Creating and Using the Clang Plugin in Xcode
- Transfer
- Tutorial
This tutorial describes how to create a plugin for Clang and covers the following steps:
- environment setting
- creating a basic plugin
- creating an Xcode project for plugin development
- alert generation
- error generation
- plugin integration in Xcode
- online warnings and error tips
TL; DR
Ready plugin can be found here.
Introduction
During the development of BloodMagic, I decided that it would be great to have a tool for finding semantic errors when using BM. For example, a property is marked as
lazyin the interface, but in the implementation it is not marked as @dynamic, or marked as lazy, but the container class does not support injection. I came to the conclusion that I’ll have to work with AST , and therefore I need a full-fledged parser. I tried different options: flex + bison , libclang , but in the end I decided to write a plugin for Clang.
For the test plugin, I set the following goals:
- use Xcode for development
- integrate a ready-made plugin into Xcode for everyday use
- the plugin should be able to generate warnings, errors and show interactive tips (through Xcode)
Features for the test plugin:
- generate a warning if the class name begins with a lowercase letter
- generate an error if the class name contains an underscore
- offer suggestions for correction
Environment setting
To develop the plugin, we need llvm / clang, compiled from source
cd /opt
sudo mkdir llvm
sudo chown `whoami` llvm
cd llvm
export LLVM_HOME=`pwd`The current version of clang on my machine is 3.3.1, so I use the appropriate version:
git clone -b release_33 https://github.com/llvm-mirror/llvm.git llvm
git clone -b release_33 https://github.com/llvm-mirror/clang.git llvm/tools/clang
git clone -b release_33 https://github.com/llvm-mirror/clang-tools-extra.git llvm/tools/clang/tools/extra
git clone -b release_33 https://github.com/llvm-mirror/compiler-rt.git llvm/projects/compiler-rt
mkdir llvm_build
cd llvm_build
cmake ../llvm -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE:STRING=Release
make -j`sysctl -n hw.logicalcpu`
Creating a basic plugin
Create a directory for the plugin
cd $LLVM_HOME
mkdir toy_clang_plugin; cd toy_clang_plugin
Our plugin is based on an example from the Clang repository and has the following structure:
ToyClangPlugin.exports
CMakeLists.txt
ToyClangPlugin.cpp
We will use one file to simplify:
ToyClangPlugin.cpp
// ToyClangPlugin.cpp
#include "clang/Frontend/FrontendPluginRegistry.h"
#include "clang/AST/AST.h"
#include "clang/AST/ASTConsumer.h"
#include "clang/Frontend/CompilerInstance.h"
using namespace clang;
namespace
{
class ToyConsumer : public ASTConsumer
{
};
class ToyASTAction : public PluginASTAction
{
public:
virtual clang::ASTConsumer *CreateASTConsumer(CompilerInstance &Compiler,
llvm::StringRef InFile)
{
return new ToyConsumer;
}
bool ParseArgs(const CompilerInstance &CI, const
std::vector& args) {
return true;
}
};
}
static clang::FrontendPluginRegistry::Add
X("ToyClangPlugin", "Toy Clang Plugin");
Data required for assembly:
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 2.6)
project (ToyClangPlugin)
set( CMAKE_RUNTIME_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/bin )
set( CMAKE_LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/lib )
set( CMAKE_ARCHIVE_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/lib )
set( LLVM_HOME /opt/llvm )
set( LLVM_SRC_DIR ${LLVM_HOME}/llvm )
set( CLANG_SRC_DIR ${LLVM_HOME}/llvm/tools/clang )
set( LLVM_BUILD_DIR ${LLVM_HOME}/llvm_build )
