Personal devices when working with corporate data: BYOD or bring your own device
One of the areas of development of modern IT is the BYOD concept (Bring Your Own Device, or literally, “Bring your own device”). The arsenal of the modern user consists of several devices: laptop, tablet, phone; each of which has its own characteristics and can operate on the basis of different operating systems. At the same time, the issue of using personal user devices for working with corporate data remains an important issue. If laptops and tablets on Windows 8 Pro can be connected to a domain without any problems, then things are not so good with all other versions of operating systems. But access to corporate resources to the user nevertheless must be provided. This begins the torment of choosing between user convenience and the security of internal information. Often, attempts to find a solution come to a standstill. However, with the release of Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, various tools have appeared that will help in solving this eternal problem and in implementing the BYOD concept. An overview of the new functionality I want to present to you as part of this article.

Traditionally, a device may or may not be included in a domain. If the device is included in the domain, then there is no problem - it is completely controlled by the IT department of your organization. If the device is not included in the domain, then the administrator faces a difficult choice: to provide access to information to a completely unknown device or to provide access to a limited number of users and only to limited information. One of the tasks during the release of Windows Server 2012 R2 was to provide the system administrator with tools that can help solve this problem and implement the BYOD concept within the organization. Today, there are several options for connecting to work files from the outside from a personal device:
The use of VDI may be justified in some scenarios, but not in all of them because of its cost, the need to work with peripherals and more. In this regard, in the framework of this article, we will consider the first three possibilities for connecting to external files from external devices.
The tools that allow you to connect to work files from outside, and also help implement the BYOD concept in your organization, include Work Folders, Workplace Join, Windows Intune (device management tool), and Web Application Proxy (like mechanism for publishing resources and applications). Next, I will tell you about the principles of operation of each of these tools and the opportunities that they provide.
Work Folders (Work Folders) provide the ability to synchronize work files on various - personal and work - devices. Work folders (Work Folders) are configured on the server in the organization, permanently stored on it and can be synchronized to various devices - both personal user devices and computers connected to the organization’s domain network.
When using Work Folders, the user gets access to working documents, even if he is not connected to the network (especially useful on business trips and other business trips, when access to the Internet may be limited). Files stored in the working folder are synchronized to the organization’s server and from there to other working folders of this user on another device. Files are stored and transmitted in encrypted form.
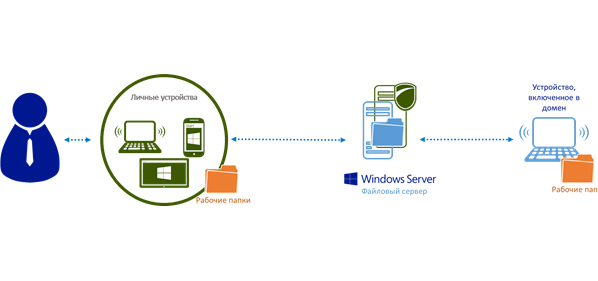
Working folders cannot be used for collaboration of several users on one file. Versioning in working folders is not supported, therefore, in case of simultaneous correction of the same file on different devices, all versions will be saved separately. In this situation, the user will have to manually view the changes and create a single version of the document.
The user can access the Work Folders by using the Control Panel and selecting the "Work Folders" item in the "System and Security" category .
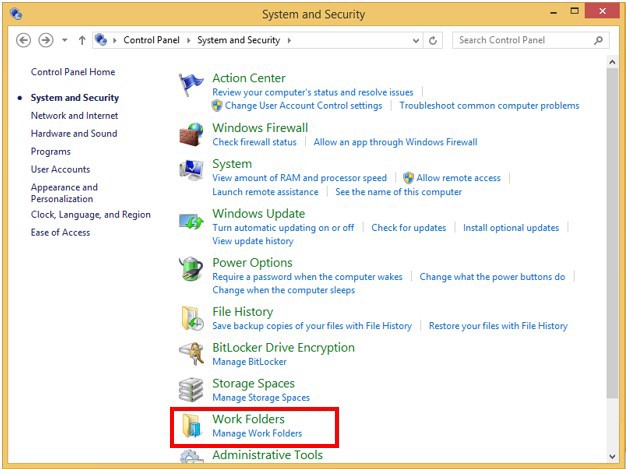
I will not dwell on the topic of working folders anymore, as I already wrote about what it is and how to configure them. Therefore, you can see more detailed information here .
Web Application Proxy was introduced with the release of Windows Server 2012 R2 and provides various features so that users can connect to applications hosted on your corporate network from any device.
An organization’s IT department can publish enterprise applications and use Web Application Proxy to provide end users with the ability to connect and work with these applications from their own devices. Thus, the user when working with internal applications is not limited to the computer that is issued to him at work and is included in the domain. Now the user can use his home computer, tablet or smartphone.
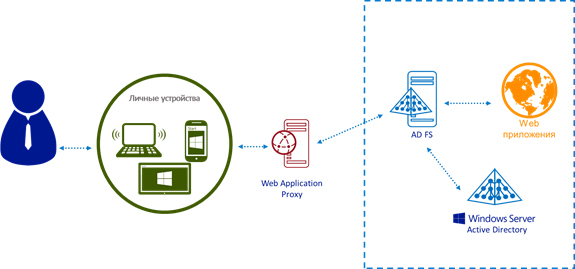
Web Application Proxy should always be deployed to your server in conjunction with Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS, Active Directory Federation Services). When trying to access the corporate application from outside, the request will be sent to the Web Application Proxy, which, in turn, will redirect it to the ADFS server. After that, the user will be prompted to go through the authentication process. The screenshot below demonstrates this process. Please note that the user accesses the application at a specific address, however, in the process of gaining access, he is redirected to the ADFS server in order to authenticate.

