Migrating Windows Server 2003 to Windows Server 2012 R2: Active Directory
It's no secret that the end of support for Windows Server 2003 is getting closer. Day X is scheduled for July 17, 2015, which means that less and less time is left to manage to transfer its infrastructure to more modern versions of the operating system. On Habré we already made several announcements about the end of support, a course on Jump Start materials was published on the Microsoft Virtual Academy portal , there is a translation of an article on transferring a file server . This article will talk about Active Directory migration and provide a step-by-step algorithm to help you with the migration process.
Migrating Active Directory from Windows Server 2003 to Windows Server 2012 R2 is one of the primary tasks that must be addressed during the migration process.
In fact, porting Active Directory is not a hassle. You need to perform only a few steps, which will be described in detail below.
First, we will perform a small configuration on the domain controller with Windows Server 2003 installed on it. Be sure to check that Windows Server 2003 is selected as the functional level for the existing domain and forest.
In order to change the domain and forest operating mode, you need to run the snap-in Active Directory Domains and Trust. To change the operating mode of the domain, right-click on the domain, for the operating mode of the forest, click on Active Directory Domains and Trusts. Choose Raise Domain Functional Level and Raise Forest Functional Level, respectively.

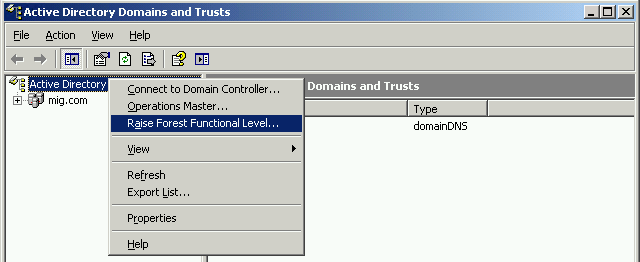
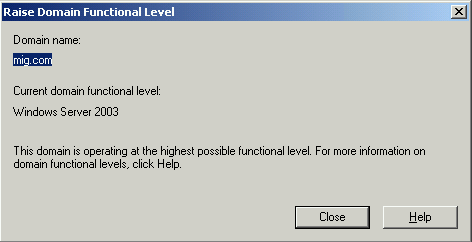
In both cases, the operating mode must be installed on Windows Server 2003.