set( CLANG_BUILD_DIR ${LLVM_HOME}/llvm_build/tools/clang)
add_definitions (-D__STDC_LIMIT_MACROS -D__STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS)
add_definitions (-D_GNU_SOURCE -DHAVE_CLANG_CONFIG_H)
set (CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "${LLVM_BUILD_DIR}/bin/clang++")
set (CMAKE_CC_COMPILER "${LLVM_BUILD_DIR}/bin/clang")
set (CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS}
-fPIC
-fno-common
-Woverloaded-virtual
-Wcast-qual
-fno-strict-aliasing
-pedantic
-Wno-long-long
-Wall
-Wno-unused-parameter
-Wwrite-strings
-fno-exceptions
-fno-rtti")
set (CMAKE_MODULE_LINKER_FLAGS "-Wl,-flat_namespace -Wl,-undefined -Wl,suppress")
set (LLVM_LIBS
LLVMJIT
LLVMX86CodeGen
LLVMX86AsmParser
LLVMX86Disassembler
LLVMExecutionEngine
LLVMAsmPrinter
LLVMSelectionDAG
LLVMX86AsmPrinter
LLVMX86Info
LLVMMCParser
LLVMCodeGen
LLVMX86Utils
LLVMScalarOpts
LLVMInstCombine
LLVMTransformUtils
LLVMipa
LLVMAnalysis
LLVMTarget
LLVMCore
LLVMMC
LLVMSupport
LLVMBitReader
LLVMOption
)
macro(add_clang_plugin name)
set (srcs ${ARGN})
include_directories( "${LLVM_SRC_DIR}/include"
"${CLANG_SRC_DIR}/include"
"${LLVM_BUILD_DIR}/include"
"${CLANG_BUILD_DIR}/include" )
link_directories( "${LLVM_BUILD_DIR}/lib" )
add_library( ${name} SHARED ${srcs} )
if (SYMBOL_FILE)
set_target_properties( ${name} PROPERTIES LINK_FlAGS
"-exported_symbols_list ${SYMBOL_FILE}")
endif()
foreach (clang_lib ${CLANG_LIBS})
target_link_libraries( ${name} ${clang_lib} )
endforeach()
foreach (llvm_lib ${LLVM_LIBS})
target_link_libraries( ${name} ${llvm_lib} )
endforeach()
foreach (user_lib ${USER_LIBS})
target_link_libraries( ${name} ${user_lib} )
endforeach()
endmacro(add_clang_plugin)
set(SYMBOL_FILE ToyClangPlugin.exports)
set (CLANG_LIBS
clang
clangFrontend
clangAST
clangAnalysis
clangBasic
clangCodeGen
clangDriver
clangFrontendTool
clangLex
clangParse
clangSema
clangEdit
clangSerialization
clangStaticAnalyzerCheckers
clangStaticAnalyzerCore
clangStaticAnalyzerFrontend
)
set (USER_LIBS
pthread
curses
)
add_clang_plugin(ToyClangPlugin
ToyClangPlugin.cpp
)
set_target_properties(ToyClangPlugin PROPERTIES
LINKER_LANGUAGE CXX
PREFIX "")
ToyClangPlugin.exports
__ZN4llvm8Registry*
Now we can generate an Xcode project based on `CMakeLists.txt`
mkdir build; cd build
cmake -G Xcode ..
open ToyClangPlugin.xcodeprojRun 'ALL_BUILD', if successful, the finished library will be here: `lib / Debug / ToyCLangPlugin.dylib`.
RecursiveASTVisitor
The AST module provides a RecursiveASTVisitor that allows you to walk through the syntax tree. All we need is to inherit and implement the methods of interest.
As a small test, display all the classes that are encountered:
class ToyClassVisitor : public RecursiveASTVisitor
{
public:
bool VisitObjCInterfaceDecl(ObjCInterfaceDecl *declaration)
{
printf("ObjClass: %s\n", declaration->getNameAsString().c_str());
return true;
}
};
class ToyConsumer : public ASTConsumer
{
public:
void HandleTranslationUnit(ASTContext &context) {
visitor.TraverseDecl(context.getTranslationUnitDecl());
}
private:
ToyClassVisitor visitor;
};
Create a test class and test the plugin
#import
@interface ToyObject : NSObject
@end
@implementation ToyObject
@end
Plugin launch
/opt/llvm/toy_clang_plugin/build $ $LLVM_HOME/llvm_build/bin/clang ../test.m \
-Xclang -load \
-Xclang lib/Debug/ToyClangPlugin.dylib \
-Xclang -plugin \
-Xclang ToyClangPlugin
The output should be a huge list of classes.
Alert generation
If the class name begins with a lowercase letter, the user will see a warning.
