ShellShock's new dangerous vulnerability allows attacking many devices, from smartphones to industrial servers
Positive Technologies experts warn of a new ShellShock vulnerability (CVE-2014-6271), the use of which allows arbitrary code to be executed. The vulnerability affected not only Internet servers and workstations, but also the devices that we use in everyday life - smartphones and tablets, home routers, laptops.
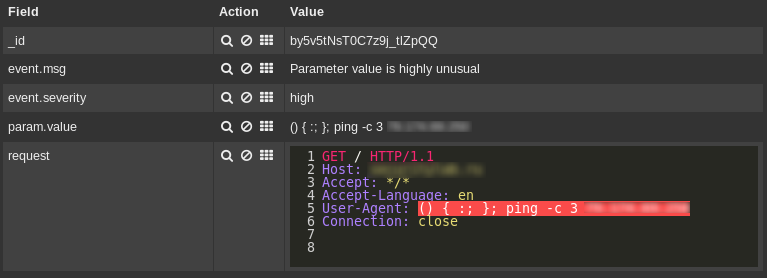
The vulnerability is present in one of the fundamental components of Linux systems, the bash shell. The mechanism for processing exported functions allows an attacker to remotely run arbitrary commands of the operating system if he has the ability to influence the environment variables of the system. A similar situation often arises in web applications when using the CGI interface (for example, an Apache server using mod_cgi or mod_cgid). Common PHP and Python online development technologies are also vulnerable when using system / exec or os.system / os.popen calls, respectively.
An example of a vulnerable application is the common cPanel hosting control panel. There are other operational methods associated with the use of ForceCommand's limited access mechanism in OpenSSH, implemented in systems such as Git and Subversion.
There is information that a number of security researchers, in particular @ErrataRob, are already actively scanning the global network in search of vulnerable servers.
Positive Technologies experts recommend urgently installing a security update on all public GNU / Linux servers, since this vulnerability could be comparable to the sensational error in OpenSSL - HeartBleed, due to negative consequences. At risk are remote server and industrial systems. Often they are developed with extensive use of shell-technologies and at the same time are rarely updated. Other potential hacking candidates using the new vulnerability are access points, routers, embedded devices, printers, and in general any devices connected with the Internet of things.
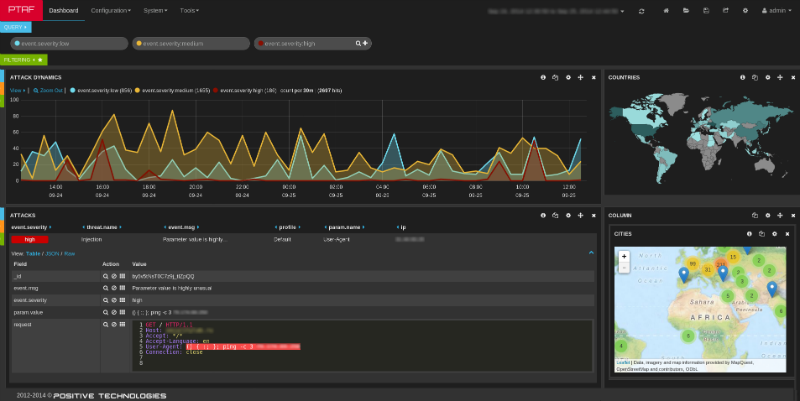
Moreover, a potential attack can also be made on user devices, such as smartphones and tablets running Android: simply connect to an attacker-controlled wireless access point. Such attacks are most dangerous in places of crowded people who actively use Wi-Fi - in a cafe, in the subway, at the airport.
“This vulnerability is noteworthy because it uses a completely“ legal ”shell mechanism, combined with the widespread use of operating system commands in the * nix community. Unfortunately, many embedded devices used both on corporate networks and on home systems are potentially vulnerable to ShellShock attacks. To make matters worse, the systems on such devices are rarely updated and often contain outdated versions of the OS and system components. Users of smartphones, tablets and laptops running Linux and Mac OS X are not recommended to connect to unfamiliar wireless access points before installing a security update, ”said Sergey Gordeychik, Deputy General Director of Positive Technologies.
Positive Technologies Application Firewall’s built-in application protection mechanisms, even in its basic configuration, allow you to identify and block ShellShock attacks. Customers of the Advanced Border Control service will receive prompt notifications of identified shortcomings.
More details about the vulnerability: www.securitylab.ru/vulnerability/458762.php

The vulnerability is present in one of the fundamental components of Linux systems, the bash shell. The mechanism for processing exported functions allows an attacker to remotely run arbitrary commands of the operating system if he has the ability to influence the environment variables of the system. A similar situation often arises in web applications when using the CGI interface (for example, an Apache server using mod_cgi or mod_cgid). Common PHP and Python online development technologies are also vulnerable when using system / exec or os.system / os.popen calls, respectively.
An example of a vulnerable application is the common cPanel hosting control panel. There are other operational methods associated with the use of ForceCommand's limited access mechanism in OpenSSH, implemented in systems such as Git and Subversion.
There is information that a number of security researchers, in particular @ErrataRob, are already actively scanning the global network in search of vulnerable servers.
Positive Technologies experts recommend urgently installing a security update on all public GNU / Linux servers, since this vulnerability could be comparable to the sensational error in OpenSSL - HeartBleed, due to negative consequences. At risk are remote server and industrial systems. Often they are developed with extensive use of shell-technologies and at the same time are rarely updated. Other potential hacking candidates using the new vulnerability are access points, routers, embedded devices, printers, and in general any devices connected with the Internet of things.

Moreover, a potential attack can also be made on user devices, such as smartphones and tablets running Android: simply connect to an attacker-controlled wireless access point. Such attacks are most dangerous in places of crowded people who actively use Wi-Fi - in a cafe, in the subway, at the airport.
“This vulnerability is noteworthy because it uses a completely“ legal ”shell mechanism, combined with the widespread use of operating system commands in the * nix community. Unfortunately, many embedded devices used both on corporate networks and on home systems are potentially vulnerable to ShellShock attacks. To make matters worse, the systems on such devices are rarely updated and often contain outdated versions of the OS and system components. Users of smartphones, tablets and laptops running Linux and Mac OS X are not recommended to connect to unfamiliar wireless access points before installing a security update, ”said Sergey Gordeychik, Deputy General Director of Positive Technologies.
Positive Technologies Application Firewall’s built-in application protection mechanisms, even in its basic configuration, allow you to identify and block ShellShock attacks. Customers of the Advanced Border Control service will receive prompt notifications of identified shortcomings.
More details about the vulnerability: www.securitylab.ru/vulnerability/458762.php