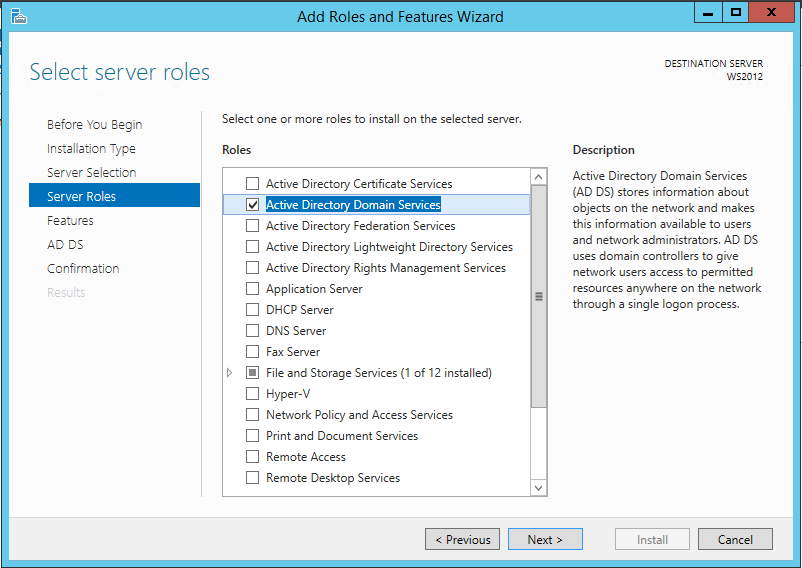
The next step is to add a second domain controller running Windows Server 2012 R2 to our network. To do this, install the Active Directory Domain Services role on a server running Windows Server 2012 R2.
After installation, add a new domain controller to the existing domain. To do this, we will need to use an account that is part of the Enterprise Admins group and has the appropriate rights.
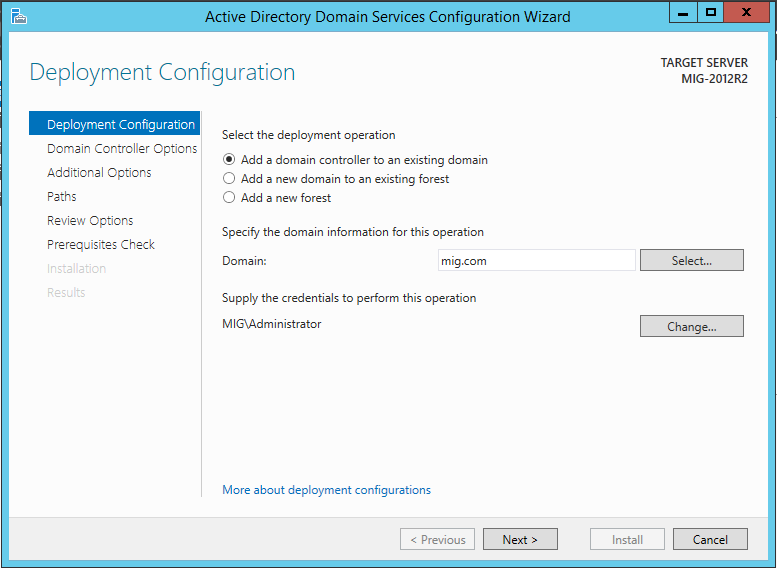
You must specify whether this server will act as the DNS server and global catalog (Global Catalog - GC).
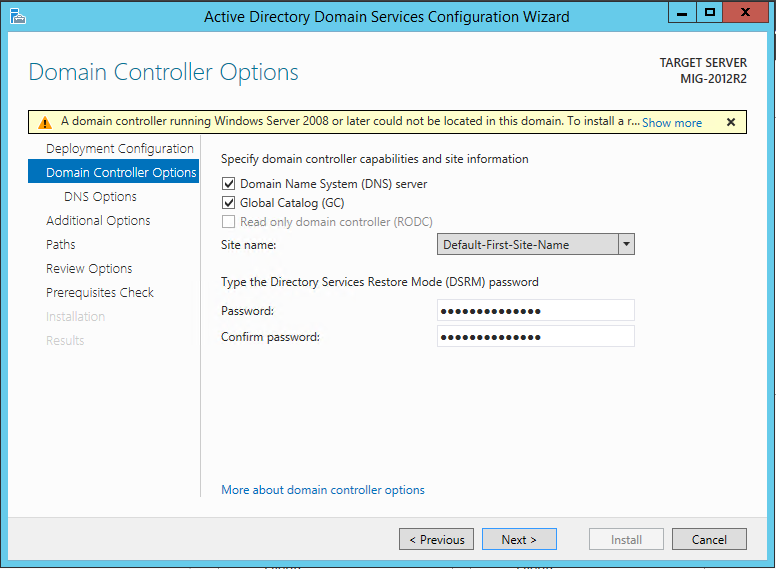
On the Additional Options screen, specify which domain controller will be replicated to the existing one. You need to select a domain controller running Windows Server 2003.
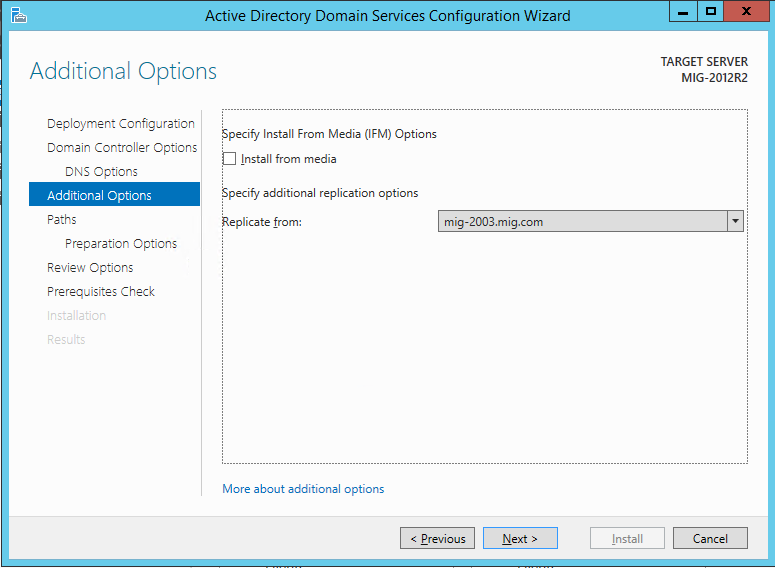
To install a domain, you must prepare the forest, domain, and schema. If earlier you needed to run the adprep command for this (and you had to do this before starting the domain configuration), now the ADDS configuration wizard takes care of this task, and the preparation can be done automatically.
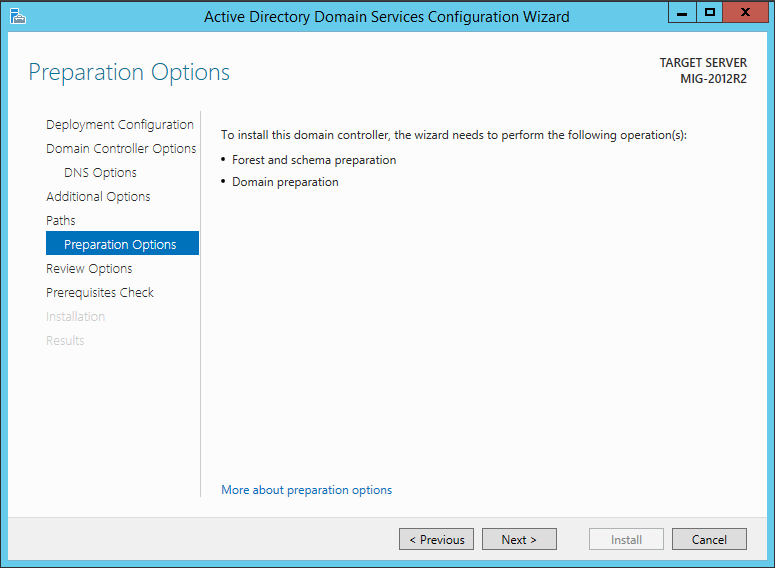
Next, you need to wait for the installation to complete and restart the computer. As a result, you will receive a domain controller with Windows Server 2012 R2 installed on it.
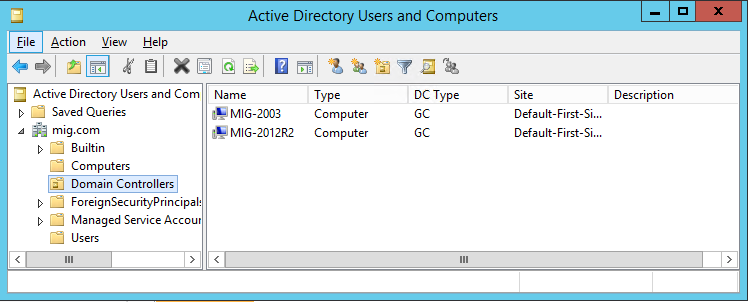
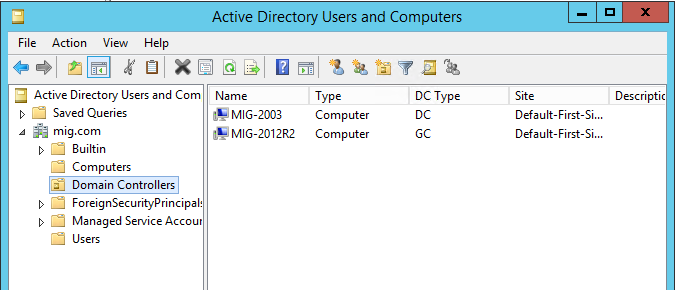
