisions regarding the need for risk treatment, as well as in choosing the appropriate treatment strategy and methods;
- Comparative risk assessment - comparing its level with the criteria established in determining the scope of risk management to determine the type of risk and its significance.
Risk assessment in the future will allow you to reasonably develop a business continuity strategy, and will also help determine the optimal scenario for its implementation.
Development of a business continuity strategy
After the requirements for continuity have been analyzed, it is necessary to select and justify possible technical and organizational solutions. In the process of choosing a solution, it is necessary to consider in detail the possible actions in relation to premises, technologies, information assets, contractors, as well as partners. These decisions, as a rule, are chosen with the aim of:
- protecting the priority activities of the company;
- their effective recovery;
- mitigation of the consequences of incidents, development of response and preventive measures.
Note: Decision selection should be based on recovery cost and downtime.
These decisions may include:
- “Mirror” sites;
- "Hot" sites;
- “Warm” platforms;
- “Cold” sites;
- Platforms for dynamic load distribution;
- Outsourcing \ Agreement;
- Mobile platforms.
Digression: the above solutions will be discussed in detail in a separate article.
The main differences between the above solutions are the cost and recovery time of the company.
Note!Solutions help implement an effective business continuity strategy. But in order to determine the best option, it is necessary to choose strategic decisions based on the results of the analysis of the impact on the business and risk assessment (this approach will help the management to justify the need for investment in a business continuity management project).
Development and implementation of business continuity plans
A plan is a pre- determined system of measures that provides for the order, sequence and timing of work.
In accordance with best practices [1, 2, 4], continuity management plans should consist of three components:
1. Emergency response - determines the sequence of actions that must be taken when an incident is detected.
2. Incident management - defines the methods necessary to mitigate or reduce the size of the incident.
3. Recovery of activity - determines the sequence of actions that must be carried out in order to restore the service at a given level.
Note: for clarity, use flow charts and other graphical ways to present information.
The approximate structure of a business continuity plan:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background information
1.2. The boundaries of the plan
1.3. Preconditions for creating a plan
2. Concept
2.1. Description of the system for ensuring continuity
2.2. Description of the stages of restoration of continuity
2.3. Roles and their responsibilities
3. Activation of the plan
3.1. Criteria and procedure for activation
3.2. Procedure for notifying interested parties
3.3. Procedure for evaluating an incident
4.
Monitoring
5. Recovery 5.1. Sequence of restoration of continuity
NIST specialists developed a guide [1], which describes in sufficient detail the necessary) business continuity plans. The following is a table that describes each of the plans (listed in the NIST manual), as well as links to standards / NLAs that require the development of such plans.
The above documents are compiled based on the needs of the company, but in practice the following types of plans are most often applied:
- Incident response plan - this type of plan may include a plan for responding to cyber incidents, a plan for unforeseen situations in information systems. This plan will help reduce the scale of the disaster and mitigate its consequences, which will provide an opportunity to save time and an additional advantage when activating the remaining types of plans;
- The personnel’s action plan in emergency situations - in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 68 68 “On the Protection of the Population and Territory from Natural and Technogenic Emergencies” and the Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 69 “On fire safety ”this plan is mandatory for all companies;
- Failure Recovery Plan - focuses on recovering critical information systems. This type of plan supports the business continuity plan and is aimed at restoring the performance of individual systems and applications;
- Business Continuity Plan - focused on supporting the company's business processes during and after an emergency; aims to ensure that the company can continue to carry out critical types of activities for it at a set acceptable level;
- Anti-crisis communications plan - this plan will help maintain the company's reputation in a crisis situation. It documents the procedure for interaction with the media, law enforcement agencies, the Ministry of Emergencies, etc.
Note!At the stage of business continuity planning, some companies focus on technical solutions and do not attach importance to organizational measures. In this regard, it is necessary to indicate the need for organizational measures along with technical ones. To do this, training seminars, test plans, training materials are issued.
