Overview and Configuration of Deduplication Tools in Windows Server 2012
Good day to all!
Today I would like to review such an interesting new feature in Windows Server 2012 as data deduplication. The feature is extremely interesting, but first you need to figure out how much it is needed ...
Every year (if not by day), the volume of hard drives is growing, and at the same time, the media themselves are becoming cheaper.
Based on this trend, the question arises: "Is data deduplication necessary at all?"
However, if you and I live in our universe and on our planet, then almost everything in this world has the property to obey Newton's 3rd law. The analogy may not be completely transparent, but I’m leading to the fact that no matter how cheap the disk systems and the disks themselves are, how much the media itself does not increase — the requirements from the business point of view for the space available for storing data are constantly growing and thereby offset the increase volume and price drop.
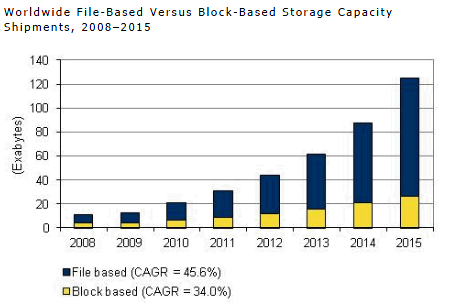
According to IDC forecasts, approximately 90 million terabytes will be required in the total volume in about a year. The volume, frankly, is not small.
And here it is just the question of data deduplication very much becomes relevant. After all, the data that we use are of different types, and their purpose can be different - somewhere it is production data, somewhere it is archives and backups, and somewhere it is streaming data - I specially cited such examples, since in the first case the effect of using deduplication will be average, in archive data it will be maximum, and in the case of streaming data it will be minimal. But still we can save space, especially since deduplication is now the lot of not only specialized storage systems, but also a component, a feature of the Windows Server 2012 server operating system.
Before moving on to an overview of the deduplication mechanism in Windows Server 2012 , let's look at what types of deduplication happen. I propose to start from top to bottom, in my opinion it will be more visual.
1) File deduplication - like any deduplication mechanism, the operation of the algorithm comes down to finding unique sets of data and repeating ones, where the second types of sets are replaced by links to the first sets. In other words, the algorithm tries to store only unique data, replacing duplicate data with unique links. As you can guess from the name of this type of deduplication - all such operations occur at the file level. If you recall the history of Microsoft products - then this approach has been repeatedly applied earlier - in Microsoft Exchange Serverand Microsoft System Center Data Protection Manager - and this mechanism was called SIS (Single Instance Storage). In the products of the Exchange line, it was abandoned at the time for performance reasons, but in Data Protection Manager this mechanism is still successfully used and it seems it will continue to do so. As you might guess, the file level is the highest (if you recall the device storage systems in general) - and therefore the effect will be the most minimal compared to other types of deduplication. Scope - this type of deduplication is mainly applied to archive data.
2) Block deduplication- this mechanism is already more interesting, since it works at the sub-file level - namely, at the level of data blocks. This type of deduplication, as a rule, is typical for industrial storage systems, and it is this type of deduplication that is used in Windows Server 2012. The mechanisms are the same as before - but at the block level (it seems, I already said that, right?). Here, the scope of deduplication is expanding and now extends not only to archive data, but also to virtualized environments, which is quite logical - especially for VDI scripts. If we take into account that VDI is a whole bunch of repeating images of virtual machines in which there are still differences from each other (that's why file deduplication is powerless here) - then block deduplication is our choice!
3) Bit deduplication- the lowest (deepest) type of data deduplication - has the highest degree of efficiency, but is also a leader in terms of resource intensity. It is understandable - to analyze data for uniqueness and plagiarism is not an easy process. Honestly, I personally do not know the storage systems that operate at this level of deduplication, but I know for sure that there are traffic deduplication systems that operate at the bit level, let’s say the same Citrix NetScaler. The meaning of such systems and applications is to save transmitted traffic - this is very critical for scenarios with geographically distributed organizations, where there are many geographically dispersed branches of the enterprise,
Microsoft’s report on USENIX 2012 , which took place in Boston in June, looks very interesting in this regard . A fairly large-scale analysis of the primary data was carried out in terms of the application of block deduplication mechanisms to them in WIndows Server 2012 - I recommend that you familiarize yourself with this material.
