Why in the presence of power need good old coal boiler in the car
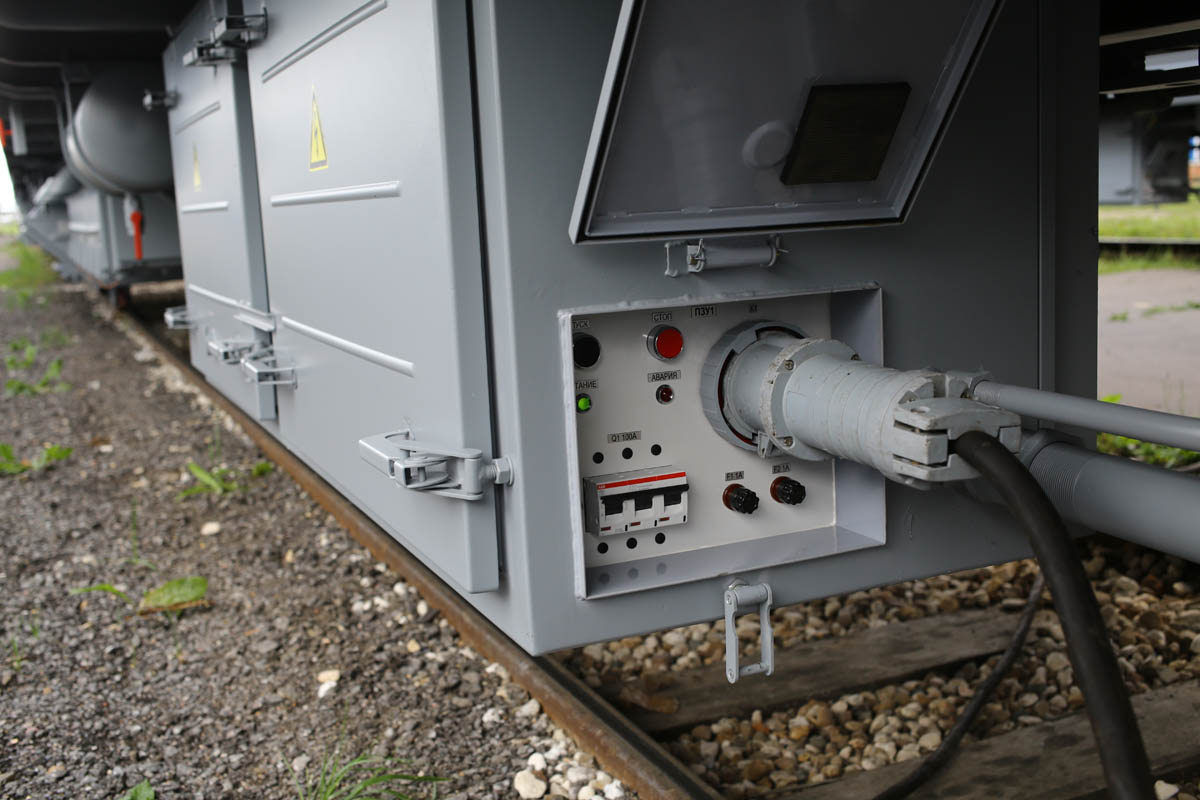

This is a power converter of a long-distance passenger car. In a modern car, electricity is needed for almost everything, starting from 5 volts in USB sockets, 220 V in sockets for passengers in each compartment and in the microwave at the conductor, 110 V for the control system. And not counting such little things as pumps, water heaters, air conditioners, disinfectants and door motors.
Without food the car does not live. At all. Even if the car battery is broken, your car will be able to use the battery of the neighboring one - this is in the energy exchange protocol (from the point of view of the second conductor, another consumer will connect to it).
And at the same time everything, even on the most modern cars, continues to put coal-fired boilers.
