Introducing PHP Messaging Services
- Transfer
Learn more about the intricacies of the basic messaging services available in PHP.
Semaphore is a PHP module that actually consists of three extensions that include semaphores, shared memory, and interprocess messaging (IPC). This module provides shells for the System V IPC family of functions, and to use it in PHP you need to enable it because it is not enabled by default, so use the option to enable support for System V PHP semaphores
* Note: Semaphore is not available on Windows platforms.
To use the interprocess communication module (IPC), there is a set of functions listed below:
Gearman is an application framework designed to work with several processes and allows programs to perform tasks in parallel and call functions between languages. Gearman can be used in a variety of applications: from high-availability websites to transmitting database replication events, and consists of two main components: a job server and a client / worker API. The client and worker API can be used in a wide variety of languages, but the job server is only available as a C library or Perl library. This fact makes it difficult to run the server on Windows, mainly due to unresolved dependency on other libraries.
You can install the Gearman application platform in two ways:
As you probably know, most of the features of JMS are for messenger services, which in the Java world are very suitable but not suitable for PHP. In order to use these functions in PHP, you must implement Java using various technologies, in this case, Quercus.
Java Message Service (JMS)is a messaging standard that allows Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE) -based application components to create, send, receive, and read messages. Data exchange can be asynchronous (the JMS provider can deliver messages to the client as they arrive; clients must not request messages in order to receive them) or reliable (the JMS API can guarantee that the message will be delivered immediately and only once. Lower reliability levels available for applications that can afford to skip messages or receive duplicate messages).
Quercusis a 100% implementation of PHP 5 under Java Caucho Technology, released under the Open Source GPL. Quercus comes with many PHP modules and extensions, such as PDF, PDO, MySQL, and JSON, and provides close integration of Java services with PHP scripts, so using PHP with JMS is very convenient. Quercus also offers a convenient messaging interface using the Java messaging service, so it allows you to send and receive messages using the Resin JMS implementation or any other messaging service that implements JMS, as you will see later in this section. To install and use Quercus, you have two options:
Quercus is part of the Resin Application Server and is built into Resin - so there is no need for an additional installation. To install Resin on Windows, follow the steps from www.caucho.com/resin-3.1/doc/resin-web-server.xtp#GettingStarted . To verify the Resin installation, go to localhost : 8080 in the browser.
and is built into Resin - so there is no need for an additional installation. To install Resin on Windows, follow the steps from www.caucho.com/resin-3.1/doc/resin-web-server.xtp#GettingStarted . To verify the Resin installation, go to localhost : 8080 in the browser.
To use JMS in Quercus, configure JMS for PHP and JAVA, for this you need to install ConnectionFactory and Queue , both are in the resin-web.xml file in the WEB-INF directory.
resin-web.xml
The Quercus interface programming model assumes a queue access interface using the java_bean () call , which will find the named object in the resin-web.xml file, in this case the queue. Precisely because Queue implements the java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue interface , the PHP script has the ability to immediately send data to the queue using offer () and receive them using poll () .
The script checks the POST variable "message" and if it is set, sends the value of this variable to the JMS queue. A message-driven entity (MDB) receives these messages and writes them. The record is displayed by the servlet.
The second way to use Quercus is to use NetBeans IDE and GlassFish as a server. To use Quercus on NetBeans, you must follow these steps:
PHPMQ is an open source peer-to-peer messaging toolkit for PHP, giving the PHP developer the ability to perform JMS operations, such as sending and receiving messages on queues and topics, while ensuring delivery and continuous messaging. This opens up new possibilities for PHP developers who can now access the data of the so-called back office, which, as a rule, is only available to application servers and old messaging solutions.
PHPMQ ( ) Mantaray (
) Mantaray (  )is a distributed, peer-to-peer, serverless system for solving the messaging problem for Java (JMS), C ++ and .NET applications, integrates with JBoss, WebLogic and WebSphere. It offers guaranteed delivery, security and transactions and supports TCP, SSL and HTTP protocols.
)is a distributed, peer-to-peer, serverless system for solving the messaging problem for Java (JMS), C ++ and .NET applications, integrates with JBoss, WebLogic and WebSphere. It offers guaranteed delivery, security and transactions and supports TCP, SSL and HTTP protocols.
Installing PHPMQ:
→ Download and install the MantaRay messaging bus
→ Configure MantaRay to enable the RMI API and create the RMI registry (See the RMI API documentation on the MantaRay project)
→ Run Mantaray as a standalone application
→ Enable PHP-Java extension in php.ini - relevant information is available at www.php.net/manual/en/ref.java.php
→ Add phpmq.jar (located here in the zip archive) and manta.jar (located in MantaRay.zip) to the php.ini “java.class.path” property
→ Run the examples (chat.php for themes and queue_receiver.php, queue_sender .php for queues)
The PHPMQ messaging API includes the following functions:
After the start of the translation, it turned out that the material does not reach the level of the Habr. I hope this does not prevent anyone from benefiting from this material.
As usual, please report all inaccuracies to Habr-mail.