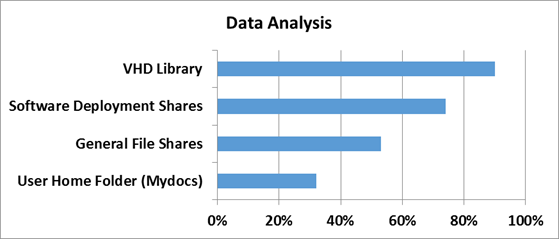
In order to understand how effective deduplication technologies are in Windows Server 2012, you first need to determine on what type of data this very effectiveness should be measured. Typical file balls, user documents from the “My Documents” folder, distribution storages and libraries, and virtual hard disk storages were taken as standards.
How effective deduplication is in terms of workloads was tested at Microsoft in the software development department.
The 3 most popular scenarios have become the objects of research:
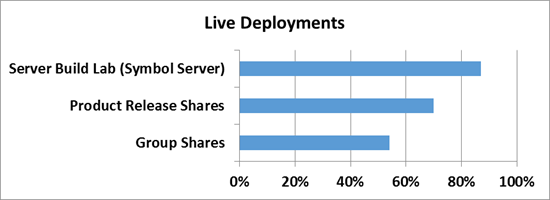
1) Build build servers - in MS every day a decent amount of builds of various products is collected. Not even a significant change in the code leads to the build process of the build - and therefore a lot of duplicate data is created
2) Balls with product distributions for release - As you might guess, all assemblies and ready-made software versions need to be placed somewhere - inside Microsoft there are special servers for this, where all versions and language editions of all products are placed - this is also a fairly effective scenario, where the effectiveness of deduplication can reach up to 70%.
3) Group balls - a combination of a ball with documents and files of developers, as well as their roaming profiles and redirected folders, which are stored in a single central space.
And now the most interesting part - below is a screenshot of the volumes in Windows Server 2012 that host all this data.
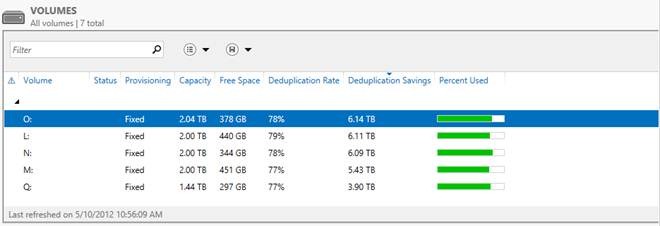
I think the words here will be superfluous - and everything is already very clear. 6TB savings on 2TB media - thermonuclear storage? Not so dangerous - but so effective!
Now let's look at the main features of deduplication in Windows Server 2012.
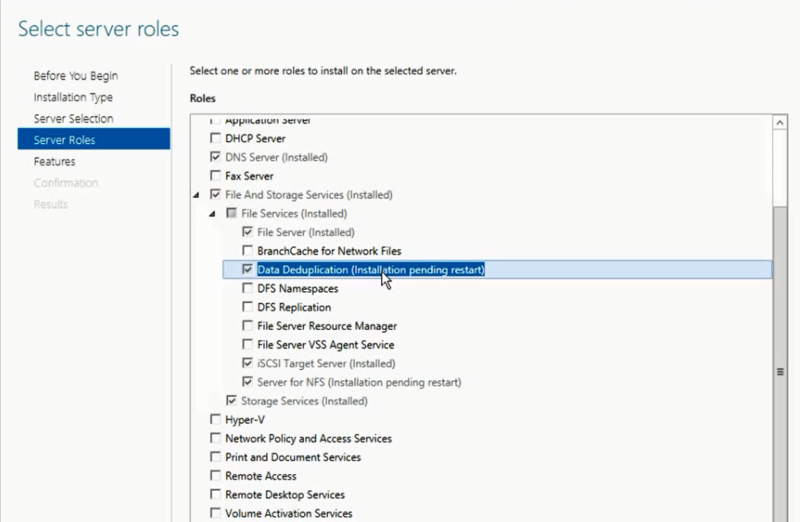
1) Transparency and ease of use - setting up deduplication is extremely simple. First, in the role wizard on Windows Server, you expand the File and Storage Services role, then File and iSCSI Services - and there you turn on the Data Deduplication option.
After that, in Server Manager, you select Fike and Storage Services, right-click - and there you select the option “Enable Volume Deduplication”. Special link for PowerShell lovers. Everything is extremely simple. From the point of view of the end user and applications, access and work with data are transparent and invisible. If we talk about deduplication from the point of view of the file system, then only NTFS is supported. ReFS cannot be deduplicated, just like volumes are protected using EFS (Encrypted Fike System). Also, files less than 32 KB and files with extended attributes do not fall under deduplication. Deduplication, however, applies to dynamic volumes, volumes encrypted using BitLocker, but does not apply to CSV volumes, as well as system volumes (which is logical).
