Phased Array Antennas
On a habr already there is an article devoted to antennas. Continuing the topic, I want to tell the habitation community about the principles of operation of phased antenna arrays (PAR). HEADLIGHTS are widely used in radar systems, missile defense, space communications; application in civilian objects (commercial) is complicated by the complexity of manufacturing and high cost. Perhaps someone will be interested in the subject and come up with an effective use of the PAR for commercial use.
A PAR is a group of emitters (phase shifters, PV), in which the relative phases of the signals change in a complex manner according to a certain law so that the effective radiation of the PAR is amplified in the desired direction and is suppressed in all others. PAR is a matrix where the PV is the element of the matrix, but of course PV in space can have other configurations. Figure 1 shows the radar of the Ginger sector survey, which is part of the S300V anti-aircraft missile system. You can see both the headlamp and the irradiating horn.

Picture 1.
There is a simple formula from the physics course: V = c / sqrt (mu * eps). In this formula, V is the phase velocity of the electromagnetic wave, c is the speed of light in vacuum, mu is the magnetic constant, eps is the dielectric constant. It can be seen from this formula that the phase velocity depends on mu and epsilon, and by changing these values we can introduce an EM wave delay through the PV. Therefore, PVs can be ferrite (we can change their magnetic permeability) and ferroelectric (we can change their dielectric constant). Power to the phase shifters is carried out through the air path (as in Fig. 1) or through waveguides (for example, in small-sized anti-aircraft missile systems, Fig. 2).

Figure 2. SAM "Tor".
PAR scheme in Fig. 4 [1]: the antenna is a line of radiators, PV is included between the power separator and the radiators. Ferrite PV is a cylindrical analog ferrite on which control windings are wound. By changing the current in the control windings (set by the PV control unit), the magnetic permeability and, accordingly, the phase velocity of the EM wave in the PV change. Thus, by sequentially changing the level of the control signal in the windings, the process of wavefront formation can be presented as shown in Figure 3, 4 (one-dimensional case). You can draw an analogy with pebbles, which are successively thrown into water. Another analogy of the operation of the PAR can be a lens. Figure 5 shows the change in the wavefront shape using a lens [4].
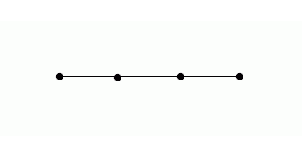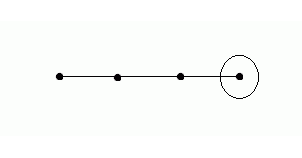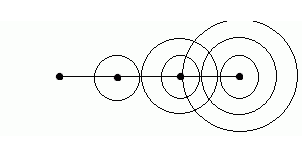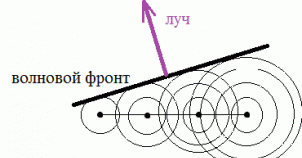
Figure 3. Wavefront formation.
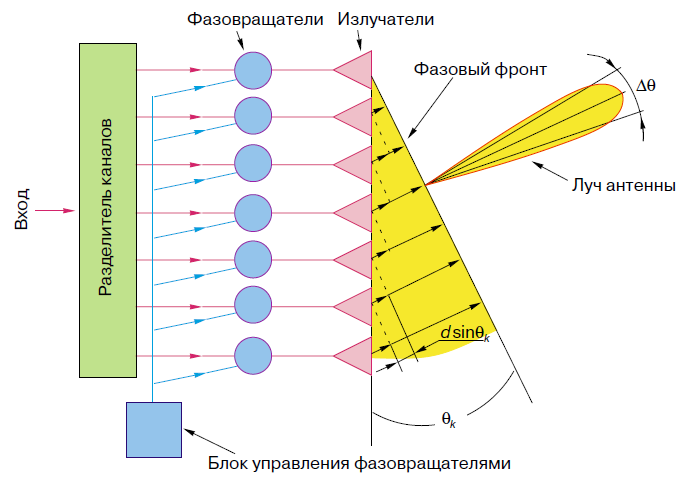
Figure 4. PAR scheme.
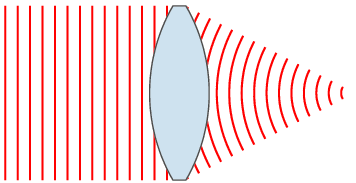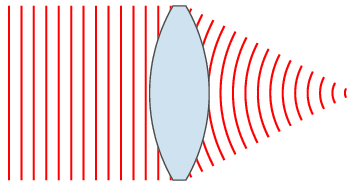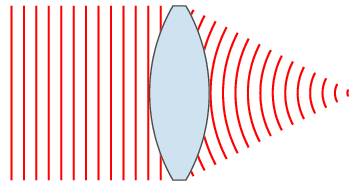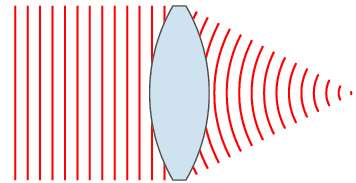
Figure 5.
The main beam is perpendicular to the phase front. It can be seen from the radiation pattern (Fig. 6) that, in addition to the main beam, there are backward and side lobes, which are parasitic and a decrease in their level is a matter of EM field distribution in the lattice aperture. The change in the position of the beam in space occurs electrically (almost inertialessly) - it is this quality that is especially important.