- Semaphores
- Gearman
- JMS with PHP via QUERCUS
- JMS with PHP via PHPMQ-> MANTARAY
1. Semaphores
Semaphore is a PHP module that actually consists of three extensions that include semaphores, shared memory, and interprocess messaging (IPC). This module provides shells for the System V IPC family of functions, and to use it in PHP you need to enable it because it is not enabled by default, so use the option to enable support for System V PHP semaphores
--enable-sysvsem; to enable System V shared memory support compile PHP using the option --enable-sysvshm; and in order to enable System V message support, compile PHP using the option --enable-sysvmsg. * Note: Semaphore is not available on Windows platforms.
To use the interprocess communication module (IPC), there is a set of functions listed below:
- msg_get_queue: Create or join a message queue.
resource msg_get_queue ( int $key [, int $perms = 0666 ] )
Returns an identifier that can be used to access the System V message queue with this key. - msg_queue_exists: Checks for the existence of a message queue.
bool msg_queue_exists ( int $key) - msg_receive: Get message from message queue.
bool msg_receive ( resource $queue , int $desiredmsgtype , int &$msgtype , int $maxsize ,mixed &$message [, bool $unserialize = true [, int $flags = 0 [, int &$errorcode ]]] )
Receive the first message from the specified queue of the type specified in desiredmsgtype. - msg_remove_queue: Destroy the message queue.
bool msg_remove_queue ( resource $queue )
Destroys the message queue specified in the queue. You should use this function only when all processes have finished working with the message queue, and you must free up system resources. - msg_send: Send a message to the message queue.
bool msg_send ( resource $queue , int $msgtype , mixed $message [, bool $serialize = true [,bool $blocking = true [, int &$errorcode ]]] )
Sends a message of type MsgType (which must be greater than 0) to the message queue specified in the queue. - msg_set_queue: Set information to the message queue data structure.
bool msg_set_queue ( resource $queue , array $data )
Allows you to change the values of msg_perm.uid, msg_perm.gid, msg_perm.mode and msg_qbytes areas of the main data structure of the message queue. - msg_stat_queue: Returns information from the message queue data structure.
array msg_stat_queue ( resource $queue )
Returns metadata for the message queue specified in queue
2. Gearman
Gearman is an application framework designed to work with several processes and allows programs to perform tasks in parallel and call functions between languages. Gearman can be used in a variety of applications: from high-availability websites to transmitting database replication events, and consists of two main components: a job server and a client / worker API. The client and worker API can be used in a wide variety of languages, but the job server is only available as a C library or Perl library. This fact makes it difficult to run the server on Windows, mainly due to unresolved dependency on other libraries.
You can install the Gearman application platform in two ways:
- Using a pure PHP wrapper called Net_Gearman, with
pear install Net_Gearman. - Specialized PHP extension. [
 ] . This extension offers an OOP interface for writing Gearman clients and workers.
] . This extension offers an OOP interface for writing Gearman clients and workers.
3. JMS with PHP through Quercus
As you probably know, most of the features of JMS are for messenger services, which in the Java world are very suitable but not suitable for PHP. In order to use these functions in PHP, you must implement Java using various technologies, in this case, Quercus.
Java Message Service (JMS)is a messaging standard that allows Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE) -based application components to create, send, receive, and read messages. Data exchange can be asynchronous (the JMS provider can deliver messages to the client as they arrive; clients must not request messages in order to receive them) or reliable (the JMS API can guarantee that the message will be delivered immediately and only once. Lower reliability levels available for applications that can afford to skip messages or receive duplicate messages).
Quercusis a 100% implementation of PHP 5 under Java Caucho Technology, released under the Open Source GPL. Quercus comes with many PHP modules and extensions, such as PDF, PDO, MySQL, and JSON, and provides close integration of Java services with PHP scripts, so using PHP with JMS is very convenient. Quercus also offers a convenient messaging interface using the Java messaging service, so it allows you to send and receive messages using the Resin JMS implementation or any other messaging service that implements JMS, as you will see later in this section. To install and use Quercus, you have two options:
Resin web server
Quercus is part of the Resin Application Server
 and is built into Resin - so there is no need for an additional installation. To install Resin on Windows, follow the steps from www.caucho.com/resin-3.1/doc/resin-web-server.xtp#GettingStarted . To verify the Resin installation, go to localhost : 8080 in the browser.
and is built into Resin - so there is no need for an additional installation. To install Resin on Windows, follow the steps from www.caucho.com/resin-3.1/doc/resin-web-server.xtp#GettingStarted . To verify the Resin installation, go to localhost : 8080 in the browser. To use JMS in Quercus, configure JMS for PHP and JAVA, for this you need to install ConnectionFactory and Queue , both are in the resin-web.xml file in the WEB-INF directory.
Hidden text

resin-web.xml
Queue #{Queue} The Quercus interface programming model assumes a queue access interface using the java_bean () call , which will find the named object in the resin-web.xml file, in this case the queue. Precisely because Queue implements the java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue interface , the PHP script has the ability to immediately send data to the queue using offer () and receive them using poll () .
offer($_POST["message"]) == TRUE) {
echo "Successfully sent message '" . $_POST["message"] . "'";
} else {
echo "Unable to send message '" . $_POST["message"] . "'";
}
}
}
?>The script checks the POST variable "message" and if it is set, sends the value of this variable to the JMS queue. A message-driven entity (MDB) receives these messages and writes them. The record is displayed by the servlet.
