Some features of using virtual machines for beginners
Virtual machines, such as Virtualbox, are used to emulate virtual hardware and run multiple operating systems on a computer. The better your CPU will be and the more RAM you have, the faster the virtual machines will run on your computer.
I offer some tips to help you save time when setting up virtual machines for the first time. This will be useful for working with virtual machines VirtualBox, VMware, Parallels, or any other.
After installing the guest operating system in the virtual machine, the first thing to do is install the virtual machine software - “Guest OS Additions for VirtualBox” or VMware Tools for VMware. These packages include special drivers that will help your guest operating system run faster using the hardware of your main machine.
Installing the package is simple - in VirtualBox, after loading the guest operating system, click the Devices menu button and select “Install Guest Additions.” If you use for VMware, select “Install VMware Tools" from the Virtual Machine menu. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation - if you use Windows as a guest operating system, it will be similar to installing any other application.

Make sure you have the latest version of Guest Additions - if you see a notification that an update is available for Guest Additions or VMware Tools, you must install it.
When creating a virtual machine, you can create two different types of virtual disks. By default, the program usually suggests using dynamically allocated disks that grow, along with the occupied space of the guest OS.
For example, if you create a new virtual machine with a dynamically allocated disk with a maximum size of 30 GB, it will not take up to 30 GB of hard disk space immediately. After installing the operating system and programs, the disk can only take up to 10 GB. As you add files to the virtual disk, it will expand to a maximum size of 30 GB.
This can be convenient - each virtual machine will not take up unreasonably much space on your hard drive. However, this is slower than creating a fixed disk size (disk with pre-allocated space). When creating a fixed disk size, all 30 GB will be taken immediately on your computer.
There is a trade-off - a fixed disk size takes up more space on your hard drive, but works with a virtual hard drive faster. You will also get rid of file fragmentation - the space will be occupied by a large block instead of adding smaller pieces throughout the disk.

Your antivirus can scan virtual machine files when they are accessed, reducing performance. Anti-Virus will not be able to detect a virus inside a virtual machine running on your guest operating system, so this check only harms.
To speed up the process, you can add your virtual machine directory to the antivirus author's exclusion list. Once it is listed, your antivirus will ignore all files in this directory.
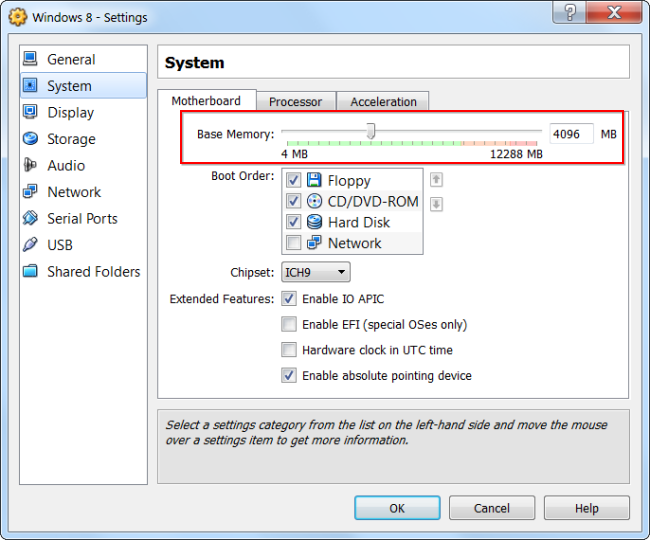
Virtual machines love a lot of virtual memory. Microsoft recommends 2 GB of RAM for 64-bit Windows 7, and this recommendation applies to Windows 7 x32 when it is running in a virtual machine. If you are running large applications in a virtual machine, you can allocate more than 2 GB of RAM.
You can allocate more RAM in the settings dialog of your virtual machine (the virtual machine must be turned off to do this). If your computer does not have enough memory to work comfortably with the virtual machine, you may notice a very large decrease in computer performance when using the swap file on the hard disk.
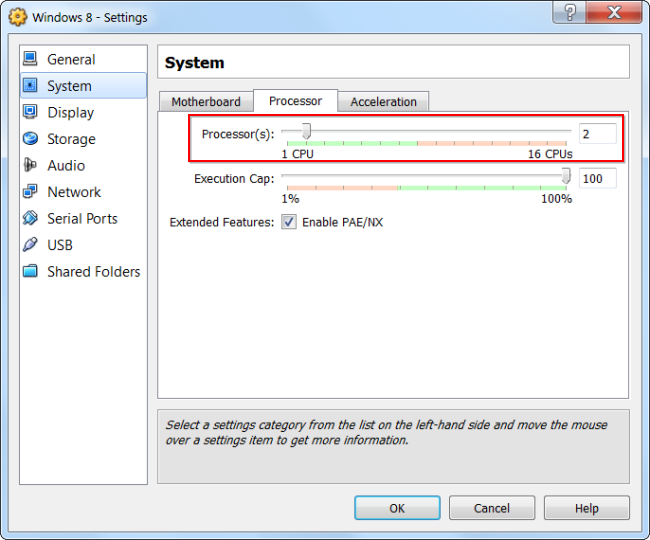
If you have a computer with several processors or cores, you can select additional processors for your virtual machine from the VM settings window. A VM with a dual-core (or quad-core) processor will respond more quickly.
If you intend to install an OS of the MS-Windows family in the future so that you can use more kernels during installation, specify 2 kernels in order to install the correct HAL, after installation you can turn off the machine and put 1 default kernel for everyday use. But for the future, you can always add kernels without uninstalling the OS. Linux VM can dynamically detect any number of cores when booting the OS.
Fine tuning the video settings and allocating more video memory will also help improve the speed of your virtual machine. For example, enabling the 2D acceleration feature in VirtualBox improves video playback in virtual machines; enabling 3D acceleration allows you to use some 3D applications.