A context is needed to generate alerts
class ToyClassVisitor : public RecursiveASTVisitor
{
private:
ASTContext *context;
public:
void setContext(ASTContext &context)
{
this->context = &context;
}
// ...
};
// ...
void HandleTranslationUnit(ASTContext &context) {
visitor.setContext(context);
visitor.TraverseDecl(context.getTranslationUnitDecl());
}
// ...
Class Name Validation:
bool VisitObjCInterfaceDecl(ObjCInterfaceDecl *declaration)
{
checkForLowercasedName(declaration);
return true;
}
// ...
void checkForLowercasedName(ObjCInterfaceDecl *declaration)
{
StringRef name = declaration->getName();
char c = name[0];
if (isLowercase(c)) {
DiagnosticsEngine &diagEngine = context->getDiagnostics();
unsigned diagID = diagEngine.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Warning, "Class name should not start with lowercase letter");
SourceLocation location = declaration->getLocation();
diagEngine.Report(location, diagID);
}
}
Now we need to add a class with a "bad" name
@interface bad_ToyObject : NSObject
@end
@implementation bad_ToyObject
@end
and check the plugin
/opt/llvm/toy_clang_plugin/build $ $LLVM_HOME/llvm_build/bin/clang ../test.m \
-Xclang -load \
-Xclang lib/Debug/ToyClangPlugin.dylib \
-Xclang -plugin \
-Xclang ToyClangPlugin
../test.m:11:12: warning: Class name should not start with lowercase letter
@interface bad_ToyObject : NSObject
^
1 warning generated.
Error generation
If the class name contains an underscore ('_'), then the user will see an error.
void checkForUnderscoreInName(ObjCInterfaceDecl *declaration)
{
size_t underscorePos = declaration->getName().find('_');
if (underscorePos != StringRef::npos) {
DiagnosticsEngine &diagEngine = context->getDiagnostics();
unsigned diagID = diagEngine.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Error, "Class name with `_` forbidden");
SourceLocation location = declaration->getLocation().getLocWithOffset(underscorePos);
diagEngine.Report(location, diagID);
}
}
bool VisitObjCInterfaceDecl(ObjCInterfaceDecl *declaration)
{
// disable this check temporary
// checkForLowercasedName(declaration);
checkForUnderscoreInName(declaration);
return true;
}
Output after launch
/opt/llvm/toy_clang_plugin/build $ $LLVM_HOME/llvm_build/bin/clang ../test.m \
-Xclang -load \
-Xclang lib/Debug/ToyClangPlugin.dylib \
-Xclang -plugin \
-Xclang ToyClangPlugin
../test.m:11:15: error: Class name with `_` forbidden
@interface bad_ToyObject : NSObject
^
1 error generated.
Uncomment the first check and the output will be both an error and a warning
/opt/llvm/toy_clang_plugin/build $ $LLVM_HOME/llvm_build/bin/clang ../test.m \
-Xclang -load \
-Xclang lib/Debug/ToyClangPlugin.dylib \
-Xclang -plugin \
-Xclang ToyClangPlugin
../test.m:11:12: warning: Class name should not start with lowercase letter
@interface bad_ToyObject : NSObject
^
../test.m:11:15: error: Class name with `_` forbidden
@interface bad_ToyObject : NSObject
^
1 warning and 1 error generated.
Xcode Integration
Unfortunately, the system (by the system I mean clang from the Xcode delivery) clang does not support plugins, so you need to download Xcode a bit to use the custom compiler
Unzip this archive and run the following commands:
sudo mv HackedClang.xcplugin `xcode-select -print-path`/../PlugIns/Xcode3Core.ideplugin/Contents/SharedSupport/Developer/Library/Xcode/Plug-ins
sudo mv HackedBuildSystem.xcspec `xcode-select -print-path`/Platforms/iPhoneSimulator.platform/Developer/Library/Xcode/Specifications
These hacks will add a new compiler to Xcode and allow them to build projects for OSX and iPhoneSimulator.
After restarting Xcode, you will see the new clang in the
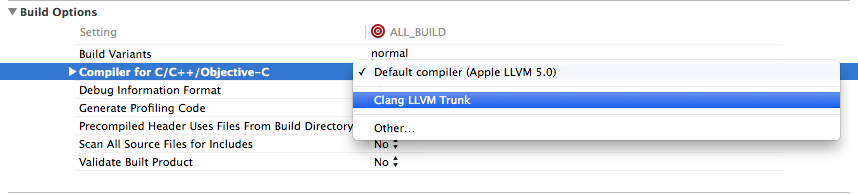
Create a new project list and select our custom clang in the 'Build settings'.