The joint deployment of ADFS and Web Application Proxy will allow you to use various features of AD FS, for example, the possibility of single sign-on (Single Sign-On). Using the single sign-on feature allows the user to enter their credentials only once, and with the next connection attempts, the user will not need to enter a login and password. It is important to understand that providing access to internal applications from unknown devices is a source of great risk. The combined use of Web Application Proxy and AD FS for authentication and authorization ensures that only users with devices that are also authenticated and authorized can access corporate resources.
Workplace Join, by and large, is a compromise between full control over a device that is included in a domain and connection to corporate resources from a completely unknown device. After the device is registered in the corporate network through Workplace Join, administrators can control the access of these devices to various corporate applications.
When a user's personal device is registered using Workplace Join, it becomes known to the network and can be used to provide access to corporate applications. At the same time, this device remains the user's personal device and is not regulated by group policies applied by the organization. By the way, Workplace Join is the only solution for devices that, in principle, cannot be included in the domain (for example, devices running iOS).
A device registered with Workplace Join is used as the second authentication factor and allows single sign-on to corporate resources. More precisely, during registration, a certificate is downloaded to the device, which will be used as an additional authentication factor.

If the device is not registered, then each time the browser is opened again, the user must enter a username and password to access the corporate application. If the device has a Workplace Join, then you only need to log in once, in all subsequent cases the user will automatically get access to corporate resources. At the same time, the system administrator can control the registered devices, and in the case of a message about the loss of a device from the user, it can prohibit this device from connecting to corporate applications, thereby securing the network.
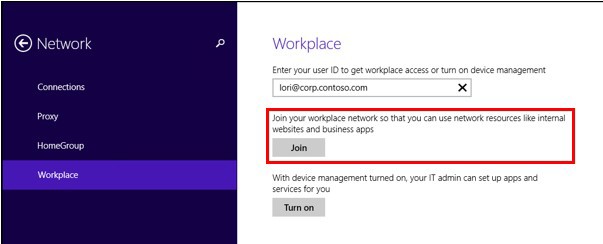
For an organization employee, setting up Workplace Join is as simple as possible. If Workplace Join is configured on the network (the Workplace Join configuration topic deserves a separate article that will appear in the near future), then the user just needs to go to PC Settings , select the Network item and the Workplace Join item . The user needs to enter their work email and click Join .
Windows Intune is a cloud-based service that can help an organization manage and protect user devices. Since Intune is a cloud service, the administrator can get access to its control panel from almost any browser.
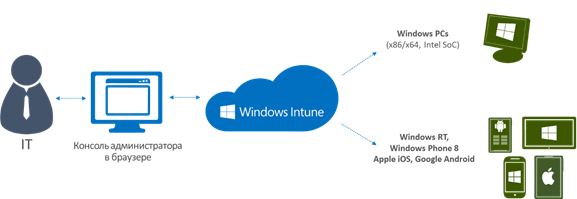
Windows Intune can be used as a separate tool for managing desktop computers and mobile devices from the cloud, or it can be integrated with System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager to configure device management policies on any operating system (Windows, Mac, Unix, or Linux).
What does the administrator get after he starts using Windows Intune? Administrators can apply various policies to user devices: set passwords and encryption settings, manage system settings, determine which applications and games can be used on the device and which are not; manage access to information, and more. As a tool for carrying out all these actions, the administrator can use two tools: the Account Portal and the Administrator Console.
In turn, the user can install the Company Portal application on his device, which is available for free for four main platforms: Windows, Windows Phone 8.1, iOS, Android.
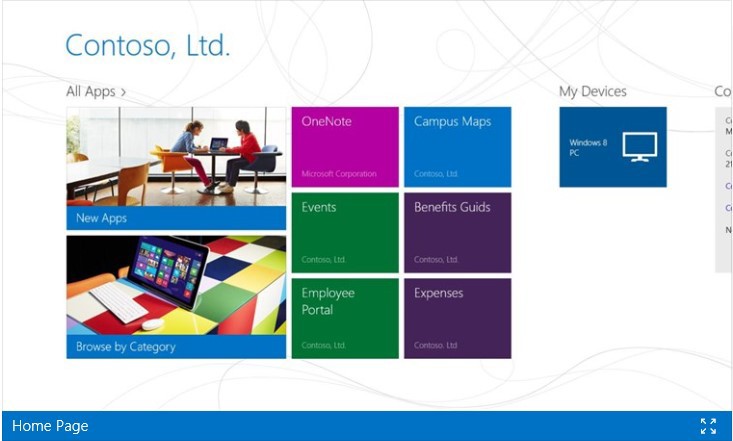
Using the Company Portal, the user can install on his device the applications allowed by the administrator that he needs to work. Installation of applications through the Company Portal does not require a connection to the corporate network. In addition, with this application you can connect or disconnect the device from Windows Intune.
Using Windows Intune, you can provide users on your corporate network with the ability to access corporate data and applications from any device without restricting them to computers included in the domain. Using Windows Intune on managed computers, you can install various software that an employee needs to work. But more importantly, Windows Intune allows you to disconnect your device from access to corporate information if it was lost or stolen. Thus, Windows Intune solves not only the problem of managing personal devices of users, but also increases the level of network security. I already mentioned that Intune can be integrated with System Center Configuration Manager to configure device management policies. Using SCCM, you can designate a device as personal or corporate;
In order to enable the device management function, the user needs to go to the settings (PC Settings) , select the Network item and the Workplace item . The user needs to enter his work email and click not Join (you need to use it if you want to configure the Workplace Join function), but Turn On .