Now in the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, we can see that there are two domain controllers in our network.
After the preliminary steps are completed, we can proceed directly to the migration of Active Directory. We will perform the necessary actions on a domain controller running Windows Server 2012 R2 in the following order:
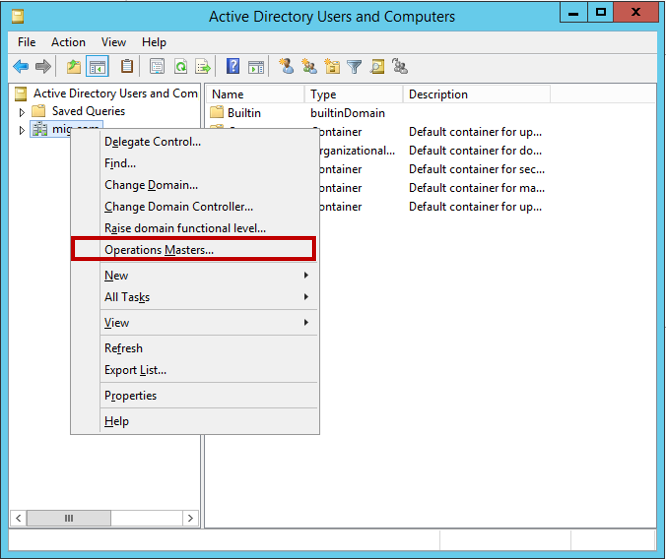
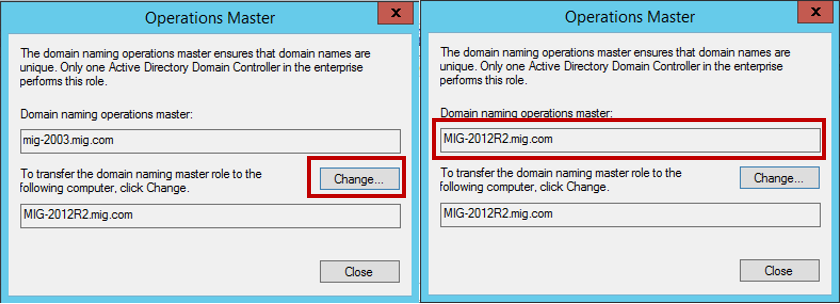
In order to transfer the role of FSMO, open the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, right-click on our domain and select Operations Masters in the submenu that appears .
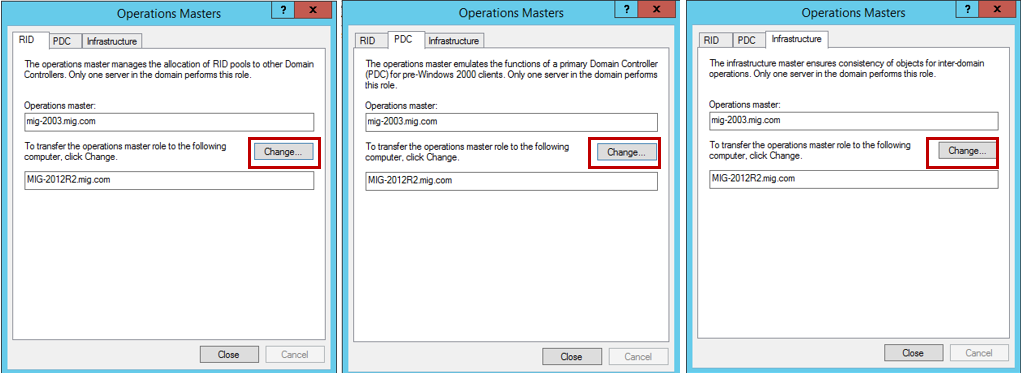
We need to transfer the role of operations master. To do this, on each tab in the newly appeared window, click the Change button and transfer the role from 2003 server to a server running 2012 R2.
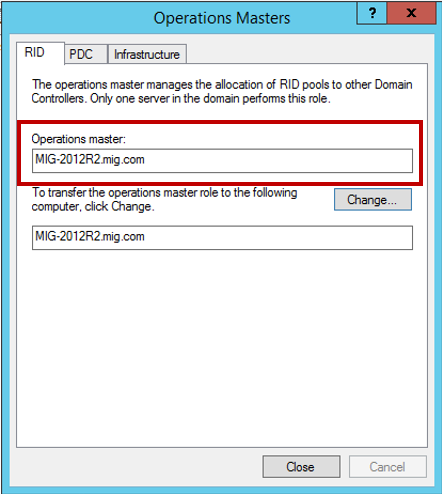
We confirm the transfer operation and wait for its successful completion. Remember to verify that, in the end, the operations master role is now on a server running Windows Server 2012 R2:
Now we move on to changing the Active Directory domain controller. Open the Active Directory Domains and Trusts console, right-click in the forest and select Change Active Directory Domain Controller .
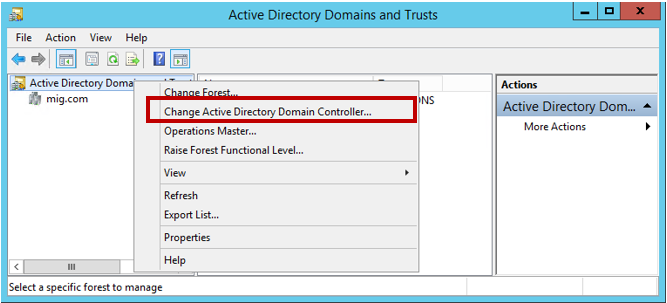
In a new window, select This Domain Controller or AD LDS instance and select a server running Windows Server 2012 R2.