To enable the plugin you need to add the following parameters to 'Other C Flags'
-Xclang -load -Xclang /opt/llvm/toy_clang_plugin/build/lib/Debug/ToyClangPlugin.dylib -Xclang -add-plugin -Xclang ToyClangPlugin

Please note that here we use the `-add-plugin`, because we want to add our` ASTAction`, and not replace the existing one.
You also need to disable the modules for this assembly:
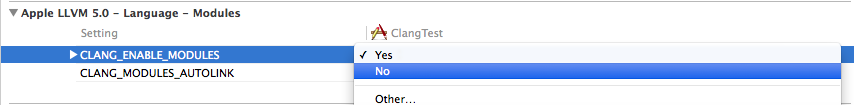
Add our `test.m` to this project or create a new class with the names matching the plugin criteria.
After assembly, you should see warnings and errors in a more familiar form:

Interactive hints
Now it’s worth adding interactive tips to fix errors and warnings.
void checkForLowercasedName(ObjCInterfaceDecl *declaration)
{
StringRef name = declaration->getName();
char c = name[0];
if (isLowercase(c)) {
std::string tempName = name;
tempName[0] = toUppercase(c);
StringRef replacement(tempName);
SourceLocation nameStart = declaration->getLocation();
SourceLocation nameEnd = nameStart.getLocWithOffset(name.size());
FixItHint fixItHint = FixItHint::CreateReplacement(SourceRange(nameStart, nameEnd), replacement);
DiagnosticsEngine &diagEngine = context->getDiagnostics();
unsigned diagID = diagEngine.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Warning, "Class name should not start with lowercase letter");
SourceLocation location = declaration->getLocation();
diagEngine.Report(location, diagID).AddFixItHint(fixItHint);
}
}
void checkForUnderscoreInName(ObjCInterfaceDecl *declaration)
{
StringRef name = declaration->getName();
size_t underscorePos = name.find('_');
if (underscorePos != StringRef::npos) {
std::string tempName = name;
std::string::iterator end_pos = std::remove(tempName.begin(), tempName.end(), '_');
tempName.erase(end_pos, tempName.end());
StringRef replacement(tempName);
SourceLocation nameStart = declaration->getLocation();
SourceLocation nameEnd = nameStart.getLocWithOffset(name.size());
FixItHint fixItHint = FixItHint::CreateReplacement(SourceRange(nameStart, nameEnd), replacement);
DiagnosticsEngine &diagEngine = context->getDiagnostics();
unsigned diagID = diagEngine.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Error, "Class name with `_` forbidden");
SourceLocation location = declaration->getLocation().getLocWithOffset(underscorePos);
diagEngine.Report(location, diagID).AddFixItHint(fixItHint);
}
}
Rebuild the plugin and run the build of the test project
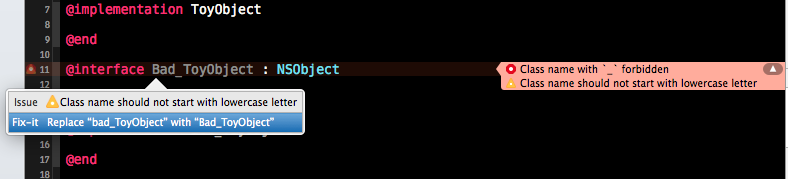

Conclusion
As you can see, creating a plugin for clang is a relatively simple task, but it requires dirty hacks with Xcode, and you need to build your own clang, so I would not recommend using a custom compiler to build applications in production. Apple provides a patched version of clang, and we cannot know what the difference is. In addition, the Clang plugin for Xcode requires a lot of effort to make it workable, which does not make it particularly usable.
There is another problem that you may encounter during development - an unstable and constantly changing API.
You can use similar plugins on your system, but please do not force other people to depend on such heavy pieces.
If you have any comments, questions or suggestions, write to twitter ,GitHub or just leave a comment here.
Happy hacking!