Testing and revision of plans
Testing is carried out to verify the operability of plans in the event of a certain set of circumstances affecting the activities of the company. The test plan is selected taking into account the type of company and its goals.
Tests are assessment tools that use quantitative metrics to verify the health of an IT system or component.
NIST Special Publication 800-84 “Guide to Test, Training, and Exercise Programs for IT Plans and Capabilities”
The goals of testing include:
- obtaining evidence of the plans' performance;
- verification of the sufficiency of methodological and technical support;
- obtaining the necessary skills and knowledge.
After the purpose of testing has been determined, a scenario is developed, the testing method is determined and agreed with the management. The most commonly used methods are [2]:
- Tabletop;
- Imitation (Imitation);
- Full testing (Full business continuity testing).
Digression: the above testing methods will be discussed in a separate article.
After testing, reports are prepared that indicate the scenarios and results of testing, as well as suggestions for improving business continuity plans.
Note! Companies should choose a testing method based on their goals and financial capabilities.
Note! Full testing is the most effective because it allows you to identify many shortcomings, but because of the high risks it is almost not used in practice. If the company decided to use this type of testing, it is necessary to enlist the support of partners or use the services of contractors to minimize risks and prevent significant downtime.
Maintenance and updating plans
As noted above, managing a company's business continuity is a cyclical process. And this means that it is impossible to limit oneself only to the formation of plans, it is necessary to maintain, update and improve them annually, and sometimes more often, for example, in the following cases:
1. Change in IT infrastructure;
2. Change in the organizational structure of the company;
3. Changes in legislation;
4. Detection of deficiencies in the plans during their testing.
In order to keep the plans up-to-date, it is necessary to perform the following actions:
- conduct internal audits, including verification of disaster recovery, continuity documentation and related procedures;
- conduct regular practical trainings on the implementation of the plan;
- integrate business continuity issues into the company's change management process.
Conclusion
Business continuity management ensures the unification of all measures applied at the enterprise into a holistic, adequate to real threats and managed complex, allowing the company to continuously provide services, avoid the impact of emergencies on activities and minimize possible damage.
This complex consists of seven stages that must be implemented in the company to ensure the continuity of services and product manufacturing.
This article describes each stage with reference to Russian realities, as well as points to which you should pay attention to when implementing this project.
References
1. ISO 22301 Societal security - Business continuity management systems - Requirements
2. GOST R 53647 “ Business continuity management ”
3. GOST R ISO / IEC 31010 - 2011. “Risk management. Risk Assessment Methods ”
4. NIST Special Publication 800-34 Rev. 1 “Contingency Planning Guide for Federal Information Systems”
5. NIST Special Publication 800-84 “Guide to Test, Training, and Exercise Programs for IT Plans and Capabilities”
6. The Definitive Handbook of Business Continuity Management Second Edition Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons Ltd,
7. Business Continuity Management How to protect your company from danger MICHAEL GALLAGHER Pearson Education Limited 2003
8. www.bcmpedia.org/wiki/BCM_Body_of_Knowledge_ (BCMBoK)
Information about the project on Softline: services.softline.ru/security/upravleniya-ib
Evgeny Kachurov, Consultant, Analytical Department, Softline

Business Continuity Management Life Cycle
Managing a company's business continuity is a cyclical process that should take into account possible changes in business, IT, legislation and other areas that affect the organization’s activities, as well as help it adapt to these changes. In other words, business continuity management is a process of continuous improvement, which, in turn, increases the company's confidence in the reliability of business continuity plans.
The life cycle of the business continuity management process includes 7 stages, each of which determines the sequence of steps and the result (the list of stages was built on the basis of the BCM Institute cycle [8]).
Initiating a project A
project is an activity aimed at creating a unique product, service or result.

Project Management Plan - A document describing how a project will be implemented, how it will be monitored and controlled.
PMBOK Handbook - Fifth Edition
At this stage, the content of the business continuity project is determined and a step-by-step plan is developed. It determines how the project will be executed, how it will be monitored, controlled and closed, and also defines the boundaries of the project, the roles of members of the project team and the objectives of the project.