NetBeans IDE and GlassFish
The second way to use Quercus is to use NetBeans IDE and GlassFish as a server. To use Quercus on NetBeans, you must follow these steps:
- Unzip Quercus-4.0.39.war (http://quercus.caucho.com/) and copy the JAR files in the WEB-INF / lib directory to GLASSFISH_HOME / domains / domain / lib.Hidden text
- Create a new web application project, “PHPexample”, using the NetBeans IDE and select GlassFish as the server:Hidden text
 Hidden text
Hidden text Hidden textAfter clicking Finish, a folder with the following structure will be created:
Hidden textAfter clicking Finish, a folder with the following structure will be created: Hidden text
Hidden text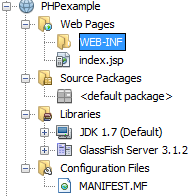
- In the WEB-INF directory, create the web.xml file (if it was not created earlier): File> New> Empty. Paste the following text into it and save:web.xmlSo we declared a servlet from PHP.web.xml
Caucho Technology's PHP Implementation, Running on GlassFish Java EE 5 Quercus Servlet com.caucho.quercus.servlet.QuercusServlet Quercus Servlet \*.php index.php - In the main project, PHPexample, create a PHP file called index.php with the context:index.phpindex.php
This page prints "Hello World!" in the browser and some PHP configuration settings. The directory structure of the created project is as follows:Hidden text
Please note that “index.jsp” is only a template file to start working with JSP, and it is not related to our tasks. - Run the PHP application in GlassFish on localhost : 8080 / PHPexample / index.php / and you should get the output below:Hidden text
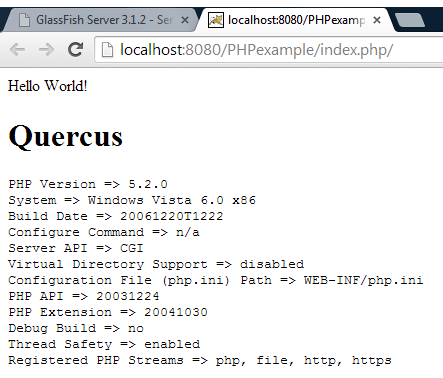
Once you see that Quercus runs on NetBeans IDE and GlassFish as a server, you can try to use all the features of JMS and all the other extensions that come with Quercus.
4. JMS with PHP through PHPMQ
PHPMQ is an open source peer-to-peer messaging toolkit for PHP, giving the PHP developer the ability to perform JMS operations, such as sending and receiving messages on queues and topics, while ensuring delivery and continuous messaging. This opens up new possibilities for PHP developers who can now access the data of the so-called back office, which, as a rule, is only available to application servers and old messaging solutions.
PHPMQ (
 ) Mantaray (
) Mantaray (  )is a distributed, peer-to-peer, serverless system for solving the messaging problem for Java (JMS), C ++ and .NET applications, integrates with JBoss, WebLogic and WebSphere. It offers guaranteed delivery, security and transactions and supports TCP, SSL and HTTP protocols.
)is a distributed, peer-to-peer, serverless system for solving the messaging problem for Java (JMS), C ++ and .NET applications, integrates with JBoss, WebLogic and WebSphere. It offers guaranteed delivery, security and transactions and supports TCP, SSL and HTTP protocols. Installing PHPMQ:
→ Download and install the MantaRay messaging bus
→ Configure MantaRay to enable the RMI API and create the RMI registry (See the RMI API documentation on the MantaRay project)
→ Run Mantaray as a standalone application
→ Enable PHP-Java extension in php.ini - relevant information is available at www.php.net/manual/en/ref.java.php
→ Add phpmq.jar (located here in the zip archive) and manta.jar (located in MantaRay.zip) to the php.ini “java.class.path” property
→ Run the examples (chat.php for themes and queue_receiver.php, queue_sender .php for queues)
The PHPMQ messaging API includes the following functions:
- enqueue : sends a message to the queue with the name $ queueName (string); $ userId (string) is the identifier on the message bus.
enqueue($userId, $queueName, $message) - dequeue : returns a text message from the queue $ queueName (string); $ userId (string) is the identifier on the message bus.
dequeue($userId, $queueName) - getQueues : returns a list of queues that are available on the message bus.
array getQueues() - getTopics : returns a list of topics that are available on the message bus.
array getTopics() - subscribe : adds a listener to the topic $ topicName (string), which will receive no more than $ messagesToCash (number) messages; $ userId (string) is the identifier on the message bus.
subscribe($userKey $topicName, $messagesToCash) - publishMessage : publishes a message with the text $ msg (string) with the topic $ topicName (string); $ userId (string) is the identifier on the message bus.
publishMessage($userKey, $topicName, $msg)
From translator
After the start of the translation, it turned out that the material does not reach the level of the Habr. I hope this does not prevent anyone from benefiting from this material.
As usual, please report all inaccuracies to Habr-mail.