How is the car
In order to understand why a coal boiler is needed, let's first understand what the main subsystems of a car are. Here is the simplest case:
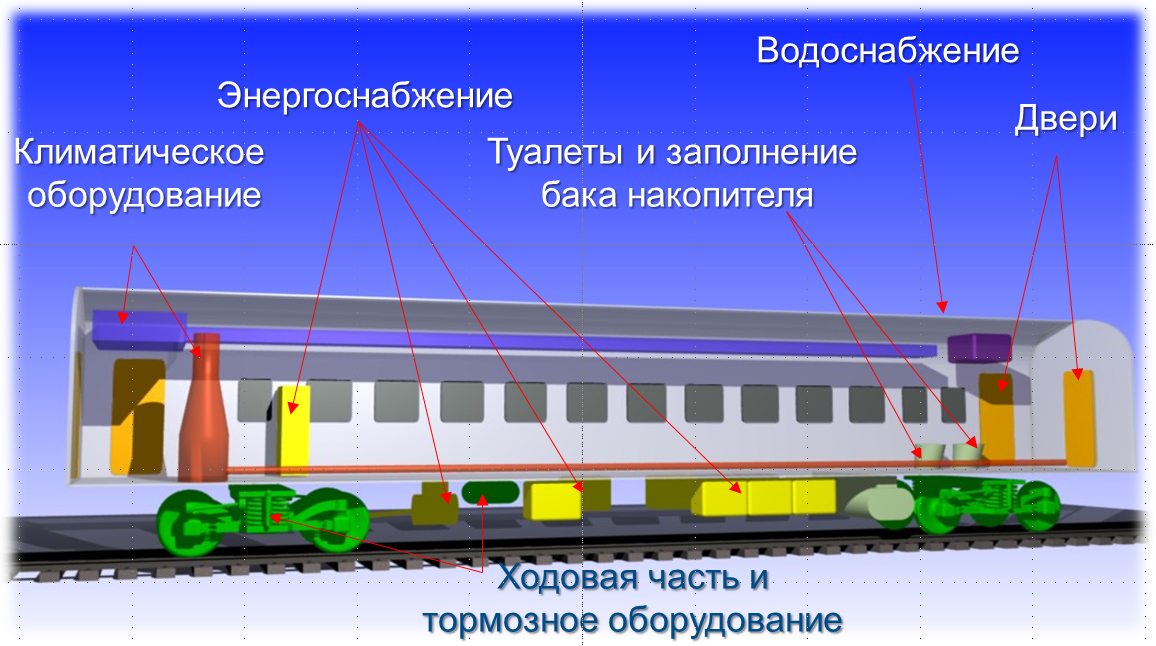
The car can cling to a diesel locomotive, an electric locomotive, or some other invention of the gloomy Russian genius. About diesel train, we have already told. There are three options to transfer electricity to the car.
On a high-voltage highway with a voltage of 3000 volts, like this:

On the “emergency” channel for powering the battery of a nearby 110-volt carriage approximately through such communications:

And also mechanically. That is, rotating its wheels. This is as elegant a solution as possible while ensuring versatility. It looks like this:

This generator, powered by the rotation of the wheelset. It is connected by a cardan with one of the wheel sets, and due to the rotation of the pair, the shaft rotates, the generator produces electricity.
Something pulls the car behind him, its wheels spin, and part of the effort is transmitted to the car generator. The generator is a standard circuit - an "inverted" electric motor.
Cardan can be manually disconnected. This is necessary in case something gets stuck in the generator and it will work as a brake. In this case, the safety clutch is triggered and the generator starts to rotate idle. Disconnecting the universal joint is an emergency case of mechanical damage. In the case of higher-level failures, the fuse is triggered and the generator starts to idle.
Differences between autonomous cars and cars with a highway
A car with such a generator obviously rolls a little worse (with greater effort) than a car without a generator. Because the work of this generator is spent mechanical energy. From the point of view of the fact that this car pulls, the autonomous model is more “rough” than without generation. This means large losses, for example, fuel. Which is quite logical.
On the other hand, autonomous cars are universal and can be part of any train. They have full backward compatibility with even locomotives (the very ones that are steamed, which stand in the form of exhibits at train stations) - if you attach them to this, you will get a mobile steam power station.
All cars are equipped with a high-voltage line (for heating). Not at all it is used to power their own needs of the car - then put the generator. The reason is that modern cars are made with a backlash-free coupling and hermetic inter-car junction, and the old coupling is an “accordion” (through which some hares are “rubberized”, and not always surviving in the process) geometrically incompatible with the new standards. The backlash-free hitch and hermetic inter-car junction are different generations of wagons. As a result, we have two standards, and everything goes to the fact that the hermetic hitch will win.