Now again, we right-click on the forest and select the item Operations Master.
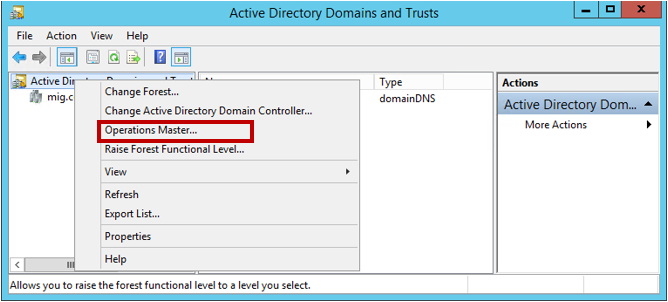
Transfer the role of the domain naming operations master by clicking Change .
Now proceed to change the Schema Master. Run the command line with Administrator rights and enter the regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll command. This command initializes the
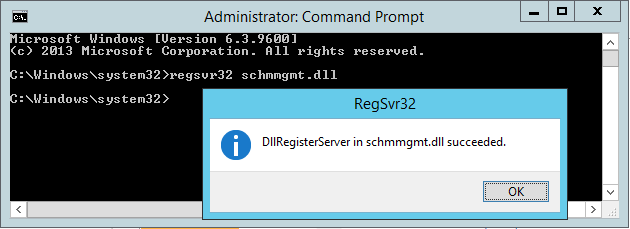
dynamic-link DLL, which is required for the Active Directory Schema snap-in.
After the command is completed, you can close the command line, start the MMC console and add the Active Directory Schema snap - in (for this, select File > Add / Remove Snap - in ).

