Likbez: why at home the Internet via Wi-Fi slows down
The classical scheme for enabling Internet services in an apartment building is as follows: TKD (collective access point) - twisted pair cable - a router in the client’s apartment, to which client devices are connected via wire and Wi-Fi.
Typical complaints of subscribers - the rate is lower than the tariff, and there are regular “fading” when working on the Internet , which is expressed by the long opening of pages in the browser, interruption of video, loss of connection with game servers, etc. This behavior is irregular, and most often occurs during the hours of the highest user activity from approximately 18:00 to 23:00, depending on the city.
There are a few simple steps that will help you determine the possible cause of such problems and solve 90% of user situations. They are lower.
The first logical step is checking the speed.
To implement this paragraph, you should minimize the number of transit devices through which the Internet is connected in the apartment. Ideally, you should connect the operator cable directly to the computer and configure the connection on it. After that, check the speed on resources providing a similar service, for example, speedtest.net. This is a special service capable of delivering data at high speed - which, alas, cannot be said about all the resources on the Internet.
If it was possible to achieve a speed close to that indicated by the tariff, then there are no problems with the operator’s equipment and the cable to the apartment. If the speed is significantly lower, the connection is constantly disconnected, you should contact the technical support of the provider for diagnostics by the operator and, possibly, repair.
Please note that all “home” contracts always have a wording in the spirit of “up to 10 Mbit / s”, where the most important part is “before”. Without this pretext, only corporate agreements are possible, where the band is guaranteed: for this guarantee you pay about 2-3 times more. But, nevertheless, the difference is more than 5-7% with the tariff rate, which is repeated with a direct connection at different times of the day - this is the problem of the provider.
The second step is to diagnose the router
Suppose you got a “direct” speed. Now you need to look at the intermediate devices. There are quite old models of routers that are still operated by users. These models have significant performance limitations that do not allow them to implement tunnel connections (L2TP / PPTP) at speeds above 20-30 Mbit / s. An example of such routers are DIR-300, ASUS WL-520 and others. Unfortunately, to solve the problem with speed in this situation, only replacing the router with a more productive one, or using a tunnelless solution, if your carrier has one, will help.
By the way, we are about to switch to IPoE instead of L2TP.
The third step - router settings
One of the first tasks is to minimize the fight against the inquisitive minds of neighbors who are trying to find the possibility of a "freebie" using standard settings, default passwords, and so on. Usually, neighbors lose interest in someone else’s network if they could not break it right away. If they manage to connect to it, then some of the client’s problems arise due to the fact that “spurious” inclusions generate a large amount of traffic (the same torrents).
There are some simple guidelines for setting up your home router.
- On DHCP, minimize the network of users from 255 hosts to the minimum number of devices + 3-5 guest by the network mask / 27 - 32 hosts, / 28 - 16 hosts, / 29 - 8 hosts. I recommend choosing / 28, as you are unlikely to have more than 16 devices on your home network.
- Choose the router address not at the beginning and at the end of the network, for example, for the network 192.168.0.0/28 (255.255.255.240), set the router address to 192.168.0.8. Recommended network is 192.168.10.32/28 (255.255.255.240), the address of the router is 192.168.10.40. Glue the new router address on the router.
- To home devices, map MAC + IP bundles in the DHCP pool so that the devices are hard-wired. Configure Wi-Fi access restriction on the MAC addresses of your devices (but then the guests at your home will not be able to connect or you will also have to register the MAC addresses of their wireless devices).
- Change the administrator password to access the router, use at least 8 characters as a password, taking into account the change of case, as well as numbers and characters. The administrator login password should immediately be written somewhere in a safe place; after such operations, we always have a lot of calls "how to reset the password."
- Configure Wi-Fi: hide SSID, set WPA2 encryption, enter a password of more than 8 characters, case sensitive and numbers / letters.
You can check the encryption type of the client part in Windows in the Wireless settings - Wireless Networks tab - select a network - Properties - Authentication (WPA2-PSK),
Fourth step - select a channel
After the router has been configured, you need to pay attention to the Wi -Fi channel on which the router and wireless clients work. When connecting their customers, many telecom operators immediately issue a router in addition. Thus, almost every apartment connected to the Internet has a wireless Wi-Fi device.
Now the vast majority of Wi-Fi equipment operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, all in all at this frequency there are 14 channels on which wireless devices can work. In addition to frequency, significant parameters are the signal-to-noise ratio, signal strength and bandwidth. If all devices work on the same channel, then conflicts will arise between them, which for the user will look like regular “friezes”, i.e. Fading when opening resources in the browser or interrupting the broadcast of video and sound.
Therefore, you must select a channel on which the least number of competitors with a signal power level are close to yours. Another option may be to “transfer” wireless devices to the 5 GHz band, but for this to be a technical possibility for the router and the wireless devices themselves.