In addition to the above actions, it is necessary to determine the need for the project. For some companies, business continuity is ensuring the effectiveness of critical business functions, as well as demonstrating the sustainability of the business to customers. But we must not forget that there are requirements of regulatory legal acts and regulatory bodies for business continuity. The table below lists and describes the standards / regulatory legal acts (NLA) that are widely used in the Russian Federation, as well as a number of requirements that these standards / NLA have for the business continuity system.
| Standard / normative | Demand | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO / IEC 27001: 2013 "Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems - Requirements" (Information technology. Security methods. Information security management systems) | Aspects security Information Part A.17 of business continuity management (information security aspects in the management of business continuity) | Continuity of information security should be built into the system of business continuity of the company. For this it is necessary: - to plan the continuity of information security; - implement information security continuity; - check, evaluate the continuity of information security. | Continuity of information security is one of the requirements if a company seeks to obtain a certificate of compliance with ISO / IEC 27001: 2013 "Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems - Requirements". |
| ISO 22301: 2012 "Societal security - Business continuity management systems - Requirements" (Social security. Business continuity management systems) | This standard focuses on business continuity. | The standard defines: - the requirements necessary to establish a business continuity management system in a company; - requirements for the functions of senior management in the business continuity management system; - requirements for setting strategic goals and guidelines for a business continuity management system; - requirements for ensuring business continuity, the procedure for developing management procedures in an incident. | The presence of BCP / DRP plans (these plans are discussed in the section "Development and implementation of plans") is a prerequisite if the company seeks to obtain a certificate of compliance with ISO 22301: 2012 "Societal security - Business continuity management systems - Requirements". |
| GOST R 53647 "Business Continuity Management" | This standard focuses on business continuity. | This International Standard establishes requirements for planning, creating, operating, monitoring, analyzing, conducting exercises, supporting and improving a documented business continuity management system. | It is recommendatory in nature. |
| STO BR IBBS-1.0-2014 "Ensuring the information security of organizations of the banking system of the Russian Federation" | 8.11. Requirements for organizing business continuity and recovery after interruptions | The organization of the banking system should determine a plan for ensuring business continuity and its recovery after a possible interruption. The plan should contain instructions and procedures for the employees of the organization of the banking system to restore the business. In particular, the plan should include: - conditions for the activation of the plan; - actions to be taken after an IS incident; - recovery procedures; - Testing and verification procedures; - a plan for training and raising awareness of employees; - duties of employees, indicating those responsible for the implementation of each of the provisions of the plan. Requirements for ensuring IS, governing issues of ensuring business continuity and its recovery after interruption, including requirements for measures to restore the necessary information, software, hardware, and communication channels, should also be established. | It is recommendatory in nature. |
| Order of the FSTEC of Russia dated February 11, 2013 No. 17 “On approval of requirements for the protection of information not constituting state secrets contained in state information systems” | X. Making Information Accessible (CCT) | In accordance with the Order of the FSTEC of Russia dated February 11, 2013 No. 17 “On approval of the requirements for the protection of information not constituting state secrets contained in state information systems” it is necessary: - to use fault-tolerant technical means; - reserve hardware, software, information transmission channels, means of ensuring the functioning of the information system; - control the trouble-free functioning of technical equipment; - to ensure the detection and localization of failures of the functioning of technical means; - take measures to restore failed funds; - test hardware; - periodically back up information to backup machine media; - provide the ability to recover information from backup machine storage media (backups) within a specified time interval; - control the condition and quality of the provision by the authorized person of computing resources (capacities), including information transfer. | If the system is classified according to security class 1 or 2, the requirements described in the order are mandatory. |
| Order of the FSTEC of Russia dated February 18, 2013 No. 21 “On the approval of the composition and content of organizational and technical measures to ensure the security of personal data during their processing in personal data information systems” | X. Ensuring the availability of personal data (CCT) | In accordance with the Order of the FSTEC of Russia dated February 18, 2013 No. 21 “On the approval of the composition and content of organizational and technical measures to ensure the security of personal data during their processing in personal data information systems”, it is necessary to ensure: - control of the trouble-free functioning of technical means; - detection and localization of operational failures; - taking measures to restore failed funds and testing them; - backing up personal data to backup machine storage media of personal data; - the ability to restore personal data from backup machine carriers of personal data (backups) within a specified time interval. | In the event that a security level of 1 or 2 is defined for the personal data information system, the requirements described in the order are mandatory. |
After the project plan is finally formed and developed, it must be sent to the company management for approval. Work on the plan should only begin after agreement with management.