In the same MMC console, right-click on the Active Directory Schema and select Change Active Directory Domain Controller. Similar to the actions that we performed in step 2, in the new window, select This Domain Controller or AD LDS instance and select the server running Windows Server 2012 R2 and click OK . A warning appears that the Active Directory Schema snap-in is not connected. Click OK to continue.
Now again, we right-click on the forest and select the item Operations Master . To transfer the schema master role in a new window, click Change .
Now you can close the MMC console, open the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, and make sure that the data is successfully replicated to your new server running Windows Server 2012 R2. Keep in mind that the replication process may take some time (it all depends on the number of Active Directory objects that need to be replicated).
It remains to remove the domain controller running Windows Server 2003 from the global catalog. To do this, open Active Directory Sites and Services, expand the Sites folder, then Default-First-Site-Name, then Servers and, finally, deploy both servers.
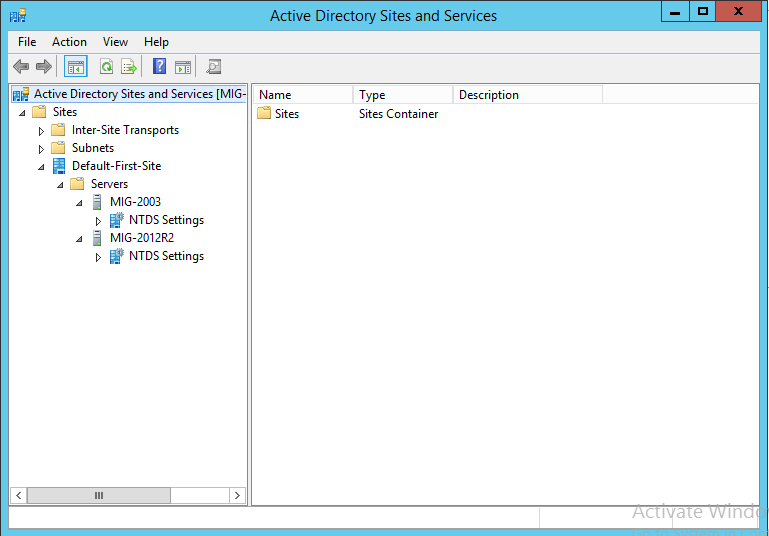
Right-click on NTDS Settings for your old server running Windows Server 2003, select Properties . In the newly appeared window, uncheck the Global Catalog item and click OK .
In Active Directory Users and Computers, the domain controller on Windows Server 2003 is no longer a global catalog.
It remains to verify that the FSMO role is now running on Windows Server 2012 R2. To do this, in the command line opened with Administrator rights, run the netdom query fsmo command

