Software package for automated audit of a virtual environment for errors in the security configuration

Today, many enterprises are at the epicenter of the changes caused by the fact that new data centers are blurring the boundaries between physical and virtual environments, between the public and private “cloud”. When modernizing and optimizing their data centers, organizations are faced with the need for continuously improving solutions to ensure the security of next-generation data centers.
In cloud computing, virtualization technology plays a critical role for the platform. The essence of the concept of cloud computing is to provide end users with remote dynamic access to services, computing resources and applications, including operating systems and infrastructure through various access channels. At the moment, “clouds” can be divided by the access method into two main types: Public clouds and Private clouds. Public clouds are usually provided by service providers via the Internet channel. Private clouds are organized inside large companies for internal needs in private Intranet networks. Both types of clouds can consist of thousands of servers hosted in the data center, providing tens of thousands of applications. An indispensable condition for the effective management of such a large-scale infrastructure is the most complete automation. To provide various types of users — cloud operators, service providers, IT administrators, application users — with secure access to computing resources, the cloud infrastructure should provide for the possibility of self-government and delegation of authority.
If we consider Public and Private clouds, then for most large companies that already have their own developed IT infrastructure and feel the need for a high level of confidentiality, performance and availability of their applications, it is preferable to switch to the Private Cloud. Public clouds are provided by service providers, therefore, there are concerns about the non-control of all processes hidden inside the cloud itself. These are concerns about guarantees of safety and protection of transmitted information between the cloud and the consumer of the service. And the inability to track the degree of security of the data center provider. The geographical location of the data center of the provider in relation to the consumer also affects, including the dependence on the constancy and reliability of the Internet connection, interruption of which will cause a complete stop of the service. In addition, providers of cloud computing providers set different values of the mean time between failures and data recovery time, which does not always guarantee the constant availability of the service. The problem of confidentiality and data security from the point of view of information security on the side of the service provider remains in doubt. It is this lack of control over internal processes in the Public Cloud that prompts large private companies to create their own Private clouds. In addition, the private cloud approach with the competent modernization of existing IT assets and secure communication channels allows you to switch to cloud computing gradually and at a lower cost to the company. In addition, providers of cloud computing providers set different values of the mean time between failures and data recovery time, which does not always guarantee the constant availability of the service. The problem of confidentiality and data security from the point of view of information security on the side of the service provider remains in doubt. It is this lack of control over internal processes in the Public Cloud that prompts large private companies to create their own Private clouds. In addition, the private cloud approach with the competent modernization of existing IT assets and secure communication channels allows you to switch to cloud computing gradually and at a lower cost to the company. In addition, providers of cloud computing providers set different values of the mean time between failures and data recovery time, which does not always guarantee the constant availability of the service. The problem of confidentiality and data security from the point of view of information security on the side of the service provider remains in doubt. It is this lack of control over internal processes in the Public Cloud that prompts large private companies to create their own Private clouds. In addition, the private cloud approach with the competent modernization of existing IT assets and secure communication channels allows you to switch to cloud computing gradually and at a lower cost to the company. The problem of confidentiality and data security from the point of view of information security on the side of the service provider remains in doubt. It is this lack of control over internal processes in the Public Cloud that prompts large private companies to create their own Private clouds. In addition, the private cloud approach with the competent modernization of existing IT assets and secure communication channels allows you to switch to cloud computing gradually and at a lower cost to the company. The problem of confidentiality and data security from the point of view of information security on the side of the service provider remains in doubt. It is this lack of control over internal processes in the Public Cloud that prompts large private companies to create their own Private clouds. In addition, the private cloud approach with the competent modernization of existing IT assets and secure communication channels allows you to switch to cloud computing gradually and at a lower cost to the company.
For use in large companies that already have their own developed IT infrastructure, or build it from scratch, it is worth considering one of the most dynamically developing VMware Private Clouds platforms using VMware vSphere virtualization system.
The use of virtualization software requires a significant change in approaches to ensuring information security of systems. It should be noted the emergence of a new fundamentally important object of virtual infrastructure - a hypervisor, which in practice is often ignored and not protected by specialized means (Figure 1.).