Note! In some companies, the project sponsor does not pay enough attention to it, and the responsibility lies with the middle manager. This can lead to communication problems among stakeholders and reduced support for senior management. This problem can be solved by creating a project committee, which will include representatives of all interested parties. The committee should periodically meet, solve problems and discuss the progress of the project.
Business Impact Analysis
Business impact analysis - a method that allows you to investigate the impact of incidents on key activities and processes of the company.
At this stage, a detailed study of the company's processes is provided. To do this, the consultant conducts interviews with the management of departments within the project area. During the conversation, information is requested about the activities of the department and a list of processes / functions that it performs is compiled. Further, for a detailed study of processes / functions, process owners are interviewed and the type of impact on the business (material, reputation) and the degree of dependence of the process on IT and external services are determined. And then the Maximum Allowable Outage is determined.
Maximum Allowable Outage - the period of time after which there is a threat of the final loss of the organization's viability in the event that the supply of products and / or the provision of services is not resumed.
GOST R ISO / IEC 31010—2011 “Risk management. Risk assessment methods ”
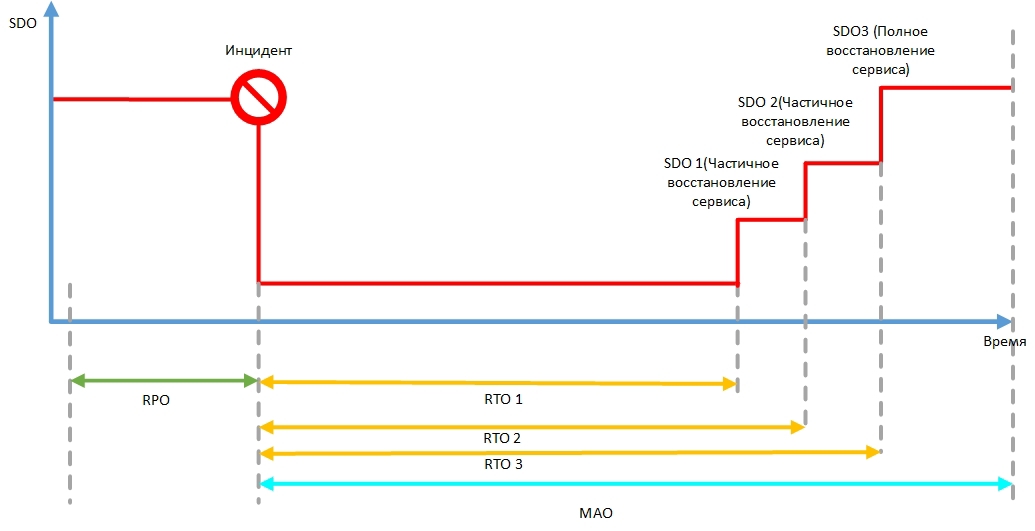
After the owner of the process / function has been determined by the MAO, the IT department (based on the MAO) determines the indicators RTO, RPO, SDO.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) . The time during which the restoration of a business function or resource should occur during an emergency.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) The recovery target point determines the amount of allowable data loss in case of interruption of operations. For example, if the RPO is 15 minutes, data loss over the past 15 minutes is allowed.
- Service Delivery Objective (SDO) . The level of service availability at a particular point in time.
The figure shows how the above metrics are determined.