. This completes the Active Directory migration. On a computer running Windows Server 2003, run dcpromo (by the way, there is no dcpromo in Windows Server 2012 R2 ) in order to downgrade the role of a computer from a domain controller. If after that you look at the Active Directory Users and Computers console, you will see that there is only one domain controller left - running Windows Server 2012 R2.
I hope you find this article useful!

Migrating Active Directory from Windows Server 2003 to Windows Server 2012 R2 is one of the primary tasks that must be addressed during the migration process.
In fact, porting Active Directory is not a hassle. You need to perform only a few steps, which will be described in detail below.
First, we will perform a small configuration on the domain controller with Windows Server 2003 installed on it. Be sure to check that Windows Server 2003 is selected as the functional level for the existing domain and forest.
In order to change the domain and forest operating mode, you need to run the snap-in Active Directory Domains and Trust. To change the operating mode of the domain, right-click on the domain, for the operating mode of the forest, click on Active Directory Domains and Trusts. Choose Raise Domain Functional Level and Raise Forest Functional Level, respectively.


In both cases, the operating mode must be installed on Windows Server 2003.


The next step is to add a second domain controller running Windows Server 2012 R2 to our network. To do this, install the Active Directory Domain Services role on a server running Windows Server 2012 R2.

After installation, add a new domain controller to the existing domain. To do this, we will need to use an account that is part of the Enterprise Admins group and has the appropriate rights.

You must specify whether this server will act as the DNS server and global catalog (Global Catalog - GC).

On the Additional Options screen, specify which domain controller will be replicated to the existing one. You need to select a domain controller running Windows Server 2003.

To install a domain, you must prepare the forest, domain, and schema. If earlier you needed to run the adprep command for this (and you had to do this before starting the domain configuration), now the ADDS configuration wizard takes care of this task, and the preparation can be done automatically.

Next, you need to wait for the installation to complete and restart the computer. As a result, you will receive a domain controller with Windows Server 2012 R2 installed on it.
Now in the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, we can see that there are two domain controllers in our network.

After the preliminary steps are completed, we can proceed directly to the migration of Active Directory. We will perform the necessary actions on a domain controller running Windows Server 2012 R2 in the following order:
- Migrating the FSMO (Flexible Single Master Operations) Role
- Changing an Active Directory Domain Controller
- Modifying a Schema Master
- Removing a Windows Server 2003-based domain controller from the Global Catalog
1. Transferring the role of FSMO (Flexible Single Master Operations)
In order to transfer the role of FSMO, open the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, right-click on our domain and select Operations Masters in the submenu that appears .

We need to transfer the role of operations master. To do this, on each tab in the newly appeared window, click the Change button and transfer the role from 2003 server to a server running 2012 R2.

We confirm the transfer operation and wait for its successful completion. Remember to verify that, in the end, the operations master role is now on a server running Windows Server 2012 R2:

2. Changing an Active Directory Domain Controller
Now we move on to changing the Active Directory domain controller. Open the Active Directory Domains and Trusts console, right-click in the forest and select Change Active Directory Domain Controller .