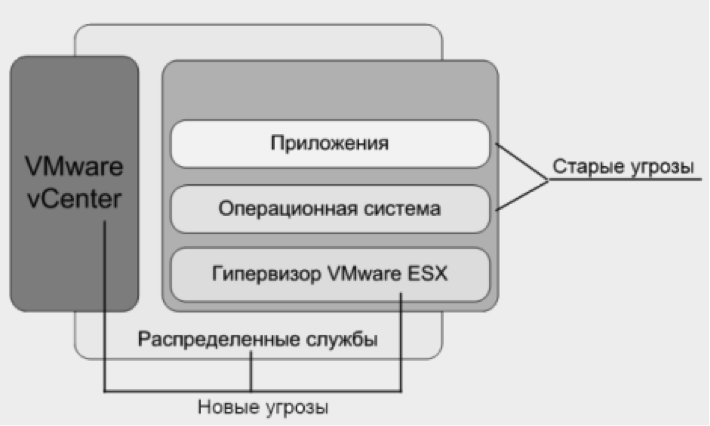
Figure 1. Old and new threats to the virtual environment
According to a Gartner study in its January 2010 press release: “By the end of 2012, 60% of virtual servers will be less secure than physical servers.” One of the main reasons for this situation, indicated in the release: “40% of virtual machines are installed without the participation of information security specialists. In Russia, this problem is supplemented by the need to comply with regulatory requirements, which are not mentioned in their governing documents on virtualization. At the enterprises in existing infrastructures, various kinds of information systems are being successfully virtualized at a fast pace, however, the methods and approaches for protecting information in this case, as a rule, are used the same as those provided for physical servers.
Virtual Infrastructure Issues
With the introduction of virtualization technologies, major changes are taking place in the physical infrastructure. From the point of view of networking, there is such a new concept as a virtual switch, which provides network interaction of virtual machines within a single virtualization host. The problem of virtual switches is that they are not controlled by intranet traffic, but also that they can listen to all network traffic between virtual machines. As a solution to the problem of listening on ports, an approach to organizing VLANs based on virtual switches is possible, where frame tagging takes place at the virtualization host level even before packets reach the physical network.
In virtual environments, unlike physical ones, where each operating system has access to its partition on a physical medium or uses a network attached storage with a dedicated logical partition, in the case of virtualization, several virtual machines are physically located in one partition in order to ensure migration and fault tolerance. Thus, having gained control of such a storage with virtual machines, an attacker gains access immediately to a group of virtual machines.
To prevent such threats in SANs, it is necessary to use zoning to provide additional protection for storage and other means of access control. In IP networks, you need to separate storage access networks physically or logically using VLANs. You should also separate public networks from networks used for migrating virtual machines, in order to avoid interception of service traffic and its subsequent analysis by an attacker.
A virtual machine is just a collection of files, so it’s easier to steal, for example, by copying to removable media. Therefore, the backup process of virtual machines should be organized using specialized software that supports encryption of the data transfer channel between the virtualization host and the backup storage, as well as encryption of the virtual machine backup files themselves.
A virtual machine is the most potentially dangerous object of a virtual infrastructure, from the point of view of information security, due to its initial complete insecurity and ease of data modification. In addition, technologies such as “live migration” and “snapshots” can serve as an excellent tool for hiding traces of the presence in the hands of an attacker. For example, an attacker, having penetrated the guest operating system of a virtual machine and having sufficient control over the virtualization host management system, can hide the traces of his stay by returning to the previous snapshot of the virtual machine disk. In addition, the theft of the virtual machine snapshot files themselves can lead to a serious information leak, since they contain all subsequent changes to the data on the virtual disk and a full snapshot of the RAM of the virtual machine from the moment the snapshot was taken. Also, one of the threats should be the possibility of intentionally seizing all the resources of a virtualization host by one virtual machine, as a result of which other virtual machines can stop their normal operation and cause a denial of service.
A separate security issue is the disk subsystem of virtual machines, which also has many vulnerabilities. The most common threats include the ability to access “old” information on the partition where the new virtual machine disk is created. Since when creating a new disk for a virtual machine, then a VM, the internal disk space becomes full as the VM itself accesses the disk sectors directly, so there is a risk that the virtual machine can access old, not yet reset sections of the partition, and then remove information from them, up to recovering fragments of files. The solution to this problem can be considered using manual zeroing of the newly created virtual disks, the so-called "eager zeroed disk".
Another problem related to the security of the disk subsystem of the virtual infrastructure may be the potentially dangerous technology of virtual machine disks, which increase as they fill up with data. Accordingly, with incorrect planning, a situation may arise when the partition on which the VM disks are stored is completely full, which is guaranteed to lead to a denial of service for all virtual machines located on the crowded storage at once.
It is known that the main server of centralized management of any virtual infrastructure is the Management Server, which is also one of the main sources of threat to infrastructure security. Having gained control of the management server, an attacker gains full access to all virtual machines, virtualization hosts, virtual networks, and data storage. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully protect the management server itself, and pay attention to the means of authentication and access rights differentiation, for which it makes sense to use additional software designed specifically for virtual infrastructures. In addition, in a virtual infrastructure, access to the virtualization server should be through a secure protocol, usually SSL, and administrators should have limited access to IP addresses. It’s also important
Virtual Infrastructure Protection Methods
The first and most important aspect of securing a virtual infrastructure is securing a hypervisor. Since, due to the compromise of the hypervisor alone, it is possible to gain control over all virtual machines under its control, and even the entire virtualization infrastructure.