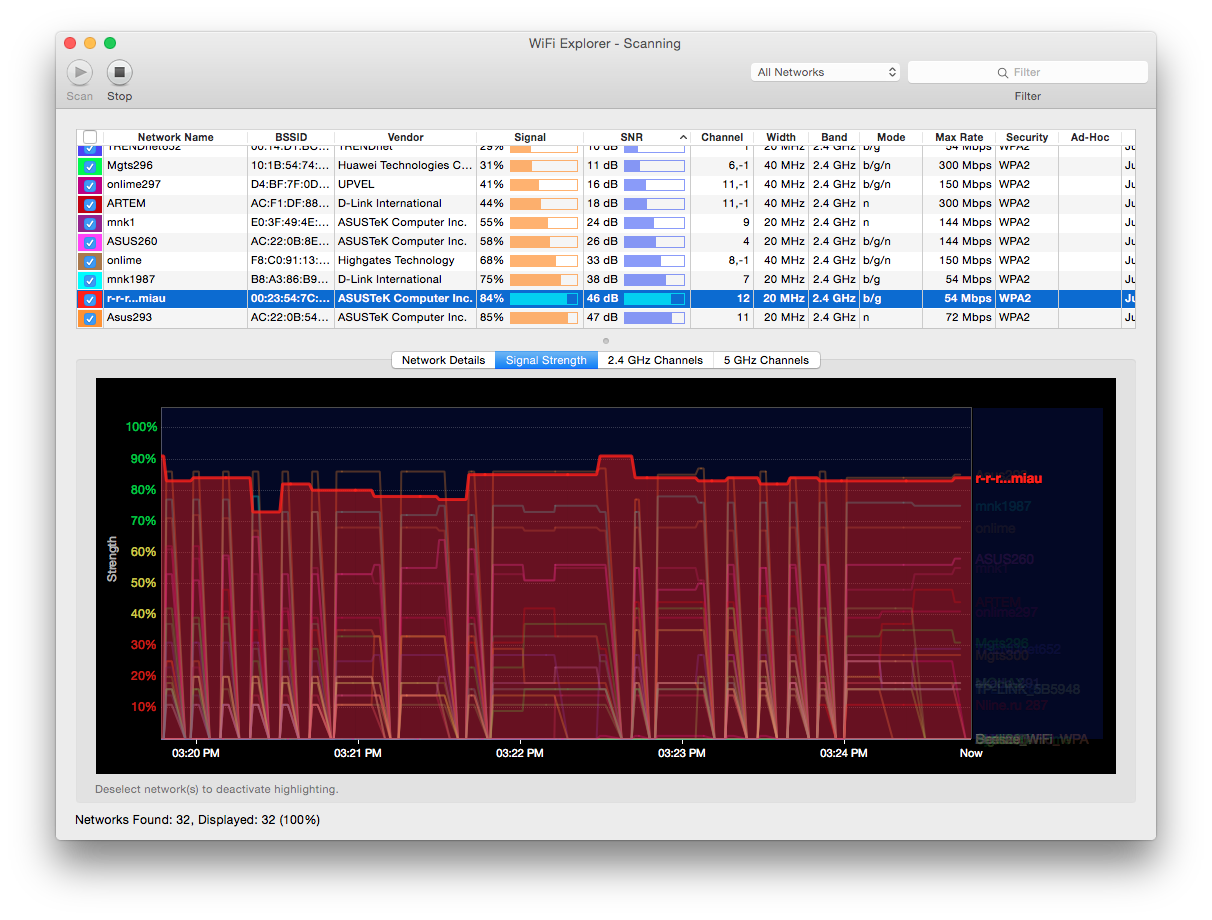
Utilities that help analyze channel occupancy are Wi-Fi Explorer for Mac, or inSSIDer for PC.

The screenshot of the WiFi Explorer program shows that the two networks Asus293 and rrr ... miau are close in signal level to each other and there may be a conflict, but they are on different channels, the first network on channel 11, the second on channel 12, which solves the problem.
Summary
You should not particularly worry about the location of the router in the apartment relative to the windows or the influence of the microwave: quite rarely this causes some problems. It is recommended to place the router “in the middle” of the apartment with the priority of placement to the most frequent point of work with wireless devices, for example, in the living room or office, and not in the kitchen or cabinet in the corridor. From the point of view of device conflicts, in my experience there was only one case when a subscriber had radio noise in the 2.4 GHz band with the Samsung HW-H450 sound bar connected via Bluetooth acting as a music center. It was possible to reveal this only empirically.
In normal cases, signal strength adjustment is not required. In multi-room apartments with concrete walls, it is sometimes important to study the radio with utilities like the ones above to decide on increasing the signal power.
According to statistics, about 90% of requests were solved in such simple ways.