The development of the BYOD concept is gaining momentum. And now it is no longer possible to blindly force users to use only issued corporate devices for work. New features in Windows Server 2012 R2 simplify the implementation of BYOD in your organization. In this article, we briefly examined each of the new features and will dwell on each in more detail in the following articles. Also, for those who wish, to get acquainted with the features of Windows Server 2012 R2 listed in the article in more detail, I recommend that you look at the "All About Windows Server 2012 R2" course on the MVA portal (Microsoft Virtual Academy). The course includes demos, so you can see how these features work.
I hope the information was useful! Thanks for attention!

Traditionally, a device may or may not be included in a domain. If the device is included in the domain, then there is no problem - it is completely controlled by the IT department of your organization. If the device is not included in the domain, then the administrator faces a difficult choice: to provide access to information to a completely unknown device or to provide access to a limited number of users and only to limited information. One of the tasks during the release of Windows Server 2012 R2 was to provide the system administrator with tools that can help solve this problem and implement the BYOD concept within the organization. Today, there are several options for connecting to work files from the outside from a personal device:
- Connection through a browser to a corporate application published for external access;
- Installing the application from the corporate application portal to devices (personal and work);
- Sync work files on different devices.
- Using VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure)
The use of VDI may be justified in some scenarios, but not in all of them because of its cost, the need to work with peripherals and more. In this regard, in the framework of this article, we will consider the first three possibilities for connecting to external files from external devices.
The tools that allow you to connect to work files from outside, and also help implement the BYOD concept in your organization, include Work Folders, Workplace Join, Windows Intune (device management tool), and Web Application Proxy (like mechanism for publishing resources and applications). Next, I will tell you about the principles of operation of each of these tools and the opportunities that they provide.
Work Folders
Work Folders (Work Folders) provide the ability to synchronize work files on various - personal and work - devices. Work folders (Work Folders) are configured on the server in the organization, permanently stored on it and can be synchronized to various devices - both personal user devices and computers connected to the organization’s domain network.
When using Work Folders, the user gets access to working documents, even if he is not connected to the network (especially useful on business trips and other business trips, when access to the Internet may be limited). Files stored in the working folder are synchronized to the organization’s server and from there to other working folders of this user on another device. Files are stored and transmitted in encrypted form.

Working folders cannot be used for collaboration of several users on one file. Versioning in working folders is not supported, therefore, in case of simultaneous correction of the same file on different devices, all versions will be saved separately. In this situation, the user will have to manually view the changes and create a single version of the document.
The user can access the Work Folders by using the Control Panel and selecting the "Work Folders" item in the "System and Security" category .

I will not dwell on the topic of working folders anymore, as I already wrote about what it is and how to configure them. Therefore, you can see more detailed information here .
Web application proxy
Web Application Proxy was introduced with the release of Windows Server 2012 R2 and provides various features so that users can connect to applications hosted on your corporate network from any device.
An organization’s IT department can publish enterprise applications and use Web Application Proxy to provide end users with the ability to connect and work with these applications from their own devices. Thus, the user when working with internal applications is not limited to the computer that is issued to him at work and is included in the domain. Now the user can use his home computer, tablet or smartphone.