By and large, you need to minimize the use of 3D, for example, Windows 7 - by disabling Aero.
Intel VT-x and AMD-V are special processor extensions that improve virtualization speed. Newer Intel and AMD processors typically include these features. However, some computers do not automatically turn on VT-x or AMD-V - you will have to enable this option in your computer's BIOS.
To determine if your Intel processor supports the Intel VT extension, use utilities that display system information. If your processor supports this function, but the option is not available in your virtual machine, you must enable this function in the BIOS of your computer. This option is usually enabled by default on motherboards with AMD processors.

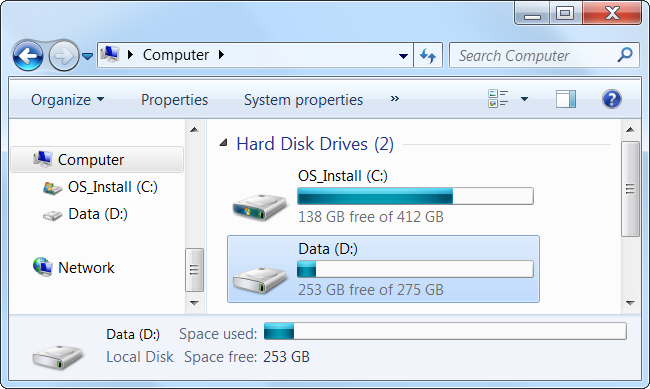
Disk performance can limit the speed of your virtual machine. Placing virtual machine files on a separate physical disk or not on a system disk can improve performance. Your virtual machine and system will not competitively read and write from the same drive.
However, you should not start the virtual machine from an external drive (USB) - it will be much slower.
I offer some tips to help you save time when setting up virtual machines for the first time. This will be useful for working with virtual machines VirtualBox, VMware, Parallels, or any other.

Be sure to install VirtualBox or VMware Tools add-ons.
After installing the guest operating system in the virtual machine, the first thing to do is install the virtual machine software - “Guest OS Additions for VirtualBox” or VMware Tools for VMware. These packages include special drivers that will help your guest operating system run faster using the hardware of your main machine.
Installing the package is simple - in VirtualBox, after loading the guest operating system, click the Devices menu button and select “Install Guest Additions.” If you use for VMware, select “Install VMware Tools" from the Virtual Machine menu. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation - if you use Windows as a guest operating system, it will be similar to installing any other application.