2) Optimization for the main data - it should be noted right away that deduplication is not an online process. Files that reach a certain level of old age in terms of policy are deduplicated. After reaching a certain shelf life, data begins to go through the deduplication process - by default this period of time is 5 days, but no one bothers you to change this parameter - but be reasonable in your experiments!
3) Planning of optimization processes - a mechanism that checks files every hour for compliance with deduplication parameters and adds them to the schedule.
4) Mechanisms for excluding objects from the deduplication area - this mechanism allows you to exclude files from the deduplication area by their type (JPG, MOV, AVI - as an example, this is streaming data - what is least deduplicated - if at all). You can also exclude immediately entire folders with files from the deduplication area (this is for lovers of German films who have their darkness and darkness).
5) Mobility - a deduplicated volume is an integral object - it can be transferred from one server to another (we are talking exclusively about Windows Server 2012). At the same time, you can easily access your data and can continue to work with them. All that is needed is the included Data Deduplication option on the target server.
6) Optimization of resource consumption - these mechanisms imply optimization of algorithms to reduce the load on read / write operations, so if we are talking about the size of the hash index of data blocks, then the size of the index per 1 data block is 6 bytes. Thus, you can even apply deduplication to very massive datasets.
Also, the algorithm always checks if there are enough memory resources to conduct the deduplication process - if the answer is no, then the algorithm will postpone the process until the necessary amount of resources is released.
7) Integration with BranchCache - indexing mechanisms for deduplication are also common for BranchCache - therefore, the effectiveness of using these technologies in conjunction is beyond doubt!
The reliability question arises extremely sharply for deduplicated data - imagine that a data block that at least 1000 files depend on is hopelessly damaged ... I think validol-e-e-service will then come in handy, but not in our case.
1) Backup - Windows Server 2012, like System Center Data Protection Manager 2012 SP1, fully supports deduplicated volumes in terms of backup processes. A special API is also available that allows third-party developers to use and support deduplication mechanisms, as well as restore data from deduplicated archives.
2) Additional copies for critical data - the data that has the most frequent access parameter is carried out by the process of creating additional backup blocks - these are the features of the mechanism algorithm. Also, in the case of using Storage Spaces mechanisms, when a bad block is found, the algorithm automatically replaces it with an integral one from a pair in the mirror.
3) By default, once a week, the process of finding garbage and bad blocks is started, which corrects the data of the acquired pathology. There is also the opportunity to manually start this process at a deeper level. If the default process corrects errors that were recorded in the event log, then a deeper process involves scanning the entire volume.
Before turning on deduplication, a normal person will always think of how effective this mechanism will be in his particular case. You can use the Deduplication Data Evaluation Tool for this .
After installing deduplication, you can find a tool called DDPEval.exe , which is located in \ Windows \ System32 \ - this utility can be ported to removable media or another volume. Supported OS Windows 7 and higher. So you can analyze your data and understand the value of sheep skin. (smile).
This concludes my review. I hope you were interested. If you have any questions - you can feel free to find me on social networks - VKontakte, Facebook - by name and surname - and I will try to help you.
For those who want to learn about new features in Windows Server 2012, as well as System Center 2012 SP1 - I invite everyone to visit IT Camp - November 26, this event will take place on the eve of TechEd Russia 2012 - I will be held by Georgy Gadzhiev and Simon Perryman, who specially flies to us from the USA.
See you at IT Camp and TechEd !
Sincerely,
Fire-Man
George A. Gadzhiev
Microsoft Corporation
Today I would like to review such an interesting new feature in Windows Server 2012 as data deduplication. The feature is extremely interesting, but first you need to figure out how much it is needed ...

Is deuplication necessary at all?
Every year (if not by day), the volume of hard drives is growing, and at the same time, the media themselves are becoming cheaper.
Based on this trend, the question arises: "Is data deduplication necessary at all?"
However, if you and I live in our universe and on our planet, then almost everything in this world has the property to obey Newton's 3rd law. The analogy may not be completely transparent, but I’m leading to the fact that no matter how cheap the disk systems and the disks themselves are, how much the media itself does not increase — the requirements from the business point of view for the space available for storing data are constantly growing and thereby offset the increase volume and price drop.