As standard methods of protection, it is recommended to use specialized products for virtual environments, integrating host servers with the Active Directory directory service, using password complexity and expiration policies, standardizing access procedures to host server management tools, and using the built-in virtualization host firewall. It is also possible to disable frequently unused services such as web access to the virtualization server. Virtualization servers, like any other operating systems, also need security measures that are commonly implemented in the physical infrastructure, for example, timely and regular updating of software components.
Based on the foregoing, it is proposed to distinguish the following main types of threats to the security of virtual environments:
1. Attack on a virtual machine by:
a) attacks from another virtual machine
b) attacks on a disk and virtual machine configuration files
c) attacks on a replication network of virtual machines
d) attacks on a network and storage system containing files of a virtual machine
e) attacks on means backup copy of the virtual machine
2. The attack on the virtualization host by:
a) attacks from the physical network
b) attack means the compromised virtual infrastructure management server
c) attacks on the internal services of the hypervisor SSH, WEB, TELNET itd
d) attacks on ar Options third-party hypervisor
3. Attack on virtual infrastructure management server by:
a) attacks on the OS providing the functioning of management services
b) attacks on the DBMS of the management server
c) attacks on the database of accounts
d) network attacks on the service of interaction and monitoring with virtualization hosts
4. Attack on the resources of the virtualization host by:
a) an uncontrolled increase in the number of virtual machines
b) incorrect planning of resource pool demarcation
c) incorrect planning of VMs growing as virtual disks fill up
d) incorrect delimitation of user rights and virtual infrastructure groups.
Today, there are already specialized virtual infrastructure protection systems that can be divided into the following classes:
1. Software products for traffic analysis and intrusion prevention, designed specifically for a virtual environment (vShield Zones from VMware, VMC from Reflex)
2. Software for differentiation of access rights in virtual infrastructure (HyTrust, vGate from the Russian company "Security Code")
3 Software for auditing the virtual environment for errors in the security configuration (vWire, VMinformer).
The entire set of these tools can significantly increase the security of the virtual infrastructure, however, none of them is able to provide a comprehensive protection of the virtual environment. Therefore, it is necessary to develop and standardize a unified approach to ensuring information security in the form of regulations and standards, be sure to take into account the recommendations of the manufacturer of the virtualization platform, since it is the technological features of the platform that determine the necessary measures to ensure security.
Software package
As one of the approaches to increase the security of cloud computing, I propose a software package for conducting automated audit of a virtual environment for errors in the security configuration of VMware vSphere virtual infrastructure. This solution is in pilot development and is a Win32 application with a graphical interface. This software uses the standard VMware vSphere SDK interface to interact with the components of the VMware vSphere virtualization platform. The program receives the address of a specific VMware ESX virtualization host or the entire VMware vCenter infrastructure management server and user credentials with read permissions.
1. Enterprise level This level is designed to protect against most typical attacks on a virtual infrastructure and ensure a high level of protection of confidential information.
2. The level of the demilitarized zone (DMZ). This level provides reliable protection for hosts and virtual machines connected to the Internet.
3. Special Purpose Zone Level with Limited Functionality (SSLF). This level is designed to provide the highest possible degree of protection for the virtual infrastructure, including through the loss of certain functionality of the virtual infrastructure in favor of protection from the most sophisticated attacks.
The report is a detailed table divided by the types of threats inherent in the virtual infrastructure that I proposed above. As security tests, tracking configuration parameters of hosts, virtual machines, a management server, and others are used, based on the recommendations that I selected from the technical literature and the recommended regulations of the platform manufacturer. These recommendations are based on the technical document VMware vSphere Hardening Guide, which describes 3 levels of security for the VMware vSphere virtual infrastructure, each of these levels corresponds to more than a hundred parameters of virtualization system objects. All these parameters are accumulated and analyzed by the program engine in automatic mode and are superimposed on a previously created threat template in terms of security level.
Conclusion
As a result of the data received, the user of the program can in detail, point by point, track what level of security the analyzed virtual infrastructure corresponds to and what parameters of the system should be paid attention to bring it in line.
The software package for conducting an automated audit of a virtual environment for errors in the security configuration of a virtual infrastructure has been repeatedly applied in practice in a system integrator as part of private cloud construction projects. A detailed practical application will be considered in detail in the next article.