Naturally, which car to choose and order, the carrier decides.
Battery
For obvious reasons, the energy is not supplied at the stations and up to the speed of 35 km / h from the generator. Therefore, you need a battery.
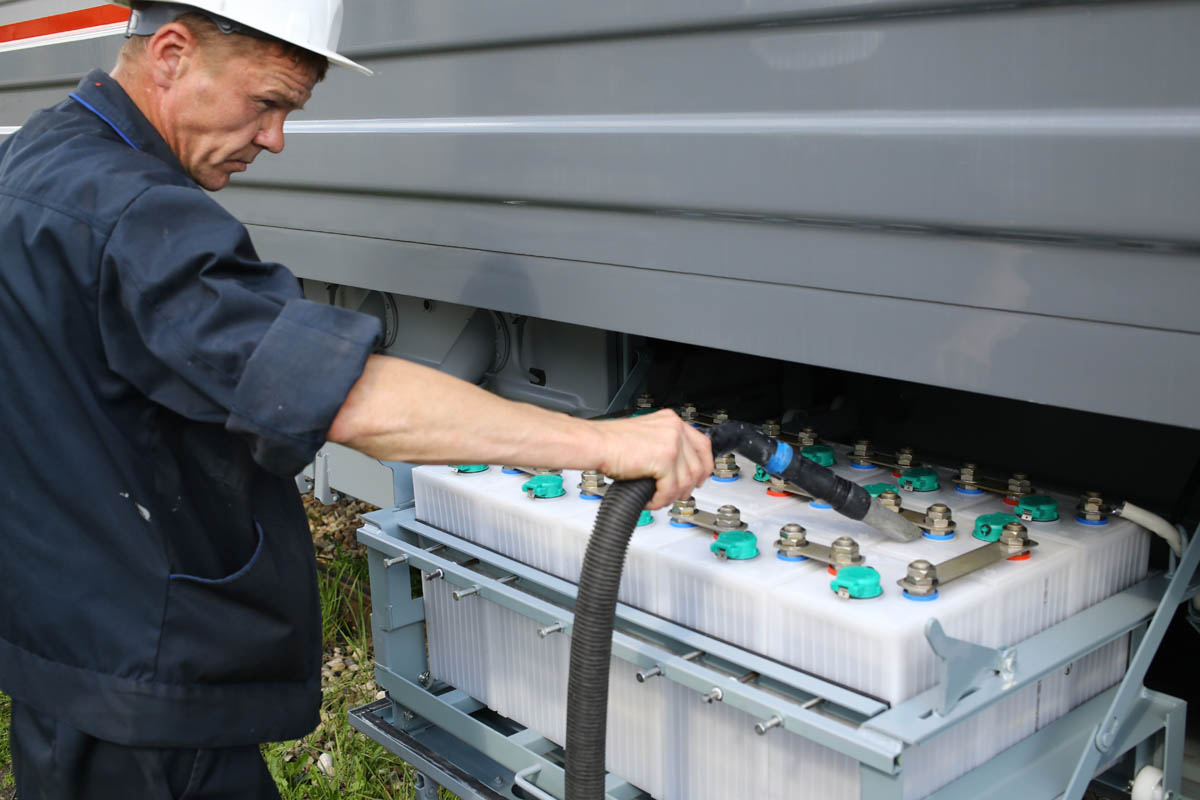

The battery is mounted in an explosion-proof box (if something goes wrong, the box wall will shoot off and the blast wave will go outside of the train, which will quickly and relatively safely extinguish it). Here is the same compartment on a double-decker car:
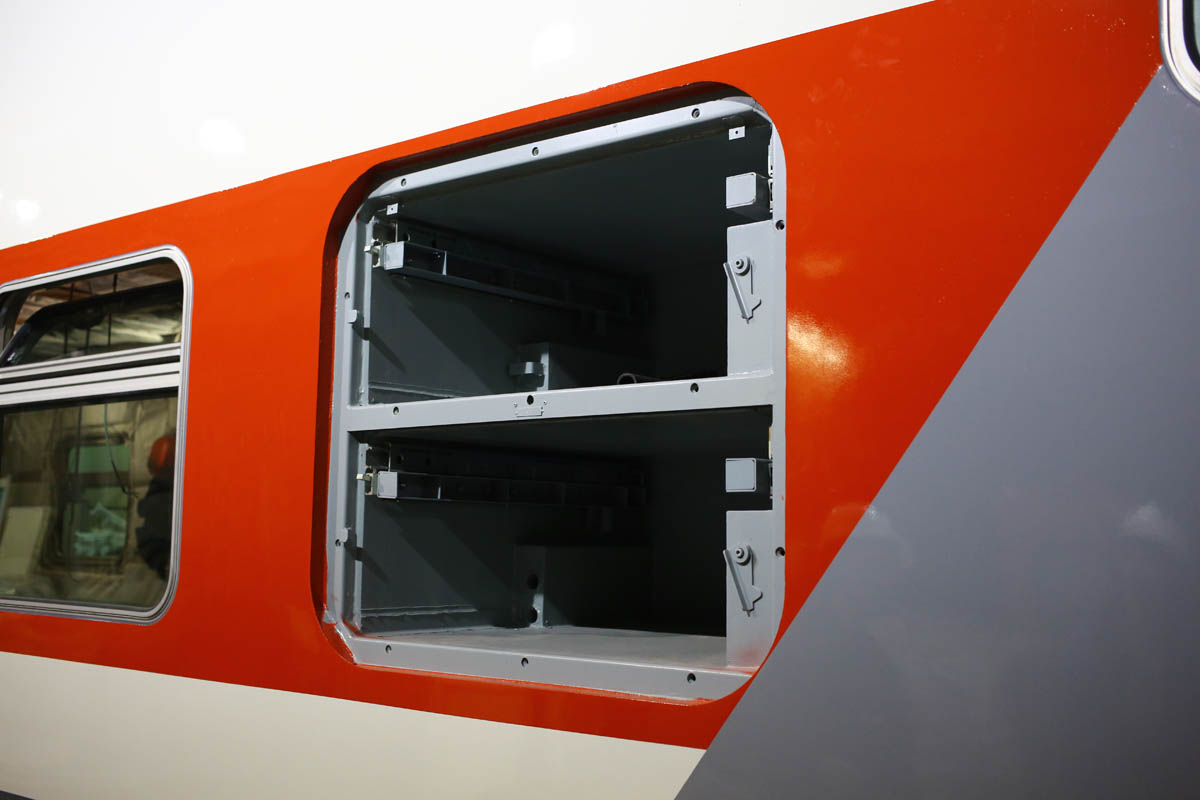

The voltage of the car’s electrical system is 110 volts. Batteries are placed both acidic and alkaline - the customer chooses different batteries by region of operation.
The period of more or less normal battery life is 5-7 years in good conditions. In practice, there are situations of deep discharge without the possibility of restoring the battery - for example, when the car was left in the field in the cold and did not touch for some time. The battery goes into a critical category, that's all.
PSN
Another box under the single-story car is PSN (own needs converter).
This device, which controls all sources of energy of the car at the entrance and distributes to all devices of the car the desired current to their inputs. Including these sockets: By the

way, the guides say that the especially thoughtful citizens already carry with them a half-kilowatt teapots. And nothing, the network stands. But this is extreme already, because the allowable power of the sockets in the coupe is 100 watts. More is a gross violation of operating conditions.
Voltage 110 Volt car network walks in the range from 100 to 144 Volts, and this is a normal situation. Previously, the conductor was a voltmeter and it was visible real voltage. Now the switch voltmeter is hidden under the touch screen panel, and on the screen you can see the monitoring data in the picture with a breakdown into subsystems: it is better to look at dozens of indicators, but earlier they were guided by experience and a voltmeter.
All onboard devices (including a water cooler, which instead of titanium in modern cars) are designed for this voltage range.
PSN also controls the charge of the battery. One of the most important parts of the car's electronics is the organization of the correct charging mode (in particular, there is a sensor in the battery box and the mode is selected depending on the temperature).
So why the boiler?