Figure 6. Typical radiation pattern.
Electric scanning provides the creation of a variety of phase shifts throughout the opening and a significant rate of change of these shifts with relatively small power losses. The operation of the phase shifters is controlled by a high-speed electronic system, which in the simplest cases controls groups of elements (for example, rows and columns in flat headlights with a rectangular arrangement of emitters), and in the most complex ones, each phase shifter individually. The beam can be swung in space both according to a predetermined law, and according to a program developed during the operation of the entire radio device, which includes the PAR (2, 3).
Figures for the article can be found in the indicated literature, except for Figure 3. For a more detailed acquaintance with the phased arrays and their management, I can recommend the book by Samoilenko and Shishov, "Management of phased antenna arrays."
1. O. G. Wendik, “Phased antenna array - the eyes of the radio system”, 1997
2. ru.wikipedia.org/wiki Phased antenna array
3. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phased_array
4. ru.wikipedia.org/ wiki / Lens
What is it?
A PAR is a group of emitters (phase shifters, PV), in which the relative phases of the signals change in a complex manner according to a certain law so that the effective radiation of the PAR is amplified in the desired direction and is suppressed in all others. PAR is a matrix where the PV is the element of the matrix, but of course PV in space can have other configurations. Figure 1 shows the radar of the Ginger sector survey, which is part of the S300V anti-aircraft missile system. You can see both the headlamp and the irradiating horn.

Picture 1.
How does phasing happen?
There is a simple formula from the physics course: V = c / sqrt (mu * eps). In this formula, V is the phase velocity of the electromagnetic wave, c is the speed of light in vacuum, mu is the magnetic constant, eps is the dielectric constant. It can be seen from this formula that the phase velocity depends on mu and epsilon, and by changing these values we can introduce an EM wave delay through the PV. Therefore, PVs can be ferrite (we can change their magnetic permeability) and ferroelectric (we can change their dielectric constant). Power to the phase shifters is carried out through the air path (as in Fig. 1) or through waveguides (for example, in small-sized anti-aircraft missile systems, Fig. 2).

Figure 2. SAM "Tor".
PAR scheme in Fig. 4 [1]: the antenna is a line of radiators, PV is included between the power separator and the radiators. Ferrite PV is a cylindrical analog ferrite on which control windings are wound. By changing the current in the control windings (set by the PV control unit), the magnetic permeability and, accordingly, the phase velocity of the EM wave in the PV change. Thus, by sequentially changing the level of the control signal in the windings, the process of wavefront formation can be presented as shown in Figure 3, 4 (one-dimensional case). You can draw an analogy with pebbles, which are successively thrown into water. Another analogy of the operation of the PAR can be a lens. Figure 5 shows the change in the wavefront shape using a lens [4].

Figure 3. Wavefront formation.

Figure 4. PAR scheme.

Figure 5.
The main beam is perpendicular to the phase front. It can be seen from the radiation pattern (Fig. 6) that, in addition to the main beam, there are backward and side lobes, which are parasitic and a decrease in their level is a matter of EM field distribution in the lattice aperture. The change in the position of the beam in space occurs electrically (almost inertialessly) - it is this quality that is especially important.
Figure 6. Typical radiation pattern.
Electric scanning provides the creation of a variety of phase shifts throughout the opening and a significant rate of change of these shifts with relatively small power losses. The operation of the phase shifters is controlled by a high-speed electronic system, which in the simplest cases controls groups of elements (for example, rows and columns in flat headlights with a rectangular arrangement of emitters), and in the most complex ones, each phase shifter individually. The beam can be swung in space both according to a predetermined law, and according to a program developed during the operation of the entire radio device, which includes the PAR (2, 3).
Figures for the article can be found in the indicated literature, except for Figure 3. For a more detailed acquaintance with the phased arrays and their management, I can recommend the book by Samoilenko and Shishov, "Management of phased antenna arrays."
Literature:
1. O. G. Wendik, “Phased antenna array - the eyes of the radio system”, 1997
2. ru.wikipedia.org/wiki Phased antenna array
3. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phased_array
4. ru.wikipedia.org/ wiki / Lens