Make sure you have the latest version of Guest Additions - if you see a notification that an update is available for Guest Additions or VMware Tools, you must install it.
Create a fixed disk size during initial setup
When creating a virtual machine, you can create two different types of virtual disks. By default, the program usually suggests using dynamically allocated disks that grow, along with the occupied space of the guest OS.
For example, if you create a new virtual machine with a dynamically allocated disk with a maximum size of 30 GB, it will not take up to 30 GB of hard disk space immediately. After installing the operating system and programs, the disk can only take up to 10 GB. As you add files to the virtual disk, it will expand to a maximum size of 30 GB.
This can be convenient - each virtual machine will not take up unreasonably much space on your hard drive. However, this is slower than creating a fixed disk size (disk with pre-allocated space). When creating a fixed disk size, all 30 GB will be taken immediately on your computer.
There is a trade-off - a fixed disk size takes up more space on your hard drive, but works with a virtual hard drive faster. You will also get rid of file fragmentation - the space will be occupied by a large block instead of adding smaller pieces throughout the disk.

Exclude the catalog of virtual machines in your antivirus
Your antivirus can scan virtual machine files when they are accessed, reducing performance. Anti-Virus will not be able to detect a virus inside a virtual machine running on your guest operating system, so this check only harms.
To speed up the process, you can add your virtual machine directory to the antivirus author's exclusion list. Once it is listed, your antivirus will ignore all files in this directory.

Allocate more memory.
Virtual machines love a lot of virtual memory. Microsoft recommends 2 GB of RAM for 64-bit Windows 7, and this recommendation applies to Windows 7 x32 when it is running in a virtual machine. If you are running large applications in a virtual machine, you can allocate more than 2 GB of RAM.
You can allocate more RAM in the settings dialog of your virtual machine (the virtual machine must be turned off to do this). If your computer does not have enough memory to work comfortably with the virtual machine, you may notice a very large decrease in computer performance when using the swap file on the hard disk.

Highlight more processors
If you have a computer with several processors or cores, you can select additional processors for your virtual machine from the VM settings window. A VM with a dual-core (or quad-core) processor will respond more quickly.
If you intend to install an OS of the MS-Windows family in the future so that you can use more kernels during installation, specify 2 kernels in order to install the correct HAL, after installation you can turn off the machine and put 1 default kernel for everyday use. But for the future, you can always add kernels without uninstalling the OS. Linux VM can dynamically detect any number of cores when booting the OS.

Set video options
Fine tuning the video settings and allocating more video memory will also help improve the speed of your virtual machine. For example, enabling the 2D acceleration feature in VirtualBox improves video playback in virtual machines; enabling 3D acceleration allows you to use some 3D applications.

By and large, you need to minimize the use of 3D, for example, Windows 7 - by disabling Aero.
Verify that Intel VT-x or AMD-V features are enabled
Intel VT-x and AMD-V are special processor extensions that improve virtualization speed. Newer Intel and AMD processors typically include these features. However, some computers do not automatically turn on VT-x or AMD-V - you will have to enable this option in your computer's BIOS.
To determine if your Intel processor supports the Intel VT extension, use utilities that display system information. If your processor supports this function, but the option is not available in your virtual machine, you must enable this function in the BIOS of your computer. This option is usually enabled by default on motherboards with AMD processors.

Place the virtual machine files on another drive
Disk performance can limit the speed of your virtual machine. Placing virtual machine files on a separate physical disk or not on a system disk can improve performance. Your virtual machine and system will not competitively read and write from the same drive.

However, you should not start the virtual machine from an external drive (USB) - it will be much slower.
Some more useful tips
- Allocating additional processors is rarely a good idea. Use 1 CPU for desktop OS.
- Try not to use graphical hypervisors for server OS.
- Do not allocate to working VMs More cores than there are on your computer.