Web Application Proxy should always be deployed to your server in conjunction with Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS, Active Directory Federation Services). When trying to access the corporate application from outside, the request will be sent to the Web Application Proxy, which, in turn, will redirect it to the ADFS server. After that, the user will be prompted to go through the authentication process. The screenshot below demonstrates this process. Please note that the user accesses the application at a specific address, however, in the process of gaining access, he is redirected to the ADFS server in order to authenticate.

The joint deployment of ADFS and Web Application Proxy will allow you to use various features of AD FS, for example, the possibility of single sign-on (Single Sign-On). Using the single sign-on feature allows the user to enter their credentials only once, and with the next connection attempts, the user will not need to enter a login and password. It is important to understand that providing access to internal applications from unknown devices is a source of great risk. The combined use of Web Application Proxy and AD FS for authentication and authorization ensures that only users with devices that are also authenticated and authorized can access corporate resources.
Workplace join
Workplace Join, by and large, is a compromise between full control over a device that is included in a domain and connection to corporate resources from a completely unknown device. After the device is registered in the corporate network through Workplace Join, administrators can control the access of these devices to various corporate applications.
When a user's personal device is registered using Workplace Join, it becomes known to the network and can be used to provide access to corporate applications. At the same time, this device remains the user's personal device and is not regulated by group policies applied by the organization. By the way, Workplace Join is the only solution for devices that, in principle, cannot be included in the domain (for example, devices running iOS).
A device registered with Workplace Join is used as the second authentication factor and allows single sign-on to corporate resources. More precisely, during registration, a certificate is downloaded to the device, which will be used as an additional authentication factor.

If the device is not registered, then each time the browser is opened again, the user must enter a username and password to access the corporate application. If the device has a Workplace Join, then you only need to log in once, in all subsequent cases the user will automatically get access to corporate resources. At the same time, the system administrator can control the registered devices, and in the case of a message about the loss of a device from the user, it can prohibit this device from connecting to corporate applications, thereby securing the network.
For an organization employee, setting up Workplace Join is as simple as possible. If Workplace Join is configured on the network (the Workplace Join configuration topic deserves a separate article that will appear in the near future), then the user just needs to go to PC Settings , select the Network item and the Workplace Join item . The user needs to enter their work email and click Join .

Windows intune
Windows Intune is a cloud-based service that can help an organization manage and protect user devices. Since Intune is a cloud service, the administrator can get access to its control panel from almost any browser.

Windows Intune can be used as a separate tool for managing desktop computers and mobile devices from the cloud, or it can be integrated with System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager to configure device management policies on any operating system (Windows, Mac, Unix, or Linux).
What does the administrator get after he starts using Windows Intune? Administrators can apply various policies to user devices: set passwords and encryption settings, manage system settings, determine which applications and games can be used on the device and which are not; manage access to information, and more. As a tool for carrying out all these actions, the administrator can use two tools: the Account Portal and the Administrator Console.
In turn, the user can install the Company Portal application on his device, which is available for free for four main platforms: Windows, Windows Phone 8.1, iOS, Android.

Using the Company Portal, the user can install on his device the applications allowed by the administrator that he needs to work. Installation of applications through the Company Portal does not require a connection to the corporate network. In addition, with this application you can connect or disconnect the device from Windows Intune.
Using Windows Intune, you can provide users on your corporate network with the ability to access corporate data and applications from any device without restricting them to computers included in the domain. Using Windows Intune on managed computers, you can install various software that an employee needs to work. But more importantly, Windows Intune allows you to disconnect your device from access to corporate information if it was lost or stolen. Thus, Windows Intune solves not only the problem of managing personal devices of users, but also increases the level of network security. I already mentioned that Intune can be integrated with System Center Configuration Manager to configure device management policies. Using SCCM, you can designate a device as personal or corporate;
In order to enable the device management function, the user needs to go to the settings (PC Settings) , select the Network item and the Workplace item . The user needs to enter his work email and click not Join (you need to use it if you want to configure the Workplace Join function), but Turn On .

The development of the BYOD concept is gaining momentum. And now it is no longer possible to blindly force users to use only issued corporate devices for work. New features in Windows Server 2012 R2 simplify the implementation of BYOD in your organization. In this article, we briefly examined each of the new features and will dwell on each in more detail in the following articles. Also, for those who wish, to get acquainted with the features of Windows Server 2012 R2 listed in the article in more detail, I recommend that you look at the "All About Windows Server 2012 R2" course on the MVA portal (Microsoft Virtual Academy). The course includes demos, so you can see how these features work.
I hope the information was useful! Thanks for attention!