The result of a business impact analysis is:
- a list of critical processes ranked by priority and the corresponding interdependencies;
- recorded economic and industrial impacts caused by the violation of critical processes;
- supporting resources needed for identified critical processes;
- Possible periods of downtime and recovery of critical processes and interconnected information technologies.
Note! Often, business process owners intentionally or unconsciously overestimate the target value of recovery standards, which contributes to the distortion of the analysis and entails unreasonable costs. To avoid this problem, it is necessary, together with the project team, as well as with interested parties, to consider the value of the business function in the context of the incident that affected the entire company. This approach will make it possible to objectively determine recovery standards.
Risk Assessment
Risk is the effect of uncertainty on goals.
Deviation: this article does not address the details of risk assessment.
Risk assessment is a process that includes risk identification, risk analysis and risk assessment.
ISO 73: 2009 “Risk management. Dictionary »
The purpose of risk assessment in the framework of business continuity management is to identify events that may lead to disruption of the company, as well as their consequences (damage).
Risk assessment provides:
- an understanding of potential hazards and the impact of their consequences on the achievement of the company's goals;
- understanding of threats and their sources;
- identification of key risk factors; vulnerabilities of the company and its systems;
- selection of risk treatment methods;
- compliance with the requirements of standards.
The risk assessment process consists of:
- Risk identification - the process of identifying risk elements, describing each of them, and compiling a list of them. The purpose of risk identification is to compile a list of sources of risk and threats that may affect the achievement of each of the established goals of the company;
- Risk analysis - the process of researching risk information. Risk analysis provides input to the overall risk assessment process, helps in making decisions regarding the need for risk treatment, as well as in choosing the appropriate treatment strategy and methods;
- Comparative risk assessment - comparing its level with the criteria established in determining the scope of risk management to determine the type of risk and its significance.
Risk assessment in the future will allow you to reasonably develop a business continuity strategy, and will also help determine the optimal scenario for its implementation.
Development of a business continuity strategy
After the requirements for continuity have been analyzed, it is necessary to select and justify possible technical and organizational solutions. In the process of choosing a solution, it is necessary to consider in detail the possible actions in relation to premises, technologies, information assets, contractors, as well as partners. These decisions, as a rule, are chosen with the aim of:
- protecting the priority activities of the company;
- their effective recovery;
- mitigation of the consequences of incidents, development of response and preventive measures.
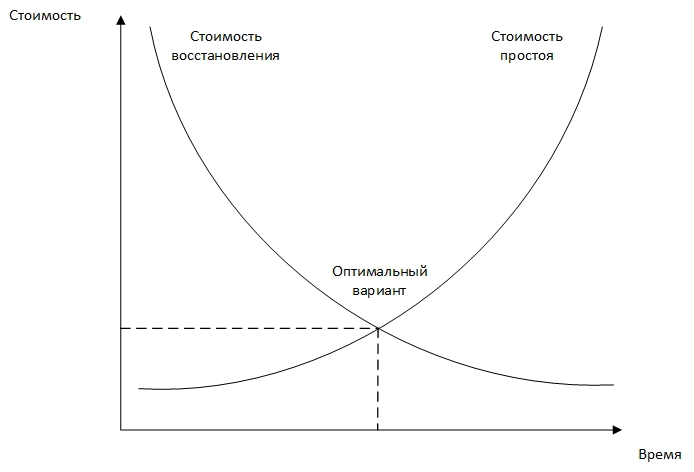
Note: Decision selection should be based on recovery cost and downtime.
These decisions may include:
- “Mirror” sites;
- "Hot" sites;
- “Warm” platforms;
- “Cold” sites;
- Platforms for dynamic load distribution;
- Outsourcing \ Agreement;
- Mobile platforms.
Digression: the above solutions will be discussed in detail in a separate article.

The main differences between the above solutions are the cost and recovery time of the company.
Note!Solutions help implement an effective business continuity strategy. But in order to determine the best option, it is necessary to choose strategic decisions based on the results of the analysis of the impact on the business and risk assessment (this approach will help the management to justify the need for investment in a business continuity management project).