Cars in Russia are designed for the range from –50 to +50 degrees. These are exactly what the Tver Carriage Works manufactures for the customer (all photos in the post from the workshops). To operate the car in conditions of -50 degrees, you need a heating system. And it requires a lot of energy. If there is a high-voltage circuit and there is voltage on it, the water heater is powered by electricity.
If the train moves along the non-electrified section of the railway and there is no powerful generator somewhere in the train (when they are, these are special cases), then you need to take additional energy for heating somewhere.
It is produced chemically - simply by burning wood and coal.
And here is how TVELs are loaded:
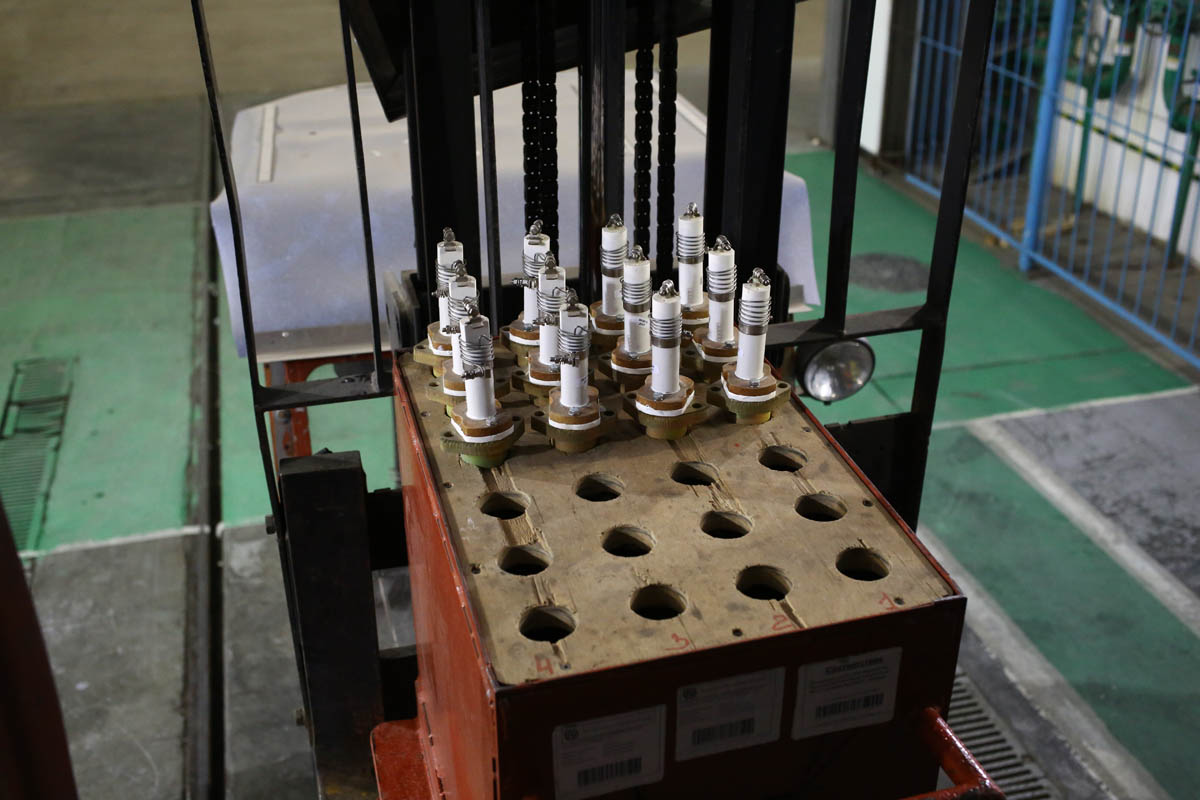

In fact, these are, of course, heaters, which are mounted in the base of the boiler.
In double-deck cars of the boiler and titanium is not, as well as water heating. Only electrics. In double-decker cars, centralized supply is everywhere: there is no 3000 Volt, the car can only work on critical systems at 110 Volts from the neighboring one. But they are allowed only along routes where there is complete electrification of the way, so there are no problems.
That's all. Yes, we are now talking about long-distance passenger carriage. In the metro cars and electric cars, another heating system can be installed - with a separate water circuit and electric air heaters or without a water circuit at all.