According to IDC forecasts, approximately 90 million terabytes will be required in the total volume in about a year. The volume, frankly, is not small.

And here it is just the question of data deduplication very much becomes relevant. After all, the data that we use are of different types, and their purpose can be different - somewhere it is production data, somewhere it is archives and backups, and somewhere it is streaming data - I specially cited such examples, since in the first case the effect of using deduplication will be average, in archive data it will be maximum, and in the case of streaming data it will be minimal. But still we can save space, especially since deduplication is now the lot of not only specialized storage systems, but also a component, a feature of the Windows Server 2012 server operating system.
Types of Deduplication and Their Application
Before moving on to an overview of the deduplication mechanism in Windows Server 2012 , let's look at what types of deduplication happen. I propose to start from top to bottom, in my opinion it will be more visual.
1) File deduplication - like any deduplication mechanism, the operation of the algorithm comes down to finding unique sets of data and repeating ones, where the second types of sets are replaced by links to the first sets. In other words, the algorithm tries to store only unique data, replacing duplicate data with unique links. As you can guess from the name of this type of deduplication - all such operations occur at the file level. If you recall the history of Microsoft products - then this approach has been repeatedly applied earlier - in Microsoft Exchange Serverand Microsoft System Center Data Protection Manager - and this mechanism was called SIS (Single Instance Storage). In the products of the Exchange line, it was abandoned at the time for performance reasons, but in Data Protection Manager this mechanism is still successfully used and it seems it will continue to do so. As you might guess, the file level is the highest (if you recall the device storage systems in general) - and therefore the effect will be the most minimal compared to other types of deduplication. Scope - this type of deduplication is mainly applied to archive data.
2) Block deduplication- this mechanism is already more interesting, since it works at the sub-file level - namely, at the level of data blocks. This type of deduplication, as a rule, is typical for industrial storage systems, and it is this type of deduplication that is used in Windows Server 2012. The mechanisms are the same as before - but at the block level (it seems, I already said that, right?). Here, the scope of deduplication is expanding and now extends not only to archive data, but also to virtualized environments, which is quite logical - especially for VDI scripts. If we take into account that VDI is a whole bunch of repeating images of virtual machines in which there are still differences from each other (that's why file deduplication is powerless here) - then block deduplication is our choice!
3) Bit deduplication- the lowest (deepest) type of data deduplication - has the highest degree of efficiency, but is also a leader in terms of resource intensity. It is understandable - to analyze data for uniqueness and plagiarism is not an easy process. Honestly, I personally do not know the storage systems that operate at this level of deduplication, but I know for sure that there are traffic deduplication systems that operate at the bit level, let’s say the same Citrix NetScaler. The meaning of such systems and applications is to save transmitted traffic - this is very critical for scenarios with geographically distributed organizations, where there are many geographically dispersed branches of the enterprise,
Microsoft’s report on USENIX 2012 , which took place in Boston in June, looks very interesting in this regard . A fairly large-scale analysis of the primary data was carried out in terms of the application of block deduplication mechanisms to them in WIndows Server 2012 - I recommend that you familiarize yourself with this material.
Performance Issues
In order to understand how effective deduplication technologies are in Windows Server 2012, you first need to determine on what type of data this very effectiveness should be measured. Typical file balls, user documents from the “My Documents” folder, distribution storages and libraries, and virtual hard disk storages were taken as standards.

How effective deduplication is in terms of workloads was tested at Microsoft in the software development department.
The 3 most popular scenarios have become the objects of research:
1) Build build servers - in MS every day a decent amount of builds of various products is collected. Not even a significant change in the code leads to the build process of the build - and therefore a lot of duplicate data is created
2) Balls with product distributions for release - As you might guess, all assemblies and ready-made software versions need to be placed somewhere - inside Microsoft there are special servers for this, where all versions and language editions of all products are placed - this is also a fairly effective scenario, where the effectiveness of deduplication can reach up to 70%.
3) Group balls - a combination of a ball with documents and files of developers, as well as their roaming profiles and redirected folders, which are stored in a single central space.

And now the most interesting part - below is a screenshot of the volumes in Windows Server 2012 that host all this data.

I think the words here will be superfluous - and everything is already very clear. 6TB savings on 2TB media - thermonuclear storage? Not so dangerous - but so effective!
Deduplication Features in Windows Server 2012
Now let's look at the main features of deduplication in Windows Server 2012.