Development and implementation of business continuity plans
A plan is a pre- determined system of measures that provides for the order, sequence and timing of work.
In accordance with best practices [1, 2, 4], continuity management plans should consist of three components:
1. Emergency response - determines the sequence of actions that must be taken when an incident is detected.
2. Incident management - defines the methods necessary to mitigate or reduce the size of the incident.
3. Recovery of activity - determines the sequence of actions that must be carried out in order to restore the service at a given level.
Note: for clarity, use flow charts and other graphical ways to present information.
The approximate structure of a business continuity plan:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background information
1.2. The boundaries of the plan
1.3. Preconditions for creating a plan
2. Concept
2.1. Description of the system for ensuring continuity
2.2. Description of the stages of restoration of continuity
2.3. Roles and their responsibilities
3. Activation of the plan
3.1. Criteria and procedure for activation
3.2. Procedure for notifying interested parties
3.3. Procedure for evaluating an incident
4.
Monitoring
5. Recovery 5.1. Sequence of restoration of continuity
NIST specialists developed a guide [1], which describes in sufficient detail the necessary) business continuity plans. The following is a table that describes each of the plans (listed in the NIST manual), as well as links to standards / NLAs that require the development of such plans.
| The name of the plan | Plan description | Standard / normative |
|---|---|---|
| Business Continuity Plan (BCP) business continuity plan | A set of documented procedures that are developed, summarized and updated with a view to their use in the event of an incident and are aimed at ensuring that the company can continue to carry out critical important activities at a set acceptable level. | ISO 22301 “Social Security. Business continuity management systems ”: 8.4.4 Business continuity plans |
| Continuity of Operations Plan (COOP) plan continuous operations | It focuses on the restoration of critical functions of the company on an alternative site and on their implementation within 30 days. | - |
| Crisis Communication Plan Plan for crisis communications | This plan documents the procedures and rules of external and internal communications in case of emergency. | Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 68 "On the Protection of the Population and Territories from Natural and Technogenic Emergencies": Article 14. Obligations of organizations in the field of protecting the population and territories from emergencies ( "Organizations are required to provide information in the established manner in the field of population protection and territories from emergency situations, as well as notify employees of organizations about the threat of occurrence or about the occurrence of emergency situations ”). |
| Critical Infrastructure Protection Plan (CIP) to protect critical infrastructure plan | The plan aims to protect key resources and components of national infrastructure. | Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of January 15, 2013 N 31s “On the creation of a state system for detecting, preventing and eliminating the consequences of computer attacks on the information resources of the Russian Federation”. |
| Cyber Incident Response Plan Response Plan on cyber incidents | A plan describing procedures for responding to incidents related to hacker attacks, intrusions into the information system, and other security issues. | GOST R ISO / IEC TO 18044-2007 “Information technology. Security methods and tools. Information Security Incident Management ”; NIST 800-61 "Computer Security. Incident Handling Guide. " |
| Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) recovery plan fails | Plan for the restoration of the company's infrastructure after an accident. | ISO 22301 “Social Security. Business Continuity Management Systems ”: 8.4.5 Recovery. |
| Information System Contingency Plan (ISCP) Emergency Plan for Information Systems | A plan for recovering systems, networks, and core applications after a crash. This plan needs to be developed for each critical system and / or application. | - |
| Occupant Emergency Plan (OEP) Personnel Emergency Plan | This plan defines the procedure for ensuring the safety of personnel and evacuation procedures in case of emergency. | Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 68 “On the Protection of the Population and Territory from Natural and Technogenic Emergencies”; Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 69 “On Fire Safety”. |
The above documents are compiled based on the needs of the company, but in practice the following types of plans are most often applied:
- Incident response plan - this type of plan may include a plan for responding to cyber incidents, a plan for unforeseen situations in information systems. This plan will help reduce the scale of the disaster and mitigate its consequences, which will provide an opportunity to save time and an additional advantage when activating the remaining types of plans;
- The personnel’s action plan in emergency situations - in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 68 68 “On the Protection of the Population and Territory from Natural and Technogenic Emergencies” and the Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 69 “On fire safety ”this plan is mandatory for all companies;
- Failure Recovery Plan - focuses on recovering critical information systems. This type of plan supports the business continuity plan and is aimed at restoring the performance of individual systems and applications;
- Business Continuity Plan - focused on supporting the company's business processes during and after an emergency; aims to ensure that the company can continue to carry out critical types of activities for it at a set acceptable level;
- Anti-crisis communications plan - this plan will help maintain the company's reputation in a crisis situation. It documents the procedure for interaction with the media, law enforcement agencies, the Ministry of Emergencies, etc.