In a new window, select This Domain Controller or AD LDS instance and select a server running Windows Server 2012 R2.

Now again, we right-click on the forest and select the item Operations Master.

Transfer the role of the domain naming operations master by clicking Change .

3. Changing the Schema Master
Now proceed to change the Schema Master. Run the command line with Administrator rights and enter the regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll command. This command initializes the

dynamic-link DLL, which is required for the Active Directory Schema snap-in.
After the command is completed, you can close the command line, start the MMC console and add the Active Directory Schema snap - in (for this, select File > Add / Remove Snap - in ).

In the same MMC console, right-click on the Active Directory Schema and select Change Active Directory Domain Controller. Similar to the actions that we performed in step 2, in the new window, select This Domain Controller or AD LDS instance and select the server running Windows Server 2012 R2 and click OK . A warning appears that the Active Directory Schema snap-in is not connected. Click OK to continue.
Now again, we right-click on the forest and select the item Operations Master . To transfer the schema master role in a new window, click Change .
Now you can close the MMC console, open the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, and make sure that the data is successfully replicated to your new server running Windows Server 2012 R2. Keep in mind that the replication process may take some time (it all depends on the number of Active Directory objects that need to be replicated).
4. Removing a domain controller running Windows Server 2003 from the global catalog (Global Catalog)
It remains to remove the domain controller running Windows Server 2003 from the global catalog. To do this, open Active Directory Sites and Services, expand the Sites folder, then Default-First-Site-Name, then Servers and, finally, deploy both servers.

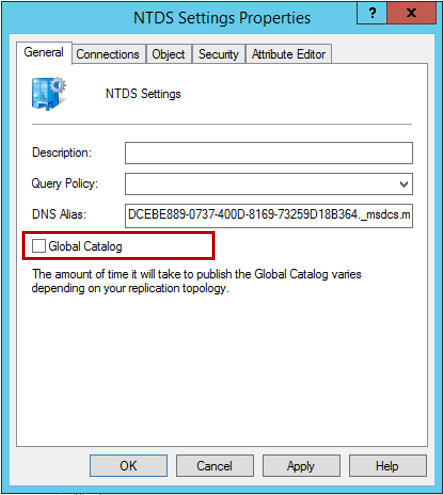
Right-click on NTDS Settings for your old server running Windows Server 2003, select Properties . In the newly appeared window, uncheck the Global Catalog item and click OK .

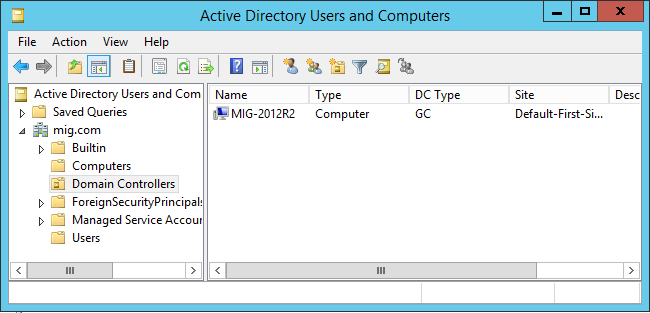
In Active Directory Users and Computers, the domain controller on Windows Server 2003 is no longer a global catalog.

It remains to verify that the FSMO role is now running on Windows Server 2012 R2. To do this, in the command line opened with Administrator rights, run the netdom query fsmo command

. This completes the Active Directory migration. On a computer running Windows Server 2003, run dcpromo (by the way, there is no dcpromo in Windows Server 2012 R2 ) in order to downgrade the role of a computer from a domain controller. If after that you look at the Active Directory Users and Computers console, you will see that there is only one domain controller left - running Windows Server 2012 R2.

I hope you find this article useful!
useful links
- Try Azure for 30 days for free!
- Learn Microsoft Virtual Academy courses
- Computer Security Basics
- Basics of building a domain network. Part 2
- Upgrading your organization’s infrastructure with Windows Server 2012 R2
- Migrating from VMware to Hyper-V
- Basics of building a domain network
- Business and the cloud: best practices solutions
- Download a trial version of Windows Server 2012 R2
- Download Free or Trial Visual Studio