1) Transparency and ease of use - setting up deduplication is extremely simple. First, in the role wizard on Windows Server, you expand the File and Storage Services role, then File and iSCSI Services - and there you turn on the Data Deduplication option.
After that, in Server Manager, you select Fike and Storage Services, right-click - and there you select the option “Enable Volume Deduplication”. Special link for PowerShell lovers. Everything is extremely simple. From the point of view of the end user and applications, access and work with data are transparent and invisible. If we talk about deduplication from the point of view of the file system, then only NTFS is supported. ReFS cannot be deduplicated, just like volumes are protected using EFS (Encrypted Fike System). Also, files less than 32 KB and files with extended attributes do not fall under deduplication. Deduplication, however, applies to dynamic volumes, volumes encrypted using BitLocker, but does not apply to CSV volumes, as well as system volumes (which is logical).
2) Optimization for the main data - it should be noted right away that deduplication is not an online process. Files that reach a certain level of old age in terms of policy are deduplicated. After reaching a certain shelf life, data begins to go through the deduplication process - by default this period of time is 5 days, but no one bothers you to change this parameter - but be reasonable in your experiments!
3) Planning of optimization processes - a mechanism that checks files every hour for compliance with deduplication parameters and adds them to the schedule.
4) Mechanisms for excluding objects from the deduplication area - this mechanism allows you to exclude files from the deduplication area by their type (JPG, MOV, AVI - as an example, this is streaming data - what is least deduplicated - if at all). You can also exclude immediately entire folders with files from the deduplication area (this is for lovers of German films who have their darkness and darkness).
5) Mobility - a deduplicated volume is an integral object - it can be transferred from one server to another (we are talking exclusively about Windows Server 2012). At the same time, you can easily access your data and can continue to work with them. All that is needed is the included Data Deduplication option on the target server.
6) Optimization of resource consumption - these mechanisms imply optimization of algorithms to reduce the load on read / write operations, so if we are talking about the size of the hash index of data blocks, then the size of the index per 1 data block is 6 bytes. Thus, you can even apply deduplication to very massive datasets.
Also, the algorithm always checks if there are enough memory resources to conduct the deduplication process - if the answer is no, then the algorithm will postpone the process until the necessary amount of resources is released.
7) Integration with BranchCache - indexing mechanisms for deduplication are also common for BranchCache - therefore, the effectiveness of using these technologies in conjunction is beyond doubt!
Reliability Considerations for Deduplicated Volumes
The reliability question arises extremely sharply for deduplicated data - imagine that a data block that at least 1000 files depend on is hopelessly damaged ... I think validol-e-e-service will then come in handy, but not in our case.
1) Backup - Windows Server 2012, like System Center Data Protection Manager 2012 SP1, fully supports deduplicated volumes in terms of backup processes. A special API is also available that allows third-party developers to use and support deduplication mechanisms, as well as restore data from deduplicated archives.
2) Additional copies for critical data - the data that has the most frequent access parameter is carried out by the process of creating additional backup blocks - these are the features of the mechanism algorithm. Also, in the case of using Storage Spaces mechanisms, when a bad block is found, the algorithm automatically replaces it with an integral one from a pair in the mirror.
3) By default, once a week, the process of finding garbage and bad blocks is started, which corrects the data of the acquired pathology. There is also the opportunity to manually start this process at a deeper level. If the default process corrects errors that were recorded in the event log, then a deeper process involves scanning the entire volume.
Where to start and how to measure
Before turning on deduplication, a normal person will always think of how effective this mechanism will be in his particular case. You can use the Deduplication Data Evaluation Tool for this .
After installing deduplication, you can find a tool called DDPEval.exe , which is located in \ Windows \ System32 \ - this utility can be ported to removable media or another volume. Supported OS Windows 7 and higher. So you can analyze your data and understand the value of sheep skin. (smile).
This concludes my review. I hope you were interested. If you have any questions - you can feel free to find me on social networks - VKontakte, Facebook - by name and surname - and I will try to help you.
For those who want to learn about new features in Windows Server 2012, as well as System Center 2012 SP1 - I invite everyone to visit IT Camp - November 26, this event will take place on the eve of TechEd Russia 2012 - I will be held by Georgy Gadzhiev and Simon Perryman, who specially flies to us from the USA.
See you at IT Camp and TechEd !
Sincerely,
Fire-Man
George A. Gadzhiev
Microsoft Corporation