Note!At the stage of business continuity planning, some companies focus on technical solutions and do not attach importance to organizational measures. In this regard, it is necessary to indicate the need for organizational measures along with technical ones. To do this, training seminars, test plans, training materials are issued.
Testing and revision of plans
Testing is carried out to verify the operability of plans in the event of a certain set of circumstances affecting the activities of the company. The test plan is selected taking into account the type of company and its goals.
Tests are assessment tools that use quantitative metrics to verify the health of an IT system or component.
NIST Special Publication 800-84 “Guide to Test, Training, and Exercise Programs for IT Plans and Capabilities”
The goals of testing include:
- obtaining evidence of the plans' performance;
- verification of the sufficiency of methodological and technical support;
- obtaining the necessary skills and knowledge.
After the purpose of testing has been determined, a scenario is developed, the testing method is determined and agreed with the management. The most commonly used methods are [2]:
- Tabletop;
- Imitation (Imitation);
- Full testing (Full business continuity testing).
Digression: the above testing methods will be discussed in a separate article.
After testing, reports are prepared that indicate the scenarios and results of testing, as well as suggestions for improving business continuity plans.
Note! Companies should choose a testing method based on their goals and financial capabilities.
Note! Full testing is the most effective because it allows you to identify many shortcomings, but because of the high risks it is almost not used in practice. If the company decided to use this type of testing, it is necessary to enlist the support of partners or use the services of contractors to minimize risks and prevent significant downtime.
Maintenance and updating plans
As noted above, managing a company's business continuity is a cyclical process. And this means that it is impossible to limit oneself only to the formation of plans, it is necessary to maintain, update and improve them annually, and sometimes more often, for example, in the following cases:
1. Change in IT infrastructure;
2. Change in the organizational structure of the company;
3. Changes in legislation;
4. Detection of deficiencies in the plans during their testing.
In order to keep the plans up-to-date, it is necessary to perform the following actions:
- conduct internal audits, including verification of disaster recovery, continuity documentation and related procedures;
- conduct regular practical trainings on the implementation of the plan;
- integrate business continuity issues into the company's change management process.
Conclusion
Business continuity management ensures the unification of all measures applied at the enterprise into a holistic, adequate to real threats and managed complex, allowing the company to continuously provide services, avoid the impact of emergencies on activities and minimize possible damage.
This complex consists of seven stages that must be implemented in the company to ensure the continuity of services and product manufacturing.
This article describes each stage with reference to Russian realities, as well as points to which you should pay attention to when implementing this project.
References
1. ISO 22301 Societal security - Business continuity management systems - Requirements
2. GOST R 53647 “ Business continuity management ”
3. GOST R ISO / IEC 31010 - 2011. “Risk management. Risk Assessment Methods ”
4. NIST Special Publication 800-34 Rev. 1 “Contingency Planning Guide for Federal Information Systems”
5. NIST Special Publication 800-84 “Guide to Test, Training, and Exercise Programs for IT Plans and Capabilities”
6. The Definitive Handbook of Business Continuity Management Second Edition Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons Ltd,
7. Business Continuity Management How to protect your company from danger MICHAEL GALLAGHER Pearson Education Limited 2003
8. www.bcmpedia.org/wiki/BCM_Body_of_Knowledge_ (BCMBoK)
Information about the project on Softline: services.softline.ru/security/upravleniya-ib
Evgeny Kachurov, Consultant, Analytical Department, Softline
